Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (21): 3431-3437.doi: 10.12307/2024.078
Previous Articles Next Articles
Experimental validation of machine learning identification of KDELR3 as a signature gene for osteoarthritis hypoxia
Xu Wenfei1, Ming Chunyu2, Mei Qijie1, Yuan Changshen1, Guo Jinrong1, Zeng Chao1, Duan Kan1
- 1Orthopedic Department of the Limbs, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Geriatrics, Ruikang Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2023-05-05Accepted:2023-06-25Online:2024-07-28Published:2023-09-28 -
Contact:Duan Kan, MD, Chief physician, Orthopedic Department of the Limbs, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Xu Wenfei, Master, Orthopedic Department of the Limbs, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82160912 (to DK); National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82060875 (to YCS); Key Topic of 2018 Guangxi First Class Discipline Construction Project, No. 2018xk074 (to DK)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Wenfei, Ming Chunyu, Mei Qijie, Yuan Changshen, Guo Jinrong, Zeng Chao, Duan Kan. Experimental validation of machine learning identification of KDELR3 as a signature gene for osteoarthritis hypoxia[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(21): 3431-3437.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
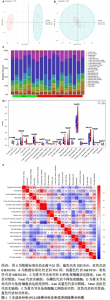
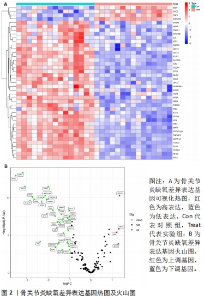
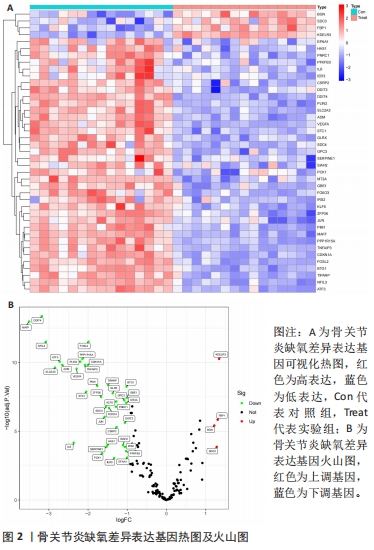
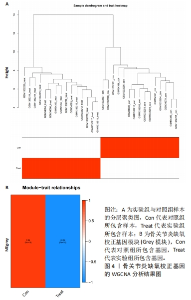
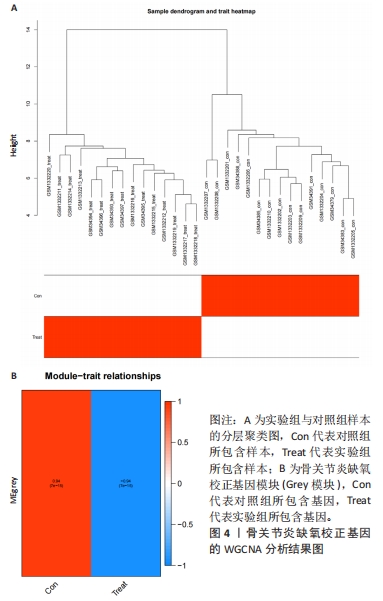
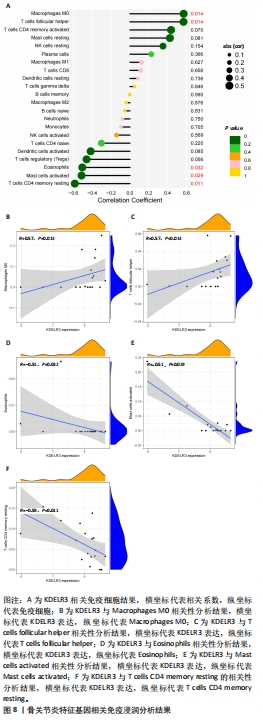
2.1 数据处理及免疫浸润分析结果 通过GEO数据库下载骨关节炎基因芯片数据集GSE55235,GSE1919,GSE82107和GSE98918,共获得37个骨关节炎样品和 34个正常样品的数据;将GSE55235和GSE1919合并、批次校正及PCA分析后得到基因8 492个,见图1A,B。运用GSEA网站hallmark基因集共获取缺氧相关基因200个。 使用CIBERSORT反卷积算法获得骨关节炎相关实验样本的免疫细胞表达情况,研究发现实验组及对照组样本主要与Macrophages M2及Mast cells resting等免疫细胞密切相关,且实验组的表达高于对照组,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图1C,D。运用R语言中的“corrplot”包分析免疫细胞之间的相关性,发现其中Dendritic cells activated与Mast cells activated密切相关(相关系数=0.9),见图1E。"
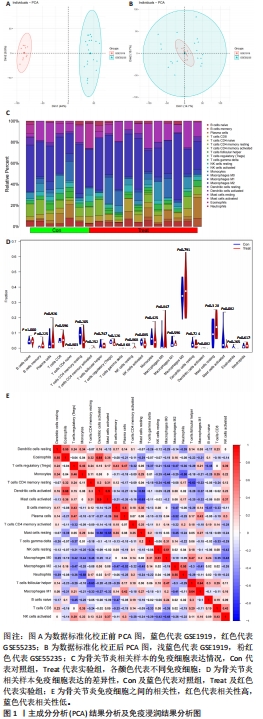
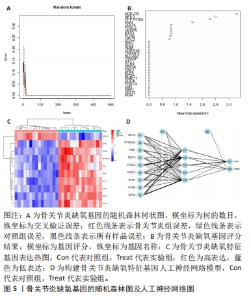
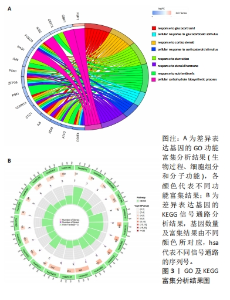
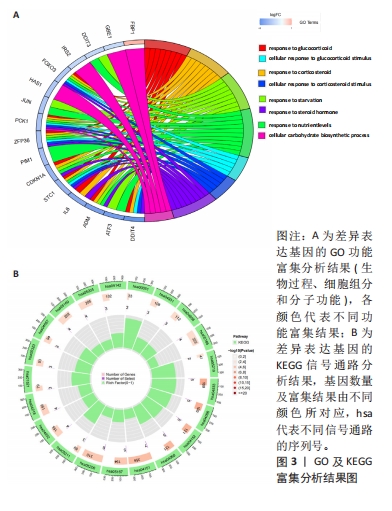
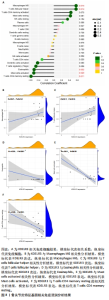
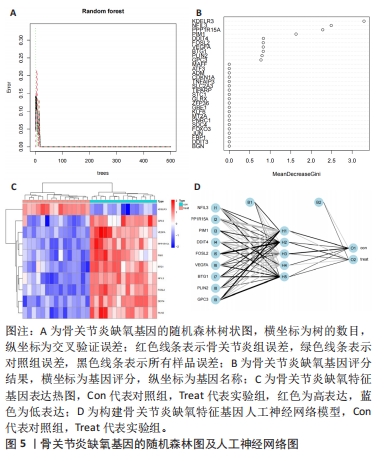
2.5 骨关节炎缺氧基因的随机森林及人工神经网络分析结果 运用R语言对骨关节炎缺氧基因进行随机森林分析,以重要性得分大于0.5共获得10种基因,包括KDELR3,NFIL3,PPP1R15A,PIM1,DDIT4,FOSL2,VEGFA,BTG1,PLIN2和GPC3,其中KDELR3是最重要的基因,见图5A,B。同时运用R语言“heatmap” 包对获得的基因表达绘制热图,发现NFIL3,PPP1R15A,PIM1,DDIT4,FOSL2,VEGFA,BTG1,PLIN2和GPC3在对照组中呈高表达,而KDELR3在实验组中呈高表达,见图5C。同时再次采用R语言对骨关节炎缺氧基因进行人工神经网络分析,根据基因的重要性评分来构建人工神经网络模型,发现实验组与对照组样本选择准确性高,见图5D。"
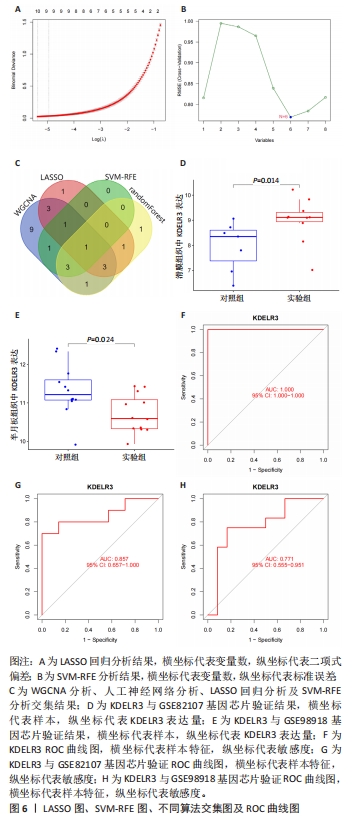
2.6 LASSO回归分析及SVM-RFE分析结果 运用R语言对骨关节炎的缺氧基因进行LASSO回归分析及SVM-RFE分析。LASSO回归分析筛选出10个特征基因(DDIT4,MAFF,NFIL3,KDELR3,ADM,VEGFA,STC1,GLRX,GBE1及GPC3),见图6A;SVM-RFE分析筛选出6个特征基因(KDELR3,MAFF,PLIN2,PPP1R15A,FOSL2及ATF3),见图6B;再采用R语言veen包对WGCNA分析、人工神经网络分析、LASSO回归分析及SVM-RFE分析进行交集,共获得1个骨关节炎缺氧的特征基因KDELR3,见图6C;将KDELR3与GSE82107,GSE98918基因芯片数据进行验证,发现在滑膜组织中实验组KDELR3的表达高于对照组(P=0.014),见图6D;在半月板组织中实验组KDELR3的表达低于对照组(P=0.024),见图6E。同时,运用ROC曲线及验证组ROC曲线能更好地判断KDELR3作为疾病特征基因的准确性,该研究显示:ROC曲线的AUC=1.00,验证组ROC曲线的AUC (GSE82107)=0.857,AUC (GSE98918)=0.771,两者均大于0.5,见图6F-G,说明KDELR3作为疾病特征基因的准确性较高。"
| [1] TANG X, WANG S, ZHAN S, et al. The prevalence of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis in china: results from the china health and retirement longitu dinal study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(3):648-653. [2] CHARLIER E, DEROYER C, CIREGIA F, et al. Chondrocyte dedifferentiation and osteoarthritis (OA). Bioc hem Pharmacol. 2019;165:49-65. [3] LEE JW, KO J, JU C, et al. Hypoxia signaling in human diseases and therapeutic targets. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51(6):1-13. [4] HENROTIN Y, KURZ B, AIGNER T. Oxygen and reactive oxygen species in cartilage degradation: friends or foes? Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005;13(8): 643-654. [5] CAMACHO DM, COLLINS KM, POWERS RK, et al. Next-Generation Machine Learning for Biological Networks. Cell. 2018;173(7):1581-1592. [6] JAMSHIDI A, PELLETIER JP, MARTEL-PELLETIER J. Machine-learning-based patient-specific prediction models for knee osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15(1):49-60. [7] LU K, WEI S, WANG Z, et al. Identification of novel biomarkers in Hunner’s interstitial cystitis using the CIBERSORT, an algorithm based on machine learning. BMC Urol. 2021;21(1):109. [8] CHEN L, ZHANG YH, WANG S, et al. Prediction and analysis of essential genes using the enrichments of gene ontology and KEGG pathways. PLoS One. 2017;12(9):e0184129. [9] KANEHISA M, FURUMICHI M, TANABE M, et al. KEGG: new perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(1): 353-361. [10] LANGFELDER P, HORVATH S. WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008;9:559. [11] CHEN X, ISHWARAN H. Random forests for genomic data analysis. Genomics. 2012;99(6):323-329. [12] ZOU J, HAN Y, SO SS. Overview of artificial neural networks. Methods Mol Biol. 2008;458:15-23. [13] LI Z, SILLANPAA MJ. Overview of LASSO-related penalized regression methods for quantitative trait mapping and genomic selection. Theor Appl Genet. 2012;125(3):419-435. [14] GAO J, KWAN PW, SHI D. Sparse kernel learning with LASSO and Bayesian inference algorithm. Neural Netw. 2010;23(2):257-264. [15] CHEN D, SHEN J, ZHAO W, et al. Osteoarthritis: toward a comprehensive understanding of pathological mechanism. Bone Res. 2017;5:16044. [16] OO WM. Prospects of disease-modifying osteoarthritis drugs. Clin Geriatr Med. 2022;38(2):397-432. [17] WONG BW, MARSCH E, TREPS L, et al. Endothelial cell metabolism in health and disease: impact of hypoxia. EMBO J. 2017;36(15):2187-2203. [18] PFANDER D, CRAMER T, SWOBODA B. Hypoxia and HIF-1alpha in osteoarthritis. Int Orthop. 2005;29(1):6-9. [19] YUDOH K, NAKAMURA H, MASUKO-HONGO K, et al. Catabolic stress induces expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 alpha in articular chondrocytes: involvement of HIF-1 alpha in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(4):904-914. [20] MARKWAY BD, CHO H, JOHNSTONE B. Hypoxia promotes redifferentiation and suppresses markers of hypertrophy and degeneration in both healthy and osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(4):92. [21] WU CL, HARASYMOWICZ NS, KLIMAK MA, et al. The role of macrophages in osteoarthritis and cartilage repair. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(5): 544-554. [22] ZHANG H, CAI D, BAI X. Macrophages regulate the progression of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(5):555-561. [23] CARDAMONE C, PARENTE R, FEO GD, et al. Mast cells as effector cells of innate immunity and regulators of adaptive immunity. Immunol Lett. 2016;178:10-14. [24] SAVVIDOU O, MILONAKI M, GOUMENOS S, et al. Glucocorticoid signaling and osteoarthritis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2019;480:153-166. [25] MATSUZAKI T, ALVAREZ-GARCIA O, MOKUDA S, et al. FoxO transcription factors modulate autophagy and proteoglycan 4 in cartilage homeostasis and osteoarthritis. Sci Transl Med. 2018;10(428):eaan0746. [26] LIN C, SHAO Y, ZENG C, et al. Blocking PI3K/AKT signaling inhibits bone sclerosis in subchondral bone and attenuates post-traumatic osteoarthritis. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(8):6135-6147. [27] TRYCHTA KA, BACK S, HENDERSON MJ, et al. KDEL receptors are differentially regulated to maintain the er proteome under calcium deficiency. Cell Rep. 2018;25(7):1829-1840. [28] SCHWARZ DS, BLOWER MD. The endoplasmic reticulum: structure, function and response to cellular signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73(1):79-94. [29] OAKES SA, PAPA FR. The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in human pathology. Annu Rev Pathol. 2015;10:173-194. [30] TAKADA K, HIROSE J, SENBA K, et al. Enhanced apoptotic and reduced protective response in chondrocytes following endoplasmic reticulum stress in osteoarthritic cartilage. Int J Exp Pathol. 2011;92(4):232-242. [31] RELLMANN Y, EIDHOF E, DREIER R. Review: ER stress-induced cell death in osteoarthritic cartilage. Cell Signal. 2021;78:109880. [32] KANG M, HUANG CC, LU Y, et al. Bone regeneration is mediated by macrophage extracellular vesicles. Bone. 2020;141:115627. [33] SHAN Y, QI C, LIU Y, et al. Increased frequency of peripheral blood follicular helper T cells and elevated serum IL21 levels in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15(3):1095-1102. [34] RAGIPOGLU D, DUDECK A, HAFFNER-LUNTZER M, et al. The role of mast cells in bone metabolism and bone disorders. Front Immunol. 2020;11:163. |
| [1] | Li Yongjie, Fu Shenyu, Xia Yuan, Zhang Dakuan, Liu Hongju. Correlation of knee extensor muscle strength and spatiotemporal gait parameters with peak knee flexion/adduction moment in female patients with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1354-1358. |
| [2] | Qi Haodong, Lu Chao, Xu Hanbo, Wang Mengfei, Hao Yangquan. Effect of diabetes mellitus on perioperative blood loss and pain after primary total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1383-1387. |
| [3] | Du Changling, Shi Hui, Zhang Shoutao, Meng Tao, Liu Dong, Li Jian, Cao Heng, Xu Chuang. Efficacy and safety of different applications of tranexamic acid in high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1409-1413. |
| [4] | Yu Weijie, Liu Aifeng, Chen Jixin, Guo Tianci, Jia Yizhen, Feng Huichuan, Yang Jialin. Advantages and application strategies of machine learning in diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1426-1435. |
| [5] | Huang Xiarong, Hu Lizhi, Sun Guanghua, Peng Xinke, Liao Ying, Liao Yuan, Liu Jing, Yin Linwei, Zhong Peirui, Peng Ting, Zhou Jun, Qu Mengjian. Effect of electroacupuncture on the expression of P53 and P21 in articular cartilage and subchondral bone of aged rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1174-1179. |
| [6] | Zhao Garida, Ren Yizhong, Han Changxu, Kong Lingyue, Jia Yanbo. Mechanism of Mongolian Medicine Erden-uril on osteoarthritis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1193-1199. |
| [7] | Li Rui, Zhang Guihong, Wang Tao, Fan Ping. Effect of ginseng polysaccharide on the expression of prostaglandin E2/6-keto-prostaglandin 1alpha in traumatic osteoarthritis model rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1235-1240. |
| [8] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [9] | Zhang Zeyi, Yang Yimin, Li Wenyan, Zhang Meizhen. Effect of foot progression angle on lower extremity kinetics of knee osteoarthritis patients of different ages: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 968-975. |
| [10] | Shen Feiyan, Yao Jixiang, Su Shanshan, Zhao Zhongmin, Tang Weidong. Knockdown of circRNA WD repeat containing protein 1 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of chondrocytes in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 499-504. |
| [11] | Maisituremu·Heilili, Zhang Wanxia, Nijiati·Nuermuhanmode, Maimaitituxun·Tuerdi. Effect of intraarticular injection of different concentrations of ozone on condylar histology of rats with early temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 505-509. |
| [12] | Qiao Hujun, Wang Guoxiang. Evaluation of rat osteoarthritis chondrocyte models induced by interleukin-1beta [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 516-521. |
| [13] | Bu Xianzhong, Bu Baoxian, Xu Wei, Zhang Chi, Zhang Yisheng, Zhong Yuanming, Li Zhifei, Tang Fubo, Mai Wei, Zhou Jinyan. Analysis of serum differential proteomics in patients with acute cervical spondylotic radiculopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 535-541. |
| [14] | Liu Yuhan, Fan Yujiang, Wang Qiguang. Comparison of protocols for constructing animal models of early traumatic knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 542-549. |
| [15] | Zhang Yaru, Chen Yanjun, Zhang Xiaodong, Chen Shenghua, Huang Wenhua. Effect of ferroptosis mediated by glutathione peroxidase 4 in the occurrence and progression of synovitis in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 550-555. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||