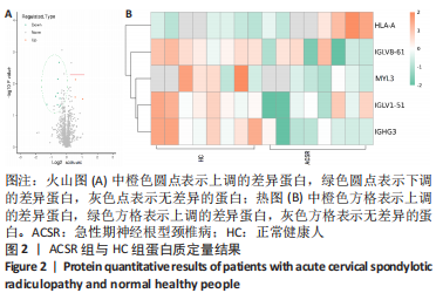
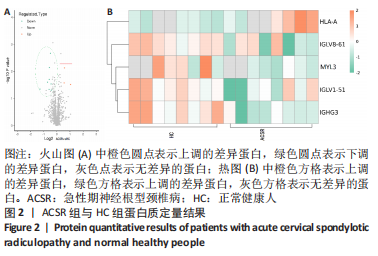
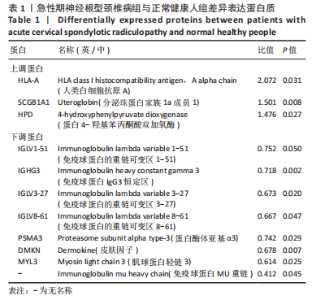
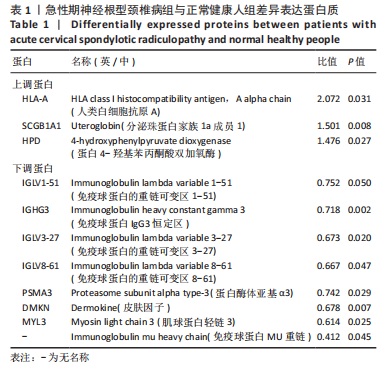
[1] 林纯瑾,邹丽芬,骆雍阳,等.独活寄生汤加减联合塞来昔布对急性期神经根型颈椎病患者的临床疗效[J].中成药,2021,43(12): 3552-3555.
[2] 白登彦,王冠,张海军,等.基于PI3K/AKT信号通路探究芍药甘草汤对神经根型颈椎病模型大鼠Bax和Bcl-2蛋白表达的影响[J].陕西中医,2022,43(1):33-37.
[3] YAO S, OUYANG B, LU T, et al. Treatment of cervical spondylotic radiculopathy with posterior percutaneous endoscopic cervical discectomy: Short-term outcomes of 24 cases. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(20):e20216.
[4] SMITH MD. Cervical radiculopathy: causes and surgical treatment. Minn Med.1995;78(4):28-30,42-45.
[5] 胡天燕,杨海洲. 温通除痹汤结合电针“青灵组穴”对神经根型颈椎病临床疗效及血清炎性指标影响研究[J].中华中医药学刊, 2020,38(8):35-39.
[6] LI X, YANG B, XIAO Z, et al. Comparison of subacute and chronic scar tissues after complete spinal cord transection. Exp Neurol. 2018;306: 132-137.
[7] 林若慧, 陈赛楠, 叶云金, 等. 基于TMT蛋白质组学分析骨疏康胶囊治疗骨质疏松模型大鼠的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(32):5141-5147.
[8] 蔺海旗,陈亮,唐璐,等.尿液蛋白质组学评估机体病理性变化的意义[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(20):3259-3266.
[9] 神经根型颈椎病诊疗规范化研究专家组.神经根型颈椎病诊疗规范化专家共识[S].中华外科杂志,2015,11(11):812-814.
[10] 杨芳洁,吴大伟,何坚.基于NLRP3炎性小体探讨芍药甘草汤对神经根型颈椎病大鼠的抗炎镇痛机制[J].福建中医药,2021,52(5): 53-54+60.
[11] 欧阳石,陈小平,程涛,等.血HLA-A、-B、-C、-DRB1、-DQB1等位基因多态性与肝细胞癌发生关联研究[J].实用肝脏病杂志,2018, 21(6):940-946.
[12] 许吉怡,赵程,王铁山,等. T细胞相关炎症因子在帕金森病发病中的作用[J].中国神经免疫学和神经病学杂志,2021,28(2):131-133+145.
[13] 郑仕杰,于洋,单伟,等.siRNA沉默HLA-A2表达的hMSCs对人异体T淋巴细胞分泌IFN-γ和IL-2功能的影响[J].解剖科学进展,2011, 17(2):147-150+153.
[14] NIMMERJAHN F, RAVETCH JV. Fcgamma receptors as regulators of immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(1):34-47.
[15] HILLIGAN KL, RONCHESE F. Antigen presentation by dendritic cells and their instruction of CD4+ T helper cell responses. Cell Mol Immunol. 2020;17(6):587-599.
[16] SCHWARTZ M, BARUCH K. The resolution of neuroinflammation in neurodegeneration: leukocyte recruitment via the choroid plexus. EMBO J. 2014;33(1):7-22.
[17] XU M, YANG W, WANG X, et al. Lung Secretoglobin Scgb1a1 Influences Alveolar Macrophage-Mediated Inflammation and Immunity. Front Immunol. 2020;11:584310.
[18] VOET S, PRINZ M, VAN LOO G. Microglia in Central Nervous System Inflammation and Multiple Sclerosis Pathology. Trends Mol Med. 2019;25(2):112-123.
[19] LI C, WU Z, ZHOU L, et al. Temporal and spatial cellular and molecular pathological alterations with single-cell resolution in the adult spinal cord after injury [published correction appears in Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):154]. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):65.
[20] KINFETM, ASIF M, CHAKRAVARTHY KV, et al. Unilateral L4-dorsal root ganglion stimulation evokes pain relief in chronic neuropathic postsurgical knee pain and changes of inflammatory markers: part II whole transcriptome profiling. J Transl Med. 2019;17(1):205.
[21] 陆兆亮. HPD调控肺癌细胞代谢和增殖的作用及机制研究[D].广州:暨南大学,2018.
[22] ZHANG Y, XU N, DING Y, et al. Chemerin suppresses neuroinflammation and improves neurological recovery via CaMKK2/AMPK/Nrf2 pathway after germinal matrix hemorrhage in neonatal rats. Brain Behav Immun. 2018;70:179-193.
[23] AARENSTRUP L, FALCH AM, JAKOBSEN KK, et al. Expression and post-translational modification of human 4-hydroxy-phenylpyruvate dioxygenase. Cell Biol Int. 2002;26(7):615-625.
[24] CHEN XJ, MOU XQ, ZOU YG, et al. Screening of key genes associated with contused rat spinal cord with DNA microarray. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013;17(21):2949-2955.
[25] ZHANG C, WANG J, WANG G, et al. Molecular cloning and mRNA expression analysis of sheep MYL3 and MYL4 genes. Gene. 2016; 577(2):209-214.
[26] PETRIEE MA, SUNEJA M, FAIDLE E, et al. Low force contractions induce fatigue consistent with muscle mRNA expression in people with spinal cord injury. Physiol Rep. 2014;2(2):e00248.
[27] PETRIE MA, SUNEJA M, FAIDLEY E, et al. A minimal dose of electrically induced muscle activity regulates distinct gene signaling pathways in humans with spinal cord injury. PLoS One. 2014;9(12):e115791.
[28] 张遥,范丹.长链非编码RNA PSMA3-AS1在人胶质瘤细胞中的表达及作用研究[J].实用肿瘤学杂志,2020,34(3):214-219.
[29] LECLERC EA, HUCHENQ A, KEZIC S, et al. Mice deficient for the epidermal dermokine β and γ isoforms display transient cornification defects. J Cell Sci. 2014;127(Pt 13):2862-2872.
[30] HUANG HM, ZHOU XR, LIU YJ, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitor givinostat alleviates liver fibrosis by regulating hepatic stellate cell activation. Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(5):305.
[31] 蒋诗超,房敏,程英武,等.神经根型颈椎病动物模型国内研究进展及评价[J].中华中医药杂志,2012,27(12):3052-3056.
[32] 杨彬,黄俊卿,张继伟.延胡索提取物通过NOD样受体蛋白3炎性通路治疗神经根型颈椎大鼠的机制研究[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2020,36(3):313-317.
[33] 刘智斌,杨晓航,王渊,等.角度牵引对神经根型颈椎病家兔模型血清β-EP和CRP的影响[J].陕西中医,2009,30(5):628-630.
[34] 朱立国,唐彬,魏戌,等.神经根型颈椎病动物模型的研究进展及评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(35):5700-5705.
[35] 方舒,吕志刚,蒋政焱.影像检查对神经根型颈椎病的诊断及应用进展[J].医学理论与实践,2019,32(20):3250-3252.
[36] 钟远鸣,叶伟权,邱伟,等.神经根型颈椎病中医药治疗进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2022,24(3):5-9.
[37] 黄琛,李兴勇,杨琛,等神经根型颈椎病手术治疗的研究进展[J].甘肃科技,2021,37(12):164-166.
|