Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (32): 5116-5121.doi: 10.12307/2024.544
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bioinformatics identification and validation of genes related to fatty acid metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis
Lu Xiaoling1, Liu Bin1, Xu Bin1, 2
- 1安徽医科大学基础医学院,安徽省合肥市 230000;2安徽医科大学第一附属医院骨科,安徽省合肥市 230000
-
Received:2023-08-21Accepted:2023-11-04Online:2024-11-18Published:2023-12-28 -
Contact:Xu Bin, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, School of Basic Medicine, Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230000, Anhui Province, China; Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230000, Anhui Province, China -
About author:Lu Xiaoling, Master candidate, School of Basic Medicine, Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230000, Anhui Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province, No. 1808085MH243 (to XB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lu Xiaoling, Liu Bin, Xu Bin. Bioinformatics identification and validation of genes related to fatty acid metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(32): 5116-5121.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
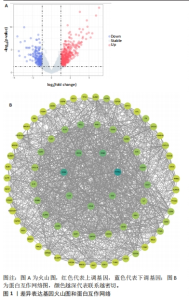
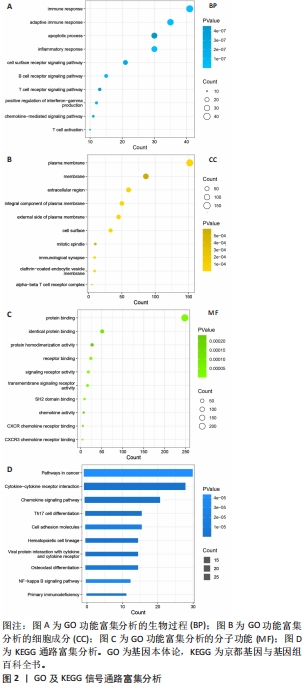
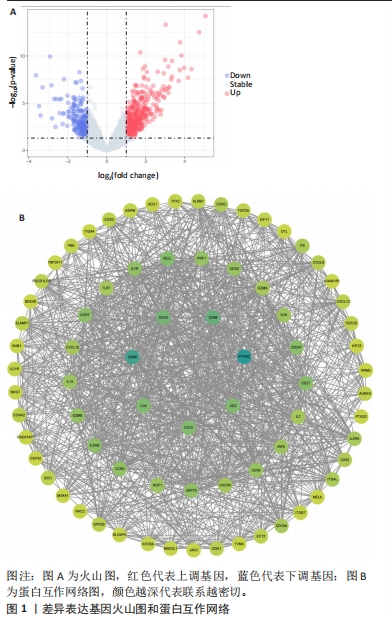
2.1 内部数据集中差异表达基因的鉴定 将来自数据集GSE55235和GSE55457的微阵列数据组合作为内部数据集,包括20个正常样本和23个类风湿关节炎样本,检测到361个差异表达基因,其中249个上调,112个下调(图1A)。用STRING数据库构建一个由已识别的差异表达基因组成的蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络,使用Cytoscape软件中的MCC模式,筛选得分前75的基因(图1B),颜色越深代表联系越密切,由图可知CD8A和PTPRC这2个基因联系最为紧密。使用GO和KEGG富集分析差异表达基因功能,采用生物过程、细胞成分和分子功能3种方法来描述GO分析。生物过程结果显示差异表达基因主要富集与免疫反应相关的生物活性(图2A),细胞成分结果显示差异表达基因主要是质膜和免疫突触(图2B),分子功能结果显示差异表达基因与蛋白质结合和趋化因子受体结合密切相关(图2C)。KEGG结果表明,差异表达基因富含细胞因子-细胞因子受体相互作用和趋化因子信号通路(图2D)。"

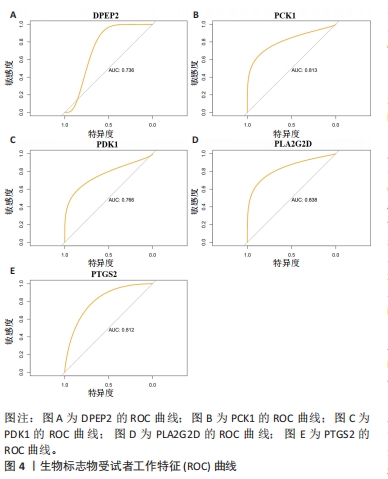
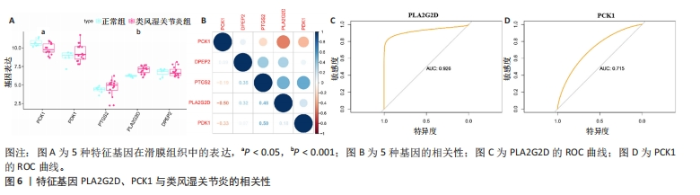
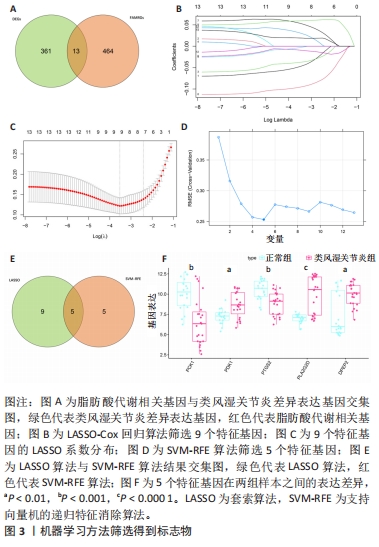
2.2 选择特征基因 从MSigDB数据库中收集464个脂肪酸代谢相关基因。韦恩图显示MsigDB的脂肪酸代谢相关基因与类风湿关节炎差异表达基因的交叉点共有13个(图3A)。通过LASSO算法筛选出13个对类风湿关节炎有很大影响的脂肪酸代谢基因中鉴定了9个特征基因(图3B,C)。使用SVM-RFE算法鉴定5个基因为类风湿关节炎的诊断标志物(图3D)。交叉后,最终鉴定出5个共同的特征基因,即PCK1、PDK1、PTGS2、PLA2G2D、DPEP2(图3E)。结果发现与正常组样本相比,类风湿关节炎患者PDK1、PLA2G2D和DPEP2表达升高,PCK1和PTGS2表达降低(图3F)。进一步研究5个基因特征的ROC,以预测5个特征基因诊断类风湿关节炎疾病的准确性。特征基因ROC曲线的曲线下面积值DPEP2为0.736(图4A),PCK1为0.813(图4B),PDK1为0.766(图4C),PLA2G2D为0.838(图4D),PTGS2为0.812(图4E)。结果显示,5个基因特征具有相当好的预测效果。"
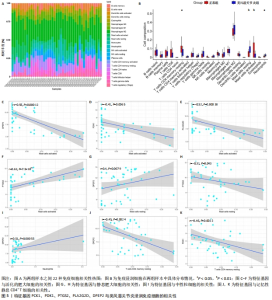
2.3 脂肪酸代谢相关基因与免疫的关系 CIBERSORT算法用于确定两组样本之间不同免疫细胞浸润水平的差异,通过堆叠直方图显示每个样本中22种免疫细胞类型的丰度分布(图5A),不同的颜色代表不同类型的免疫细胞,每种颜色的高度表示样品中细胞的百分比,百分比之和为1。箱式图中红色代表正常样本,蓝色代表类风湿关节炎样本(图5B),结果显示类风湿关节炎滑膜通常含有更高比例的静息肥大细胞(P < 0.01)和中性粒细胞(P < 0.05),而正常滑膜含有更高比率的记忆性静息CD4+ T细胞(P < 0.05)和活化肥大细胞(P < 0.01)。同时计算免疫细胞含量与脂肪酸代谢相关基因之间的相关性,结果表明DPEP2(r=-0.55,P=0.000 12)、PDK1(r=-0.41,P=0.006 5)、PLA2G2D(r=-0.52,P=0.000 038)与活化的肥大细胞呈负相关;PTGS2与活化肥大细胞呈正相关(r=0.62,P=7.5×10-6);DPEP2与静息肥大细胞正相关(r=0.4,P=0.007 9),与记忆性静息CD4+ T细胞(r=0.51,P=0.000 55)呈负相关;PDK1与记忆性静息CD4+ T细胞呈负相关(r=-0.46,P=0.002 2),见图5C-K。这些结果表明特征基因与类风湿关节炎患者的免疫细胞浸润水平密切相关。"

| [1] SCHERER HU, HÄUPL T, BURMESTER GR. The etiology of rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun. 2020;110:102400. [2] 汤纪丰,俞子晴,林锦骠. 致病性Th17细胞在类风湿关节炎中的研究进展[J].中国免疫学杂志,2023,39(4):865-870. [3] SPARKS JA. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 2019;170(1):ITC1-ITC16. [4] ZHAO J, GUO S, SCHRODI SJ, et al. Molecular and Cellular Heterogeneity in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Front Immunol. 2021;12:790122. [5] AKIYAMA M, KANEKO Y. Pathogenesis, clinical features, and treatment strategy for rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Autoimmun Rev. 2022;21(5):103056. [6] RODGERS LC, COLE J, RATTIGAN KM, et al. The rheumatoid synovial environment alters fatty acid metabolism in human monocytes and enhances CCL20 secretion. Rheumatology(Oxford). 2020;59(4):869-878. [7] YAO Y, CAI X, ZHENG Y, et al. Short-chain fatty acids regulate B cells differentiation via the FFA2 receptor to alleviate rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Pharmacol. 2022;179(17):4315-4329. [8] TAKALA R, RAMJI DP, ANDREWS R, et al. Anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory effects of pinolenic acid in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2022;61(3):992-1004. [9] HUANG Z, LUO R, YANG L, et al. CPT1A-Mediated Fatty Acid Oxidation Promotes Precursor Osteoclast Fusion in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:838664. [10] SIGAUX J, BELLICHA A, BUSCAIL C, et al. Serum Fatty Acid Profiles Are Associated with Disease Activity in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results from the ESPOIR Cohort. Nutrients. 2022;14(14):2947. [11] SCHÖNENBERGER KA, SCHÜPFER AC, GLOY VL, et al. Effect of Anti-Inflammatory Diets on Pain in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2021;13(12):4221. [12] IMAS JJ, RUIZ ZAMARREÑO C, ZUBIATE P, et al. Optical Biosensors for the Detection of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Biomarkers: A Comprehensive Review. Sensors (Basel). 2020;20(21):6289. [13] KONDO N, KURODA T, KOBAYASHI D. Cytokine Networks in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(20):10922. [14] FINCKH A, GILBERT B, HODKINSON B, et al. Global epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(10):591-602. [15] DEANE KD, HOLERS VM. Rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis, prediction, and prevention: An emerging paradigm shift. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021;73: 181-193. [16] ZHOU S, LU H, XIONG M. Identifying Immune Cell Infiltration and Effective Diagnostic Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Bioinformatics Analysis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:726747. [17] ZHAO Z, REN J, XIE S, et al. Identification of biomarkers associated with CD8+ T cells in rheumatoid arthritis and their pan-cancer analysis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1044909. [18] NIU D, CHEN Y, MI H, et al. The epiphany derived from T-cell-inflamed profiles: Pan-cancer characterization of CD8A as a biomarker spanning clinical relevance, cancer prognosis, immunosuppressive environment, and treatment responses. Front Genet. 2022;13:974416. [19] AL BARASHDI MA, ALI A, MCMULLIN MF, et al. Protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type C (PTPRC or CD45). J Clin Pathol. 2021;74(9):548-552. [20] WU X, LIU Y, JIN S, et al. Single-cell sequencing of immune cells from anticitrullinated peptide antibody positive and negative rheumatoid arthritis.Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):4977. [21] SATO H, TAKETOMI Y, MIKI Y, et al. Secreted Phospholipase PLA2G2D Contributes to Metabolic Health by Mobilizing ω3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in WAT. Cell Rep. 2020;31(5):107579. [22] XIA W, XIE L, CAO B, et al. Genes involved in leukotriene synthesis pathway are dynamically regulated during lung development in Rhesus monkeys. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2017;122:1-6. [23] BICKFORD JS, MUELLER C, NEWSOM KJ, et al. Effect of allergy and inflammation on eicosanoid gene expression in CFTR deficiency. J Cyst Fibros. 2013;12(3):258-265. [24] LI R, PENG X, WU Y, et al. Exposure to PM during pregnancy causes lung inflammation in the offspring: Mechanism of action of mogrosides. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021;228:112955. [25] LI C, TAO Y, CHEN Y, et al. Development of a metabolism-related signature for predicting prognosis, immune infiltration and immunotherapy response in breast cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2022;12(12):5440-5461. [26] DONG Y, ZHAO Z, SIMAYI M, et al. Transcriptome profiles of fatty acid metabolism-related genes and immune infiltrates identify hot tumors for immunotherapy in cutaneous melanoma. Front Genet. 2022;13:860067. [27] YE Q, LIU Y, ZHANG G, et al. Deficiency of gluconeogenic enzyme PCK1 promotes metabolic-associated fatty liver disease through PI3K/AKT/PDGF axis activation in male mice. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):1402. [28] SHEN Q, ZHONG YT, LIU XX, et al. Platycodin D ameliorates hyperglycaemia and liver metabolic disturbance in HFD/STZ-induced type 2 diabetic mice. Food Funct. 2023;14(1):74-86. [29] KO CW, COUNIHAN D, WU J, et al. Macrophages with a deletion of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1 (Pck1) gene have a more proinflammatory phenotype. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(9):3399-3409. [30] LEE KH, KRONBICHLER A, PARK DD, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in autoimmune diseases: A comprehensive review. Autoimmun Rev. 2017;16(11):1160-1173. [31] VERMA ND, LAM AD, CHIU C, et al. Multiple sclerosis patients have reduced resting and increased activated CD4+CD25+FOXP3+T regulatory cells. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):10476. |
| [1] |
Song Jiating, Chen Jianmin, Wang Kewen, Huang Lanying, Xu Senming, Gui Yuchang, Xu Jianwen.
Metabolomics analysis of serum and urine in patients with traumatic spinal cord injury #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(在线): 1-6.
|
| [2] | Bu Xianzhong, Bu Baoxian, Xu Wei, Zhang Chi, Zhang Yisheng, Zhong Yuanming, Li Zhifei, Tang Fubo, Mai Wei, Zhou Jinyan. Analysis of serum differential proteomics in patients with acute cervical spondylotic radiculopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 535-541. |
| [3] | Song Jiating, Chen Jianmin, Wang Kewen, Huang Lanying, Xu Senming, Gui Yuchang, Xu Jianwen. Metabolomics analysis of serum and urine in patients with traumatic spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(32): 5085-5090. |
| [4] | Li Shudong, Liang Xuezhen, Luo Di, Li Jiacheng, Yan Bozhao, Li Gang. Identification of biomarkers associated with ferroptosis and pyroptosis for the potential diagnosis of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4511-4515. |
| [5] | Liu Jing, Liang Fangyuan, Li Jia, Wang Hua. Mechanisms of acupuncture in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea based on proteomics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4129-4136. |
| [6] | Xu Chenghan, Zhuo Hanjie, Chai Xubin, Huang Yong, Zhang Bowen, Chen Qin, Hao Yupeng, Li Lin, Zhou Yingjie. Meta-analysis of the incidence and related factors for cervical spine instability in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(24): 3922-3929. |
| [7] | Wu Ruiqi, Zhou Yi, Xia Tian, Zhang Chi, Yang Qipei, Zhang Xuan, Zhang Yazhong, Cui Wei. Mendelian randomization study on the association between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporosis and bone mineral density [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3715-3721. |
| [8] | Xu Wenfei, Ming Chunyu, Mei Qijie, Yuan Changshen, Guo Jinrong, Zeng Chao, Duan Kan. Experimental validation of machine learning identification of KDELR3 as a signature gene for osteoarthritis hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(21): 3431-3437. |
| [9] | Liu Baofang, Xu Bin, Chen Lei. Pueraria decoction in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and animal model validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 193-199. |
| [10] | Ran Lei, Han Haihui, Xu Bo, Wang Jianye, Shen Jun, Xiao Lianbo, Shi Qi. Molecular docking analysis of the anti-inflammatory mechanism of Cibotium barometz and Epimedium for rheumatoid arthritis: animal experiment validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 208-215. |
| [11] | Xia Tian, Li Binglin, Xiao Fayuan, Zheng Enze, Chen Yueping. CeRNA interaction network and immune manifestation of ferroptosis-related signature genes in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(16): 2561-2567. |
| [12] | Yuan Tianyi, Liu Hongjiang, Yang Zengqiang, Lu Xingbao, Maimaitiyibubaji, Zhou Zhiheng, Cui Yong. Identification of differences in N6-methyladenosine-related genes in steroid-induced femoral head necrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2159-2165. |
| [13] | Hu Mengfan, Yan Qiuhui, Deng Mengran, Liang Meimei, Liang Liang, Yi Sisi, Deng Jiagang, Yun Chenxia. Mangiferin inhibits proliferation, migration and inflammatory factor expression of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(11): 1690-1695. |
| [14] | Liang Xuezhen, Luo Di, Li Jiacheng, Wen Mingtao, Zhang Jian, Xu Bo, Li Gang. PTGS2 and STAT3 in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head: ferroptosis-related potential diagnostic biomarkers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(36): 5898-5904. |
| [15] | Qi Xue, Li Jiahui, Zhu Yuanfeng, Yu Lu, Wang Peng. Phosphorylation modification of alpha synuclein in serum of patients with Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(35): 5577-5582. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||