Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (28): 4525-4532.doi: 10.12307/2023.567
Previous Articles Next Articles
Screening and identification of Hub genes in osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics
Wu Suwen1, Chen Zheng1, Jiang Yuankang1, Chen Leilei2
- 1The Third Clinical Medical College, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Joint, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510145, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2022-07-21Accepted:2022-09-15Online:2023-10-08Published:2023-01-29 -
Contact:Chen Leilei, MD, Associate chief physician, Department of Joint, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510145, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Wu Suwen, Master candidate, The Third Clinical Medical College, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81673999 (to CLL); Science Foundation for Outstanding Youth of Guangdong Province, No. 2015A030306037 (to CLL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Suwen, Chen Zheng, Jiang Yuankang, Chen Leilei. Screening and identification of Hub genes in osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(28): 4525-4532.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
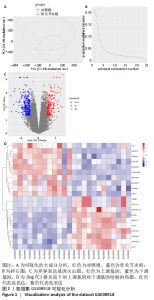
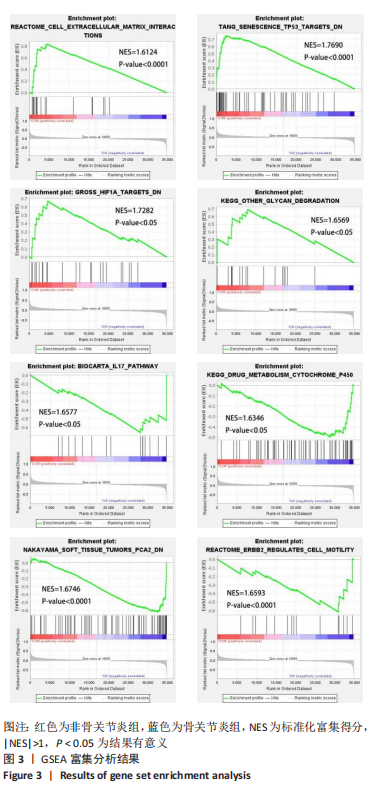
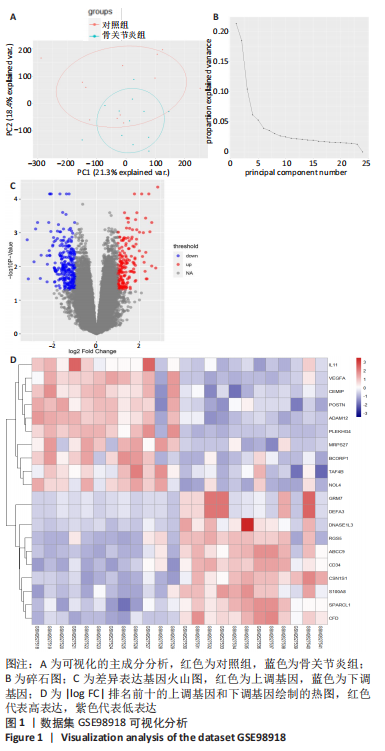
2.1 差异表达基因的生物信息学筛选及分析 2.1.1 数据集获取 在GEO数据库中获取符合筛选条件的数据集GSE98918,该数据集包含12例骨关节炎患者的半月板组织和12例非骨关节炎(关节镜下半月板部分切除术)患者的半月板组织。 2.1.2 数据处理及差异表达基因的筛选 使用GEO2R分析获得差异表达基因列表并下载差异基因列表和矩阵文件,使用R语言devtools包及ggbiplot包对数据集进行可视化的主成分分析和碎石图的绘制,如图1A,B所示,主成分分析显示两组样本间有明显的群体偏差聚类,碎石图显示参考提取因子个数为4时,累计方差解释率就可达到90%以上,提取因子个数为6时,曲线趋于平缓,说明骨关节炎患者组与正常对照组半月板组织的基因表达谱有显著差异,分析结果可信度高。 用Excel筛选列表中的差异表达基因,条件为adj.P. Value < 0.05,|log FC|> 1,得到上调基因147个、下调基因212个。使用R语言ggplot2包对筛选出的差异表达基因绘制火山图,见图1C。选取|log FC|排名前十的上调基因和下调基因,使用R语言pheatmap包进行热图的绘制,见图1D。"
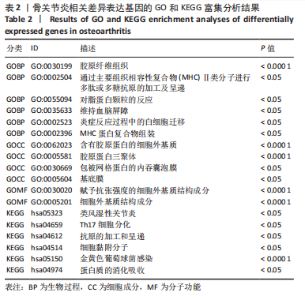
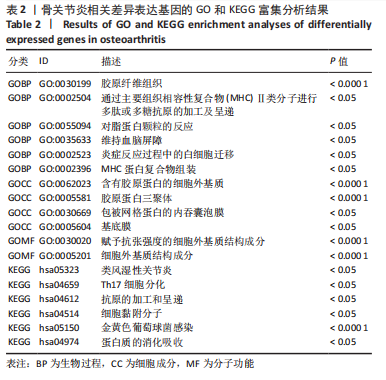
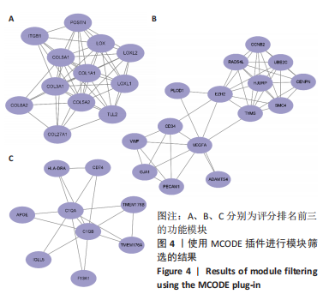
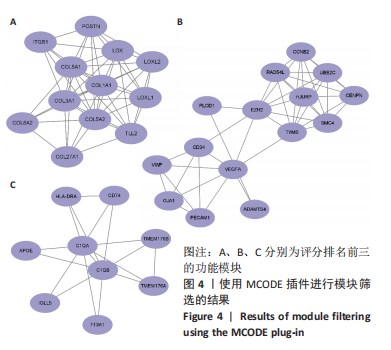
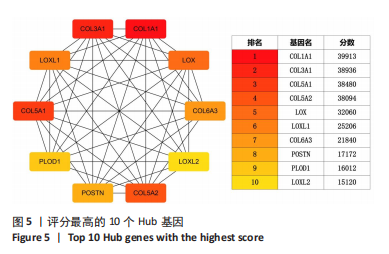
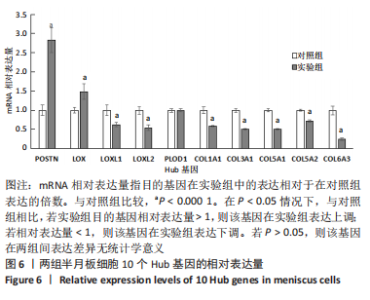
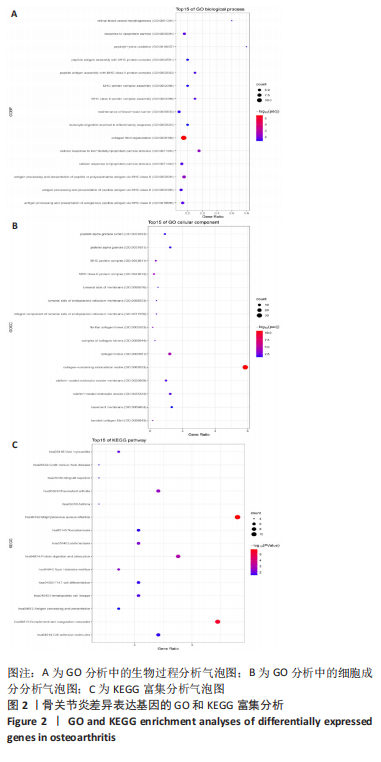
2.1.3 GO分析和KEGG分析 在GENE ONTOLOGY网站上对差异基因进行GO分析,生物过程结果显示,筛选出的差异表达基因主要在胶原纤维组织、对脂蛋白颗粒的反应、维持血脑屏障、MHC蛋白复合物组装、炎症反应过程中的白细胞迁移等子集中富集,见图2A。细胞成分结果显示,差异表达基因主要在含有胶原蛋白的细胞外基质、胶原蛋白三聚体、包被网格蛋白的内吞囊泡膜、基底膜等子集中富集,见图2B;分子功能结果显示,差异表达基因主要富集在赋予抗张强度的细胞外基质结构成分和细胞外基质结构成分。 在DAVID数据库中对差异表达基因进行KEGG通路富集分析,结果表明,差异基因在类风湿性关节炎、Th17细胞分化、抗原的加工和呈递、细胞黏附分子、金黄色葡萄球菌感染、蛋白质的消化吸收等通路中富集,见图2C。GO分析和KEGG分析结果及P值如表2所示。"
| [1] BOYAN BD, TOSI L, COUTTS R, et al. Sex differences in osteoarthritis of the knee. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012;20(10):668-669. [2] LESPASIO MJ, PIUZZI NS, HUSNI ME, et al. Knee Osteoarthritis: A Primer. Perm J. 2017;21:16-183. [3] 韩明睿,刘倩倩,孙洋.骨关节炎发病机制及药物调控新进展[J].中国药理学通报,2022,38(6):807-812. [4] RIM YA, JU JH. The Role of Fibrosis in Osteoarthritis Progression. Life (Basel). 2020;11(1):3. [5] RIM YA, NAM Y, JU JH. The Role of Chondrocyte Hypertrophy and Senescence in Osteoarthritis Initiation and Progression. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(7):2358. [6] ENGLUND M, GUERMAZI A, LOHMANDER SL. The role of the meniscus in knee osteoarthritis: a cause or consequence? Radiol Clin North Am. 2009;47(4):703-712. [7] BROPHY RH, SANDELL LJ, CHEVERUD JM, et al. Gene expression in human meniscal tears has limited association with early degenerative changes in knee articular cartilage. Connect Tissue Res. 2017;58(3-4):295-304. [8] 姚佳炜,徐雄峰,易鹏,等.骨关节炎滑膜组织差异表达基因筛选及关键基因的验证结果[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(18):2881-2887. [9] 朱义芳,郭莉,陈露,等.骨关节炎的潜在生物标志物筛选及关键基因验证[J].四川医学,2021,42(10):969-975. [10] 李升扬.基于生物信息学方法筛选骨关节炎相关关键分子靶点[D].长春:吉林大学,2021. [11] 王海明,张驰,魏向阳,等.膝骨关节炎软骨细胞中差异基因表达的生物信息学分析[J].华西医学,2021,36(5):623-631. [12] 杨威,袁普卫,韩清民.基于生物信息学筛选骨关节炎诊疗相关的关键基因[J].中华实验外科杂志,2022,39(1):44-44. [13] BROPHY RH, ZHANG B, CAI L, et al. Transcriptome comparison of meniscus from patients with and without osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(3): 422-432. [14] 李明秀,王轩,杨杰,等.骨关节炎体外模型特点及设计新思路[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(2):300-306. [15] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2):293-311. [16] PEAT G, THOMAS MJ. Osteoarthritis year in review 2020: epidemiology & therapy. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(2):180-189. [17] DELPLACE V, BOUTET MA, LE VISAGE C, et al. Osteoarthritis: From upcoming treatments to treatments yet to come. Joint Bone Spine. 2021; 88(5):105206. [18] ZHAO J, LU Q, LIU Y, et al. Th17 Cells in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Cytokines, Plasticity, and Therapies. J Immunol Res. 2021;2021:8816041. [19] SCANZELLO CR, GOLDRING SR. The role of synovitis in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Bone. 2012;51(2):249-257. [20] WOODELL-MAY JE, SOMMERFELD SD. Role of Inflammation and the Immune System in the Progression of Osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(2):253-257. [21] PARK J, LEE HS, GO EB, et al. Proteomic Analysis of the Meniscus Cartilage in Osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(15):8181. [22] PENG Z, SUN H, BUNPETCH V, et al. The regulation of cartilage extracellular matrix homeostasis in joint cartilage degeneration and regeneration. Biomaterials. 2021;268:120555. [23] SHI Y, HU X, CHENG J, et al. A small molecule promotes cartilage extracellular matrix generation and inhibits osteoarthritis development. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1914. [24] Semenza GL.Hypoxia-inducible factors in physiology and medicine. Cell. 2012;148(3):399-408. [25] YUDOH K, NAKAMURA H, MASUKO-HONGO K, et al. Catabolic stress induces expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 alpha in articular chondrocytes: involvement of HIF-1 alpha in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(4):R904-R914. [26] BOHENSKY J, SHAPIRO IM, LESHINSKY S, et al. HIF-1 regulation of chondrocyte apoptosis: induction of the autophagic pathway. Autophagy. 2007;3(3):207-214. [27] ZHANG FJ, LUO W, LEI GH. Role of HIF-1αand HIF-2αin osteoarthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2015;82(3):144-147. [28] ECKE A, LUTTER AH, SCHOLKA J, et al. Tissue Specific Differentiation of Human Chondrocytes Depends on Cell Microenvironment and Serum Selection. Cells. 2019;8(8):934. [29] LI S, WANG H, ZHANG Y, et al. COL3A1 and MMP9 Serve as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers of Osteoarthritis and Are Associated With Immune Cell Infiltration. Front Genet. 2021;12:721258. [30] BAYRAM B, THALER R, BETTENCOURT JW, et al. Human outgrowth knee fibroblasts from patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty exhibit a unique gene expression profile and undergo myofibroblastogenesis upon TGFβ1 stimulation. J Cell Biochem. 2022;123(5):878-892. [31] KE H, MOU X, XIA Q. Remifentanil repairs cartilage damage and reduces the degradation of cartilage matrix in post-traumatic osteoarthritis, and inhibits IL-1β-induced apoptosis of articular chondrocytes via inhibition of PI3K/AKT/NF-κB phosphorylation. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(22):1487. [32] REMST DF, BLOM AB, VITTERS EL, et al. Gene expression analysis of murine and human osteoarthritis synovium reveals elevation of transforming growth factor β-responsive genes in osteoarthritis-related fibrosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(3):647-656. [33] JANG I, BENINGO KA. Integrins, CAFs and Mechanical Forces in the Progression of Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11(5):721. [34] PICKUP MW, MOUW JK, WEAVER VM. The extracellular matrix modulates the hallmarks of cancer. EMBO Rep. 2014;15(12):1243-1253. [35] PRIETO TG, MACHADO-RUGOLO J, BALDAVIRA CM, et al. The Fibrosis-Targeted Collagen/Integrins Gene Profile Predicts Risk of Metastasis in Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. Front Oncol. 2021;11:706141. [36] WU Y, XU Y. Integrated bioinformatics analysis of expression and gene regulation network of COL12A1 in colorectal cancer. Cancer Med. 2020; 9(13):4743-4755. [37] FLOOD HM, BOLTE C, DASGUPTA N, et al. The Forkhead box F1 transcription factor inhibits collagen deposition and accumulation of myofibroblasts during liver fibrosis. Biol Open. 2019;8(2):bio039800. [38] LI C, LUO J, XU X, et al. Single cell sequencing revealed the underlying pathogenesis of the development of osteoarthritis. Gene. 2020;757:144939. [39] CHEN W, YANG A, JIA J, et al. Lysyl Oxidase (LOX) Family Members: Rationale and Their Potential as Therapeutic Targets for Liver Fibrosis. Hepatology. 2020;72(2):729-741. [40] 刘荣清,孙伯坚,林佳静,等.类风湿关节炎和骨关节炎活动期赖氨酰氧化酶的比较[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2013,17(2): 95-97,插1. [41] 吴嘉钦,杨力,许康,等.赖氨酰氧化酶LOX在OA疾病发生发展中的调控作用及其干预机制研究[J].医用生物力学,2021,36(S1):21. [42] 许春明.赖氨酰氧化酶LOX在骨关节炎软骨中的调控作用及机制研究[D].重庆:重庆大学,2020. [43] YANG A, YAN X, FAN X, et al. Hepatic stellate cells-specific LOXL1 deficiency abrogates hepatic inflammation, fibrosis, and corrects lipid metabolic abnormalities in non-obese NASH mice. Hepatol Int. 2021;15(5):1122-1135. [44] TASHKANDI MM, ALSAQER SF, ALHOUSAMI T, et al. LOXL2 promotes aggrecan and gender-specific anabolic differences to TMJ cartilage. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):20179. [45] 周鑫,邢露,贺春霞,等.骨膜蛋白—一种有潜力的疾病早期诊断分子标志物[J].中国药理学通报,2022,38(5):650-654. [46] KKUDO A. The Structure of the Periostin Gene, Its Transcriptional Control and Alternative Splicing, and Protein Expression. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019; 1132:7-20. [47] 曾峰,黄建芬,余新林,等.骨膜蛋白的研究新进展[J].中国医学创新,2021,18(7):171-176. [48] BROPHY RH, TYCKSEN ED, SANDELL LJ, et al. Changes in Transcriptome-Wide Gene Expression of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears Based on Time From Injury. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(8):2064-2075. [49] BROPHY RH, ZHANG B, CAI L, et al. Transcriptome comparison of meniscus from patients with and without osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(3):422-432. [50] CHOU CH, WU CC, SONG IW, et al. Genome-wide expression profiles of subchondral bone in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(6):R190. [51] TAJIKA Y, MOUE T, ISHIKAWA S, et al. Influence of Periostin on Synoviocytes in Knee Osteoarthritis. In Vivo. 2017;31(1):69-77. [52] 王安琪,刘云鹏,卢文卿,等.PLOD家族在肿瘤中的研究进展[J].中国医药导报,2019,16(24): 29-31+39. [53] WANG H, LUO W, DAI L. Expression and Prognostic Role of PLOD1 in Malignant Glioma. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:13285-13297. [54] KOENIG SN, CAVUS O, WILLIAMS J, et al. New mechanistic insights to PLOD1-mediated human vascular disease. Transl Res. 2022;239:1-17. [55] AYDıN N, KARAISMAILOĞLU B, ALAYLıOĞLU M, et al. Gene expression profiling of primary fibrochondrocyte cultures in traumatic and degenerative meniscus lesions. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2021;29(1): 23094990211000168. |
| [1] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Zhu Guangyu, Wang Rongtian, Wang Jian, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Changes of lower limb force line and knee function after high tibial osteotomy in osteoporotic medial ventricular knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [3] | Huang Linke, Wei Linhua, Jiang Jie, Liu Qian, Chen Weiwei. Effects of estrogen combined with treadmill exercise on bone mass and articular cartilage in ovariectomized mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [4] | Li Long, Li Guangdi, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 751-757. |
| [5] | Yuan Changshen, Guan Yanbing, Li Zhe, Rong Weiming, Liao Shuning, Chen Lewei, Mei Qijie, Duan Kan. Screening and verification of key genes of necroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 695-700. |
| [6] | Liu Guangluan, Guo Zonglei, Ge Jin, Huang Dong, Wang Yehua. Anatomic risk factors for medial meniscus posterior root tears combined with anterior cruciate ligament injuries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 663-668. |
| [7] | Wan Guoli, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan, Li Ang, Shi Xunda, Cai Yi. Retrospective analysis of the influencing factors of chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 558-564. |
| [8] | Gu Mingxi, Wang Bo, Tian Fengde, An Ning, Hao Ruihu, Wang Changcheng, Guo Lin. Comparison of early efficacy and safety of simultaneous and staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 565-571. |
| [9] | Yu He, Zheng Jiafa, Song Xiufeng, Guan Shengyi. Tibiotalocalcaneal arthrodesis with blood supplied fibular flap combined with hollow screw in the treatment of end-stage ankle osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 588-593. |
| [10] | Guo Yingqi, Gong Xianxu, Zhang Yan, Xiao Han, Wang Ye, Gu Wenguang. Meniscus extrusion and patellofemoral joint cartilage injury and bone marrow lesions: MRI semi-quantitative score [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 600-605. |
| [11] | Yu Jiaan, Liu Xinwei, Lian Hongyu, Liu Kexin, Li Zitao. Medial open-wedge tibial osteotomy versus lateral closed-wedge tibial osteotomy for unicompartmental knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 632-639. |
| [12] | Huang Yuying, Guo Yi, Han Xinzuo, Min Hongwei, Li Xuemei, Liu Kemin. Functional correlation between the elasticity of the quadriceps and its tendons and osteoarthritis of the knee based on shear wave elastography measurements [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 4971-4976. |
| [13] | Chen Jingtao, Chen You, Li Yujing, Liu Zhigang. Astragalus polysaccharide inhibits Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor kappaB p65 pathway in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 5002-5008. |
| [14] | Chen Jianchao, Song Huiping. Distribution characteristics of bone mass in different parts of postmenopausal women with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 5035-5039. |
| [15] | Yang Chaoqiang, Zhang Hulin, Wang Xiaomin, Wang Liang, Wang Yican. Prevention and treatment of bone-related diseases by regulating macrophages with Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 5064-5070. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||