Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (18): 2918-2924.doi: 10.12307/2024.060
Previous Articles Next Articles
Research status of traditional Chinese medicine monomer mediating related signaling pathways in treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration
Yang Yunyun1, Chen Qiqing2, Zhao Jirong1, Zhu Bao2, Ma Dong1, Huang Junkai1, An Dehao1, Zou Jipeng1, Liu Weihang3
- 1Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730030, Gansu Province, China; 2Gansu Provincial Hospital of TCM, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China; 3Yi County Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Yi County 074200, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2023-02-28Accepted:2023-05-10Online:2024-06-28Published:2023-08-26 -
Contact:Chen Qiqing, MD, Associate chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Gansu Provincial Hospital of TCM, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China -
About author:Yang Yunyun, Master candidate, Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730030, Gansu Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81760877 (to ZJR); Gansu Provincial Major Science and Technology Project, No. 21ZD4FA009 (to ZJR); Gansu Provincial Innovation Base and Talent Plan - Natural Science Foundation, No. 17JR5RA051 (to CQQ); Gansu Provincial Hospital of TCM Doctoral Scientific Research Initiation Fund, No. 2018-01 (to CQQ); National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Project, No. [2023]24 (to CQQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Yunyun, Chen Qiqing, Zhao Jirong, Zhu Bao, Ma Dong, Huang Junkai, An Dehao, Zou Jipeng, Liu Weihang. Research status of traditional Chinese medicine monomer mediating related signaling pathways in treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(18): 2918-2924.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
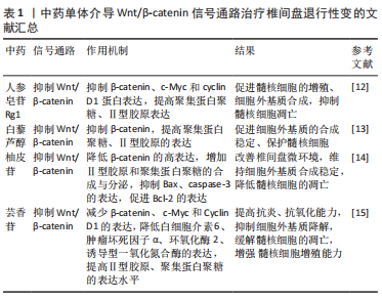
2.1 Wnt/β-catenin信号通路与椎间盘退行性变 Wnt信号通路是细胞发育和稳态过程的关键,由β-连环蛋白依赖性/非依赖性信号通路组成[6]。 典型的Wnt/β-catenin信号通路十分保守,靠β-catenin蛋白介导,参与细胞的增殖、代谢和生长,并与导致或加速IVDD密切相关[7-8]。该信号通路的异常激活参与降低髓核细胞对CCN2 mRNA和蛋白质的表达,抑制髓核细胞的增殖和细胞外基质的合成[9]、诱导髓核细胞衰老、凋亡,下调Ⅱ型胶原、聚集蛋白聚糖、Sox-9的表达,提高分解代谢基因基质金属蛋白酶13和金属肽酶含血小板反应蛋白(A disintegrin and metalloproteas,ADAMTS)5的表达水平[10-11]。根据大量实验结果,抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路可以增殖髓核细胞,促进细胞外基质的合成,抑制髓核细胞凋亡、衰老,维持椎间盘正常生理功能,达到治疗IVDD的目的。 YU等[12]实验发现,人参皂苷Rg1可抑制β-catenin、c-Myc和cyclin D1蛋白表达,提高细胞外基质的关键生物标志物(聚集蛋白聚糖、Ⅱ型胶原)表达,促进大鼠髓核细胞的增殖、细胞外基质合成,抑制其凋亡,从而改善髓核细胞功能及增加髓核含水量,改善椎间盘结构,从而有效延缓IVDD进程。LIU等[13]实验发现,白藜芦醇通过降低髓核细胞中β-catenin的高表达,提高聚集蛋白聚糖、Ⅱ型胶原的表达,减少细胞外基质的分解,促进细胞外基质的合成稳定、保护髓核细胞,使椎间盘的正常生理功能得以维持,有效改善IVDD。苑珍珍等[14]通过研究柚皮苷对人退变椎间盘髓核细胞凋亡的影响,发现20 μg/mL的柚皮苷能够显著降低β-catenin的高表达,通过调节Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路,增加Ⅱ型胶原和聚集蛋白聚糖的合成与分泌,改善椎间盘微环境,维持细胞外基质合成稳定,降低髓核细胞的凋亡。同时,柚皮苷可抑制促凋亡蛋白(Bax、caspase-3)的表达,促进抗凋亡蛋白(Bcl-2)的表达,进而延缓IVDD。许大勇等[15]通过芸香苷对大鼠IVDD的实验发现,100 μg/mL的芸香苷通过抑制Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路的激活,减少β-catenin、c-Myc和Cyclin D1的表达,降低白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、环氧化酶2(COX-2)、诱导型一氧化氮合酶(iNOS)的表达,提高Ⅱ型胶原、聚集蛋白聚糖的表达水平,通过抗炎、抗氧化及抑制细胞外基质降解缓解髓核细胞的凋亡,增强髓核细胞增殖能力,从而改善IVDD。 Wnt/β-catenin信号通路广泛存在于多种细胞类型中,该通路过度活化将导致细胞增殖、分化、凋亡等生物学过程的失控,从而引发多种疾病。而Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在IVDD的发病机制中也扮演着重要的角色,其异常激活会导致髓核细胞凋亡、衰老和细胞外基质分解代谢的加速,从而加速IVDD的进程。一些中药成分,如人参皂苷Rg1、白藜芦醇、柚皮苷和芸香苷等,均可以通过干预Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,促进髓核细胞增殖和细胞外基质合成,抑制髓核细胞凋亡和细胞外基质分解,从而有效改善IVDD的病理进程,见表1。这些研究结果为中药治疗IVDD提供了一定的理论依据和实验基础。"
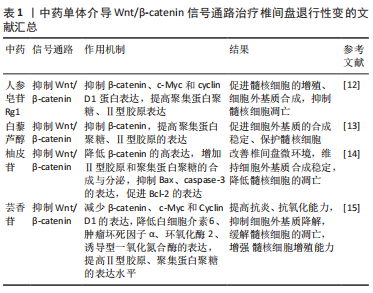
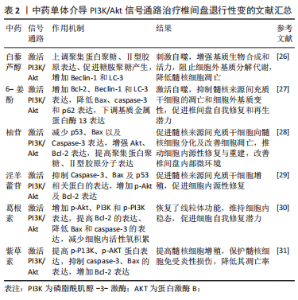
2.2 PI3K/Akt信号通路与椎间盘退行性变 PI3K/Akt信号通路在细胞增殖、存活、生长及凋亡等生理过程中起着关键作用[16]。PI3K和Akt是PI3K/Akt信号通路的关键蛋白,其中Akt在该信号传导中扮演着关键角色,PI3K的激活可刺激Akt磷酸化[17]。活化的AKT可以启动蛋白激酶、细胞周期调节剂和其他下游底物[18],调节细胞凋亡相关蛋白、聚集蛋白聚糖、Ⅱ型胶原分子[19-21],减弱氧化应激反应[22],刺激细胞自噬功能[23]。 既往研究发现,活化的PI3K/AKT通路参与调节髓核细胞增殖、凋亡、衰老和细胞外基质代谢平衡,并且还被证明与髓核变性显著相关[24-25]。 GAO等[26]实验发现,白藜芦醇可激活PI3K/Akt信号通路,上调聚集蛋白聚糖、Ⅱ型胶原分子表达,促进糖胺聚糖(GAG)产生,并增加自噬相关标志物(Beclin-1和LC-3)刺激细胞自噬,以此增强髓核细胞基质生物合成和细胞活力,阻止细胞外基质的分解代谢,降低髓核细胞的凋亡,有效延缓IVDD的进展。NAN等[27]实验发现,6-姜酚通过活化PI3K/Akt信号通路,增加Bcl-2、Beclin-1和LC-3表达,降低Bax、caspase-3和p62的表达来激活自噬,下调基质金属蛋白酶13表达,抑制髓核来源间充质干细胞(nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cell,NPMSC)的凋亡和细胞外基质变性,有效促进椎间盘自我修复和再生潜力,从而有利IVDD的治疗。南利平等[28]实验发现,柚苷可影响PI3k/Akt信号通路相关蛋白,减少p53、Bax以及Caspase-3表达,增强Akt、Bcl-2表达,提高人NPMSC中聚集蛋白聚糖、Ⅱ型胶原分子表达,促进人NPMSC向髓核细胞分化及改善细胞凋亡,推动细胞内源性修复与重建,改善椎间盘内部微环境,延缓IVDD。张文捷等[29]通过研究淫羊藿苷对大鼠NPMSC的影响,发现淫羊藿苷通过激活PI3K/Akt信号通路,抑制Caspase-3、Bax及p53相关蛋白的表达,增加p-Akt及Bcl-2表达,减少NPMSC凋亡,并以浓度依赖性方式促进NPMSC增殖,促进细胞内源性修复,进而在一定程度改善IVDD。HUANG等[30]实验发现,葛根素通过增加人NPMSC中p-Akt、PI3K和p-PI3K表达,促进PI3K/Akt信号通路的激活,提高Bcl-2的表达、降低Bax和caspase-3的表达,减少细胞内活性氧积累,恢复线粒体功能障碍,维持细胞内稳态,从而增强NPMSC对压缩刺激的耐受性,挽救压缩诱导的细胞死亡和形态受损,促进细胞自我修复潜力,对延缓IVDD具有一定的效果。叶禾等[31]通过研究紫草素对人退变椎间盘髓核细胞凋亡的影响,发现紫草素能通过激活P13K/AKT通路,提高p-P13K蛋白和p-AKT蛋白表达,抑制人髓核细胞中凋亡蛋白caspase-3和Bax的表达,增加Bcl-2的表达,提高髓核细胞增殖率,保护髓核细胞免受炎性损伤,降低其凋亡率,进而延缓IVDD。 PI3K/Akt信号通路在调节多种细胞及分子生理过程中具有的重要作用,一些天然产物如白藜芦醇、6-姜酚、柚苷、淫羊藿苷和葛根素,通过活化PI3K/Akt信号通路,促进细胞自噬、基质生物合成、提高细胞抗炎和抗氧化能力、减少细胞凋亡和细胞外基质分解代谢,促进细胞自我修复和再生潜力,调节髓核细胞增殖、衰老,增强椎间盘的功能,通过多种作用机制干预椎间盘退变,有望成为IVDD治疗的候选物质,为深入研究IVDD的治疗提供了重要的理论基础,见表2。"
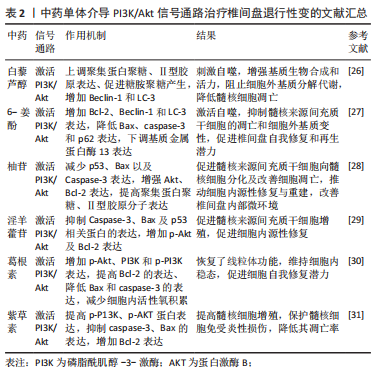
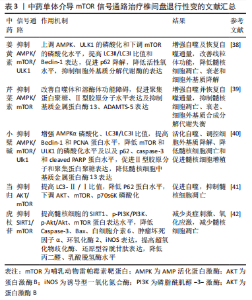
2.3 mTOR信号通路与椎间盘退行性变 mTOR是一种演化中保守的丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶,参与蛋白质的合成、细胞衰老、自噬、细胞凋亡和免疫[32]。mTOR作为激活细胞自噬的主要负调节因子,存在于mTOR复合物1(mTORC1)和mTOR复合物2(mTORC2)中[33]。mTORC1由Akt上游调节,而Akt磷酸化与PI3K和mTORC2有关[34]。mTORC1可诱导p70/S6激酶(p70/S6K)、抑制真核转化启动因子4E结合蛋白1(4E-BP1)来调控细胞周期和增殖,并通过抑制促凋亡蛋白及对转录因子的影响,提高细胞生存能力[35]。LC3是细胞自噬过程中至关重要的一个蛋白质,具有LC3-Ⅰ/LC3-Ⅱ型[36],与自噬水平关系密切;Beclin-1也是与自噬相关另一基因,其参与自噬体的形成及自噬过程的正常发挥。既往研究发现,通过对mTOR信号通路的调控,调节凋亡蛋白和保持细胞膜完整性在促进髓核细胞存活和活力方面起着关键作用[37]。 KANG等[38]通过AMP活化蛋白激酶(AMP-activated protein kinase,AMPK)/mTOR/ULK1信号通路恢复自噬通量实验中发现,姜黄素通过上调AMPK和ULK1的磷酸化和下调mTOR的磷酸化水平,提高LC3Ⅱ/LC3Ⅰ比值和Beclin-1表达,促进p62降解,增强自噬及恢复自噬通量,降低人髓核细胞中的活性氧水平,抑制细胞外基质分解代谢酶的表达,改善线粒体功能障碍,从而降低髓核细胞凋亡、衰老和细胞外基质降解,达到缓解IVDD的目的。XIE等[39]在芹菜素通过恢复髓核细胞中自噬通量来缓解IVDD实验中发现,芹菜素能有效改善自噬体和溶酶体功能障碍,增强自噬并恢复自噬通量,促进聚集蛋白聚糖、Ⅱ型胶原分子水平表达及抑制基质金属蛋白酶13、ADAMTS-5表达,从而有效抑制髓核细胞凋亡、衰老,细胞外基质合成代谢和分解代谢失衡,延缓IVDD进展。HUANG等[40]实验发现,小檗碱显著增强了AMPKα磷酸化和自噬相关蛋白LC3Ⅱ/LC3Ⅰ比值,提高了Beclin-1和PCNA的蛋白水平,降低了mTOR和UNC-51样激酶1(ULK1)的磷酸化水平及以及p62、caspase-3和cleaved PARP的蛋白水平,通过活化自噬,促进Ⅱ型胶原分子和聚集蛋白聚糖的表达,降低髓核细胞中基质金属蛋白酶13的表达,从而调控细胞外基质降解、降低髓核细胞凋亡和促进髓核细胞增殖,进而对IVDD产生一定的影响。 刘汝银等[41]通过当归对大鼠椎间盘髓核细胞自噬及氧化应激损伤的研究发现,1 mg/mL当归注射液能够进一步提高髓核细胞中LC3-Ⅱ/Ⅰ的比值,降低P62蛋白水平,下调AKT、mTOR、p70s6K的磷酸化,抑制AKT/mTOR信号通路的激活,从而促进髓核细胞自噬水平,调节髓核细胞凋亡,达到延缓IVDD的目的。左斌等[42]通过研究虎杖苷对小鼠腰椎间盘退变髓核细胞凋亡的影响,发现虎杖苷可以通过SIRT1/mTOR信号通路有效提高髓核细胞的SIRT1、p-PI3K/PI3K、p-Akt/Akt、mTOR蛋白的表达水平,降低Caspase-3、Bax、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、环氧化酶2、诱导型一氧化氮合酶的表达,提高超氧化物歧化酶、还原型谷胱甘肽的表达,降低丙二醛、乳酸脱氢酶的水平,通过抑制炎症因子、氧化应激因子的产生,减少髓核细胞凋亡,从而达到延缓IVDD的目的。 mTOR 作为自噬的主要负调节因子,与自噬通量紧密相关,在IVDD的发生和发展中发挥着重要作用。mTOR信号通路是一种重要的细胞代谢途径,姜黄素、芹菜素、小檗碱等天然物质通过抑制mTOR信号通路,促进细胞自噬来清除损伤的蛋白质和细胞器,从而保护椎间盘细胞免受氧化应激反应、炎症刺激,降低分解代谢酶的表达,提高细胞外基质关键生物标志物的表达,从而抑制细胞衰老、凋亡和细胞外基质降解等生物学过程,为中药在治疗IVDD方面的研究提供了有用的信息和参考,见表3。"

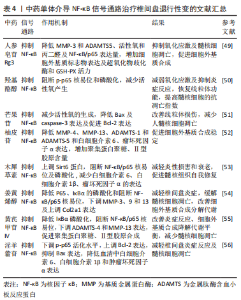
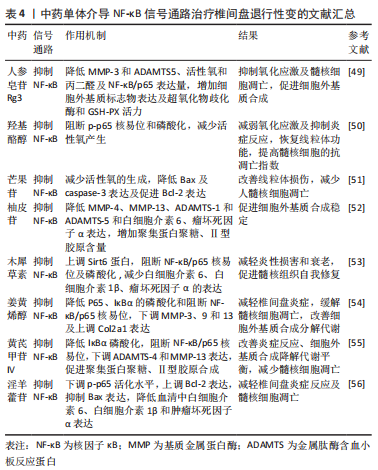
2.4 NF-κB信号通路与椎间盘退行性变 NF-κB是一种常见的基因转录因子,由5个亚基组成,p50/p65二聚体是最常见的形式,也是最为典型的复合物之一, 在炎症反应、细胞增殖、凋亡等方面发挥着关键的作用[43-44]。静息状态时,NF-κB在细胞质中以不活跃的状态与抑制蛋白(IκBα)结合,从而阻碍其向细胞核的渗透[45]。在经过多种诱发因子的刺激或IκBα的磷酸化作用后,p65的亚基易位到细胞核中与NF-κB结合位点的基质金属蛋白酶启动子区相结合,进而起到调节转录的功能[46]。研究发现,在IVDD过程中,许多因素通过激活NF-κB信号通路直接或间接诱导基质降解酶(如基质金属蛋白酶和ADAMTSs)的表达和释放和促炎细胞因子(白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α)上调,从而加速细胞细胞外基质的分解代谢水平,特别是聚集蛋白聚糖、Ⅱ型胶原降解,从而加剧IVDD[47-48]。 CHEN等[49]通过实验发现,人参皂苷Rg3通过抑制NF-κB信号通路激活,降低人类髓核细胞的细胞外基质降解基因(基质金属蛋白酶3和ADAMTS5)的表达量、活性氧和丙二醛含量以及NF-κB/p65的表达量,增加细胞外基质标志物的表达以及超氧化物歧化酶和GSH-PX等抗氧化酶的活力,从而抑制氧化应激及髓核细胞的凋亡,促进髓核细胞的细胞外基质的合成,延缓IVDD。YU等[50]通过实验发现,羟基酪醇可通过阻断p-p65核易位和磷酸化抑制NF-κB信号通路的激活,减少人类髓核细胞中活性氧的产生,降低线粒体转换孔的开放及膜电位的丧失,减弱氧化应激及抑制炎症反应,从而使线粒体的机能得到修复,提高人类髓核细胞的抗凋亡指数,以此维持椎间盘稳态。YU等[51]通过实验发现,芒果苷通过抑制NF-κB信号通路的活化,减少髓核细胞中活性氧的生成,改善线粒体损伤,从而降低Bax及caspase-3的表达及促进Bcl-2表达,减少人髓核细胞凋亡,有助于缓解IVDD。 GAO等[52]通过实验发现,柚皮苷通过降低人髓核细胞的细胞外基质分解代谢酶(基质金属蛋白酶4、基质金属蛋白酶13、ADAMTS-1和ADAMTS-5)和促炎细胞因子(白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α)的表达,增加聚集蛋白聚糖、Ⅱ型胶原的含量,促进细胞外基质的合成稳定,从而在IVDD的防治中具有一定的潜力。XIE等[53]通过实验发现,木犀草素通过上调长寿基因(Sirt6)蛋白,阻断NF-κB/p65核易位及磷酸化的过程,抑制下游NF-κB信号通路,减少促炎因子白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α的表达,从而减轻人髓核细胞的炎性损害和衰老,增强其活性促进髓核组织自我修复,达到治疗IVDD目的。YANG等[54]通过实验发现,姜黄烯醇通过降低P65、IκBα的磷酸化和阻断NF-κB/p65的核易位,下调髓核细胞中基质金属蛋白酶家族(基质金属蛋白酶3、9和13)及上调软骨生成标志物(Col2a1)的表达,减轻大鼠椎间盘炎症,缓解大鼠髓核细胞的凋亡,改善细胞外基质合成分解代谢状态,维持椎间盘的稳定,从而缓解IVDD的进展。TIAN等[55]实验发现,黄芪甲苷IV降低了白细胞介素1β诱导的IκBα磷酸化,阻断NF-κB/p65的核易位,并下调细胞外基质分解代谢因子ADAMTS-4和基质金属蛋白酶13的表达,促进聚集蛋白聚糖、Ⅱ型胶原的合成,从而改善炎症反应、细胞外基质合成降解代谢平衡,减少髓核细胞的凋亡,延缓IVDD。康小彪等[56]实验发现,淫羊藿苷可抑制NF-κB信号通路,下调p-p65的活化水平,上调 Bcl-2表达,抑制Bax表达,减少髓核细胞凋亡;同时,淫羊藿苷可降低血清中白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达,减轻椎间盘炎症反应,从而改善椎间盘病理性损害,延缓IVDD的进展。 NF-κB信号通路 是一条重要的细胞内信号传导通路,IVDD的许多因素可通过激活NF-κB信号通路直接或间接诱导基质降解酶、炎性因子、氧化应激反应,加速细胞细胞外基质的分解代谢水平,加剧IVDD。人参皂苷Rg3、羟基酪醇、木犀草素等可以通过不同途径靶向NF-κB信号通路的关键分子,如IKK、IκB、p65等,抑制NF-κB的活化保护椎间盘细胞免受不利因素损害,从而减轻IVDD的病理改变,见表4。因此,对中药干预NF-κB信号通路的深入研究有助于揭示相关疾病的发病机制,为相关疾病的治疗提供新的思路。"
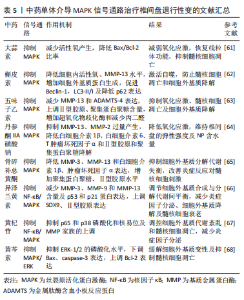
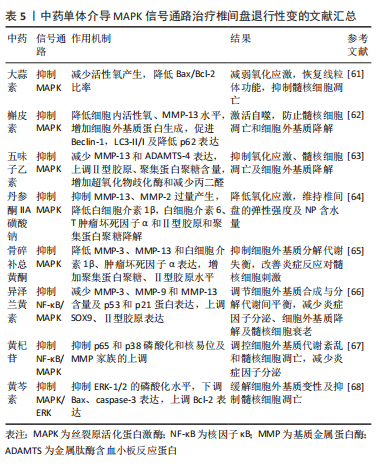
2.5 MAPK信号通路与椎间盘退行性变 MAPK是涉及多种细胞外源刺激信号传导的一类蛋白激酶家族。MAPK信号通路是一个重要的细胞信号传导网络,参与细胞增殖、分化、凋亡和自噬过程的调节[57]。MAPKs由p38-MAPK、ERK、JNK三大类组成,而细胞凋亡与p38-MAPK信号通路的活化有很大关系[58]。研究发现,p38-MAPK对髓核细胞的炎性反应起着关键作用,其中由p38-MAPK介导的细胞因子可以诱导分解代谢酶的表达[59],导致细胞外基质代谢失衡,细胞衰老和凋亡,增强氧化应激、炎症反应及异常自噬[60],导致椎间盘组织的退化,促进IVDD的发展。因此,通过抑制MAPK信号通路的活化,降低炎性细胞因子和髓核细胞的过度凋亡,对IVDD的治疗具有一定的效果。 XIANG等[61]通过观察大蒜素对人髓核细胞的影响,发现大蒜素可以通过抑制p38-MAPK信号通路保护髓核细胞免受高级氧化蛋白产物介导的氧化应激,减少活性氧产生,降低Bax/Bcl-2比率,恢复线粒体功能,从而阻碍线粒体凋亡途径保护髓核细胞免于凋亡,进而对IVDD的进展起到延缓作用。ZHANG等[62]通过观察槲皮素对叔丁基过氧化氢诱导下大鼠髓核细胞的影响,发现槲皮素可通过抑制p38-MAPK信号通路改善氧化应激下细胞内活性氧水平,降低基质金属蛋白酶13水平,增加细胞外基质蛋白的生成,并促进Beclin-1,LC3-II/I及降低p62的表达,介导自噬的激活,防止髓核细胞凋亡和细胞外基质降解,从而延缓IVDD。张海丹等[63]通过五味子乙素对髓核细胞凋亡实验研究,发现五味子乙素通过下调 p-p38 MAPK/p38 MAPK 的比值,抑制p38-MAPK 信号通路的激活,减少髓核细胞中基质金属蛋白酶13和ADAMTS-4的表达,上调Ⅱ型胶原、聚集蛋白聚糖的含量,通过调控细胞外基质代谢维持髓核细胞结构基础,并能通过增加超氧化物歧化酶和减少丙二醛抑制髓核细胞氧化应激反应,减轻髓核细胞损伤,从而抑制髓核细胞凋亡和细胞外基质降解,最终缓解IVDD。DAI等[64]通过观察丹参酮IIA磺酸钠对损伤诱导大鼠椎间盘变性的影响,发现丹参酮IIA磺酸钠能通过降低氧化应激反应,抑制细胞内基质金属蛋白酶13、基质金属蛋白酶2的过量产生,并使白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α炎症因子含量下降,降低Ⅱ型胶原和聚集蛋白聚糖的降解,维持椎间盘的弹性强度及髓核的含水量,从而抑制IVDD的进展。 ZHAO等[65]通过研究骨碎补总黄酮对颈椎间盘退行性改变大鼠模型的影响,发现骨碎补总黄酮通过抑制MAPK信号通路,降低细胞内基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶13和炎症因子白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α的表达,通过增加聚集蛋白聚糖、Ⅱ型胶原水平,抑制细胞外基质分解代谢失衡,改善炎症反应对髓核细胞的刺激,延缓IVDD。YANG等[66]实验发现,异泽兰黄素通过阻断肿瘤坏死因子α诱导NF-κB、MAPK信号通路的活化,减少髓核细胞中基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶9和基质金属蛋白酶13的含量及细胞老化经典标志物(p53和p21蛋白)的表达,上调SOX9、Ⅱ型胶原的表达,从而调节细胞外基质合成与分解代谢间的动态平衡,炎减少症因子分泌、细胞外基质的降解及髓核细胞的衰老,从而有效缓解IVDD的进展。LI等[67]实验发现,黄杞苷通过抑制p65和p38的磷酸化和核易位,阻断NF-κB和MAPK信号通路的激活,有效改善肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的炎症递质和基质金属蛋白酶家族的上调,调控细胞外基质代谢紊乱和髓核细胞凋亡,发挥对大鼠椎间盘的保护作用,从而延缓IVDD。刘伟等[68]通过研究黄芩素对压力诱导的人椎间盘髓核细胞凋亡的影响,发现黄芩素能够有效抑制ERK-1/2的磷酸化水平,下调Bax、caspase 3的表达,上调Bcl-2的表达,缓解细胞外基质的变性及抑制髓核细胞的凋亡,从而延缓IVDD。 在IVDD的病理过程中,椎间盘细胞遭受外界刺激,如机械压力、氧化应激等,会引发MAPK信号通路的激活,从而导致细胞内基因和蛋白的表达发生变化,引起细胞凋亡、炎症反应、细胞外基质降解等一系列病理生理变化。因此,抑制MAPK信号通路的激活,是治疗IVDD的一个重要策略。许多中药有效成分被证明可以对MAPK信号通路发挥抑制作用,如大蒜素、槲皮素、五味子乙素等中药有效成分均被证明在治疗IVDD具有一定的潜力,通过抑制炎症反应、细胞外基质降解、减轻氧化应激、防止髓核细胞凋亡和细胞外基质降解,从而有效缓解IVDD,见表5。"

IVDD是一种常见的慢性病变,其发病机制涉及到多种信号通路,且信号通路之间存在相互作用和交叉调控是非常复杂的,并且在不同细胞类型和病理状态下可能存在差异。β-catenin是Wnt/β-catenin信号通路中的重要分子,PI3K/Akt下游蛋白激酶Akt可以通过直接磷酸化β-catenin,在细胞质中促进β-catenin的降解,从而抑制Wnt信号通路的激活,同时,β-catenin也可以促进PI3K/Akt激活,通过调节其下游基因表达来影响细胞的增殖和存活;mTOR是PI3K/Akt及AMPK信号通路下游因子,Akt激活后,可以通过抑制TSC1/2复合物来促进mTOR的激活,而Akt和AMPK的作用相反,但一些信号分子如mTOR,可以同时影响Akt和AMPK的活化;NF-κB与MAPK、Wnt/β-catenin信号通路也可相互作用来调节炎症反应和细胞凋亡。中药治疗IVDD可以涉及多条信号通路,并且这些信号通路之间是相互关联的,在干预一条或多条信号通路时也可能存在不良反应和相互制约的情况,因此需要在以后的实验中进行深入的研究和分析错综复杂的关系网,以便更好地开发和利用中药。"

| [1] CHEN J, YANG X, FENG Y, et al. Targeting Ferroptosis Holds Potential for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Therapy. Cells. 2022;11(21):3508. [2] LUO J, YANG Y, WANG X, et al. Role of Pyroptosis in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration and Its Therapeutic Implications. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(12):1804. [3] XIN J, WANG Y, ZHENG Z, et al. Treatment of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(7):1271-1280. [4] ZHENG-WEI S, YUAN T, CHAO-SHUAI F, et al. Roles of Hippo-YAP/TAZ signalling in intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023; 159:114099. [5] KRUT Z, PELLED G, GAZIT D, et al. Stem Cells and Exosomes: New Therapies for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Cells. 2021;10(9):2241. [6] HUANG S, ZHONG J, QI Q, et al. CircRNA expression profile and potential role of hsa_circ_0040039 in intervertebral disc degeneration. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(32):e30035. [7] SHI Z, HE J, HE J, et al. High hydrostatic pressure (30 atm) enhances the apoptosis and inhibits the proteoglycan synthesis and extracellular matrix level of human nucleus pulposus cells via promoting the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Bioengineered. 2022;13(2):3070-3081. [8] WANG JJ, LIU XY, DU W, et al. RBMS3 delays disc degeneration by inhibiting Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020; 24(2):499-507. [9] HIYAMA A, MORITA K, SAKAI D, et al. CCN family member 2/connective tissue growth factor (CCN2/CTGF) is regulated by Wnt-beta-catenin signaling in nucleus pulposus cells. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):217. [10] JIANG C, SUN Z M, ZHU DC, et al. Inhibition of Rac1 activity by NSC23766 prevents cartilage endplate degeneration via Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(6):3582-3592. [11] ZHAN S, WANG K, SONG Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR modulates intervertebral disc degenerative changes via Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):201. [12] YU L, HAO Y, PENG C, et al. Effect of Ginsenoside Rg1 on the intervertebral disc degeneration rats and the degenerative pulposus cells and its mechanism. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;123:109738. [13] LIU H, SHEN J, ZHOU H, et al. Resveratrol regulate the extracellular matrix expression via Wnt/β-catenin pathway in nucleus pulposus cells. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018;32(4):476-483. [14] 苑珍珍,范桐顺,杨召,等.柚皮苷通过Wnt/β-连环蛋白通路调控人髓核细胞凋亡的机制[J].中华实验外科杂志,2018,35(11):2003-2005. [15] 许大勇,李云朋,魏景梅,等.芸香苷改善大鼠椎间盘退变的机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(14):2139-2145. [16] YAO M, ZHANG J, LI Z, et al. Liraglutide Protects Nucleus Pulposus Cells Against High-Glucose Induced Apoptosis by Activating PI3K/Akt/ mTOR/Caspase-3 and PI3K/Akt/GSK3beta/Caspase-3 Signaling Pathways. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:630962. [17] XIAO CL, YIN WC, ZHONG YC, et al. The role of PI3K/Akt signalling pathway in spinal cord injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;156:113881. [18] XIAO Q, TENG Y, XU C, et al. Role of PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway in Nucleus Pulposus Cells. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:9941253. [19] LIU W, NIU F, SHA H, et al. Apelin-13/APJ system delays intervertebral disc degeneration by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(6):2820-2828. [20] TIAN D, LIU J, CHEN L, et al. The protective effects of PI3K/Akt pathway on human nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cells against hypoxia and nutrition deficiency. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):29. [21] GUO X, BAI X, ZHANG F, et al. Resveratrol protects against apoptosis induced by interleukin-1beta in nucleus pulposus cells via activating mTOR/caspase-3 and GSK-3beta/caspase-3 pathways. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(7): BSR20202019. [22] WANG JW, ZHU L, SHI PZ, et al. 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) Mitigates Oxidative Stress-Induced Damage to Nucleus Pulposus-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells through PI3K/Akt Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:1427110. [23] NAN LP, WANG F, LIU Y, et al. 6-gingerol protects nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells from oxidative injury by activating autophagy. World J Stem Cells. 2020;12(12):1603-1622. [24] WANG Z, ZHAO Y, LIU Y, et al. Circ0007042 alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration by adsorbing miR-369 to upregulate BMP2 and activate the PI3K/AKt pathway. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022;24(1):214. [25] WANG D, CHEN Y, CAO S, et al. Cyclic Mechanical Stretch Ameliorates the Degeneration of Nucleus Pulposus Cells through Promoting the ITGA2/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:6699326. [26] GAO J, ZHANG Q, SONG L. Resveratrol enhances matrix biosynthesis of nucleus pulposus cells through activating autophagy via the PI3K/Akt pathway under oxidative damage. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(4):BSR20180544. [27] NAN LP, WANG F, LIU Y, et al. 6-gingerol protects nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells from oxidative injury by activating autophagy. World J Stem Cells. 2020;12(12):1603-1622. [28] 南利平,王静成,王峰,等.柚苷对髓核间充质干细胞生物学性能的影响及其相关机制[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2019,29(4):364-370. [29] 张文捷,张勇,史明,等.淫羊藿苷调控髓核来源间充质干细胞凋亡修复椎间盘退变[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(24):3803-3809. [30] HUANG D, PENG Y, MA K, et al. Puerarin Relieved Compression-Induced Apoptosis and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Human Nucleus Pulposus Mesenchymal Stem Cells via the PI3K/Akt Pathway. Stem Cells Int. 2020; 2020:7126914. [31] 叶禾,张智,郑佳状,等.紫草素对椎间盘髓核细胞凋亡的影响[J].西部医学,2020,32(4):500-504. [32] CHEN HW, ZHOU JW, ZHANG GZ, et al. Emerging role and therapeutic implication of mTOR signalling in intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Prolif. 2023;56(1):e13338. [33] DELEYTO-SELDAS N, EFEYAN A. The mTOR-Autophagy Axis and the Control of Metabolism. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:655731. [34] YURUBE T, ITO M, KAKIUCHI Y, et al. Autophagy and mTOR signaling during intervertebral disc aging and degeneration. JOR Spine. 2020;3(1):e1082. [35] KAKIUCHI Y, YURUBE T, KAKUTANI K, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of mTORC1 but not mTORC2 protects against human disc cellular apoptosis, senescence, and extracellular matrix catabolism through Akt and autophagy induction. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(6):965-976. [36] TAKEOKA Y, YURUBE T, NISHIDA K. Gene Therapy Approach for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: An Update. Neurospine. 2020;17(1):3-14. [37] CHEN W, YASEN M, WANG H, et al. Celecoxib activates autophagy by inhibiting the mTOR signaling pathway and prevents apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2022;23(1):90. [38] KANG L, XIANG Q, ZHAN S, et al. Restoration of Autophagic Flux Rescues Oxidative Damage and Mitochondrial Dysfunction to Protect against Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019; 2019:7810320. [39] XIE C, SHI Y, CHEN Z, et al. Apigenin Alleviates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration via Restoring Autophagy Flux in Nucleus Pulposus Cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:787278. [40] HUANG L, CHEN J, WU D, et al. Berberine Attenuates IL-1β-Induced Damage of Nucleus Pulposus Cells via Activating the AMPK/mTOR/Ulk1 Pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022:6133629. [41] 刘汝银,彭晓艳,岳宗进,等.当归对大鼠椎间盘髓核细胞自噬及氧化应激损伤的作用及机制研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2018,28(2):176-182. [42] 左斌,夏晓枫,车彪,等.虎杖苷对小鼠腰椎间盘退变髓核细胞凋亡及SIRT1/mTOR通路的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(35):5619-5625. [43] ZHANG Y, YI W, XIA H, et al. A20 regulates inflammation through autophagy mediated by NF-kappaB pathway in human nucleus pulposus cells and ameliorates disc degeneration in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;549:179-186. [44] YI W, WEN Y, TAN F, et al. Impact of NF-kappaB pathway on the apoptosis-inflammation-autophagy crosstalk in human degenerative nucleus pulposus cells. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(17):7294-7306. [45] LIU Y, ZHOU W, CHEN FF, et al. Overexpression of LMP-1 Decreases Apoptosis in Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells via Suppressing the NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:8189706. [46] ZHANG C, TONG T, MIAO DC, et al. Vitamin D inhibits TNF-alpha induced apoptosis of human nucleus pulposus cells through regulation of NF-kB signaling pathway. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):411. [47] ZHANG GZ, LIU MQ, CHEN HW, et al. NF-kappaB signalling pathways in nucleus pulposus cell function and intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(7):e13057. [48] CHEN L, XIE ZY, LIU L, et al. Nuclear factor-kappa B-dependent X-box binding protein 1 signalling promotes the proliferation of nucleus pulposus cells under tumour necrosis factor alpha stimulation. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(2):e12542. [49] CHEN J, LIU GZ, SUN Q, et al. Protective effects of ginsenoside Rg3 on TNF-α-induced human nucleus pulposus cells through inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2019;216:1-9. [50] YU H, ZHANG Z, WEI F, et al. Hydroxytyrosol Ameliorates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration and Neuropathic Pain by Reducing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:2240894. [51] YU H, HOU G, CAO J, et al. Mangiferin Alleviates Mitochondrial ROS in Nucleus Pulposus Cells and Protects against Intervertebral Disc Degeneration via Suppression of NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:6632786. [52] GAO G, CHANG F, ZHANG T, et al. Naringin Protects Against Interleukin 1β (IL-1β)-Induced Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells Degeneration via Downregulation Nuclear Factor kappa B (NF-κB) Pathway and p53 Expression. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:9963-9972. [53] XIE T, YUAN J, MEI L, et al. Luteolin suppresses TNF-α-induced inflammatory injury and senescence of nucleus pulposus cells via the Sirt6/NF-κB pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2022;24(1):469. [54] YANG X, LI B, TIAN H, et al. Curcumenol Mitigates the Inflammation and Ameliorates the Catabolism Status of the Intervertebral Discs In Vivo and In Vitro via Inhibiting the TNFα/NFκB Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:905966. [55] TIAN Y, CHU X, HUANG Q, et al. Astragaloside IV attenuates IL-1β-induced intervertebral disc degeneration through inhibition of the NF-κB pathway. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):545. [56] 康小彪,李鹏飞,滕元平,等.淫羊藿苷通过核转录因子KappaB通路减轻大鼠椎间盘退变[J].广州中医药大学学报,2022,39(08):1878-1885. [57] ZHANG HJ, LIAO HY, BAI DY, et al. MAPK /ERK signaling pathway: A potential target for the treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;143:112170. [58] JIANG Z, ZENG Q, LI D, et al. Long non‑coding RNA MALAT1 promotes high glucose‑induced rat cartilage endplate cell apoptosis via the p38/MAPK signalling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2020;21(5):2220-2226. [59] CUI S, ZHANG L. microRNA-129-5p shuttled by mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration via blockade of LRG1-mediated p38 MAPK activation. J Tissue Eng. 2021; 12:1758511983. [60] SUN K, ZHU J, YAN C, et al. CGRP Regulates Nucleus Pulposus Cell Apoptosis and Inflammation via the MAPK/NF-kappaB Signaling Pathways during Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:2958584. [61] XIANG Q, CHENG Z, WANG J, et al. Allicin Attenuated Advanced Oxidation Protein Product-Induced Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Apoptosis in Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:6685043. [62] ZHANG S, LIANG W, ABULIZI Y, et al. Quercetin Alleviates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Modulating p38 MAPK-Mediated Autophagy. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:6631562. [63] 张海丹,李培武,张玲.五味子乙素通过调控p38 MAPK信号通路对IL-1β诱导的髓核细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 医学分子生物学杂志,2019,16(2): 120-125. [64] DAI S, SHI X, QIN R, et al. Sodium Tanshinone IIA Sulfonate Ameliorates Injury-Induced Oxidative Stress and Intervertebral Disc Degeneration in Rats by Inhibiting p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:5556122. [65] ZHAO K, CHEN M, LIU T, et al. Rhizoma drynariae total flavonoids inhibit the inflammatory response and matrix degeneration via MAPK pathway in a rat degenerative cervical intervertebral disc model. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;138:111466. [66] YANG H, YANG X, RONG K, et al. Eupatilin attenuates the senescence of nucleus pulposus cells and mitigates intervertebral disc degeneration via inhibition of the MAPK/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:940475. [67] LI B, YANG X, ZHANG P, et al. Engeletin Alleviates the Inflammation and Apoptosis in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration via Inhibiting the NF-kappaB and MAPK Pathways. J Inflamm Res. 2022;15:5767-5783. [68] 刘伟,冯晶,夏平,等.黄芩素对压力诱导的人椎间盘髓核细胞凋亡的影响[J].实用医学杂志,2019,35(19):3033-3037. [69] DU X, WANG X, CUI K, et al. Tanshinone IIA and Astragaloside IV Inhibit miR-223/JAK2/STAT1 Signalling Pathway to Alleviate Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Damage in Nucleus Pulposus Cells. Dis Markers. 2021;2021:6554480. [70] XIONG Z, DING J, ZHOU J, et al. Correlation between the HIF-1alpha/Notch signaling pathway and Modic changes in nucleus pulposus cells isolated from patients with low back pain. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):500. [71] RAJESH D, DAHIA CL. Role of Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Intervertebral Disc Formation and Maintenance. Curr Mol Biol Rep. 2018; 4(4):173-179. [72] CHEN S, LEI L, LI Z, et al. Grem1 accelerates nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis and intervertebral disc degeneration by inhibiting TGF-beta-mediated Smad2/3 phosphorylation. Exp Mol Med. 2022;54(4):518-530. |
| [1] | Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [2] | Yu Weijie, Liu Aifeng, Chen Jixin, Guo Tianci, Jia Yizhen, Feng Huichuan, Yang Jialin. Advantages and application strategies of machine learning in diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1426-1435. |
| [3] | Wei Juan, Li Ting, Huan Mengting, Xie Ying, Xie Zhouyu, Wei Qingbo, Wu Yunchuan. Mechanism by which static exercise improves insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1271-1276. |
| [4] | Lin Zeyu, Xu Lin. Research progress in gout-induced bone destruction mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1295-1300. |
| [5] | Yue Yun, Wang Peipei, Yuan Zhaohe, He Shengcun, Jia Xusheng, Liu Qian, Li Zhantao, Fu Huiling, Song Fei, Jia Menghui. Effects of croton cream on JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1186-1192. |
| [6] | Liu Xin, Hu Man, Zhao Wenjie, Zhang Yu, Meng Bo, Yang Sheng, Peng Qing, Zhang Liang, Wang Jingcheng. Cadmium promotes senescence of annulus fibrosus cells via activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1217-1222. |
| [7] | Ma Shuwei, He Sheng, Han Bing, Zhang Liaoyun. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of animals with acute liver failure: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1137-1142. |
| [8] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [9] | Li Jiaqi, Huang Yuanli, Li Yan, Wang Chunren, Han Qianqian. Mechanism and influencing factors in molecular weight degradation of non-cross-linked hyaluronic acid [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 747-752. |
| [10] | Xu Rong, Wang Haojie, Geng Mengxiang, Meng Kai, Wang Hui, Zhang Keqin, Zhao Huijing. Research advance in preparation and functional modification of porous polytetrafluoroethylene artificial blood vessels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 759-765. |
| [11] | Chen Xiaofang, Zheng Guoshuang, Li Maoyuan, Yu Weiting. Preparation and application of injectable sodium alginate hydrogels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 789-794. |
| [12] | Liu Chuang, Shan Shuo, Yu Tengbo, Zhou Huan, Yang Lei. Advantages, discomfort and challenges of clinical application of orthopedic hemostatic materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 795-803. |
| [13] | Zhang Ming, Wang Bin, Jia Fan, Chen Jie, Tang Wei. Application of brain-computer interface technology based on electroencephalogram in upper limb motor function rehabilitation of stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 581-586. |
| [14] | Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo. The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 587-593. |
| [15] | He Yuanjie, Chen Yuheng, Zhao Yongchao, Wang Zhenglong. Progress in epigenetic regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell remodeling in the occurrence and development of aortic aneurysms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 602-608. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||