Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (15): 2351-2357.doi: 10.12307/2024.270
Previous Articles Next Articles
Cytocompatibility of electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride piezoelectric bionic periosteum
Wei Suiyan1, Cao Yijing1, Zhao Shuai1, Li Dongyao1, Wei Qin2, Xu Yan3, Xu Guoqiang1, 4
- 1Department of Prosthodontics and Implantology, First Affiliated Hospital (Affiliated Stomatological Hospital) of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Central Laboratory of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 3College of Mechanical Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830047, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 4Insitute of Stomatology, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2023-03-09Accepted:2023-05-08Online:2024-05-28Published:2023-09-19 -
Contact:Xu Guoqiang, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Prosthodontics and Implantology, First Affiliated Hospital (Affiliated Stomatological Hospital) of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; Insitute of Stomatology, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wei Suiyan, Master candidate, Department of Prosthodontics and Implantology, First Affiliated Hospital (Affiliated Stomatological Hospital) of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 51965057 (to XY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wei Suiyan, Cao Yijing, Zhao Shuai, Li Dongyao, Wei Qin, Xu Yan, Xu Guoqiang. Cytocompatibility of electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride piezoelectric bionic periosteum[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(15): 2351-2357.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
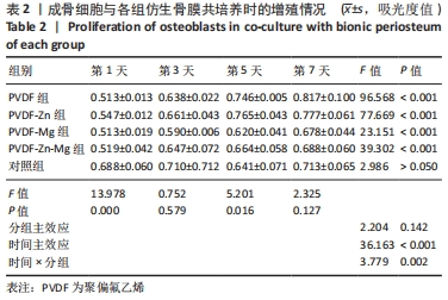
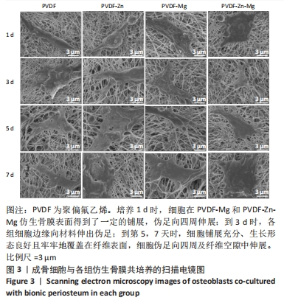
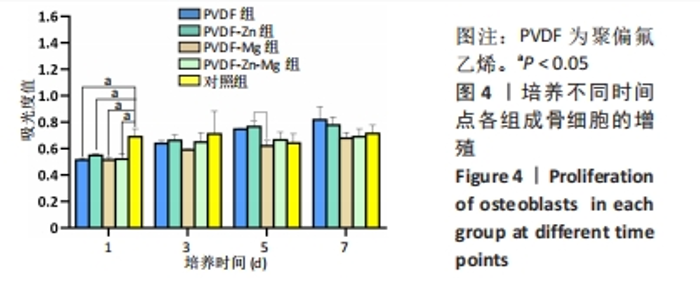
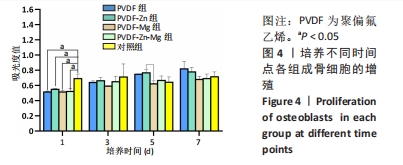
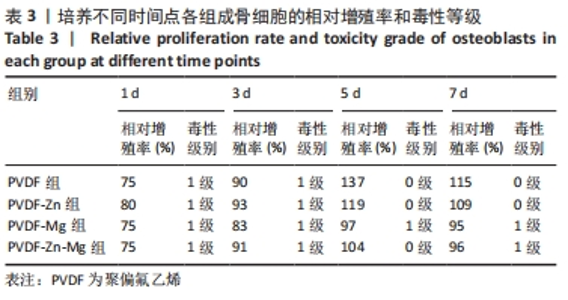
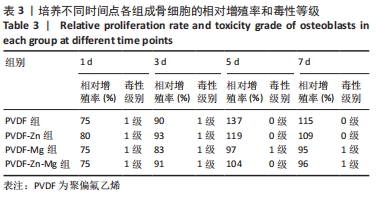
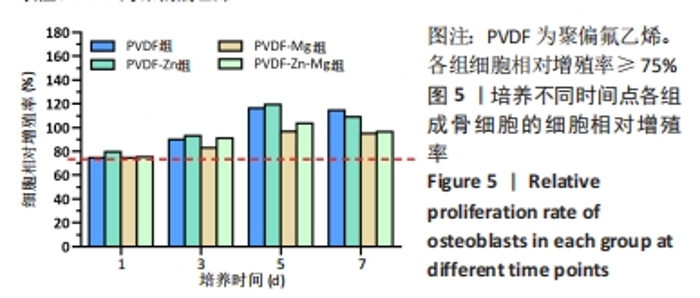
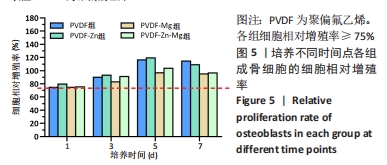
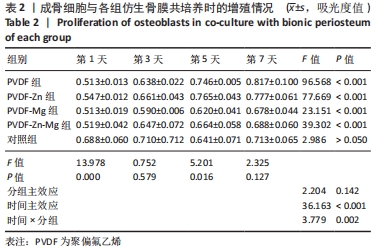
2.2.3 CCK-8法检测细胞增殖 对成骨细胞吸光度值进行重复测量方差分析,不同时间点间的细胞增殖差异有显著性意义(P < 0.001),不同仿生骨膜组别之间的细胞增殖差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),而时间和分组之间有交互作用。 随着时间推移,各组细胞增殖呈上升趋势,培养第1天时,4组仿生骨膜上的细胞增殖吸光度值低于对照组(P < 0.05);培养第3,5,7天时,4组仿生骨膜上的细胞增殖吸光度值与对照组比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05);培养第1,3,7天时,4组仿生骨膜上的细胞增殖吸光度值两两比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);培养第5天时,PVDF-Zn组与PVDF-Mg组细胞增殖吸光度值相比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),如表2和图4所示。表3、图5所示,细胞毒性随着时间的推移逐渐减少,各组细胞相对增殖率≥75%,各组仿生骨膜细胞毒性等级逐渐趋于0级,根据细胞毒性等级标准可以得出,PVDF组、PVDF-Zn组PVDF-Zn组和PVDF-Zn-Mg组仿生骨膜均无细胞毒性,具有良好的细胞相容性。"
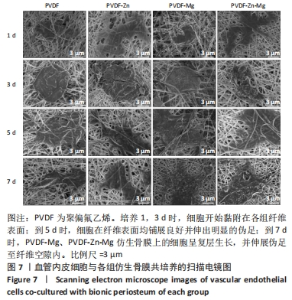
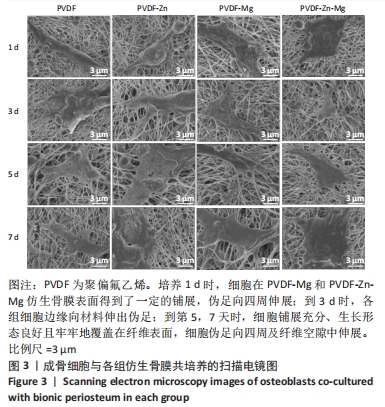
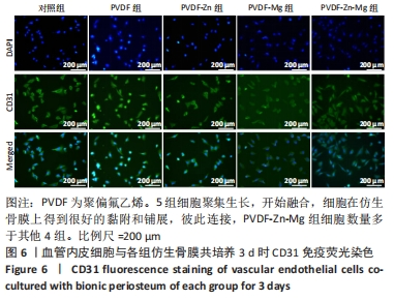
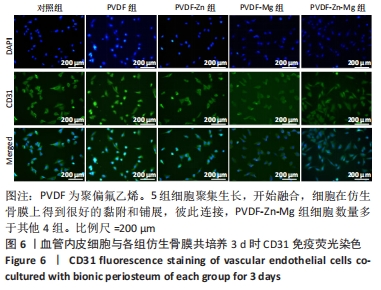
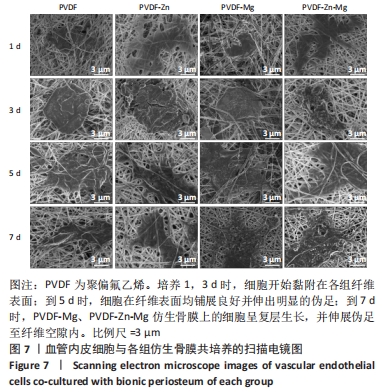
2.3.2 扫描电镜观察 血管形成是骨骼形成和再生所必需的,骨组织的修复需要骨毛细血管来运输氧气和营养物质,由于骨缺损的修复不仅是骨的再生,也是血管再生的过程,因此研究了血管内皮细胞在静电纺丝仿生骨膜上的黏附情况,如图7所示,培养第1,3天时,细胞形态并未伸展完全,细胞开始黏附在纤维表面;培养到第5天时,细胞在各组复合纤维表面均铺展良好,并且可以观察到明显的伪足,细胞在4组仿生骨膜表面均得到了充分的伸展,伪足向四周伸展;培养到第7天时,相比较于PVDF、PVDF-Zn仿生骨膜,PVDF-Mg、PVDF-Zn-Mg仿生骨膜上的血管内皮细胞呈复层生长,具有良好的延伸性,伪足伸展至纤维空隙内,牢牢地附着于纤维膜上。综上,PVDF、PVDF-Zn、PVDF-Mg、PVDF-Zn-Mg仿生骨膜有利于血管内皮细胞的生长。"
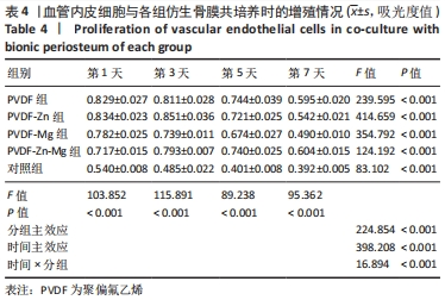
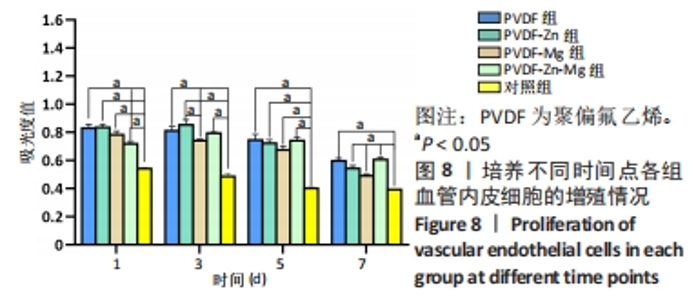
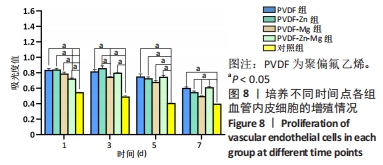
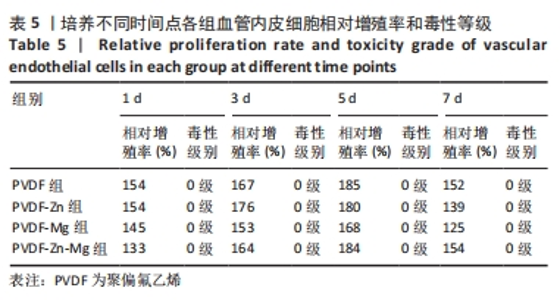
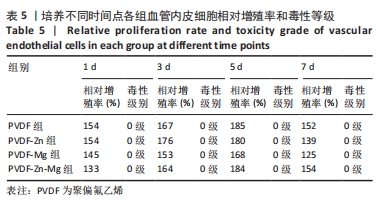
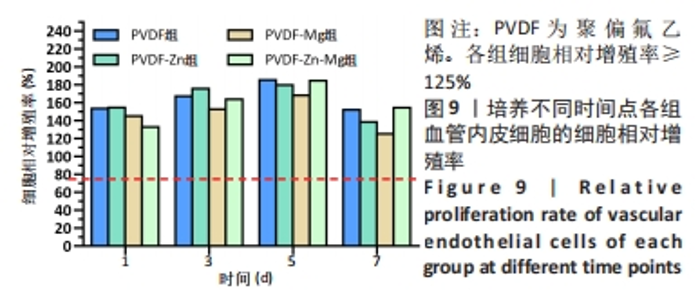
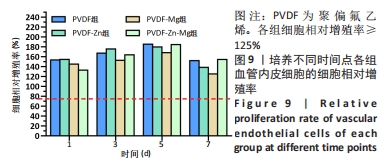
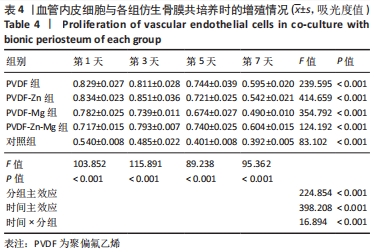
2.3.3 CCK-8法检测细胞增殖 对血管内皮细胞增殖吸光度值进行重复测量方差分析,不同的时间点相比较细胞增殖差异有显著性意义(P < 0.001),不同仿生骨膜组别之间的细胞增殖差异有显著性意义(P < 0.001),并且时间和分组之间有交互作用。 随着时间推移,各组仿生骨膜的血管内皮细胞增殖呈下降趋势,培养第1天时,4组仿生骨膜上的细胞增殖吸光度值均高于对照组(P < 0.001),PVDF-Zn-Mg组细胞增殖吸光度值低于PVDF组、PVDF-Zn组、PVDF-Mg组(P < 0.05);培养第3天时,4组仿生骨膜上的细胞增殖吸光度值均高于对照组(P < 0.001),PVDF-Mg组细胞增殖吸光度值低于PVDF组、PVDF-Zn组(P < 0.05);培养第5天时,4组仿生骨膜上的细胞增殖吸光度值均高于对照组(P < 0.001),其余实验组两两比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05);培养第7天时,4组仿生骨膜上的细胞增殖吸光度值均高于对照组(P < 0.001),PVDF组、PVDF-Zn-Mg组细胞增殖吸光度值高于PVDF-Zn组、PVDF-Mg组(P < 0.05),如表4、图8所示。如表5、图9所示,各组细胞相对增殖率≥125%,根据细胞毒性分级标准,各组仿生骨膜的细胞毒性等级均为0级,表明各组仿生骨膜具有优良的细胞相容性。"
| [1] 陈海松,柳澄.骨膜反应对骨病变的诊断价值[J].中国中西医结合影像学杂志,2020,18(1):104-108. [2] ZHANG X, AWAD HA, O’KEEFE RJ, et al. A perspective: engineering periosteum for structural bone graft healing. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(8):1777-1787. [3] WU L, GU Y, LIU L, et al. Hierarchical micro/nanofibrous membranes of sustained releasing VEGF for periosteal regeneration. Biomaterials. 2020;227:119555. [4] 蒋昇源,宫智浩,宋凯凯,等.骨膜在骨折愈合及骨组织修复过程中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(30):4860-4865. [5] CHEN X, YU B, WANG Z, et al. Progress of Periosteal Osteogenesis: The Prospect of In Vivo Bioreactor. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(9):1930-1939. [6] LI H, WANG H, PAN J, et al. Nanoscaled Bionic Periosteum Orchestrating the Osteogenic Microenvironment for Sequential Bone Regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(33):36823-36836. [7] FUKADA E, YASUDA I. On the Piezoelectric Effect of Bone. J Phys Soc Jpn. 2007; 12(10):1158-1162. [8] HOLLENBERG AM, HUBER A, SMITH CO, et al. Electromagnetic stimulation increases mitochondrial function in osteogenic cells and promotes bone fracture repair. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):19114. [9] ZHENG T, HUANG Y, ZHANG X, et al. Mimicking the electrophysiological microenvironment of bone tissue using electroactive materials to promote its regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(45):10221-10256. [10] SAMADI A, SALATI MA, SAFARI A, et al. Comparative review of piezoelectric biomaterials approach for bone tissue engineering. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2022;33(12):1555-1594. [11] KITSARA M, BLANQUER A, MURILLO G, et al. Permanently hydrophilic, piezoelectric PVDF nanofibrous scaffolds promoting unaided electromechanical stimulation on osteoblasts. Nanoscale. 2019;11(18):8906-8917. [12] AGHAYARI S. PVDF composite nanofibers applications. Heliyon. 2022;8(11): e11620. [13] WANG YW, WU Q, CHEN J, et al. Evaluation of three-dimensional scaffolds made of blends of hydroxyapatite and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) for bone reconstruction. Biomaterials. 2005;26(8):899-904. [14] CHEN WC, HUANG BY, HUANG SM, et al. In vitro evaluation of electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride hybrid nanoparticles as direct piezoelectric membranes for guided bone regeneration. Biomater Adv. 2023;144:213228. [15] LAKHKAR NJ, LEE IH, KIM HW, et al. Bone formation controlled by biologically relevant inorganic ions: role and controlled delivery from phosphate-based glasses. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(4):405-420. [16] MA J, ZHAO N, BETTS L, et al. Bio-Adaption between Magnesium Alloy Stent and the Blood Vessel: A Review. J Mater Sci Technol. 2016; 32(9):815-826. [17] SU Y, COCKERILL I, WANG Y, et al. Zinc-Based Biomaterials for Regeneration and Therapy. Trends Biotechnol. 2019;37(4):428-441. [18] ZHAO Z, LI G, RUAN H, et al. Capturing Magnesium Ions via Microfluidic Hydrogel Microspheres for Promoting Cancellous Bone Regeneration. ACS Nano. 2021; 15(8):13041-13054. [19] MIHAILESCU N, STAN GE, DUTA L, et al. Structural, compositional, mechanical characterization and biological assessment of bovine-derived hydroxyapatite coatings reinforced with MgF2 or MgO for implants functionalization. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;59:863-874. [20] MEHRJOU B, DEHGHAN-BANIANI D, SHI M, et al. Nanopatterned silk-coated AZ31 magnesium alloy with enhanced antibacterial and corrosion properties. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;116:111173. [21] DIOMEDE F, MARCONI GD, FONTICOLI L, et al. Functional Relationship between Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis in Tissue Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(9):3242. [22] 龚鑫,许燕,周建平,等.β 相 PVDF 纤维膜制备及其工艺参数优化[J].工程塑料应用,2022,50(2):82-87. [23] WILLERSHAUSEN B, MARROQUIN BB, SCHAFER D, et al. Cytotoxicity of root canal filling materials to three different human cell lines. J Endod. 2000;26(12):703-707. [24] ZHANG F, REN L F, LIN HS, et al. The optimal dose of recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 enhances differentiation of mouse osteoblast-like cells: an in vitro study. Arch Oral Biol. 2012;57(5):460-468. [25] WU S, DONG T, LI Y, et al. State-of-the-art review of advanced electrospun nanofiber yarn-based textiles for biomedical applications. Appl Mater Today. 2022;27:101473. [26] UNNITHAN AR, BARAKAT N, PICHIAH P, et al. Wound-dressing materials with anti-bacterial activity from electrospun polyurethane–dextran nanofiber mats containing ciprofloxacin HCl. Carbohydr Polym. 2012; 90(4):1786-1793. [27] ZOU B, LIU Y, LUO X, et al. Electrospun fibrous scaffolds with continuous gradations in mineral contents and biological cues for manipulating cellular behaviors. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(4):1576-1585. [28] YANG Z, YI P, LIU Z, et al. Stem Cell-Laden Hydrogel-Based 3D Bioprinting for Bone and Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:865770. [29] TANDON B, BLAKER JJ, CARTMELL SH. Piezoelectric materials as stimulatory biomedical materials and scaffolds for bone repair. Acta Biomater. 2018;73:1-20. [30] SAMADI A, AHMADI R, HOSSEINI SM. Influence of TiO2-Fe3O4-MWCNT hybrid nanotubes on piezoelectric and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of electrospun PVDF nanocomposites. Org Electron. 2019;75:105405. [31] GUILLOT-FERRIOLS M, RODRIGUEZ-HERNANDEZ JC, CORREIA DM, et al. Poly(vinylidene) fluoride membranes coated by heparin/collagen layer-by-layer, smart biomimetic approaches for mesenchymal stem cell culture. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;117:111281. [32] SAMADI A, POURAHMAD S. Flexible piezoelectriccum-electromagnetic-absorbingmultifunctional nanocomposites based on electrospun poly (vinylidene fluoride) incorporated with synthesized porouscore-shellnanoparticles. Int J Energ Res. 2020;(13):44. [33] HAN J, YANG Y, LU J, et al. Sustained release vancomycin-coated titanium alloy using a novel electrostatic dry powder coating technique may be a potential strategy to reduce implant-related infection. Biosci Trends. 2017;11(3):346-354. [34] HE Y, ZHANG Y, SHEN X, et al. The fabrication and in vitro properties of antibacterial polydopamine-LL-37-POPC coatings on micro-arc oxidized titanium. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;170:54-63. [35] WANG X, LIU S, LI M, et al. The synergistic antibacterial activity and mechanism of multicomponent metal ions-containing aqueous solutions against Staphylococcus aureus. J Inorg Biochem. 2016;163:214-220. [36] SHEN X, ZHANG Y, MA P. Fabrication of magnesium/zinc-metal organic framework on titanium implants to inhibit bacterial infection and promote bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2019;212:1-16. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.05.008. [37] PRASAD AS. Zinc: an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent: role of zinc in degenerative disorders of aging. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2014;28(4):364-371. [38] CHENG H, MAO L, XU X, et al. The bifunctional regulation of interconnected Zn-incorporated ZrO2 nanoarrays in antibiosis and osteogenesis. Biomater Sci. 2015;3(4):665-680. [39] PENG F, WANG D, ZHANG D, et al. PEO/Mg-Zn-Al LDH Composite Coating on Mg Alloy as a Zn/Mg Ion-Release Platform with Multifunctions: Enhanced Corrosion Resistance, Osteogenic, and Antibacterial Activities. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018; 4(12):4112-4121. [40] RUDE RK, GRUBER HE, NORTON HJ, et al. Dietary magnesium reduction to 25% of nutrient requirement disrupts bone and mineral metabolism in the rat. Bone. 2005;37(2):211-219. [41] ZREIQAT H, HOWLETT CR, ZANNETTINO A, et al. Mechanisms of magnesium-stimulated adhesion of osteoblastic cells to commonly used orthopaedic implants. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002;62(2):175-184. [42] HU H, ZHANG W, QIAO Y, et al. Antibacterial activity and increased bone marrow stem cell functions of Zn-incorporated TiO2 coatings on titanium. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(2):904-915. [43] KIM BS, KIM JS, PARK YM, et al. Mg ion implantation on SLA-treated titanium surface and its effects on the behavior of mesenchymal stem cell. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013;33(3):1554-1560. [44] 康雯,徐国强,迪丽努尔·阿吉,等.羟基磷灰石/钛酸钡压电陶瓷涂层的体外细胞毒性[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(34):5466-5472. [45] NAGANAWA T, ISHIHARA Y, IWATA T, et al. In vitro biocompatibility of a new titanium-29niobium-13tantalum-4.6zirconium alloy with osteoblast-like MG63 cells. J Periodontol. 2004;75(12):1701-1707. [46] 林红赛,王春仁,王志杰,等.生物材料的细胞生物相容性评价方法的研究进展[J].中国医疗器械信息,2011,17(9):10-14. [47] 章晓云,陈跃平,宋世雷,等.丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架有良好的细胞相容性与渗透性[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(16):2544-2550. [48] 韩雪,许亦权,李大伟,等.新型矿化胶原膜的体外细胞相容性评价[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2021,30(4):225-229. [49] SCHOTT NG, FRIEND NE, STEGEMANN JP. Coupling Osteogenesis and Vasculogenesis in Engineered Orthopedic Tissues. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2021; 27(3):199-214. |
| [1] | Yang Yufang, Yang Zhishan, Duan Mianmian, Liu Yiheng, Tang Zhenglong, Wang Yu. Application and prospects of erythropoietin in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1443-1449. |
| [2] | Dai Yuexing, Zheng Liqin, Wu Minhui, Li Zhihong, Li Shaobin, Zheng Desheng, Lin Ziling. Effect of vessel number on computational fluid dynamics in vascular networks [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1206-1210. |
| [3] | Wang Shanshan, Shu Qing, Tian Jun. Physical factors promote osteogenic differentiation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1083-1090. |
| [4] | Lan Weiwei, Yu Yaodong, Huang Di, Chen Weiyi. In vitro degradation behavior of Mg-Zn-Ca alloys [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 717-723. |
| [5] | Zhou Xiaowen, Fu Zuchang, Huang Fei, Ai Jianguo, Zhao Feng. Bone defect blocked by bone cement segmental filling in single-plane tibial bone transport [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 736-740. |
| [6] | Zhu Liwei, Wang Jiangyue, Bai Ding. Application value of nanocomposite gelatin methacryloyl hydrogels in different bone defect environments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 753-758. |
| [7] | Xu Rong, Wang Haojie, Geng Mengxiang, Meng Kai, Wang Hui, Zhang Keqin, Zhao Huijing. Research advance in preparation and functional modification of porous polytetrafluoroethylene artificial blood vessels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 759-765. |
| [8] | Yin Tong, Yang Jilei, Li Yourui, Liu Zhuoran, Jiang Ming. Application of core-shell structured nanofibers in oral tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 766-770. |
| [9] | Wang Jiani, Chen Junyu. Angiogenesis mechanism of metal ions and their application in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 804-812. |
| [10] | Yang Yuqing, Chen Zhiyu. Role and application of early transient presence of M1 macrophages in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 594-601. |
| [11] | Zhou Shibo, Guan Jianbin, Yu Xing, Zhao He, Yang Yongdong, Liu Tao. Animal models of femoral bone defects: preparation status and characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 633-638. |
| [12] | Zeng Zhikui, Xiong Wei, Liang Weidong, Qian Guowen, Liang Chaoyi, Pan Bin, Guo Ling, Wei Wenqiang, Qiu Xunxiang, Deng Wenfang, Yuan Lingmei. Bone remodeling in the Masquelet-induced membrane model of rat femur by modulation of H-type vessels by total flavonoids of rhizome drynariae [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(32): 5130-5135. |
| [13] | Kong Xiangyu, Wang Xing, Pei Zhiwei, Chang Jiale, Li Siqin, Hao Ting, He Wanxiong, Zhang Baoxin, Jia Yanfei. Biological scaffold materials and printing technology for repairing bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 479-485. |
| [14] | Dai Jing, Liu Shasha, Shen Mingjing. Exosome-loaded injectable hydrogel for repairing bone defects around implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 347-354. |
| [15] | Gao Xueyu, Zhang Wentao, Sun Tianze, Zhang Jing, Li Zhonghai. Application of metal ions in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 439-444. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||