Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (15): 2358-2363.doi: 10.12307/2024.407
Previous Articles Next Articles
Visualization analysis of hot spots and trends in material biomechanics
Hong Jing1, Lu Congfei1, Huang Chenbin1, Jiang Qian1, Liu Jingxiong2
- 1School of Physical Education and Sport Science, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou 350117, Fujian Province, China; 2Liling Institute of Ceramic Technology, Hunan University of Technology, Zhuzhou 412217, Hunan Province, China
-
Received:2023-05-26Accepted:2023-07-22Online:2024-05-28Published:2023-09-19 -
Contact:Liu Jingxiong, PhD, Lecturer, Liling Institute of Ceramic Technology, Hunan University of Technology, Zhuzhou 412217, Hunan Province, China -
About author:Hong Jing, Master candidate, School of Physical Education and Sport Science, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou 350117, Fujian Province, China -
Supported by:Hunan Natural Science Foundation, No. 2021JJ40174 (to LJX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hong Jing, Lu Congfei, Huang Chenbin, Jiang Qian, Liu Jingxiong. Visualization analysis of hot spots and trends in material biomechanics[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(15): 2358-2363.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
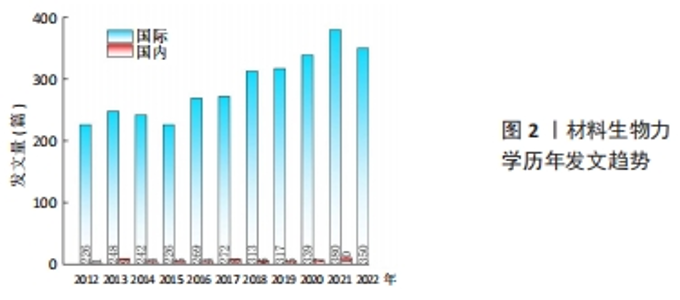
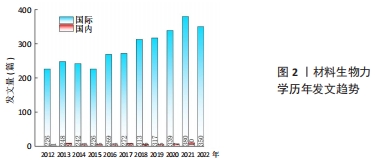
2.1 材料生物力学文献产出 2.1.1 发文趋势与学科基础分析 2012-2022年间共发表关于材料生物力学研究文献3 182篇,文章数量整体呈逐年上升趋势(图2),具体可分为2个阶段:平稳发展阶段(2012-2015年)和快速发展阶段(2016-2022年)。其中,中国历年发文在国际上相对较少,但总体趋势以增长为主。材料生物力学研究的快速增长可以用2个因素来解释:第一,全球正处于新的产业革命时代,着力提升国家制造业基础是提升综合国力的重要支点,材料科学的发展与进步是制造业产业升级与改革的关键基础[6];第二,人工智能的引入改变了制造产业格局,生物医学工程技术作为人工智能领域提升发展质量、降低成本的利器,针对生物医学工程研究也成为推动制造业高质量发展的重要保障[7],这意味着涌现出越来越多关于生物材料的科学研究,与此同时对材料生物力学主题的文献计量分析也更加可靠。"
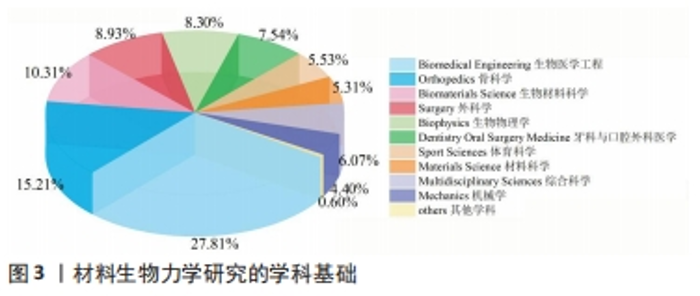
随着材料生物力学的研究越来越多,不同学科的专业手段、知识也被应用至材料生物力学的研究中(图3)。27.81%的文章涉及生物医学工程领域,研究面临各种生物医学材料的设计、制造和功能化问题,旨在突破生物材料与生物内部环境在时空尺度上的相互作用,这将加深对于生物材料潜在作用机制的探索。值得注意的是,生物医学工程单一学科已无法满足材料生物力学的研究需求,骨科学、体育科学、口腔外科医学、机械学等医学、体育学、工程学多学科介入,依据胶原蛋白[8]、光弹性材料[9]、钛合金等生物材料的力学特性[10],从工艺路线、反应机制等方面出发,为特定的疾病病例治疗与康复提供手段,致使材料生物力学研究走向多学科交叉融合体系。例如,太原理工大学团队建立不同生物材料的膝关节有限元模型,通过计算机、工程力学与数学方法计算股骨的应力分布情况,结果发现功能梯度生物材料在减少应力遮挡和聚乙烯衬垫磨损时效果最为显著[11]。"
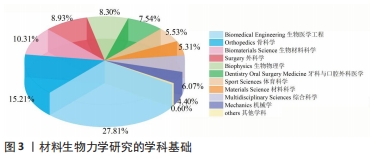
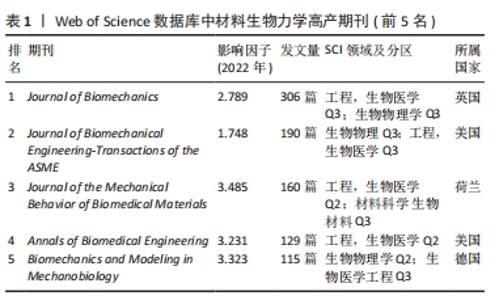
2.1.2 期刊与高频被引文献分析 表1中列出材料生物力学研究前5高产期刊的影响因子、发文量等信息。有关材料生物力学的文献分布于数百种期刊上,前5的高产期刊发文量占总发文量的28%。其中,《Journal of Biomechanics》是发文量首位,近十年累计发文306篇,是一本发表关于使用力学原理探索生物学问题的原创性期刊。发文量第二的是《Journal of Biomechanical Engineering-Transactions of the ASME》,涉猎人体器官和假体、生物材料、生物工程、细胞力学等方向。高产期刊所涉猎领域与其学科基础相匹配(图3),旨在关注人体组织、器官在运动过程中的力学响应,探究人体内部结构与损伤的相关性。"
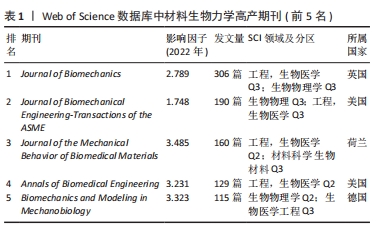
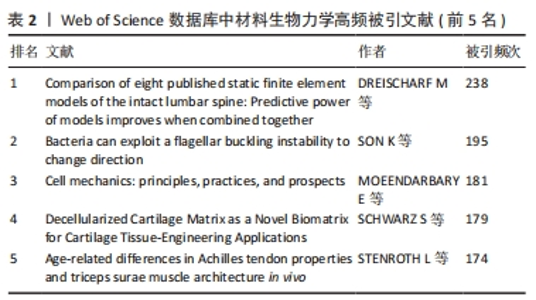
文献的被引频次可以反映出相关文献在该领域的学术影响力,是一种呈现文献、期刊或作者之间关系程度的研究方法[12]。表2描述了材料生物力学研究中高频被引文献,以应用研究为主,研究对象大至关节、肌腱、软骨,小至细胞结构。被引频次最高的文章是DREISCHARF团队[13]通过建立腰椎有限元模型预测不同负荷下腰椎各节段的力学响应,同时提出使用单一模型推广至人群中的假设,并通过概率统计方法的个体模型结果作为预测工具进行检验。被引频次第二的是SON等[14]基于高速视频显微镜和机械稳定性理论使用Matlab跟踪细胞,测量其形状大小并识别鞭毛细丝,以此揭示灵活性在生物材料中的新作用。计算机技术被广泛应用到生物材料的研究中,有限元分析作为计算机技术与力学分析相结合的方法,在计算过程中不会受到形状和材料的限制,通过不同边界条件分析不同工况下的受力情况已成为材料生物力学研究的有力工具。"


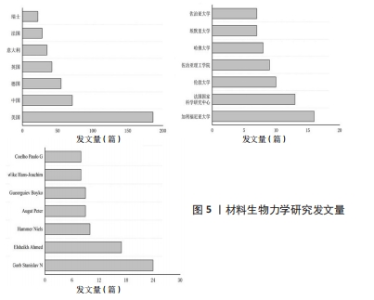
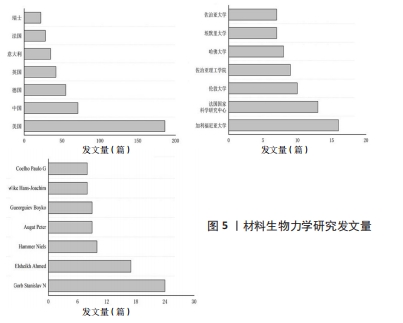
2.2 材料生物力学研究分布 CiteSpace提供包括宏观国家合作网络、中观机构合作网络和微观作者合作网络3个层次的科学网络图谱。网络图谱的基本原理是2个节点间通过连线连接,节点代表国家、机构或作者,2个节点之间连线长短、粗细与二者间合作关系强度有关[15]。 2012-2022年间材料生物力学研究的国家合作关系网中共生成62个节点和178条连线,密度为0.094(图4)。国家发文量与其科研机构和项目资助相关,同时可以反映出该国家对于材料生物力学领域研究的关注程度。由图5可见,材料生物力学研究发文量前三的国家是美国、中国和德国,除中国外均有本土期刊属于该领域的高产期刊(表1),说明中国在该领域的研究依赖于国外期刊发表。此外,欧洲在国家间合作中扮演重要的角色,发文量前7的国家中欧洲国家占据5位,西方国家对于生物材料的投资强度高、研究内容广泛、发展规划长远[16],致使欧洲国家对于材料生物力学领域研究颇为重视,例如德国伯恩大学团队[17]以两种载荷条件分析钛、金合金和氧化锆3种材料作为种植体的应力和应变值,以寻求最佳的骨骼种植体。同样作为生物材料市场主要力量的中国,对于体外实验研究关注度较高[18-19]。体外研究中尸体标本通常是研究的最佳选择,但是人类标本的稀缺性以及离体材料难以模拟真实的运动状态,使得体外实验探索具体的生物力学问题时会受到局限。"

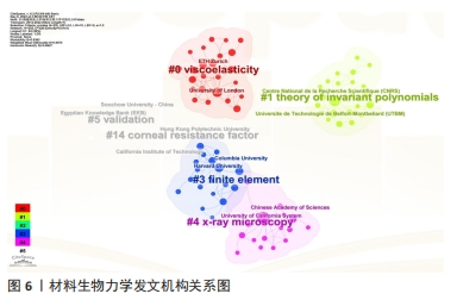
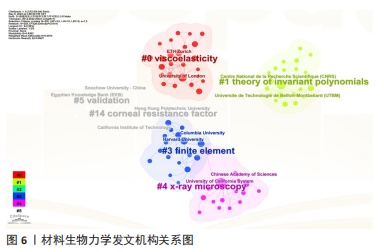
2012-2022年机构网络合作共生成255个节点和328条连线,密度为0.010(图6)。在发文量前列的机构中,美国的加利福尼亚大学以16篇文章领先,该机构在数学、物理学、化学、地质学、生物学等领域研究成果突出,其研究涵盖多形性胶质母细胞瘤模型构建[20]、断层影像分析等[21],对特定疾病发病机制、个性化药物筛选具有重要的研究价值。紧随其后的是法国国家科学研究中心(13篇)、伦敦大学(10篇)、佐治亚理工学院(9篇)(图5)。美国是材料生物力学研究的主要贡献者,加利福尼亚大学、佐治亚理工学院、哈佛大学、埃默里大学、佐治亚大学位列发文量最高的7个机构之中,研究方向侧重于材料黏弹性、有限元建模等。综上,机构主要集中在大学,少数位于科学研究所。"
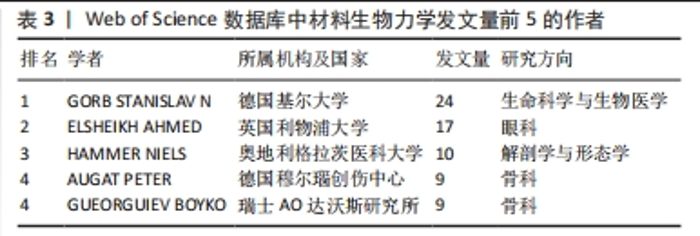
2012-2022年间作者合作关系共生成463个节点和569条连线,密度为0.005 3。合作关系以机构内部作者合作为主,机构与机构间合作较少。通过普赖斯定律可以确定该领域的核心作者群[22],反映该研究领域的发展趋势与科研动态,计算得出核心作者共57位,共发文313篇,尚不构成核心作者群,排名靠前的作者与后续作者之间发文数量差异较大,说明出版文章主要来自排名靠前的作者(图5)。表3列出发文量前5的作者,研究方向集中在生物医学领域,反映出材料生物力学研究的目的旨在解决生物医学问题,例如人体结构生物力学变化与损伤机制分析[23]、体外植入物选择[17]、手术方案预演等[24]。值得注意的是,德国基尔大学的STANISLAV教授以24篇发文量位居第一,以研究各类生物的形态结构、运动表现为主,例如探寻瓢虫的黏性跗骨材料组成和结构特性以提高其黏合剂系统性能[25]。"


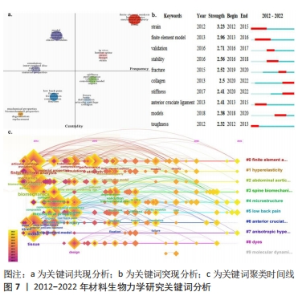
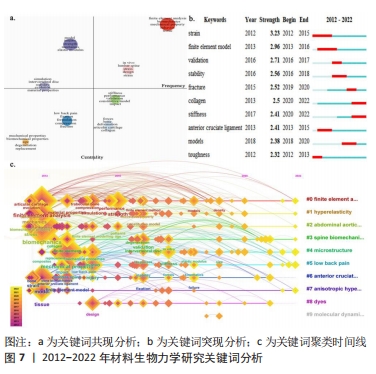
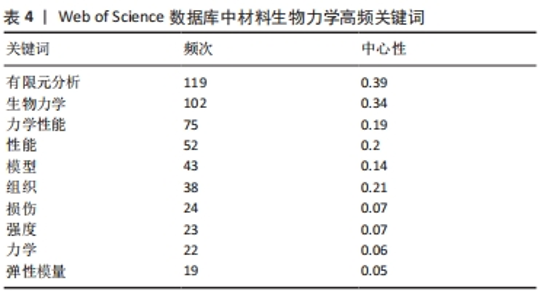
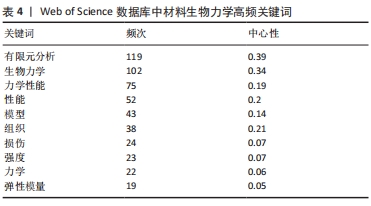
通过关键词突现可以发现近期内剧增的关键词,从更深度的层面观察该领域的发展变化。关键词突现结果显示(图7b所示),2012-2022年间,材料生物力学研究中突现强度最大的关键词是“应变(strain)”,与“有限元模型(finite element model)”均为突现时间最长的关键词。“应变(strain)”“稳定性(stability)”“断裂(fracture)”的突现时间具有延续性,表明拉伸、破坏、稳定等材料结构、性能变化是该领域关注的热点。此外,目前仍然存在的关键词为“胶原蛋白(collagen)”“刚性(stiffness)”,这说明生物材料的结构、性能研究将持续受到关注。 对数极大似然率(likelihood rate,LLR)表示随时间变化发生不同概率现象的可能性,更容易对概率现象进行估计。基于LLR得到关键词聚类科学图谱(图7c和表5),关键词是文献内容的高度概括,通过关键词聚类能够了解材料生物力学研究的热点与动态演变。此次研究共生成10大聚类:#0 有限元分析(finite element analysis)、#1 超弹性(hyperelasticity)、#2 腹主动脉瘤(abdominal aortic aneurysm)、#3 脊柱生物力学(spine biomechanics)、#4 微结构(microstructure)、#5 腰痛(low back pain)、#6 前交叉韧带(anterior cruciate ligament)、#7 各向异性(anisotropic)、#8 染料(dyes)、#9 分子动力学(molecular dynamics)。图7c中节点圆环半径代表关键词的频次,节点间连线代表两个关键词在同一篇文献中出现,颜色线条对应时间线。模块化Q和平均轮廓值S是评估聚类的两个指标,当Q > 0.3时说明聚类结构是显著,S > 0.7时认为聚类具有高效率的信服度。通过LLR计算得到关键词图谱的模块化Q=0.439,平均轮廓值S=0.763,表明聚类结构显著且一致性高。"

| [1] 姜宗来.发展生物力学 造福人类健康——“十四五”我国生物力学研究发展战略思考[J].医用生物力学,2021,36(5):671-675. [2] 陈振银,吕永钢. 材料生物力学2021年研究进展[J].医用生物力学, 2022,37(2):211-218. [3] 于振涛,余森,程军,等.新型医用钛合金材料的研发和应用现状[J].金属学报,2017,53(10):1238-1264. [4] 魏俊超,李晓娜.圆锥角膜生物力学研究进展[J].太原理工大学学报, 2022,53(3):443-449. [5] 康巍,徐鹏,卜伟平,等.生物软组织力学测试及相关理论研究[J].兵工学报,2022,43(9):2164-2171. [6] 林伟坚,张博文,汪卫华.从全球气候变化、制造业产业升级、国家安全及材料基因工程维度探讨材料科学发展趋势[J].中国科学院院刊, 2022,37(3):336-342. [7] 万遂人,顾晓松,骆清铭,等.生物医学工程发展方向和我国高端医疗器械突破点[J] 广西医科大学学报, 2023,40(4):543-548. [8] SIONKOWSKA A. Collagen Based Materials for Biomedical Applications: Preparation and Properties. Mater Sci Forum. 2012;706-709(1):595-599. [9] RACHEL T, ZEIKE T. Photoelastic materials and methods for tissue biomechanics applications. Opti Eng. 2015;54(8):081208. [10] YANG HL, XU H, WU YK, et al. Methods of Porous Biomedical Material Fabrication. Adv Mater Res. 2013;750-752(3):1468-1471. [11] 贾巍,张满栋,陈维毅,等.股骨假体材料对人工膝关节置换性能的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(10):1477-1481. [12] 黄茂茂,胡月,王彬川,等.缺血性脑卒中康复近10年国际文献计量学及可视化分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(23):3725-3733. [13] DREISCHARF M, ZANDER T, SHIRAZI-ADL A, et al. Comparison of eight published static finite element models of the intact lumbar spine: Predictive power of models improves when combined together. J Biomech. 2014;47(8):1757-1766. [14] SON K, GUASTO JS, STOCKER R. Guasto,Roman Stocker. Bacteria can exploit a flagellar buckling instability to change direction. Nat Phys. 2013;9(8):494-498. [15] 李文斌,洪靖.近十年国内外体育传播研究述评[J].情报探索,2023, 305(3):128-134. [16] 赵稼祥,吴方才.国外生物材料和加工的发展[J].宇航材料工艺,1992, 21(1):48-49. [17] HASAN I, KEILIG L, BOURAUEL C, et al. The effect of screw preload and framework material on the success of cementable fixed partial prostheses: A finite element study. Ann Anat. 2015;199:58-66. [18] YANG M, XIANG D, WANG S, et al. In Vitro Studies for Investigating Creep of Intervertebral Discs under Axial Compression: A Review of Testing Environment and Results. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(7):2500. [19] 钱蕾,欧阳钧.两种新型椎弓根螺钉固定强度的体外生物力学研究[J].医用生物力学,2021,36(S1):22. [20] TANG M, TIWARI SK, AGRAWAL K, et al. Rapid 3D Bioprinting of Glioblastoma Model Mimicking Native Biophysical Heterogeneity. Small. 2021;17(15): 2006050. [21] BAY BK, SMITH TS, FYHRIE DP, et al. Digital volume correlation: Three-dimensional strain mapping using X-ray tomography. Exp Mech. 1999;39(3): 217-226. [22] 丁学东.文献计量学基础[M].北京: 北京大学出版社,1992:204-209. [23] MA Z, VYHLIDAL MJ, LI DX, et al. Mechano-bioengineering of the knee meniscus. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022;323(6):C1652-C1663. [24] LI RL, RUSS J, PASCHALIDES C, et al. Mechanical considerations for polymeric heart valve development: Biomechanics, materials, design and manufacturing. Biomaterials. 2019;225:119493. [25] PEISKER H, MICHELS J, GORB SN. Evidence for a material gradient in the adhesive tarsal setae of the ladybird beetle Coccinella septempunctata. Nat Commun. 2013;4:1661. [26] 刘镕阁,徐雁.三维有限元建模分析在髋关节撞击综合征诊疗中的应用研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2021,40(4):317-321. [27] 周玉,龙小安,李宁,等.有限元法分析髌腱炎状态时的生物力学变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(8):1280-1286. [28] KUMAR A, SHITOLE P, GHOSH R, et al. Experimental and numerical comparisons between finite element method, element-free Galerkin method, and extended finite element method predicted stress intensity factor and energy release rate of cortical bone considering anisotropic bone modelling. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2019;233(8):823-838. [29] FUKSA AK, RACHOWICZ W. Numerical simulations of arteries with an adaptive finite element method. J Theor App Mech-Pol. 2014;52(4):917-925. [30] WAN C, HAO Z, WEN S. The Effect of the Variation in ACL Constitutive Model on Joint Kinematics and Biomechanics Under Different Loads: A Finite Element Study. J Biomech Eng. 2013;135(4):041002. [31] CHOKHANDRE S, HALLORAN JP, VAN DEN BOGERT AJ, et al. A Three-Dimensional Inverse Finite Element Analysis of the Heel Pad. J Biomech Eng. 2012;134(3):031002. [32] GUO LX, LI WJ. Finite element modeling and static/dynamic validation of thoracolumbar-pelvic segment. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2020;23(2):69-80. [33] LIU J, QU X, LIU Y. Influence of Load Knowledge on Biomechanics of Asymmetric Lifting. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(6):3207. [34] WAN C, HAO ZX, WEN SZ. The effect of the material property change of anterior cruciate ligament by ageing on joint kinematics and biomechanics under tibial varus/valgus torques. Biomed Mater Eng. 2014;24(1): 1375-1382. [35] HOU JY, ZHANG SQ, KE L. The Application of Metal Materials in Exercise-Induced Bone Injury. Adv Mater Res. 2013;675(3):205-208. [36] LU C,FAN Y,YU G, et al. Asymptomatic foot and ankle structural injuries: a 3D imaging and finite element analysis of elite fencers. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2022;14(1):50. [37] SEYED SAS, FARZAN G, IMAN ZO. A scaled boundary finite element formulation for solving plane-strain viscoelastic problems. Eur J Mech A Solids. 2022;96(8):104755. [38] CORTEZ S, FREITAS FL, COMPLETO A, et al. A 3D finite element model to predict the arcade-like collagen structure in a layered PCL scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2017;20(sup1):47-48. [39] MELONI GR, FISHER MB, STOECKL BD, et al. Biphasic Finite Element Modeling Reconciles Mechanical Properties of Tissue-Engineered Cartilage Constructs Across Testing Platforms. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017;23(13-14): 663-674. [40] BAS O, DE-JUAN-PARDO EM, MEINERT C, et al. Biofabricated soft network composites for cartilage tissue engineering. Biofabrication. 2017;9(2): 025014. [41] WEISS JA, GARDINER JC. Computational modeling of ligament mechanics. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2001;29(3):303-371. [42] SPARKS JL, VAVALLE NA, KASTING KE, et al. Use of silicone materials to simulate tissue biomechanics as related to deep tissue injury. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2015;28(2):59-68. [43] GRYKO A, PROCHOR P, SAJEWICZ E. Finite element analysis of the influence of porosity and pore geometry on mechanical properties of orthopaedic scaffolds. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2022;132:105275. [44] 杨顺清,毛萱.无机生物材料学[M].广州:华南理工大学出版社,2008: 3-15. [45] CIAPETTI G, DI POMPO G, AVNET S, et al. Osteoclast differentiation from human blood precursors on biomimetic calcium-phosphate substrates. Acta Biomater. 2017;50:102-113. [46] RODRIGUEZ-FONTAN F. Fracture healing, the diamond concept under the scope: hydroxyapatite and the hexagon. Medicina. 2022;82(5): 764-769. [47] DOMENICI P, SEEBACHER F. The impacts of climate change on the biomechanics of animals: Themed Issue Article: Biomechanics and Climate Change. Conserv Physiol. 2020;8(1):coz102. [48] ESTER C, FACUNDO JB, SERGIO O. A generalized finite-strain damage model for quasi-incompressible hyperelasticity using hybrid formulation. Int J Numer Methods Eng. 2015;105(10):781-800. [49] SUYA PREM ANAND P, ARUNACHALAM N, VIJAYARAGHAVAN L. Investigation on Grindability of Medical Implant Material Using a Silicon Carbide Wheel with Different Cooling Conditions. Procedia Manufacturing. 2017;10(9): 417-428. [50] DISCHER D, DONG C, FREDBERG JJ, et al. Biomechanics: Cell Research and Applications for the Next Decade. Ann Biomed Eng. 2009;37(5):847-859. [51] RENNEKAMP B, KUTZKI F, OBARSKA-KOSINSKA A, et al. Hybrid Kinetic Monte Carlo/Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Bond Scissions in Proteins. J Chem Theory Comput. 2020;16(1):553-563. [52] LAI ZB, BAI R, LEI Z, et al. Interfacial mechanical behaviour of protein–mineral nanocomposites: A molecular dynamics investigation. J Biomech. 2018;73:161-167. [53] JIANG LG, WU HA, ZHOU XZ, et al. Coarse-Grained Molecular Dynamics Simulation of a Red Blood Cell. Chin Phys Lett. 2010;27(2):028704. [54] FILIPOWSKA J, TOMASZEWSKI KA, NIEDŹWIEDZKI Ł, et al. The role of vasculature in bone development, regeneration and proper systemic functioning. Angiogenesis. 2017;20(3):291-302. [55] BENJAMIN SH, SHINJI I, DANIEL JR, et al. Continuum mechanical parameterisation of cytoplasmic dynein from atomistic simulation. Methods. 2021;185(2):39-48. [56] MICHAEL ES, RICHARD AR,VIRGINIA LF. A poroelastic finite element model of the bone–cartilage unit to determine the effects of changes in permeability with osteoarthritis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2017;20(3):319-331. |
| [1] | Li Zhifei, Yang Yin, Chen Hualong, Liang Qinqiu, Zhong Yuanming, Zhang Yisheng. Finite element analysis of the correlation between tilt angle of titanium cage and postoperative subsidence of titanium cage after anterior subtotal cervical corpectomy, decompression and fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1313-1319. |
| [2] | Ouyang Beiping, Ma Xiangyang, Luo Chunshan, Zou Xiaobao, Lu Tingsheng, Chen Qiling. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new horizontal screw-screw crosslink in posterior atlantoaxial internal fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1320-1324. |
| [3] | Chen Mengmeng, Bao Li, Chen Hao, Jia Pu, Feng Fei, Shi Guan, Tang Hai. Biomechanical characteristics of a novel interspinous distraction fusion device BacFuse for the repair of lumbar degenerative disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1325-1329. |
| [4] | Liang Cheng, Zhang Linqi, Wang Guan, Li Wen, Duan Ke, Li Zhong, Lu Xiaobo, Zhuo Naiqiang. Finite element and biomechanical analysis of different implants in repair for unilateral unstable pelvic posterior ring injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1336-1341. |
| [5] | Guo Sutong, Feng Dehong, Guo Yu, Wang Ling, Ding Yujian, Liu Yi, Qian Zhengying, Li Mingyang. Construction and finite element analysis of normal and osteoporotic hip models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1342-1346. |
| [6] | Yang Junliang, Lu Tan, Xu Biao, Jiang Yaqiong, Wang Fucheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of effects of partial anterior cruciate ligament rupture on knee joint stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1347-1353. |
| [7] | Li Chaojie, Gulati•Maitirouzi, Aierxiding•Abulaiti, Zheng Hui, Tu Hudi. Finite element analysis of medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction at different flexion angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1359-1364. |
| [8] | Feng Tianxiao, Bu Hanmei, Wang Xu, Zhu Liguo, Wei Xu. Interpretation of key points of International Framework for Examination of the Cervical Region for potential of vascular pathologies of the neck prior to Orthopaedic Manual Therapy (OMT) Intervention: International IFOMPT Cervical Framework [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1420-1425. |
| [9] | Weng Rui, Lin Dongxin, Guo Haiwei, Zhang Wensheng, Song Yuke, Lin Hongheng, Li Wenchao, Ye Linqiang. Abnormal types of intervertebral disc structure and related mechanical loading with biomechanical factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1436-1442. |
| [10] | Bai Chen, Yang Wenqian, Meng Zhichao, Wang Yuze. Strategies for repairing injured anterior cruciate ligament and promoting graft healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1457-1463. |
| [11] | Xiaheida·Yilaerjiang, Nijiati·Tuerxun, Reyila·Kuerban, Baibujiafu·Yelisi, Chen Xin. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the distribution pattern of stress in bone tissues with different characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1277-1282. |
| [12] | Qi Xue, Li Jiahui, Zhu Yuanfeng, Yu Lu, Wang Peng. Abnormal modification of alpha-synuclein and its mechanism in Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1301-1306. |
| [13] | Li Longyang, Zhang Songjiang, Zhao Xianmin, Zhou Chunguang, Gao Jianfeng. Electroacupuncture intervention on the proliferation and differentiation of hippocampal neurons and oligodendrocytes in Alzheimer’s disease model mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1029-1035. |
| [14] | Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Lei, Wu Fangting, Wang Jiahui, Duan Xuelin, Zhao Tiejian, Zhao Bin, Zheng Yang. Bibliometric analysis of researches on liver organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1099-1104. |
| [15] | Liu Hanfeng, Wang Jingjing, Yu Yunsheng. Artificial exosomes in treatment of myocardial infarction: current status and prospects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1118-1123. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||