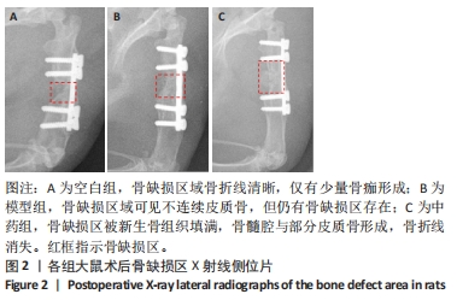
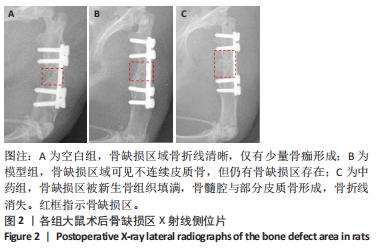
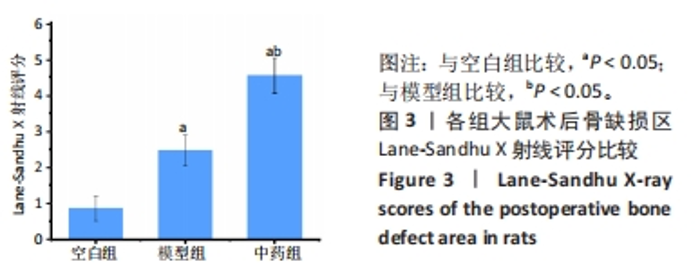
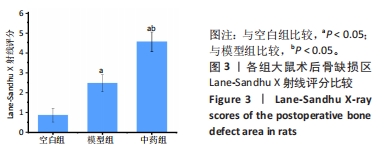
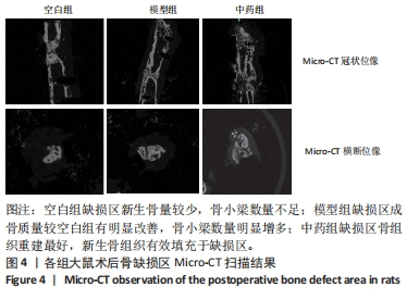
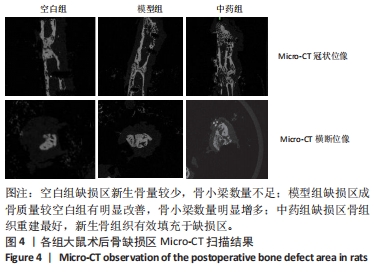
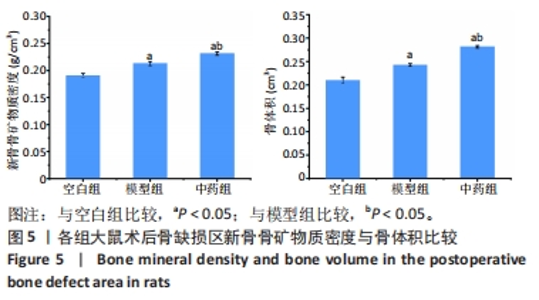
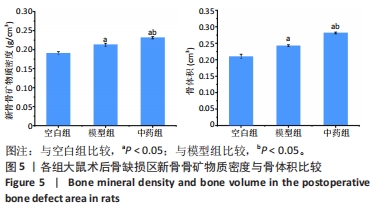
[1] NORRIS BL, VANDERKARR M, SPARKS C, et al. Treatments, cost and healthcare utilization of patients with segmental bone defects. Injury. 2021;52(10):2935-2940.
[2] BALL AN, DONAHUE SW, WOJDA SJ, et al. The challenges of promoting osteogenesis in segmental bone defects and osteoporosis. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(6):1559-1572.
[3] MIGLIORINI F, MAFFULLI N, BARONCINI A, et al. Allograft Versus Autograft Osteochondral Transplant for Chondral Defects of the Talus: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2022;50(12): 3447-3455.
[4] MATIĆ S, VUČKOVIĆ Č, LEŠIĆ A, et al. Pedicled vascularized bone grafts compared with xenografts in the treatment of scaphoid nonunion. Int Orthop. 2021;45(4):1017-1023.
[5] YANG N, MA T, LIU L, et al. Shortening/re-lengthening and nailing versus bone transport for the treatment of segmental femoral bone defects. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):13288.
[6] LENZE U, O SULLIVAN M, MCCOMBE D, et al. Intramedullary Fixation of Double-Barrel Vascularised Fibula Grafts With Subsequent Lengthening for Reconstruction of the Distal Femur in Patients With Osteosarcoma. J Orthop. 2022;42(6):e674-e681.
[7] DAHL MT, MORRISON S. Segmental Bone Defects and the History of Bone Transport. J Orthop. Trauma. 2021;35(4): S1-S7.
[8] OLIVA F, MIGLIORINI F, CUOZZO F, et al. Outcomes and complications of the reamer irrigator aspirator versus traditional iliac crest bone graft harvesting: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Traumatol. 2021;22(1):50.
[9] MASQUELET AC, FITOUSSI F, BEGUE T, et al.Reconstruction of the long bones by the induced membrane and spongy autograft. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2000;45(3):346-353.
[10] DIOMEDE F, MARCONI GD, FONTICOLI L, et al. Functional Relationship between Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis in Tissue Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(9):3242.
[11] KUSUMBE AP, RAMASAMY SK, ADAMS RH. Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel subtype in bone. Nature. 2014; 507(7492):323-328.
[12] PENG Y, WU S, LI Y, et al. Type H blood vessels in bone modeling and remodeling. Theranostics. 2020;10(1):426-436.
[13] ZHANG J, PAN J, JING W. Motivating role of type H vessels in bone regeneration. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(9):e12874.
[14] 申震,陈泽华,郭英,等.骨碎补总黄酮对牵张成骨模型大鼠中H血管及成血管-成骨耦联的作用[J].中华中医药杂志,2022,37(3): 1352-1356.
[15] 黄敏玲,卢赵琦,申震,等.骨碎补总黄酮干预Notch信号通路影响骨重建过程中成血管-成骨耦联[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(32):5116-5122.
[16] 曾志奎,黄枫,李悦,等.骨碎补总黄酮对大鼠Masquelet诱导膜血管新生因子表达的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2019,37(10): 2345-2348.
[17] 曾志奎,黄枫,黄培镇,等.大鼠股骨Masquelet诱导膜实验模型的建立[J].山东医药,2017,57(48):1-4.
[18] LANE JM, SANDHU HS. Current approaches to experimental bone grafting. Orthop Clin North Am. 1987;18(2):213-225.
[19] WANG L, YOU X, ZHANG L, et al. Mechanical regulation of bone remodeling. Bone Res. 2022;10(1):16.
[20] GROSSO A, BURGER MG, LUNGER A, et al. It Takes Two to Tango: Coupling of Angiogenesis and Osteogenesis for Bone Regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2017;5:68.
[21] SCHIPANI E, MAES C, CARMELIET G, et al. Regulation of osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling by HIFs and VEGF. J Bone Miner Res. 2009;24: 1347-1353.
[22] IGNATIUS A, TUCKERMANN J. New horizons for osteoanabolic treatment? Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14(9):508-509.
[23] 黄敏玲,卢赵琦,申震,等.骨碎补总黄酮干预Notch信号通路影响骨重建过程中成血管-成骨耦联[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(32):5116-5122.
[24] XU R, YALLOWITZ A, QIN A, et al. Targeting skeletal endothelium to ameliorate bone loss. Nat Med. 2018;24(6): 823-833.
[25] XIE H, CUI Z, WANG L, et al. PDGF-BB secreted by preosteoclasts induces angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis. Nat Med. 2014;20(11):1270-1278.
[26] PENG Y, WU S, LI Y, et al. Type H blood vessels in bone modeling and remodeling. Theranostics. 2020;10(1):426-436.
[27] ALFORD AI, NICOLAOU D, HAKE M, et al. Masquelet’s induced membrane technique: Review of current concepts and future directions. J Orthop Res. 2021;39(4):707-718.
[28] 连霄,顾晓民,孙洪军,等.植骨后外固定支架固定联合健骨促愈中药治疗胫骨骨折不愈合的临床研究[J].中华中医药学刊,2017, 35(10):2643-2645.
[29] 傅淑平,杨丽,龚理,等.梓醇促大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞骨向分化的机制研究[J].中国病理生理杂志,2019,35(5):907-913.
[30] 熊伟,袁灵梅,钱国文,等.“补肾壮骨”中药应用于骨组织工程支架修复节段性骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(21):3438-3444.
[31] 陈桂锋,尚奇,沈耿杨,等.从“肾主骨生髓”揭示骨质疏松症炎症微环境的中医理论基础[J].中华中医药杂志,2022,37(12):6906-6909.
[32] 李建国,谢兴文,李鼎鹏,等.从BMSCs探讨“肾主骨生髓”理论指导下中医药治疗骨质疏松症的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2022,28(8):1205-1207,1218.
[33] LI S, ZHOU H, HU C, et al. Corrigendum: Total Flavonoids of Rhizoma Drynariae Promotes Differentiation of Osteoblasts and Growth of Bone Graft in Induced Membrane Partly by Activating Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:726831.
|