Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (15): 2325-2332.doi: 10.12307/2023.370
Previous Articles Next Articles
Identification and function of differentially expressed long noncoding RNAs in the chondrogenesis of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells
Sun Hong1, 2, Deng Jin2, 3, Peng Guoxuan1, 2, Zhuang Yong1, Liu Miao1, Ning Xu1, Yang Hua1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, 3Department of Emergency Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2School of Clinical Medicine, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2022-05-05Accepted:2022-06-28Online:2023-05-28Published:2022-10-17 -
Contact:Yang Hua, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Sun Hong, Master, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; School of Clinical Medicine, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Science and Technology Fund of Guizhou Provincial Health Commission, No. gzwjkj2020-1-120 (to SH); Science and Technology Fund of Guizhou Provincial Health Commission, No. gzwkj2021-261 (to YH); Fundamental Research Program of Science and Technology Department of Guizhou Province, No. [2021] 391 (to YH); National Natural Science Foundation Youth Fund Cultivation Program of Guizhou Medical University Affiliated Hospital, No. gyfynsfc-2021-12 (to SH); Project of Guizhou Provincial Postgraduate Scientific Research Fund, No. YJSKYJJ[2021]157 (to SH); Planning of Guiyang Science and Technology Bureau, No. [2018]1-78 (to ZY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sun Hong, Deng Jin, Peng Guoxuan, Zhuang Yong, Liu Miao, Ning Xu, Yang Hua. Identification and function of differentially expressed long noncoding RNAs in the chondrogenesis of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2325-2332.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
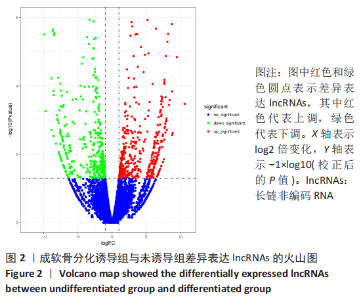
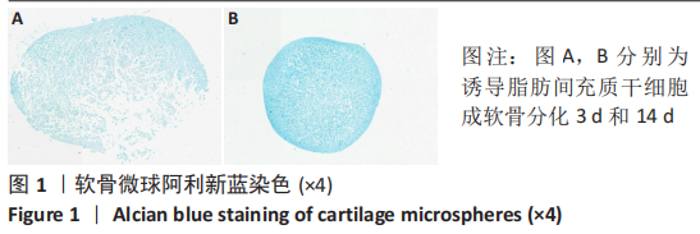
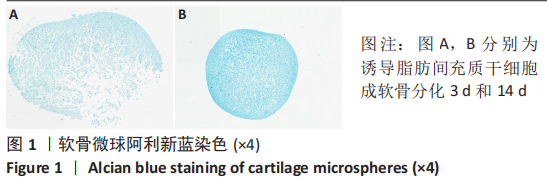
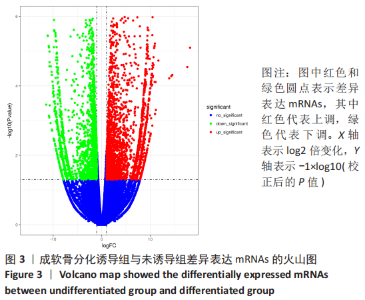
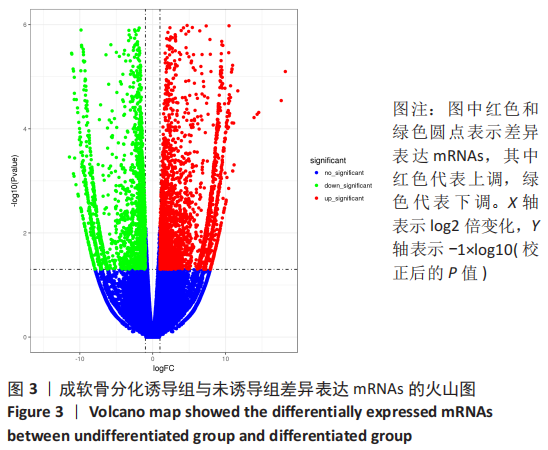
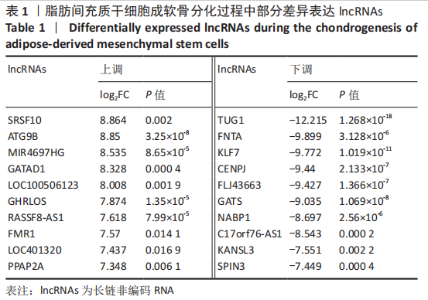
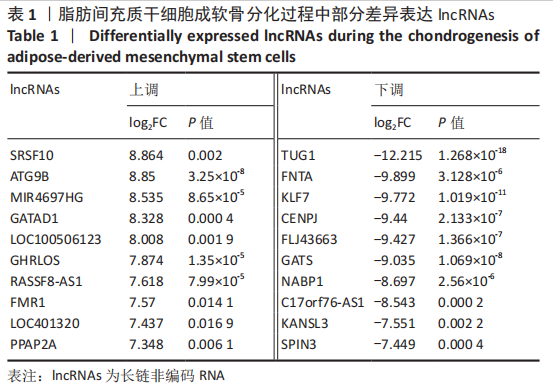
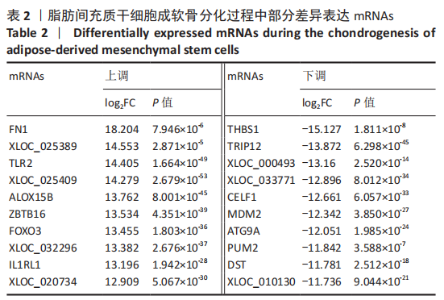
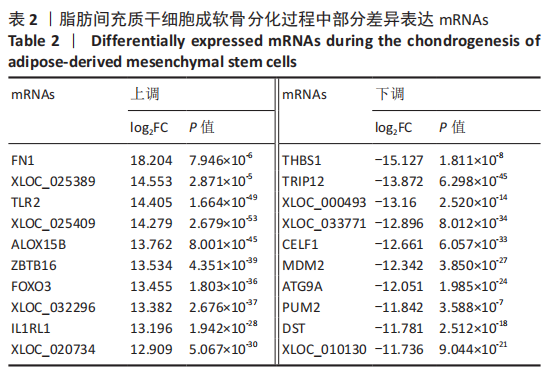
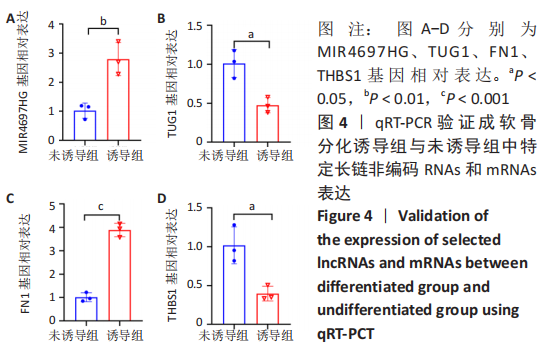
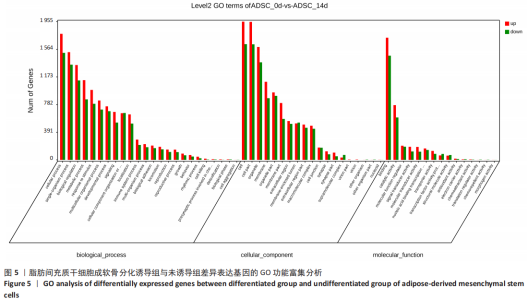
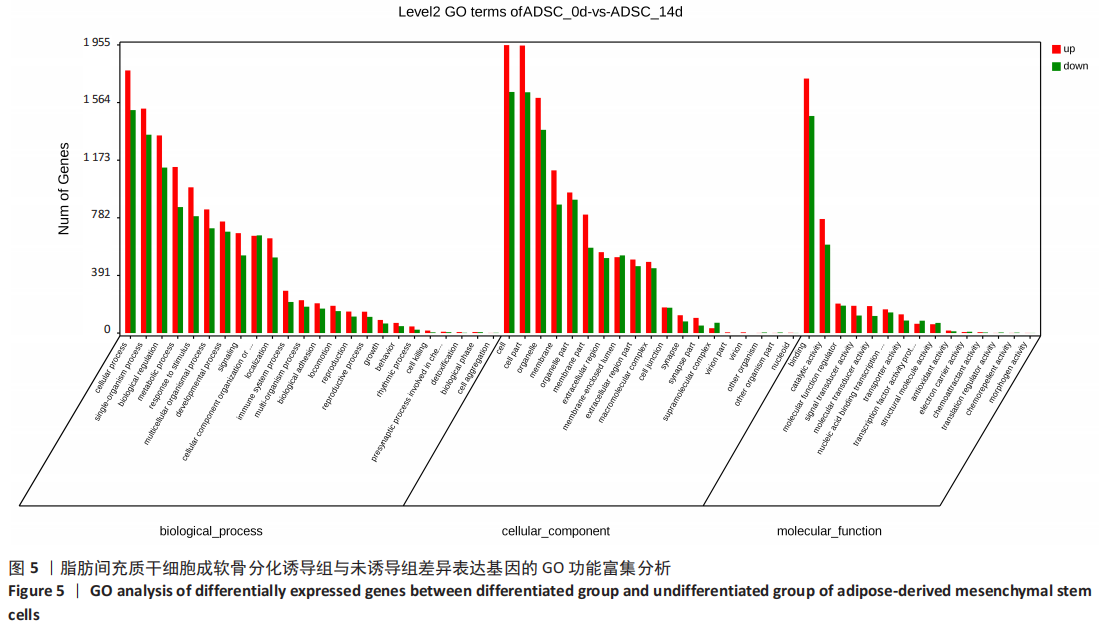
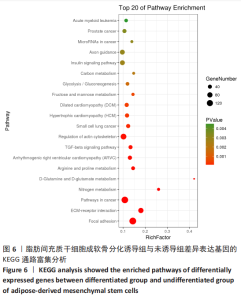
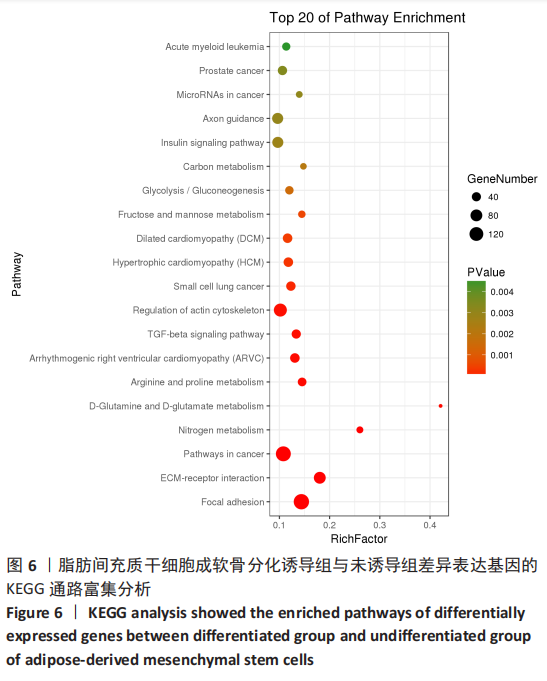
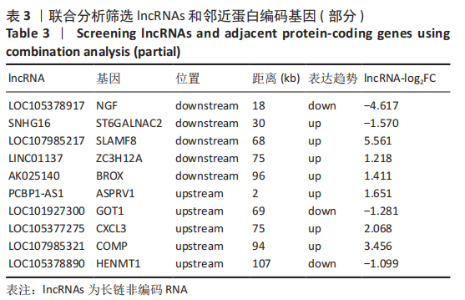
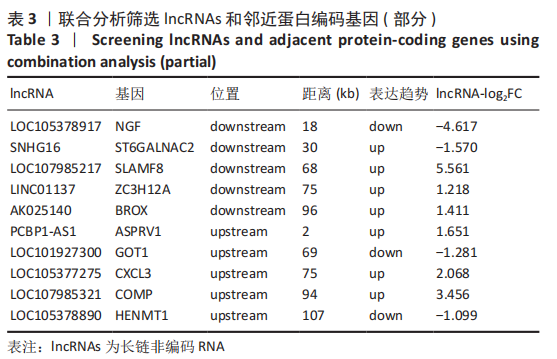
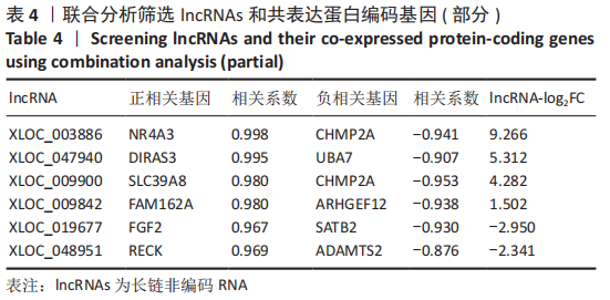
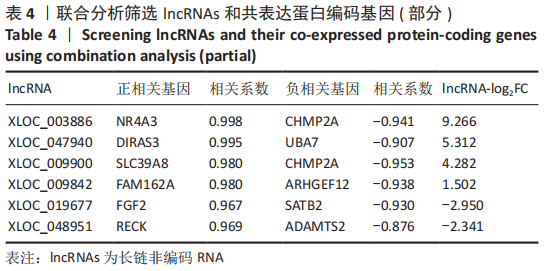
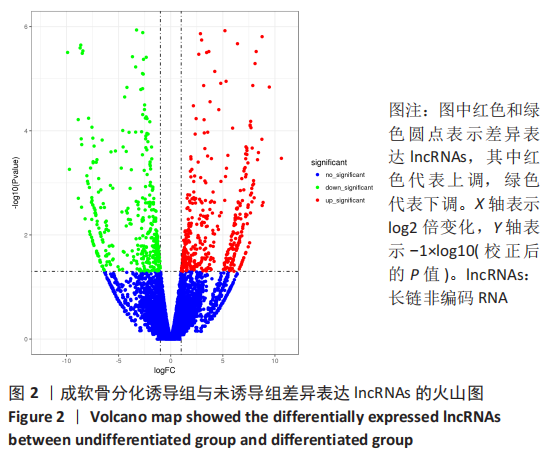
2.2 lncRNAs和mRNAs表达谱分析 转录组测序结果表明,脂肪间充质干细胞向软骨分化过程中lncRNAs和mRNAs表达谱发生了明显改变,见图2,3。与未诱导组相比,诱导组lncRNAs表达差异倍数变化2倍以上者共有816条,其中442条表达升高,374条表达降低。|log2FC|> 5的lncRNAs共有307条,其中189条上调和118条下调。与未诱导组相比,诱导组mRNAs表达差异倍数变化2倍以上者共有5 138条,其中2 931条表达升高,2 207条表达降低。|log2FC|> 5的mRNAs共有2 008条,其中1 234条表达升高,774条表达下降。部分表达差异改变的lncRNAs和mRNAs见表1,2。同时挑选2个lncRNAs包括MIR4697HG(log2FC=8.535)、TUG1(log2FC=-12.215)以及2个mRNAs包括FN1(log2FC=18.204)、THBS1(log2FC=-15.127)进行qRT-PCR验证,结果表明与测序结果表达趋势一致,见图4。"
| [1] BORRELLI J JR, OLSON SA, GODBOUT C, et al. Understanding Articular Cartilage Injury and Potential Treatments. J Orthop Trauma. 2019;33 Suppl 6:S6-S12. [2] ANDERSSON JK, HAGERT E, BRITTBERG M. Cartilage Injuries and Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis in the Wrist: A Review. Cartilage. 2021; 13(1_suppl):156S-168S. [3] ZHAO X, HU DA, WU D, et al. Applications of Biocompatible Scaffold Materials in Stem Cell-Based Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:603444. [4] MENDE W, GÖTZL R, KUBO Y, et al. The Role of Adipose Stem Cells in Bone Regeneration and Bone Tissue Engineering. Cells. 2021;10(5):975. [5] SHI YY, NACAMULI RP, SALIM A, et al. The osteogenic potential of adipose-derived mesenchymal cells is maintained with aging. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005;116(6):1686-1696. [6] PUISSANT B, BARREAU C, BOURIN P, et al. Immunomodulatory effect of human adipose tissue-derived adult stem cells: comparison with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Br J Haematol. 2005;129(1):118-129. [7] MAZINI L, ROCHETTE L, AMINE M, et al. Regenerative Capacity of Adipose Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs), Comparison with Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs). Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(10):2523. [8] KOPP F, MENDELL JT. Functional Classification and Experimental Dissection of Long Noncoding RNAs. Cell. 2018;172(3):393-407. [9] RANSOHOFF JD, WEI Y, KHAVARI PA. The functions and unique features of long intergenic non-coding RNA. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(3): 143-157. [10] SUN H, PENG G, NING X, et al. Emerging roles of long noncoding RNA in chondrogenesis, osteogenesis, and osteoarthritis. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(1):16-30. [11] HUYNH NP, GLOSS CC, LORENTZ J, et al. Long non-coding RNA GRASLND enhances chondrogenesis via suppression of the interferon type II signaling pathway. Elife. 2020;9:e49558. [12] YANG Q, HAN Y, LIU P, et al. Long Noncoding RNA GAS5 Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells by Regulating GDF5 and p38/JNK Signaling Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:701. [13] XU Y, DUAN L, LIU S, et al. Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 00707 regulates chondrocyte apoptosis and proliferation in osteoarthritis by serving as a sponge for microRNA-199-3p. Bioengineered. 2022;13(4):11137-11145. [14] BUNNELL BA, FLAAT M, GAGLIARDI C, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells: isolation, expansion and differentiation. Methods. 2008;45(2):115-120. [15] 李聪聪,姚楠,黄丹娥,等.人髌下脂肪垫干细胞的鉴定及成软骨分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(19):2976-2981. [16] ZHANG Z, KANG Y, ZHANG Z, et al. Expression of microRNAs during chondrogenesis of human adipose-derived stem cells. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(12):1638-1646. [17] ZHANG Z, HUANG G, MAO G, et al. Characterization of exosomal long non-coding RNAs in chondrogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476(3):1411-1420. [18] LI H, ZHAO X, WEN X, et al. Inhibition of miR-490-5p Promotes Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Chondrogenesis and Protects Chondrocytes via the PITPNM1/PI3K/AKT Axis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:573221. [19] STATELLO L, GUO CJ, CHEN LL, et al. Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22(2): 96-118. [20] URLIĆ I, IVKOVIĆ A. Cell Sources for Cartilage Repair-Biological and Clinical Perspective. Cells. 2021;10(9):2496. [21] PANG HL, ZHAO QQ, MA Y, et al. Long Noncoding RNA H19 Participates in the Regulation of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Cartilage Differentiation. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:2139814. [22] MICHIGAMI T. Current understanding on the molecular basis of chondrogenesis. Clin Pediatr Endocrinol. 2014;23(1):1-8. [23] 彭旭,张晓梅,魏诗航,等.骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨及骨分化:Wnt5a/PCP信号通路作用的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(51):7717-7723. [24] 刘宽,吴兴. Hedgehog信号调控骨髓间充质干细胞成软骨细胞分化:调控方式及其串话机制尚待研究[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(37):6040-6045. [25] ZHOU D, GAN L, PENG Y,et al. Epigenetic Regulation of Dental Pulp Stem Cell Fate. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:8876265. [26] DYKES IM, EMANUELI C. Transcriptional and Post-transcriptional Gene Regulation by Long Non-coding RNA. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2017;15(3):177-186. [27] WANG L, LI Z, LI Z, et al. Long noncoding RNAs expression signatures in chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;456(1):459-464. [28] CAO Z, HUANG S, LI J, et al. Long noncoding RNA expression profiles in chondrogenic and hypertrophic differentiation of mouse mesenchymal stem cells. Funct Integr Genomics. 2017;17(6):739-749. [29] SOMOZA RA, WELTER JF, CORREA D, et al. Chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells: challenges and unfulfilled expectations. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2014;20(6):596-608. [30] SHIN H, LEE MN, CHOUNG JS, et al. Focal Adhesion Assembly Induces Phenotypic Changes and Dedifferentiation in Chondrocytes. J Cell Physiol. 2016;231(8):1822-1831. [31] YU H, LIU Y, YANG X, et al. Strontium ranelate promotes chondrogenesis through inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):296. [32] MATTA C, MOBASHERI A. Regulation of chondrogenesis by protein kinase C: Emerging new roles in calcium signalling. Cell Signal. 2014; 26(5):979-1000. [33] FISCHER J, KNOCH N, SIMS T, et al. Time-dependent contribution of BMP, FGF, IGF, and HH signaling to the proliferation of mesenchymal stroma cells during chondrogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(11):8962-8970. [34] KOVERMANN NJ, BASOLI V, DELLA BELLA E, et al. BMP2 and TGF-β Cooperate Differently during Synovial-Derived Stem-Cell Chondrogenesis in a Dexamethasone-Dependent Manner. Cells. 2019; 8(6):636. [35] DUAN J, SHEN T, DONG H, et al. Association of the Expression Levels of Long-Chain Noncoding RNA TUG1 and Its Gene Polymorphisms with Knee Osteoarthritis. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2021;25(2):102-110. [36] TANG LP, DING JB, LIU ZH, et al. LncRNA TUG1 promotes osteoarthritis-induced degradation of chondrocyte extracellular matrix via miR-195/MMP-13 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(24):8574-8581. [37] HAN H, LIU L. Long noncoding RNA TUG1 regulates degradation of chondrocyte extracellular matrix via miR-320c/MMP-13 axis in osteoarthritis. Open Life Sci. 2021;16(1):384-394. [38] LI Z, WANG J, YANG J. TUG1 knockdown promoted viability and inhibited apoptosis and cartilage ECM degradation in chondrocytes via the miR-17-5p/FUT1 pathway in osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(6):154. [39] JIANG H, PANG H, WU P, et al. LncRNA SNHG5 promotes chondrocyte proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in osteoarthritis by regulating miR-10a-5p/H3F3B axis. Connect Tissue Res. 2021;62(6):605-614. [40] SUN Y, KANG S, PEI S, et al. MiR93-5p inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis in osteoarthritis by targeting lncRNA CASC2. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):26. [41] SHI C, ZHENG W, WANG J. lncRNA-CRNDE regulates BMSC chondrogenic differentiation and promotes cartilage repair in osteoarthritis through SIRT1/SOX9. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476(4):1881-1890. [42] MAO G, KANG Y, LIN R, et al. Long Non-coding RNA HOTTIP Promotes CCL3 Expression and Induces Cartilage Degradation by Sponging miR-455-3p. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019;7:161. [43] FENG L, YANG ZM, LI YC, et al. Linc-ROR promotes mesenchymal stem cells chondrogenesis and cartilage formation via regulating SOX9 expression. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(4):568-578. [44] CHENG W, HAO CY, ZHAO S, et al. SNHG16 promotes the progression of osteoarthritis through activating microRNA-93-5p/CCND1 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(21):9222-9229. [45] FAN H, DING L, YANG Y. lncRNA SNHG16 promotes the occurrence of osteoarthritis by sponging miR‑373‑3p. Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(2):117. [46] ZHU J, YU W, WANG Y, et al. lncRNAs: function and mechanism in cartilage development, degeneration, and regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):344. [47] MA C, WU L, SONG L, et al. The pro-inflammatory effect of NR4A3 in osteoarthritis. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(1):930-940. [48] SONG J, KIM D, LEE CH, et al. MicroRNA-488 regulates zinc transporter SLC39A8/ZIP8 during pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. J Biomed Sci. 2013;20(1):31. [49] KIM JH, JEON J, SHIN M, et al. Regulation of the catabolic cascade in osteoarthritis by the zinc-ZIP8-MTF1 axis. Cell. 2014;156(4):730-743. [50] ELLMAN MB, YAN D, AHMADINIA K, et al. Fibroblast growth factor control of cartilage homeostasis. J Cell Biochem. 2013;114(4):735-742. [51] VAN LENT PL, SPAN PN, SLOETJES AW, et al. Expression and localisation of the new metalloproteinase inhibitor RECK (reversion inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs) in inflamed synovial membranes of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64(3): 368-374. [52] KIMURA T, OKADA A, YATABE T, et al. RECK is up-regulated and involved in chondrocyte cloning in human osteoarthritic cartilage. Am J Pathol. 2010;176(6):2858-2867. |
| [1] | Gao Yujin, Peng Shuanglin, Ma Zhichao, Lu Shi, Cao Huayue, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. Osteogenic ability of adipose stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 999-1004. |
| [2] | Wang Hui, Wang Cuiju, Zheng Junyuan, Wang Hua, Guo Baojuan, Chen Pei, Yang Xufang. Modified primary culture and identification of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 5002-5007. |
| [3] | Lin Bo, Chen Xinyu, Jin Qiu, Zhu Zhiman, Zhao Wenhui. Effects of miR-126-3p from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell released exosomes on human umbilical vein endothelial cell glucolipotoxicity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(30): 4773-4779. |
| [4] | Xu Manman, Ji Zhe, Ou Lingdong, Li Ang, Shen Caiqi, Jin Peisheng. Biological characteristics of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in diabetic patients and their effect on promoting wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 3956-3960. |
| [5] | Li Jinglu, Wang Sainan, Wang Yangyang, Fu Guiqiang, Wang Ying, Hu Jianguo, Tang Jie, Lyu Hezuo. CRID3, a blocker of apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a card, influences local gene transcription in mice with acute spinal cord injury: a transcriptomic analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(23): 3620-3632. |
| [6] | Qiao Linghui, Yuan Tao, Han Jie, Wang Guancheng, Gu Yanglin. Screening and biological function analysis of inflammation-related circRNAs in synovial tissue of patients with primary knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(23): 3683-3690. |
| [7] | Liu Haiqin, Ma Huagen, Tang Yuanyu. Expansion and identification of primary rat adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 2953-2957. |
| [8] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [9] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [10] | Zhang Jianhui, Ma Heran, Tan Yi, Wang Zhihui. Knee injury repair using human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells-based scaffold-free three-dimensional gel-like construct in pigs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2969-2975. |
| [11] | Yuan Changshen, Rong Weiming, Lu Zhixian, Duan Kan, Guo Jinrong, Mei Qijie. Construction of osteosarcoma miRNA-mRNA regulatory network based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2740-2746. |
| [12] | Yang Zhen, Li Hao, Gao Cangjian, Fu Liwei, Tian Guangzhao, Zha Kangkang, Sun Zhiqiang, Li Xu, Guo Weimin, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Liu Shuyun, Lu Shibi, Guo Quanyi . Regulation of stem cells by transforming growth factor β3/polylactic acid-glycolic acid microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(28): 4540-4546. |
| [13] | Lin Jiaying, Chen Shuyi, Chen Shengfeng, Wang Bingyun, Chen Zhisheng, Liu Canying, Bai Yinshan, Ji Huiqin, Xie Shiting. Canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes in the repair of gentamicin-induced renal tubular epithelial cell injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 3959-3965. |
| [14] | Sui Xiang, Tian Guangzhao, Yang Zhen, Li Xu, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi. Application potential of CD146 positive subpopulation as seed cells for cartilage tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(19): 2997-3003. |
| [15] | Xiong Kun, Deng Jiang, Huang Wenliang, Yuan Cheng, Ruan Shiqiang, Ma Xianming, Li Maolun, Ding Chuan. Long noncoding RNAs are involved in osteoblast differentiation and osteoclast production [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(14): 2229-2234. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||