Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (31): 5002-5008.doi: 10.12307/2023.184
Previous Articles Next Articles
Astragalus polysaccharide inhibits Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor kappaB p65 pathway in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis in rats
Chen Jingtao, Chen You, Li Yujing, Liu Zhigang
- Department of Orthopedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University, Kaifeng 475001, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2022-03-17Accepted:2022-05-24Online:2023-11-08Published:2023-01-31 -
Contact:Liu Zhigang, Master, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University, Kaifeng 475001, Henan Province, China -
About author:Chen Jingtao, Master, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University, Kaifeng 475001, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Kaifeng Municipal Science and Technology Development Program, No. 2003028 (to CY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Jingtao, Chen You, Li Yujing, Liu Zhigang. Astragalus polysaccharide inhibits Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor kappaB p65 pathway in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 5002-5008.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
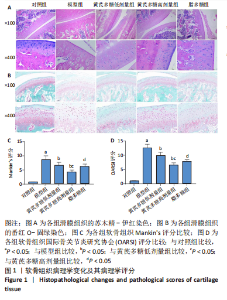
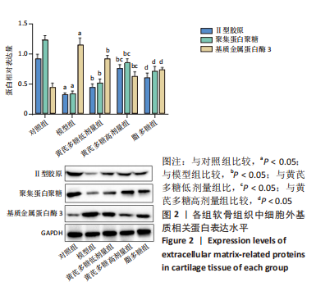
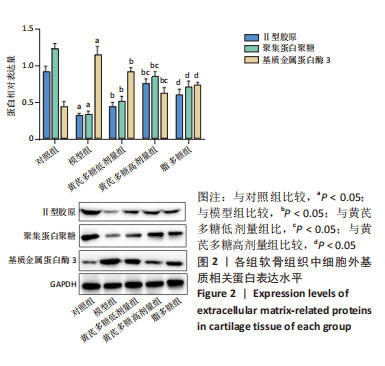
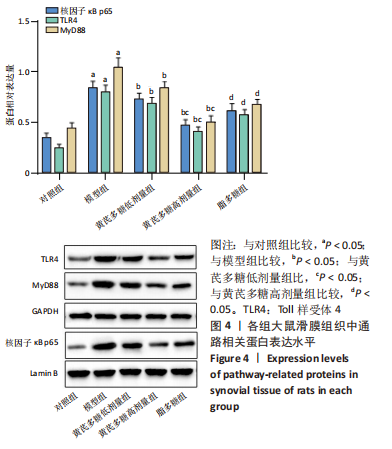
2.1 实验动物数量分析 实验选用40只SD大鼠,分为5组,实验过程中无脱失,全部纳入结果分析。 2.2 软骨组织病理学变化 苏木精-伊红染色结果显示,与对照组相比,模型组的软骨层状结构消失,软骨表面粗糙不平,软骨层变薄,细胞排列紊乱,数量减少,大小不一;与模型组相比,黄芪多糖低、高剂量组软骨组织病理学表现均有所改善;与各黄芪多糖组相比,脂多糖组病理学变化加重,见图1A。Mankin’s评分结果显示,与对照组相比,模型组Mankin’s评分显著升高(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,黄芪多糖低、高剂量组Mankin’s评分均显著降低,且高剂量组低于低剂量组(P < 0.05);与黄芪多糖高剂量组相比,脂多糖组Mankin’s评分升高(P < 0.05),见图1C。 番红O-固绿染色结果显示,与对照组相比,模型组的软骨中的蛋白多糖大量丢失,软骨基质着色不明显,软骨发生退行性改变;与模型组相比,黄芪多糖低、高剂量组病理学变化均有所改善,且高剂量组优于低剂量组;与黄芪多糖组相比,脂多糖组软骨组织病理学变化加重,见图1B。OARSI评分比较结果显示,与对照组相比,模型组OARSI评分显著升高(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,黄芪多糖低、高剂量组均显著降低,且高剂量组低于低剂量组(P < 0.05);与黄芪多糖高剂量组相比,脂多糖组OARSI评分升高(P < 0.05),见图1D。"


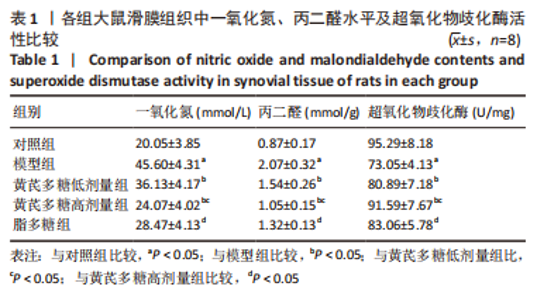
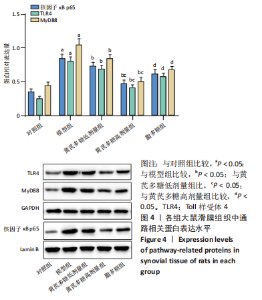
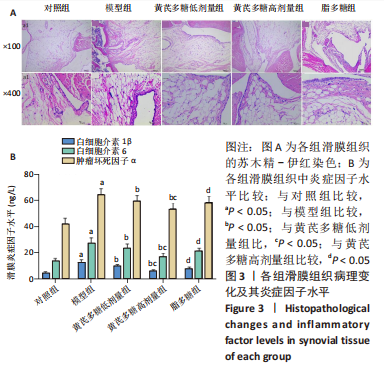
2.4 滑膜组织病理及其炎症因子水平变化 苏木精-伊红染色结果显示,与对照组相比,模型组滑膜组织可见大量的炎症细胞浸润(如单核巨噬细胞聚集),滑膜增生明显;与模型组相比,黄芪多糖低、高剂量组滑膜组织病理学表现均有所改善;与黄芪多糖高剂量组相比,脂多糖组滑膜组织病理学变化加重,见图3A。滑膜炎症因子检测结果显示,与对照组比,模型组大鼠的白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α水平升高(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,黄芪多糖低、高剂量白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α水平均显著降低(P < 0.05),且高剂量组低于低剂量组(P < 0.05);与黄芪多糖高剂量组相比,脂多糖组的白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α水平均显著升高(P < 0.05),见图3B。"
| [1] VINA ER, KWOH CK. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: literature update. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2018;30(2):160-167. [2] LATOURTE A, KLOPPENBURG M, RICHETTE P. Emerging pharmaceutical therapies for osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(12):673-688. [3] 李辉明,魏国俊,丁玉芬,等.膝关节关节腔内药物注射治疗KOA的进展[J].实用中西医结合临床,2020,20(7):157-158. [4] 李珍一, 杨关林, 闫承慧, 等. 黄芪多糖应用的相关研究进展[J]. 辽宁中医杂志,2016,43(7):1553-1555. [5] XIONG J, JIANG B, LUO Y, et al. Multifunctional Nanoparticles Encapsulating Astragalus Polysaccharide and Gold Nanorods in Combination with Focused Ultrasound for the Treatment of Breast Cancer. Int J Nanomed. 2020;15(10):4151-4169. [6] 袁普卫, 杨威, 康武林,等. 骨性关节炎发病机制研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2016,22(7):902-906. [7] 胡爱心, 陈廖斌, 汪晖,等. 黄芪多糖对大鼠骨关节炎的影响[J]. 武汉大学学报(医学版),2008,29(2):157-161. [8] CHOI MC, JO J, PARK J, et al. NF-κB Signaling Pathways in Osteoarthritic Cartilage Destruction. Cells. 2019;8(7):734-738. [9] 李胜陶. 黄芪多糖对异丙肾上腺素诱导大鼠心肌肥厚中TLR4/NF-κB信号通路的影响[D]. 锦州:辽宁医学院,2015. [10] PANICKER S, BORGIA J, FHIED C, et al. Oral glucosamine modulates the response of the liver and lymphocytes of the mesenteric lymph nodes in a papain-induced model of joint damage and repair. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009;17(8):1014-1021. [11] 胡爱心,陈廖斌,汪晖,等.黄芪多糖对大鼠骨关节炎的影响[J].武汉大学学报(医学版),2008,29(2):157-161. [12] MANKIN HJ, LIPPIELLO L. Biochemical and metabolic abnormalities in articular cartilage from osteo-arthritic human hips. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970;52(3):424-434. [13] GLASSON SS, CHAMBERS MG, VAN DEN BERG WB, et al. The OARSI histopathology initiative - recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in the mouse. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(3):17-23. [14] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2):293-311. [15] WANG XX, CAI L. Expression level of proteoglycan, collagen and type II collagen in osteoarthritis rat model is promoted and degradation of cartilage is prevented by glucosamine methyl ester. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(11):3609-3616. [16] MALEK S, WENG HY, MARTINSON SA, et al. Evaluation of serum MMP-2 and MMP-3, synovial fluid IL-8, MCP-1, and KC concentrations as biomarkers of stifle osteoarthritis associated with naturally occurring cranial cruciate ligament rupture in dogs. PLoS One. 2020;15(11):125-129. [17] WOODELL-MAY JE, SOMMERFELD SD. Role of Inflammation and the Immune System in the Progression of Osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(2):253-257. [18] ORHAN C, JUTURU V, SAHIN E, et al. Undenatured Type II Collagen Ameliorates Inflammatory Responses and Articular Cartilage Damage in the Rat Model of Osteoarthritis. Front Vet Sci. 2021;8(12):6-10. [19] FEI J, LIANG B, JIANG C, et al. Luteolin inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammation in rat chondrocytes and attenuates osteoarthritis progression in a rat model. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109(21):1586-1592. [20] ANSARI MY, AHMAD N, HAQQI TM. Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: Role of polyphenols. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;129:110452. [21] 陈瑜, 王锐卿, 刘敬萱, 等. 艾灸对膝骨关节炎患者炎性因子及氧化应激因子的影响:随机对照研究[J]. 中国针灸,2020,384(9):5-9. [22] 王淳, 吴丽, 刘畅, 等. 利湿活血方及其拆方减轻高尿酸血症大鼠氧化应激损伤的探讨及机制研究[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2018,33(1): 85-88. [23] 刘芬之, 郭珈宜, 李峰, 等. 独活寄生汤辨证治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的临床效果及对血清和关节腔液相关炎症细胞因子的影响[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2020,38(9):75-78. [24] WEI B, ZHANG Y, TANG L, et al. Protective effects of quercetin against inflammation and oxidative stress in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis. Drug Dev Res. 2019;80(3):360-367. [25] 刘洋, 杜婧, 沈颜红. 10种药用黄芪属植物化学成分及药理作用的研究进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2017,23(18):222-234. [26] 韩亚琨,于程程.黄芪多糖对实验性牙周炎骨吸收的影响[J]. 中草药,2019,50(2):423-427. [27] 申冬冬,袁飞,侯江红. 黄芪多糖对幼鼠肠缺血再灌注损伤肠组织TNF-α、ICAM-1、IL-6及免疫功能的影响[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2017,35(6):1528-1532. [28] 杨彬, 黄俊卿, 张继伟. 黄芪多糖对颈椎病模型大鼠颈椎间盘纤维环MMP2和MMP9表达的影响[J]. 中国病理生理杂志,2018, 34(10):156-163. [29] DING Y, WANG L, ZHAO Q, et al. MicroRNA93 inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammation in osteoarthritis by targeting the TLR4/NFκB signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2019;43(2):779-790. [30] 庄宁彤,赵冬久,史丽云. Toll样受体4(TLR4)的内吞通路及其调控机制研究进展[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2016,32(11):1574-1578. [31] HUANG X, QIAO F, XUE P. The protective role of microRNA-140-5p in synovial injury of rats with knee osteoarthritis via inactivating the TLR4/Myd88/NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell Cycle. 2019;18(18):2344-2358. [32] ZHANG Y, ZENG Y. Curcumin reduces inflammation in knee osteoarthritis rats through blocking TLR4 /MyD88/NF-κB signal pathway. Drug Dev Res. 2019;80(3):353-359. [33] LI Z, ZOU Y, FAN D, et al. The mechanism of medial collateral ligament repair in knee osteoarthritis based on the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB inflammatory signaling pathway. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2020;20(3):398-403. [34] BARRETO G, SENTURK B, COLOMBO L, et al. Lumican is upregulated in osteoarthritis and contributes to TLR4-induced pro-inflammatory activation of cartilage degradation and macrophage polarization. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(1):92-101. [35] ZHANG X. STING promotes senescence, apoptosis, and extracellular matrix degradation in osteoarthritis via the NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(1):13-17. [36] WANG XZ, DING DF, XUE Y, et al. Role of TLR4/NF-κB pathway for early change of synovial membrane in knee osteoarthritis rats. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2019;32(1):68-71. [37] 蔡松涛, 孙京涛, 魏瑄. 枸杞多糖抑制核因子κB(NF-κB)通路降低骨关节炎软骨细胞炎性细胞因子水平[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2018,34(11):989-993. [38] 陈俊, 林洁, 赵忠胜, 等. 乌头汤对膝骨关节炎模型大鼠滑膜组织TLR4/NF-κB信号通路的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(27): 4381-4386. [39] 吴佳, 尧雪洲. 在慢阻肺炎症反应中黄芪多糖的抗炎作用及抑制TLR4/NF-κB通路的机制[J]. 西安交通大学学报(医学版),2018, 39(5):760-764. |
| [1] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | Fang Xingyan, Tian Zhenli, Zhao Zheyi, Wen Ping, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and sphingosine kinases 1/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling axis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [3] | He Xi, Wan Yu, Tang Yuting, Yang Anning, Wu Kai, Jiao Yun, Bai Zhigang, Jiang Yideng, Shen Jiangyong. Erastin inhibits proliferation of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-. |
| [4] | Zhong Yizheng, Huang Peizhen, Cai Qunbin, Zheng Liqin, He Xingpeng, Dong Hang. Microstructural indexes that determine the trabecular bone maximum stress of micro-finite element models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1313-1318. |
| [5] | Cao Sheng, Kong Lingwei, Xu Kun, Sun Zhijie. Correlation of cervical sagittal force line parameters with degenerative segment and Pfirrmann classification in patients with cervical intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1319-1324. |
| [6] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Zhu Guangyu, Wang Rongtian, Wang Jian, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Changes of lower limb force line and knee function after high tibial osteotomy in osteoporotic medial ventricular knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [7] | Ke Yuqi, Chen Changjian, Wu Hao, Zheng Lianjie. Comparison of 12-month follow-up results of primary total hip arthroplasty between modified direct anterior approach and direct anterior approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1377-1382. |
| [8] | Zhang Lichuang, Gao Huali, Wang Jingchao, Lin Huijun, Wu Chonggui, Ma Yinghui, Huang Yunfei, Fang Xue, Zhai Weitao. Effect of tendon manipulation with equal emphasis on muscles and bones on accelerating the functional rehabilitation of quadriceps femoris after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1383-1389. |
| [9] | Du Xueting, Zhang Xiaodong, Chen Yanjun, Wang Mei, Chen Wubiao, Huang Wenhua. Application of compressed sensing technology in two-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging of the ankle joint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1396-1402. |
| [10] | You Zhengqiu, Zhang Zhongzu, Wang Qunbo. Early symptomatic intervertebral disc pseudocysts after discectomy detected on MRI [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1403-1409. |
| [11] | Li Chao, Zhang Peipei, Xu Mengting, Li Linlin, Ding Jiangtao, Liu Xihua, Bi Hongyan. Respiratory training improves morphological changes of the multifidus muscle in patients with chronic nonspecific lower back pain assessed by musculoskeletal ultrasound [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1417-1421. |
| [12] | He Yinhao, Li Xiaosheng, Chen Hongwen, Chen Tiezhu. 3D printed porous tantalum metal in the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip: current status and application prospect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1455-1461. |
| [13] | Jiang Xiaocheng, Shi Lu, Wang Yinbin, Li Qiujiang, Xi Chuangzhen, Ma Zefeng, Cai Lijun. Systematical evaluation of bone fusion rate after interbody fusion in patients with osteoporosis and lumbar degenerative disease treated with teriparatide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1427-1433. |
| [14] | Tang Liang, Li Xiheng, Niu Ruijuan, Li Xinyue, Zou Xinying, Mao Tianjiao, Li Jiang. Naringin regulates the function of RAW264.7 macrophages to affect the osteogenic differentiation of MC-3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1205-1210. |
| [15] | Li Mengfei, Zhang Hong, Zhao Shaojian, Yin Guanghao, Wang Qibao. Expression of forkhead box protein 3 in refractory periapical periodontitis in rats with Enterococcus faecalis infection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1187-1192. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||