Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (11): 1669-1676.doi: 10.12307/2023.181
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bioinformatics analysis of cuproptosis genes in immune infiltration of osteoarthritis
Wang Weiwei1, Ou Zhixue2, Zhou Yi1, Li Tong1
- 1Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Guilin Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guilin 541002, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2022-05-07Accepted:2022-06-25Online:2023-04-18Published:2022-09-27 -
Contact:Ou Zhixue, MD, Chief physician, Guilin Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guilin 541002, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wang Weiei, Master candidate, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Guangxi Natural Science Foundation, No. 2021GXNSFAA196033 (to ZY [project participant]); Guangxi Traditional Chinese Medicine Appropriate Technology Development and Promotion Project, No. GZSY21-78 (to OZX); Guangxi Innovation Program for Postgraduate Education, No. YCSY2020080 (to ZY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Weiwei, Ou Zhixue, Zhou Yi, Li Tong. Bioinformatics analysis of cuproptosis genes in immune infiltration of osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(11): 1669-1676.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
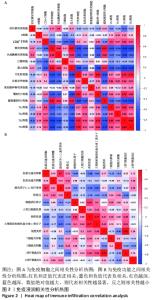
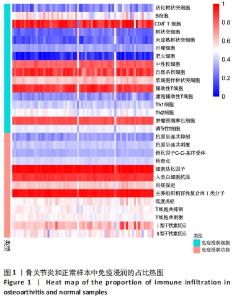
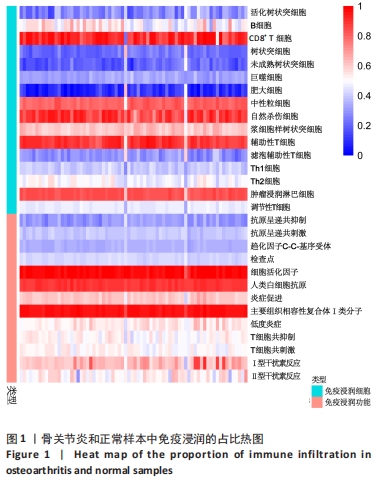
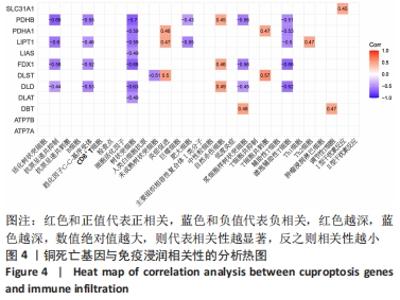
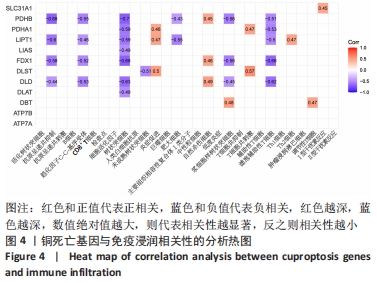
2.2 免疫浸润相关性及差异性分析 免疫细胞相关性热图展示了树状突细胞和肥大细胞呈极强的正相关性(r=0.87),肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞和调节性T细胞呈极强的正相关性(r=0.84),中性粒细胞和辅助性T细胞呈极强的正相关性(r=0.81),树状突细胞和滤泡辅助性T细胞呈极强的正相关性(r=0.81),中性粒细胞和调节性T细胞呈强的正相关性(r=0.79),中性粒细胞和肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞呈强正相关性(r=0.75),辅助性T细胞和肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞呈强正相关性(r=0.74),肥大细胞和滤泡辅助性T细胞呈强正相关性(r=0.73);肥大细胞和肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞呈极强的负相关性(r=-0.81),肥大细胞和调节性T细胞呈强负相关性(r=-0.79),滤泡辅助性T细胞和调节性T细胞呈强负相关性(r=-0.72),见图2A。免疫功能相关性热图展示了低度炎症和Ⅰ型干扰素反应呈极强的正相关性(r=0.93),炎症促进和主要组织相容性复合体Ⅰ类分子呈强正相关性(r=0.77),抗原呈递共抑制和趋化因子C-C-基序受体呈强正相关性(r=0.7),见图2B。"

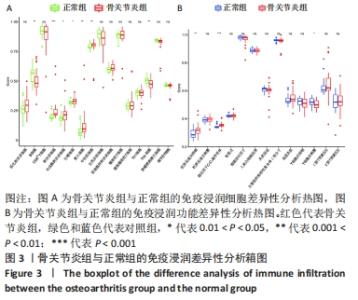
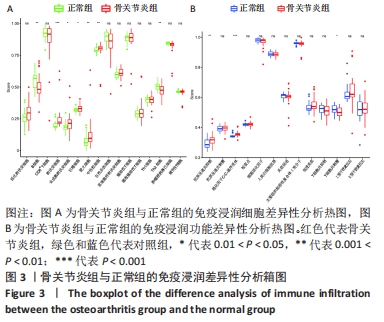
通过箱图对骨关节炎患者与健康人群的外周血进行组间免疫浸润细胞和功能差异分析,见图3,P < 0.05则代表差异有显著性意义。结果显示,在骨关节炎组中树状突细胞(P < 0.001)、未成熟树状突细胞(0.01 < P < 0.05)、巨噬细胞(0.01 < P < 0.05)、肥大细胞(0.001 < P < 0.01)、中性粒细胞(0.001 < P < 0.01)、抗原呈递共抑制(0.001 < P < 0.01)和趋化因子C-C-基序受体(P < 0.001)显著增加,而B细胞(0.001 < P < 0.01)、Th2细胞(0.001 < P < 0.01)和T细胞共刺激(0.01 < P < 0.05)则显著减少。 "
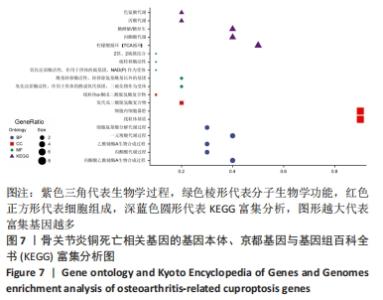
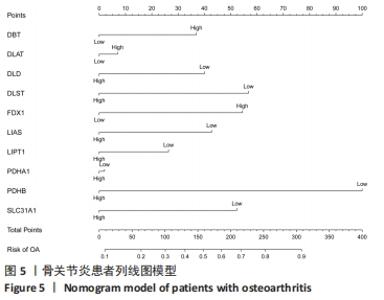
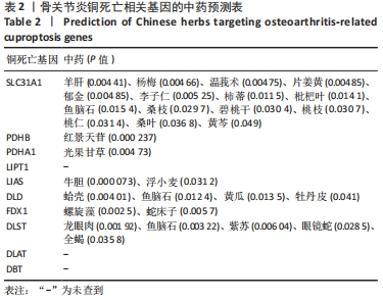
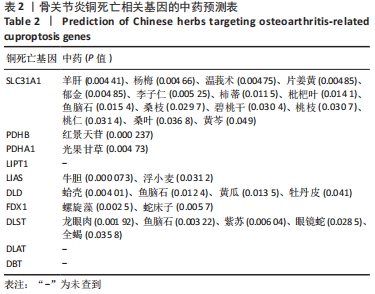
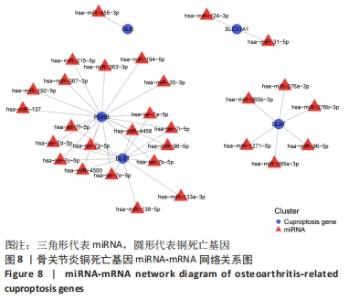
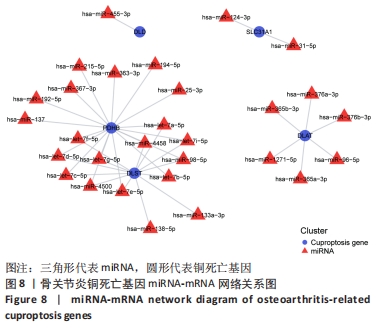
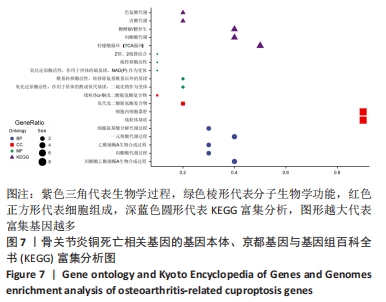
2.5 功能相关性分析及药物预测 将筛选到的10个铜死亡基因上传至仙桃学术平台,进行富集分析。基因本体富集分析由生物学过程、细胞组成和分子生物学功能三部分组成,用于分析骨关节炎的功能富集。结果显示,铜死亡基因主要与丙酮酸乙酰辅酶A生物合成过程、丙酮酸代谢过程、乙酰辅酶A生物合成过程、一元羧酸代谢过程、细胞氨基酸分解代谢过程等生物学过程以及氧化还原酶活性(作用于供体的醛或氧代基团,二硫化物作为受体)、酰基转移酶活性(转移除氨基酰基以外的基团)、氧化还原酶活性[作用于供体的硫基团,NAD(P)作为受体]、硫转移酶活性、2铁和2硫簇结合等分子生物学功能密切相关,其过程涉及线粒体基质、细胞内细胞器腔、氧代戊二酸脱氢酶复合物、线粒体α-酮戊二酸脱氢酶复合物等细胞组分(图7)。KEGG结果显示,铜死亡基因主要富集在三羧酸循环循环、丙酮酸代谢、糖酵解/糖异生、丙酸代谢、色氨酸代谢相关信号通路上(图7)。"
| [1] BERENBAUM F. Osteoarthritis as an inflammatory disease (osteoarthritis is not osteoarthrosis!). Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(1):16-21. [2] LO J, CHAN L, FLYNN S. A Systematic Review of the Incidence, Prevalence, Costs, and Activity and Work Limitations of Amputation, Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Back Pain, Multiple Sclerosis, Spinal Cord Injury, Stroke, and Traumatic Brain Injury in the United States: A 2019 Update. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2021;102(1):115-131. [3] GOLDRING SR, GOLDRING MB. Changes in the osteochondral unit during osteoarthritis: structure, function and cartilage-bone crosstalk. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(11):632-644. [4] KATZ JN, ARANT KR, LOESER RF. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review. JAMA. 2021;325(6):568-578. [5] FAUST HJ, ZHANG H, HAN J, et al. IL-17 and immunologically induced senescence regulate response to injury in osteoarthritis. J Clin Invest. 2020;130(10):5493-5507. [6] MA Y, YANG H, ZONG X, et al. Artificial M2 macrophages for disease-modifying osteoarthritis therapeutics. Biomaterials. 2021;274:120865. [7] CHEN Z, MA Y, LI X, et al. The Immune Cell Landscape in Different Anatomical Structures of Knee in Osteoarthritis: A Gene Expression-Based Study. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:9647072. [8] RAJANDRAN SN, MA CA, TAN JR, et al. Exploring the Association of Innate Immunity Biomarkers With MRI Features in Both Early and Late Stages Osteoarthritis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020;7:554669. [9] KRIEGOVA E, MANUKYAN G, MIKULKOVA Z, et al. Gender-related differences observed among immune cells in synovial fluid in knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(9):1247-1256. [10] LOHMANN N, SCHIRMER L, ATALLAH P, et al. Glycosaminoglycan-based hydrogels capture inflammatory chemokines and rescue defective wound healing in mice. Sci Transl Med. 2017;9(386):eaai9044. [11] KIM BE, NEVITT T, THIELE DJ. Mechanisms for copper acquisition, distribution and regulation. Nat Chem Biol. 2008;4(3):176-185. [12] GE EJ, BUSH AI, CASINI A, et al. Connecting copper and cancer: from transition metal signalling to metalloplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022;22(2): 102-113. [13] LUTSENKO S. Human copper homeostasis: a network of interconnected pathways. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2010;14(2):211-217. [14] TSVETKOV P, COY S, PETROVA B, et al. Copper induces cell death by targeting lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science. 2022;375(6586):1254-1261. [15] TAN HY, WANG N, ZHANG C, et al. Lysyl Oxidase-Like 4 Fosters an Immunosuppressive Microenvironment During Hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology. 2021;73(6):2326-2341. [16] CHOI BY, JANG BG, KIM JH, et al. Copper/zinc chelation by clioquinol reduces spinal cord white matter damage and behavioral deficits in a murine MOG-induced multiple sclerosis model. Neurobiol Dis. 2013;54: 382-391. [17] ZHU Y, WU G, YAN W, et al. miR-146b-5p regulates cell growth, invasion, and metabolism by targeting PDHB in colorectal cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2017;7(5):1136-1150. [18] SAUNIER E, BENELLI C, BORTOLI S. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in cancer: An old metabolic gatekeeper regulated by new pathways and pharmacological agents. Int J Cancer. 2016;138(4):809-817. [19] SMOLLE M, LINDSAY JG. Molecular architecture of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex: bridging the gap. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006; 34(Pt 5):815-818. [20] LANGSTON PK, NAMBU A, JUNG J, et al. Glycerol phosphate shuttle enzyme GPD2 regulates macrophage inflammatory responses. Nat Immunol. 2019;20(9):1186-1195. [21] PARK S, BAEK IJ, RYU JH, et al. PPARα-ACOT12 axis is responsible for maintaining cartilage homeostasis through modulating de novo lipogenesis. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):3. [22] ECHEVERRI RNP, MOHAN V, WU J, et al. Dynamic regulation of mitochondrial pyruvate metabolism is necessary for orthotopic pancreatic tumor growth. Cancer Metab. 2021;9(1):39. [23] FENG X, ZHANG L, XU S, et al. ATP-citrate lyase (ACLY) in lipid metabolism and atherosclerosis: An updated review. Prog Lipid Res. 2020;77:101006. [24] PATEL MS, NEMERIA NS, FUREY W, et al. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes: structure-based function and regulation. J Biol Chem. 2014; 289(24):16615-16623. [25] STIFEL U, WOLFSCHMITT EM, VOGT J, et al. Glucocorticoids coordinate macrophage metabolism through the regulation of the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Mol Metab. 2022;57:101424. [26] MICHELUCCI A, CORDES T, GHELFI J, et al. Immune-responsive gene 1 protein links metabolism to immunity by catalyzing itaconic acid production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(19):7820-7825. [27] CORDES T, WALLACE M, MICHELUCCI A, et al. Immunoresponsive Gene 1 and Itaconate Inhibit Succinate Dehydrogenase to Modulate Intracellular Succinate Levels. J Biol Chem. 2016;291(27):14274-14284. [28] LAMPROPOULOU V, SERGUSHICHEV A, BAMBOUSKOVA M, et al. Itaconate Links Inhibition of Succinate Dehydrogenase with Macrophage Metabolic Remodeling and Regulation of Inflammation. Cell Metab. 2016;24(1):158-166. [29] MILLS EL, RYAN DG, PRAG HA, et al. Itaconate is an anti-inflammatory metabolite that activates Nrf2 via alkylation of KEAP1. Nature. 2018; 556(7699):113-117. [30] LEE J, PROHASKA JR, DAGENAIS SL, et al. Isolation of a murine copper transporter gene, tissue specific expression and functional complementation of a yeast copper transport mutant. Gene. 2000; 254(1-2):87-96. [31] HODGKINSON V, PETRIS MJ. Copper homeostasis at the host-pathogen interface. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(17):13549-13555. [32] ABDUL SZ, CERO C, PIERCE AE, et al. Combining a β3 adrenergic receptor agonist with alpha-lipoic acid reduces inflammation in male mice with diet-induced obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2022;30(1): 153-164. [33] MAYR JA, FEICHTINGER RG, TORT F, et al. Lipoic acid biosynthesis defects. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2014;37(4):553-563. [34] FROMMER KW, HASSELI R, SCHAFFLER A, et al. Free Fatty Acids in Bone Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Diseases. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2757. [35] STRUSHKEVICH N, MACKENZIE F, CHERKESOVA T, et al. Structural basis for pregnenolone biosynthesis by the mitochondrial monooxygenase system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(25):10139-10143. [36] ZHANG Z, MA Y, GUO X, et al. FDX1 can Impact the Prognosis and Mediate the Metabolism of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:749134. [37] UDUMULA MP, SAKR S, DAR S, et al. Ovarian cancer modulates the immunosuppressive function of CD11b+Gr1+ myeloid cells via glutamine metabolism. Mol Metab. 2021;53:101272. [38] COLLIOU N, GE Y, SAHAY B, et al. Commensal Propionibacterium strain UF1 mitigates intestinal inflammation via Th17 cell regulation. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(11):3970-3986. [39] AHN SH, YANG HY, TRAN GB, et al. Interaction of peroxiredoxin V with dihydrolipoamide branched chain transacylase E2 (DBT) in mouse kidney under hypoxia. Proteome Sci. 2015;13:4. [40] ALAHDAL M, ZHANG H, HUANG R, et al. Potential efficacy of dendritic cell immunomodulation in the treatment of osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;60(2):507-517. [41] GUO W, WEI B, SUN J, et al. Suppressive oligodeoxynucleotide-induced dendritic cells rein the aggravation of osteoarthritis in mice. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2018;40(5):430-436. [42] BISCHOFF SC. Role of mast cells in allergic and non-allergic immune responses: comparison of human and murine data. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7(2):93-104. [43] FARINELLI L, AQUILI A, MATTIOLI BM, et al. Synovial mast cells from knee and hip osteoarthritis: histological study and clinical correlations. J Exp Orthop. 2022;9(1):13. [44] LI Y, GAO H, BRUNNER TM, et al. Menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stromal cells efficiently ameliorate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by inhibiting T cell activation in mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):155. [45] WANG Z, WANG B, ZHANG J, et al. Chemokine (C-C Motif) Ligand 2/Chemokine Receptor 2 (CCR2) Axis Blockade to Delay Chondrocyte Hypertrophy as a Therapeutic Strategy for Osteoarthritis. Med Sci Monit. 2021;27:e930053. [46] 张尚霞,王宇红,龙红萍,等.基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS法的郁金水提物的化学成分研究[J].中南药学,2021,19(5):820-826. [47] AGGARWAL BB, Gupta SC, Sung B. Curcumin: an orally bioavailable blocker of TNF and other pro-inflammatory biomarkers. Br J Pharmacol. 2013;169(8):1672-1692. [48] HENROTIN Y, CLUTTERBUCK AL, ALLAWAY D, et al. Biological actions of curcumin on articular chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010; 18(2):141-149. [49] 常青,王伟,杨增华,等.黄芩苷对IL-1β诱导大鼠软骨细胞凋亡和炎症反应的抑制作用及相关机制研究[J].中国免疫学杂志,2020, 36(21):2603-2607+2618. [50] 丁童,周彦鹏,冯立平.红景天苷对骨关节炎大鼠软组织损伤和免疫失衡的调节作用[J].沈阳药科大学学报,2020,37(3):268-274. [51] ZHANG L, LIU T, CHEN H, et al. Predicting lncRNA-miRNA interactions based on interactome network and graphlet interaction. Genomics. 2021;113(3):874-880. [52] CHEN X, XIE D, ZHAO Q, et al. MicroRNAs and complex diseases: from experimental results to computational models. Brief Bioinform. 2019;20(2):515-539. |
| [1] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Zhu Guangyu, Wang Rongtian, Wang Jian, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Changes of lower limb force line and knee function after high tibial osteotomy in osteoporotic medial ventricular knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [2] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [3] | Huang Linke, Wei Linhua, Jiang Jie, Liu Qian, Chen Weiwei. Effects of estrogen combined with treadmill exercise on bone mass and articular cartilage in ovariectomized mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [4] | Qin Yuxing, Ren Qiangui, Li Zilong, Quan Jiaxing, Shen Peifeng, Sun Tao, Wang Haoyu. Action mechanism and prospect of bone microvascular endothelial cells for treating femoral head necrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 955-961. |
| [5] | Chen Guanting, Zhang Linqi, Li Qingru. Meta-analysis of the value of exosomal miRNA for the diagnosis of chronic kidney disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 970-976. |
| [6] | Li Long, Li Guangdi, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 751-757. |
| [7] | Yuan Changshen, Guan Yanbing, Li Zhe, Rong Weiming, Liao Shuning, Chen Lewei, Mei Qijie, Duan Kan. Screening and verification of key genes of necroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 695-700. |
| [8] | Wan Guoli, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan, Li Ang, Shi Xunda, Cai Yi. Retrospective analysis of the influencing factors of chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 558-564. |
| [9] | Gu Mingxi, Wang Bo, Tian Fengde, An Ning, Hao Ruihu, Wang Changcheng, Guo Lin. Comparison of early efficacy and safety of simultaneous and staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 565-571. |
| [10] | Yu He, Zheng Jiafa, Song Xiufeng, Guan Shengyi. Tibiotalocalcaneal arthrodesis with blood supplied fibular flap combined with hollow screw in the treatment of end-stage ankle osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 588-593. |
| [11] | Guo Yingqi, Gong Xianxu, Zhang Yan, Xiao Han, Wang Ye, Gu Wenguang. Meniscus extrusion and patellofemoral joint cartilage injury and bone marrow lesions: MRI semi-quantitative score [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 600-605. |
| [12] | Yu Jiaan, Liu Xinwei, Lian Hongyu, Liu Kexin, Li Zitao. Medial open-wedge tibial osteotomy versus lateral closed-wedge tibial osteotomy for unicompartmental knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 632-639. |
| [13] | Li Mingxiu, Wang Xuan, Yang Jie, Li Yi. An osteoarthritis model in vitro: characteristics and new design idea [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 300-306. |
| [14] | Liu Yinghong, Yi Yating. Mechanism and implication of angiogenesis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 307-313. |
| [15] | Xie Pingjin, Luo Zhen, Lu Qigui, Guo Yanxing, Chen Qunqun, Li Feilong. Effect of ligustrazine and overexpression of miR-20b-5p on synovial, cartilage and subchondral bone angiogenesis in rats with early-stage knee osteoarthritis: a histological observation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 237-245. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||