Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (21): 3438-3444.doi: 10.12307/2024.068
Integrative analyses of pyroptosis-related genes associated with intervertebral disc degeneration
Xie Yue1, 2, Zhai Weifeng2, Guo Ji2, Jia Yongwei2
- 1Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200120, China; 2Guanghua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China
-
Received:2023-03-08Accepted:2023-04-24Online:2024-07-28Published:2023-09-28 -
Contact:Jia Yongwei, MD, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Guanghua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China -
About author:Xie Yue, Master candidate, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200120, China; Guanghua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81972118 (to JYW); Medical Innovation Research Project of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission, No. 20Y11913000 (to JYW); Changning District Doctor Innovation Base Project, No. RCJD2021B06 (to JYW); Project of Changning District Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai, No. CNKW2022Y20 (to JYW); Project within the Budget of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. 2021LK012 (to ZWF)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xie Yue, Zhai Weifeng, Guo Ji, Jia Yongwei. Integrative analyses of pyroptosis-related genes associated with intervertebral disc degeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(21): 3438-3444.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
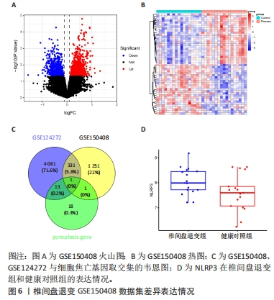
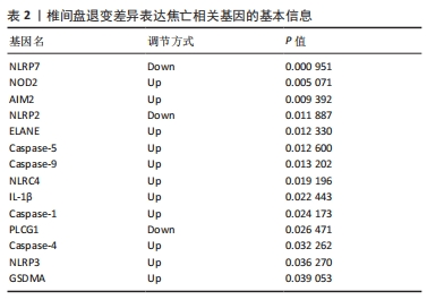
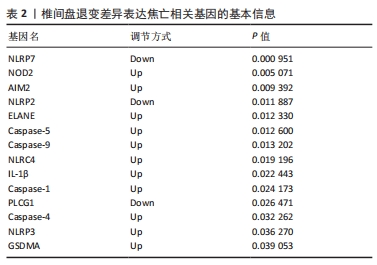
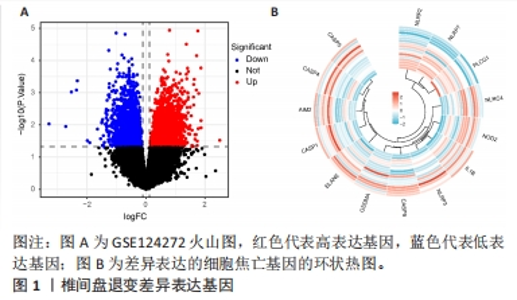
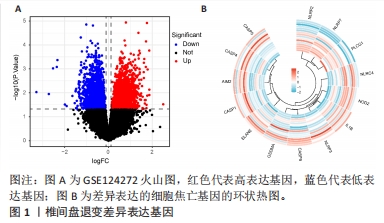
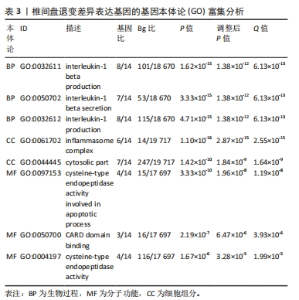
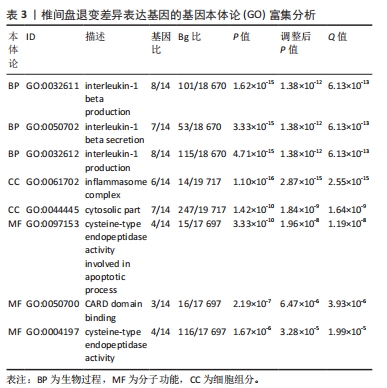
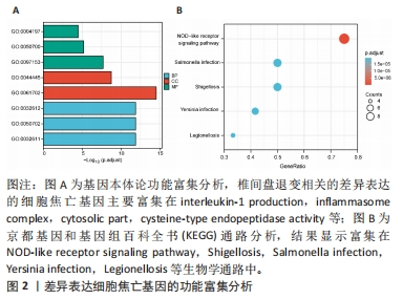
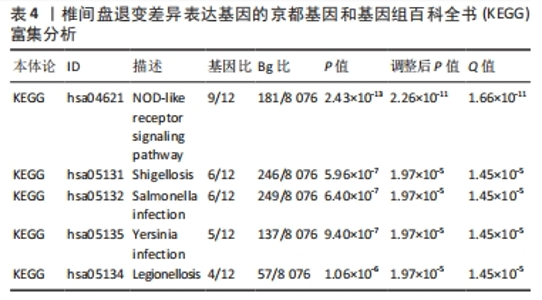
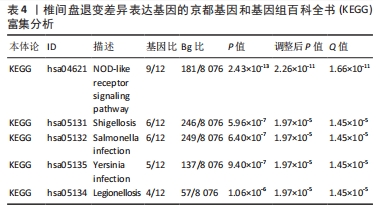
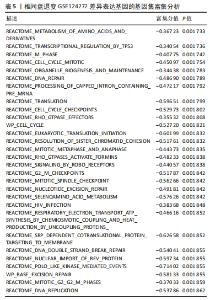
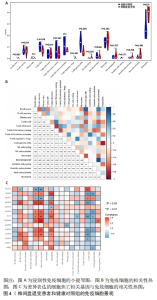
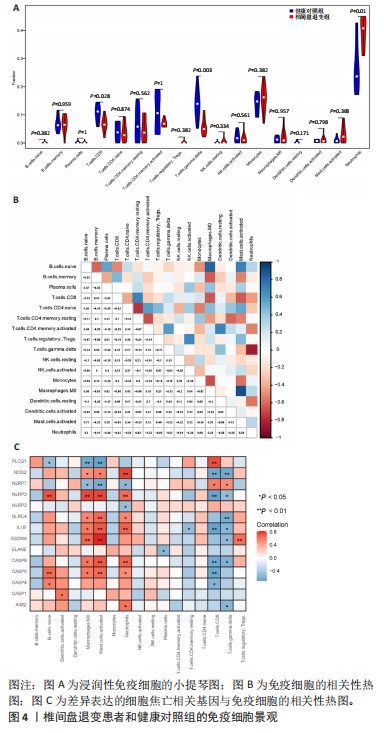
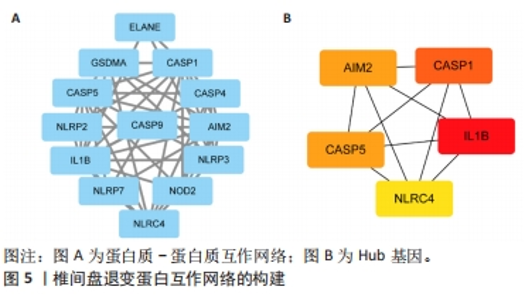
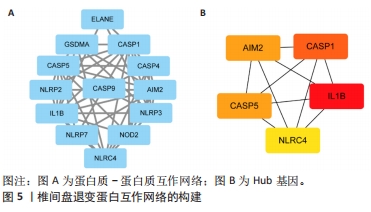
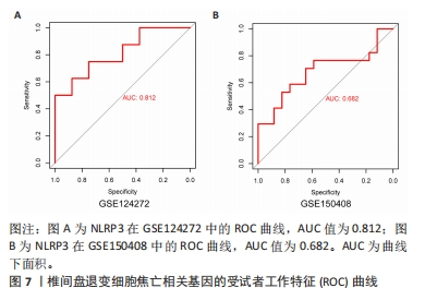
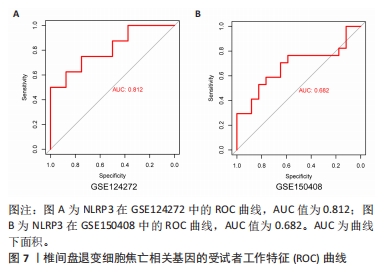
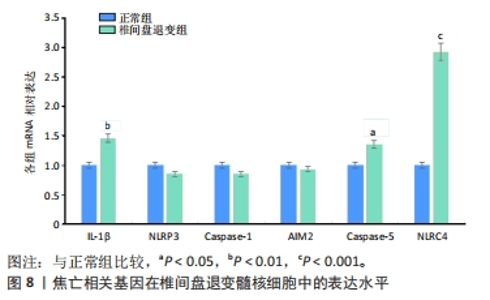
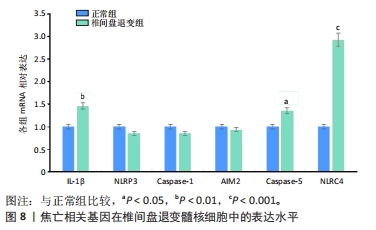
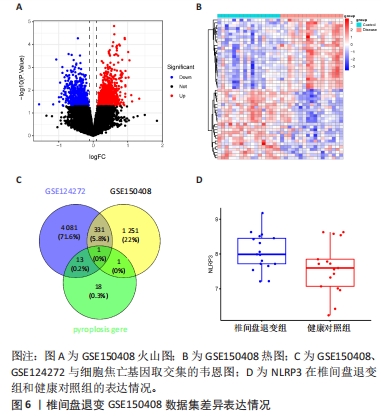
2.6 椎间盘退变关键生物标志物的获取及鉴定 利用GSE150408数据集对上述筛选到的椎间盘退变差异表达的细胞焦亡基因进行验证。使用limma包进行差异分析,共得到了1 584个差异表达的基因,其中包括927个上调基因和657个下调基因,利用差异表达基因和数据分组绘制了火山图热图(图6A,B)。将GSE150408和GSE124272两组数据集差异表达的基因与细胞焦亡基因取交集后(图6C),得到1个差异表达的细胞焦亡相关基因——NLRP3,通过GSE150408验证结果发现,该基因在椎间盘退变患者中高表达(图6D)。同时,将筛选出来的关键细胞焦亡相关基因在2个数据集中进行了ROC分析并计算了曲线下面积。结果显示2个数据集中曲线下面积值均大于0.6,表明NLRP3基因能准确区分椎间盘退变患者和健康对照,具有潜在的诊断价值(图7)。"
| [1] SCHWARZER AC, APRILL CN, DERBY R, et al. The prevalence and clinical features of internal disc disruption in patients with chronic low back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995;20(17):1878-1883. [2] ZHAO K, AN R, XIANG Q, et al. Acid-sensing ion channels regulate nucleus pulposus cell inflammation and pyroptosis via the NLRP3 inflammasome in intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(1):e12941. [3] CUNHA C, SILVA AJ, PEREIRA P, et al. The inflammatory response in the regression of lumbar disc herniation. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):251. [4] WANG Y, CHE M, XIN J, et al. The role of IL-1beta and TNF-alpha in intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131: 110660. [5] VANDE WL, LAMKANFI M. Pyroptosis. Curr Biol. 2016;26(13):R568-R572. [6] ZENG C, WANG R, TAN H. Role of Pyroptosis in Cardiovascular Diseases and its Therapeutic Implications. Int J Biol Sci. 2019;15(7):1345-1357. [7] ZU Y, MU Y, LI Q, et al. Icariin alleviates osteoarthritis by inhibiting NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):307. [8] SONG Y, WANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Advanced glycation end products regulate anabolic and catabolic activities via NLRP3-inflammasome activation in human nucleus pulposus cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(7): 1373-1387. [9] TANG P, GU JM, XIE ZA, et al. Honokiol alleviates the degeneration of intervertebral disc via suppressing the activation of TXNIP-NLRP3 inflammasome signal pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2018;120:368-379. [10] WANG Y, DAI G, LI L, et al. Transcriptome signatures reveal candidate key genes in the whole blood of patients with lumbar disc prolapse. Exp Ther Med. 2019;18(6):4591-4602. [11] WANG Y, DAI G, JIANG L, et al. Microarray analysis reveals an inflammatory transcriptomic signature in peripheral blood for sciatica. BMC Neurol. 2021; 21(1): 50. [12] BARRETT T, TROUP DB, WILHITE SE, et al. NCBI GEO: mining tens of millions of expression profiles--database and tools update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007; 35(Database issue):D760-D765. [13] DAVIS S, MELTZER PS. GEOquery: a bridge between the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and BioConductor. Bioinformatics. 2007;23(14): 1846-1847. [14] RITCHIE ME, PHIPSON B, WU D, et al. Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(7):e47. [15] FU XW, SONG CQ. Identification and Validation of Pyroptosis-Related Gene Signature to Predict Prognosis and Reveal Immune Infiltration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:748039. [16] YOU X, VLATKOVIC I, BABIC A, et al. Neural circular RNAs are derived from synaptic genes and regulated by development and plasticity. Nat Neurosci. 2015;18(4):603-610. [17] KANEHISA M, GOTO S. KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000;28(1):27-30. [18] YU G, WANG LG, HAN Y, et al. Cluster Profiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS. 2012;16(5):284-287. [19] SUBRAMANIAN A, TAMAYO P, MOOTHA VK, et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(43):15545-15550. [20] STEEN CB, LIU CL, ALIZADEH AA, et al. Profiling Cell Type Abundance and Expression in Bulk Tissues with CIBERSORTx. Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2117: 135-157. [21] SZKLARCZYK D, GABLE AL, LYON D, et al. STRING v11: protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019; 47(D1):D607-D613. [22] ZHOU G, SOUFAN O, EWALD J, et al. NetworkAnalyst 3.0: a visual analytics platform for comprehensive gene expression profiling and meta-analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(W1):W234-W241. [23] ROBIN X, TURCK N, HAINARD A, et al. pROC: an open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011;12: 77. [24] LIVSHITS G, POPHAM M, MALKIN I, et al. Lumbar disc degeneration and genetic factors are the main risk factors for low back pain in women: the UK Twin Spine Study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(10):1740-1745. [25] FENG Y, EGAN B, WANG J. Genetic factors in intervertebral disc degeneration. Genes Dis. 2016;3(3):178-185. [26] ADAMS MA, ROUGHLEY PJ. What is intervertebral disc degeneration, and what causes it? Spine. 2006;31(18):2151-2161. [27] MAYER JE, IATRIDIS JC, CHAN D, et al. Genetic polymorphisms associated with intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine J. 2013;13(3):299-317. [28] YANG S, ZHANG F, MA J, et al. Intervertebral disc ageing and degeneration: The antiapoptotic effect of oestrogen. Ageing Res Rev. 2020;57:100978. [29] WANG SZ, RUI Y, TAN Q, et al. Enhancing intervertebral disc repair and regeneration through biology: platelet-rich plasma as an alternative strategy. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(5):220. [30] ROUGHLEY PJ. Biology of intervertebral disc aging and degeneration: involvement of the extracellular matrix. Spine. 2004;29(23):2691-2699. [31] PRIYADARSHANI P, LI Y, YAO L. Advances in biological therapy for nucleus pulposus regeneration. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2016;24(2):206-212. [32] ZHAO K, AN R, XIANG Q, et al. Acid-sensing ion channels regulate nucleus pulposus cell inflammation and pyroptosis via the NLRP3 inflammasome in intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(1):e12941. [33] GE Y, CHEN Y, GUO C, et al. Pyroptosis and Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Implications. J Inflamm Res. 2022;15: 5857-5871. [34] LI L, HE J, ZHANG G, et al. Role of Caspase Family in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration and Its Therapeutic Prospects. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(8):1074. [35] ZHANG H, YAO S, ZHANG Z, et al. Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation to Reveal the Pharmacological Mechanisms of Liuwei Dihuang Decoction Against Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021;15:4911-4924. [36] ZHAO F, GUO Z, HOU F, et al. Magnoflorine Alleviates “M1” Polarized Macrophage-Induced Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Through Repressing the HMGB1/Myd88/NF-κB Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:701087. [37] CHAO-YANG G, PENG C, HAI-HONG Z. Roles of NLRP3 inflammasome in intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(6): 793-801. [38] RISBUD MV, SHAPIRO IM. Role of cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: pain and disc content. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10(1):44-56. |
| [1] | Weng Rui, Lin Dongxin, Guo Haiwei, Zhang Wensheng, Song Yuke, Lin Hongheng, Li Wenchao, Ye Linqiang. Abnormal types of intervertebral disc structure and related mechanical loading with biomechanical factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1436-1442. |
| [2] | Liu Xin, Hu Man, Zhao Wenjie, Zhang Yu, Meng Bo, Yang Sheng, Peng Qing, Zhang Liang, Wang Jingcheng. Cadmium promotes senescence of annulus fibrosus cells via activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1217-1222. |
| [3] | Li Yangfeng, Tian Xin, He Fan, Yang Huilin. Melatonin-loaded gelatin methacryloyl microspheres delay nucleus pulposus degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 676-681. |
| [4] | Tian Xin, Liu Tao, Yang Huilin, He Fan. In vitro evaluation of sustained release Kartogenin by gelatin methacryloyl microspheres for repairing nucleus pulposus degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 724-730. |
| [5] | Cao Sheng, Kong Lingwei, Xu Kun, Sun Zhijie. Effect of gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel loaded with salvianolic acid B on intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 380-386. |
| [6] | Huang Jie, Jiang Qiang, Han Jiaheng, Liu Jiang, Zhang Yan, Lu Zhencao, Ding Yu. Mechanism by which interleukin-1beta regulates the expression of Semaphorin 3A to induce intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3680-3685. |
| [7] | Xu Wenfei, Ming Chunyu, Mei Qijie, Yuan Changshen, Guo Jinrong, Zeng Chao, Duan Kan. Experimental validation of machine learning identification of KDELR3 as a signature gene for osteoarthritis hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(21): 3431-3437. |
| [8] | Zhou Shuliang, Xu Liang, Qian Xuefeng, Zeng Jincai, Zhu Lifan. Correlation between the expression of miRNA-142-3p, mixed lineage kinase 3 and interleukin-1beta in nucleus pulposus and the degree of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 165-171. |
| [9] | Wang Qian, Lu Ziang, Li Lihe, Lyu Chaoliang, Wang Meng, Zhang Cunxin. Sinomenine effectively inhibits interleukin-1beta-induced apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 224-230. |
| [10] | Li Feifei, Deng Jiang. Effects and problems of growth differentiation factor 5-induced multidirectional differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(19): 3084-3089. |
| [11] | Yang Yunyun, Chen Qiqing, Zhao Jirong, Zhu Bao, Ma Dong, Huang Junkai, An Dehao, Zou Jipeng, Liu Weihang. Research status of traditional Chinese medicine monomer mediating related signaling pathways in treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(18): 2918-2924. |
| [12] | Kou Yu, Gu Yong, Chen Liang. Mechanism of black phosphorus regulating oxidative stress-inflammation cascade in retarding intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(15): 2338-2345. |
| [13] | Yuan Tianyi, Liu Hongjiang, Yang Zengqiang, Lu Xingbao, Maimaitiyibubaji, Zhou Zhiheng, Cui Yong. Identification of differences in N6-methyladenosine-related genes in steroid-induced femoral head necrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2159-2165. |
| [14] | Xie Wenguan, Liu Yutao, Cui Wenbo, Kuang Mingye. Melatonin inhibits hydrogen peroxide-induced injury of human nucleus pulposus cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2180-2185. |
| [15] | Deng Fahua, Hu Huali, Wang Siqi, Xu Jianxia, Lu Tingting, Huang Hai, Wei Sixi. Screening and verification of genes related to immune infiltration between myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(13): 2082-2089. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||