Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (15): 2333-2338.doi: 10.12307/2023.387
Previous Articles Next Articles
Transcriptome sequencing analysis of osteogenic rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced by osteomyelitis
Wen Hongjie1, Chen Zhong1, Yang Huagang1, Xu Yongqing2
- 1Department of Orthopedic and Trauma Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Yunnan University, Second People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650021, Yunnan Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, 920 Hospital of Joint Logistics Support Force of Chinese PLA, Kunming 650021, Yunnan Province, China
-
Received:2022-04-27Accepted:2022-07-14Online:2023-05-28Published:2022-10-17 -
Contact:Xu Yongqing, MD, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, 920 Hospital of Joint Logistics Support Force of Chinese PLA, Kunming 650021, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Wen Hongjie, MD, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedic and Trauma Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Yunnan University, Second People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650021, Yunnan Province, China -
Supported by:Kunming Medical Joint Special Project of Basic Research Program of Yunnan Province, No. 202201AY070001-274 (to WHJ); Scientific Research Foundation of Yunnan Education Department, No. 2022J0016 (to WHJ); National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 82072392 (to XYQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wen Hongjie, Chen Zhong, Yang Huagang, Xu Yongqing. Transcriptome sequencing analysis of osteogenic rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced by osteomyelitis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2333-2338.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
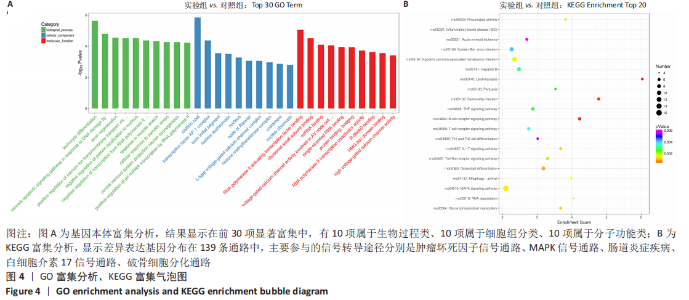
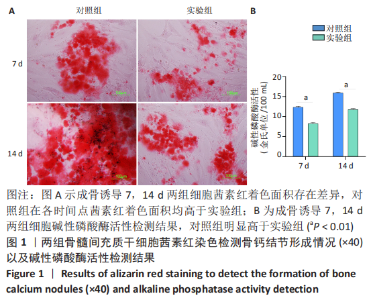
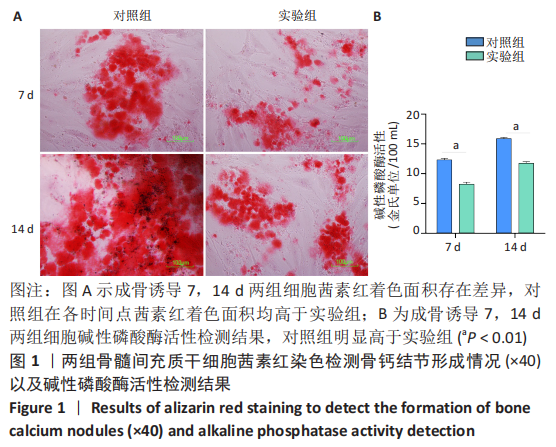
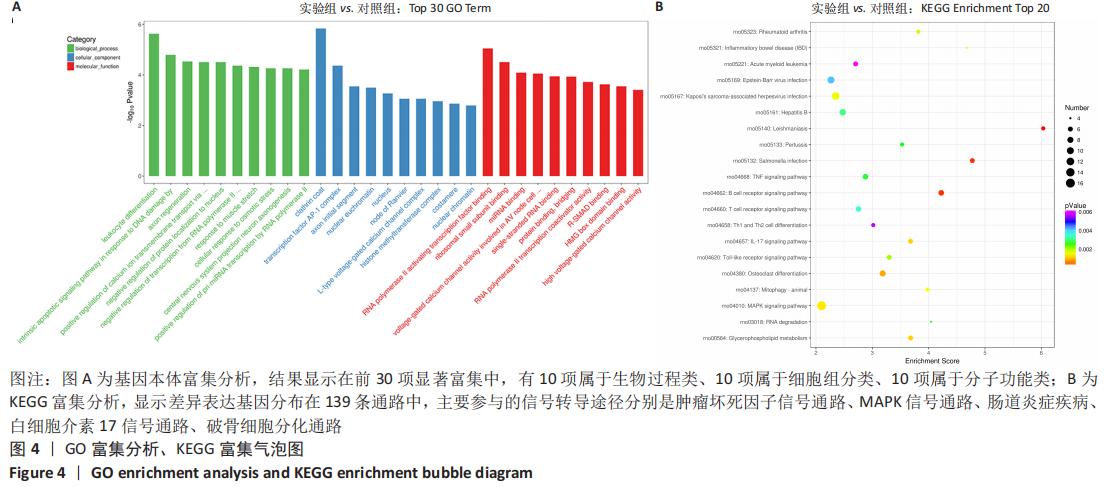
对差异表达基因进行基因本体富集分析,以探究这些差异表达基因的生物学功能。在前30项显著富集中,有10项属于生物过程类(前10项分别是:白细胞分化、DNA损伤相关内在凋亡信号通路、轴突再生、钙离子跨膜转运的正调控作用、负调控蛋白定位到细胞核、RNA聚合酶的转录负调控、肌肉拉伸反应、细胞对渗透压的反应、中枢神经系统投射神经元轴突形成、RNA聚合酶Ⅱ对pri-miRNA转录的正向调控),10项属于细胞组分类(网格蛋白、转录因子AP-1复合物、轴突的初始部分、核常染色质、细胞核、郎飞氏结、L型电压门控钙通道复合物、组蛋白甲基转移酶、肌节与细胞膜连接成分、核染色质),10项属于分子功能类(激活转录因子结合的RNA聚合酶Ⅱ、核糖体小亚基结合、miRNA的绑定、参与房室结细胞的电压门控钙通道活性、单链RNA绑定、蛋白质绑定桥接、RNA聚合酶Ⅱ转录共激活因子活性、R-SMAD绑定、HMG区域结合、高电压门控钙通道活性),见图4A。结果显示,差异表达基因与细胞发育和代谢过程密切相关。 KEGG 富集分析发现,这些差异表达基因分布在139条通路中。主要参与的信号转导途径分别是肿瘤坏死因子信号通路、MAPK信号通路、肠道炎症疾病、白细胞介素17信号通路、破骨细胞分化、B细胞受体、T细胞受体、线粒体自噬、甘油磷脂代谢通路,见图4B。这些结果表明,葡萄球菌A蛋白模拟的骨髓炎环境影响了骨形成与骨代谢的多个信号通路。"
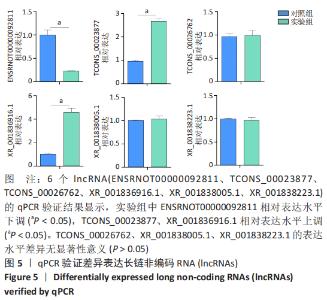
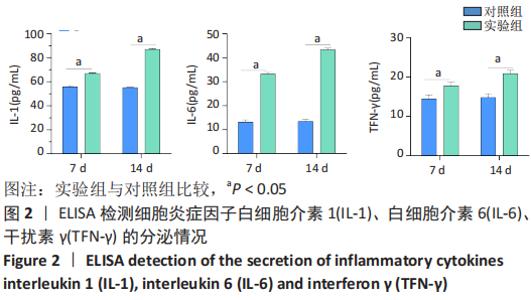
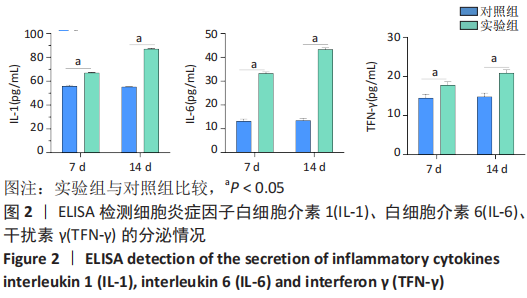
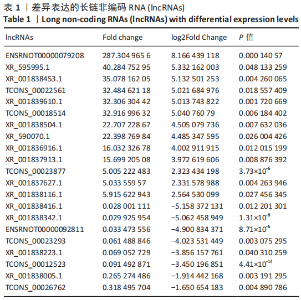
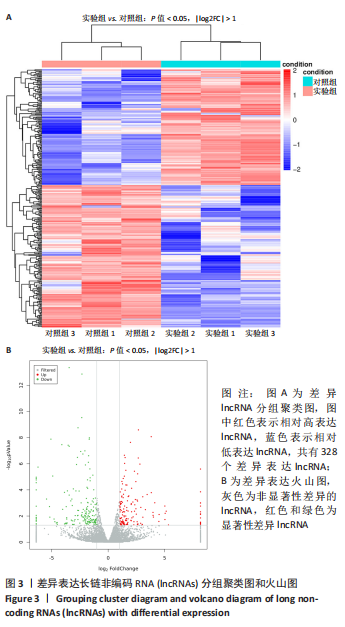
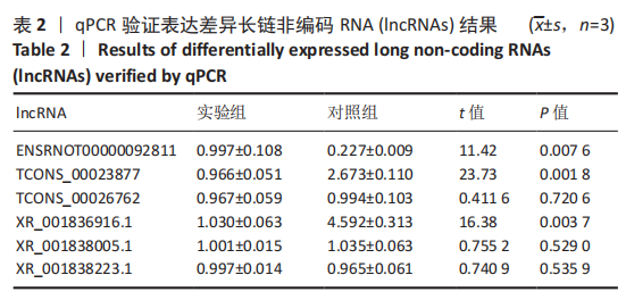
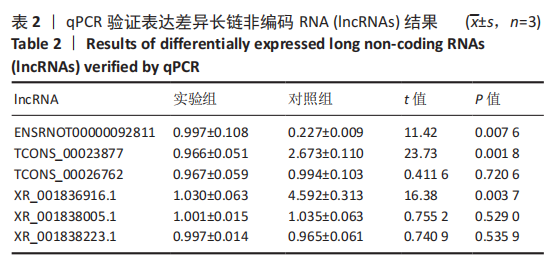
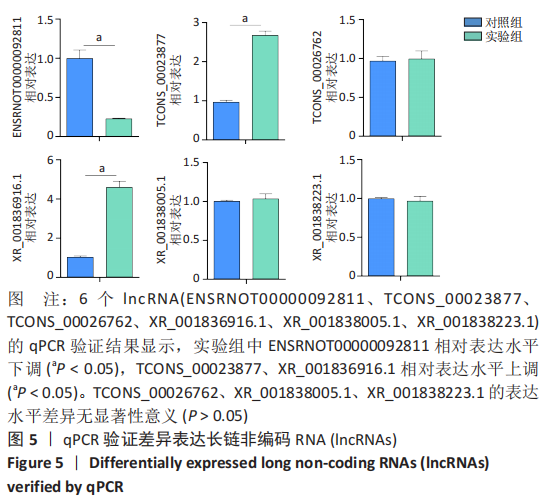
2.4 qPCR验证 将选出的与成骨分化及骨代谢密切相关的6个lncRNAs(ENSRNOT00000092811、TCONS_00023877、TCONS_00026762、XR_001836916.1、XR_001838005.1、XR_001838223.1),通过qPCR测定其相对表达水平。结果显示,与对照组相比,实验组中ENSRNOT00000092811相对表达水平下调,TCONS_00023877、XR_001836916.1相对表达水平上调(P < 0.05),TCONS_00026762、XR_001838005.1、XR_001838223.1的表达水平差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图5和表2。"
| [1] BOFFELI TJ, LUER SA, BRETT KM, et al. A Review of Consecutive Cases to Identify the Rate of Underlying Osteomyelitis in Patients Undergoing Surgical Treatment of Gangrene of the Forefoot and Impact of Acute Infection on Outcome Following Amputation. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2022;61(2):286-292. [2] CARUSO P, GICCHINO M, LONGO M, et al. When amputation is not the end of the challenge: A successful therapy for osteomyelitis and soft tissue infection in a patient with type 1 diabetes. J Diabetes Investig. 2022;13(1):209-212. [3] CONCHA S, HERNÁNDEZ-OJEDA A, CONTRERAS O, et al. Chronic nonbacterial osteomyelitis in children: a multicenter case series. Rheumatol Int. 2020;40(1): 115-120. [4] MORLEY R, ROTHWELL M, STEPHENSON J, et al. Complex Foot Infection Treated With Surgical Debridement and Antibiotic Loaded Calcium Sulfate-A Retrospective Cohort Study of 137 Cases. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2022;61(2):239-247. [5] 马敬龙,阳富春.成人慢性骨髓炎的临床诊断和治疗进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(5):651-655. [6] CROES M, VAN DER WAL BCH, VOGELY HC. Impact of Bacterial Infections on Osteogenesis: Evidence From In Vivo Studies. J Orthop Res. 2019;37(10):2067-2076. [7] JIN T, LU Y, HE QX, et al. The Role of MicroRNA, miR-24, and Its Target CHI3L1 in Osteomyelitis Caused by Staphylococcus aureus. J Cell Biochem. 2015;116(12): 2804-2813. [8] WEN H, CHEN Z, CUI Y, et al. LncRNA NONHSAT009968 inhibits the osteogenic differentiation of hBMMSCs in SA-induced inflammation via Wnt3a. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;577:24-31. [9] WU H, CAO F, ZHOU W, et al. Long Noncoding RNA FAM83H-AS1 Modulates SpA-Inhibited Osteogenic Differentiation in Human Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2020;40(5):e00362-19. [10] FU W, HE W, REN Y, et al. Distinct expression trend of signature antigens of Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis correlated with clinical outcomes. J Orthop Res. 2021;39(2):265-273. [11] JIN T, ZHU YL, LI J, et al. Staphylococcal protein A, Panton-Valentine leukocidin and coagulase aggravate the bone loss and bone destruction in osteomyelitis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;32(2):322-333. [12] 宋明瑞,侯毅龙,林艺煌,等.金黄色葡萄球菌感染所致骨量丢失的分子机制研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2021,23(4):349-358. [13] 文强强,刘岩,苏子龙,等.金黄色葡萄球菌骨髓炎发病机制的研究进展[J].实用骨科杂志,2020,26(10):901-905. [14] CHEN R, HUANG H, LIANG L, et al. Improving the repair mechanism and miRNA expression profile of tibial defect in rats based on silent information regulator 7 protein analysis of mesenchymal stem cells. Bioengineered. 2022;13(3):4674-4687. [15] LIU Z, DENG Y, LI T, et al. The opposite functions of miR-24 in the osteogenesis and adipogenesis of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells are mediated by the HOXB7/β-catenin complex. FASEB J. 2020;34(7):9034-9050. [16] TENG Z, ZHU Y, HAO Q, et al. Long non-coding RNA taurine upregulated gene 1 is downregulated in osteoporosis and influences the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. PeerJ. 2021;9:e11251. [17] TENG ZW, ZHU Y, NA Q, et al. Regulatory effect of miRNA on multi-directional differentiation ability of mesenchymal stem cell in treatment of osteoporosis. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2016;30(2):345-352. [18] CUI Y, LU S, TAN H, et al. Silencing of Long Non-Coding RNA NONHSAT009968 Ameliorates the Staphylococcal Protein A-Inhibited Osteogenic Differentiation in Human Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;39(4):1347-1359. [19] YU G, WANG LG, HAN Y, et al. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS. 2012;16(5):284-287. [20] JIN QY, ZHU QH, DENG W, et al. Follistatin-like 1 suppresses osteoblast differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal cells during inflammation. Arch Oral Biol. 2022;135:105345. [21] KUANG W, ZHENG L, XU X, et al. Dysregulation of the miR-146a-Smad4 axis impairs osteogenesis of bone mesenchymal stem cells under inflammation. Bone Res. 2017;5:17037. [22] ZHU K, YANG C, DAI H, et al. Crocin inhibits titanium particle-induced inflammation and promotes osteogenesis by regulating macrophage polarization. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;76:105865. [23] GUO Y, SONG G, SUN M, et al. Prevalence and Therapies of Antibiotic-Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020;10:107. [24] BASKAR K, ANUSUYA T, DEVANAND VENKATASUBBU G. Mechanistic investigation on microbial toxicity of nano hydroxyapatite on implant associated pathogens. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;73:8-14. [25] DING R, WEI S, HUANG M. Long non-coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 overexpression promotes osteogenic differentiation of staphylococcus aureus-infected human bone mesenchymal stem cells by sponging microRNA miR-29b-3p. Bioengineered. 2022;13(3):5855-5867. [26] KAVANAGH N, O’BRIEN FJ, KERRIGAN SW. Staphylococcus aureus protein A causes osteoblasts to hyper-mineralise in a 3D extra-cellular matrix environment. PLoS One. 2018;13(6):e0198837. [27] REN LR, WANG H, HE XQ, et al. Staphylococcus aureus Protein A induces osteoclastogenesis via the NF‑κB signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(5): 6020-6028. [28] FAN Q, LI Y, SUN Q, et al. miR-532-3p inhibits osteogenic differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells by downregulating ETS1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020; 525(2):498-504. [29] JI Y, FANG QY, WANG SN, et al. Lnc-RNA BLACAT1 regulates differentiation of bone marrow stromal stem cells by targeting miR-142-5p in osteoarthritis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(6):2893-2901. [30] BEHERA J, KUMAR A, VOOR MJ, et al. Exosomal lncRNA-H19 promotes osteogenesis and angiogenesis through mediating Angpt1/Tie2-NO signaling in CBS-heterozygous mice. Theranostics. 2021;11(16):7715-7734. [31] BAI Y, GONG X, DONG R, et al. Long non-coding RNA HCAR promotes endochondral bone repair by up regulating VEGF and MMP13 in hypertrophic chondrocyte through sponging miR-15b-5p. Genes Dis. 2020;9(2):456-465. |
| [1] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [2] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [3] | Yang Zhishan, Tang Zhenglong. YAP/TAZ, a core factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, is involved in bone formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| [4] | Zhao Wei, Feng Wei, Yang Tieyi, Ren Wei, Wang Yuxin, Lyu Huicheng, Chang Zhiqiang, Feng Xiaodong, Wang Ziheng, Guo Shibing. Antibiotic bone cement intramedullary nail prepared using 3D printed mold for the treatment of long bone infection in lower limbs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1023-1030. |
| [5] | Li Xinyue, Li Xiheng, Mao Tianjiao, Tang Liang, Li Jiang. Three-dimensional culture affects morphology, activity and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 846-852. |
| [6] | Li Qicheng, Deng Jin, Fu Xiaoyang, Han Na. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on hypoxia-treated myoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 853-859. |
| [7] | Wang Min, Yin Xiushan, Wang Yingxi, Zhang Yan, Zhao Long, Xia Shuyue. Inhalation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviates inflammatory injury in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 827-834. |
| [8] | Yuan Wei, Liu Jingdong, Xu Guanghui, Kang Jian, Li Fuping, Wang Yingjie, Zhi Zhongzheng, Li Guanwu. Osteogenic differentiation of human perivascular stem cells and its regulation based on Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 866-871. |
| [9] | Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 840-845. |
| [10] | Long Yanming, Xie Mengsheng, Huang Jiajie, Xue Wenli, Rong Hui, Li Xiaojie. Casein kinase 2-interaction protein-1 regulates the osteogenic ability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in osteoporosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 878-882. |
| [11] | Li Rui, Liu Zhen, Guo Zige, Lu Ruijie, Wang Chen. Aspirin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles and polydopamine modified titanium sheets improve osteogenic differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 374-379. |
| [12] | Dai Xianglin, Zhang Wenfeng, Yao Xijun, Shang Jiaqi, Huang Qiujin, Ren Yifan, Deng Jiupeng. Barium titanate/polylactic acid piezoelectric composite film affects adhesion, proliferation, and osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 367-373. |
| [13] | Ling Xuwei, Sun Jie, Liu Chang, Wang Yi, Shi Qin, Yang Huilin. Valproic acid promotes osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2304-2310. |
| [14] | Cai Bo, Li Xiaoxiao, Zhang Linghan, Liu Yanxing, Mao Genhong. Editing immune-related gene HLA-DRA for the first time by CRISPR/Cas9 technology combined with liposome transfection of endometrial cancer cells with single-plasmid gene knockout method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2356-2362. |
| [15] | He Zike, Wang Shangzeng. Eucommia ulmoides Oliver aqueous extract promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and osteoblastic differentiation through upregulating Nur77 protein expression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2371-2378. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||