Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (9): 1359-1364.doi: 10.12307/2024.001
Previous Articles Next Articles
Finite element analysis of medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction at different flexion angles
Li Chaojie1, Gulati•Maitirouzi1, Aierxiding•Abulaiti2, Zheng Hui2, Tu Hudi1
- 1College of Mechanical Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830017, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830092, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2023-01-16Accepted:2023-02-20Online:2024-03-28Published:2023-07-25 -
Contact:Gulati•Maitirouzi, Associate professor, College of Mechanical Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830017, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Li Chaojie, Master candidate, College of Mechanical Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830017, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 2019D01C245 (to ZH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Chaojie, Gulati•Maitirouzi, Aierxiding•Abulaiti, Zheng Hui, Tu Hudi. Finite element analysis of medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction at different flexion angles[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1359-1364.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
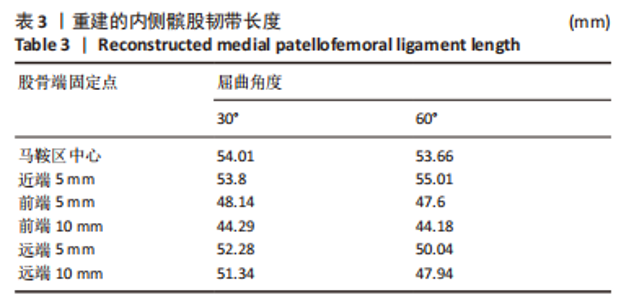
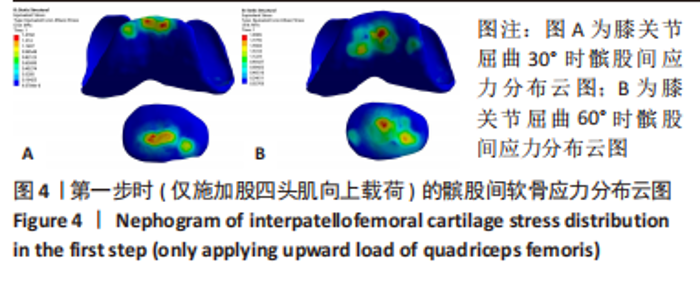
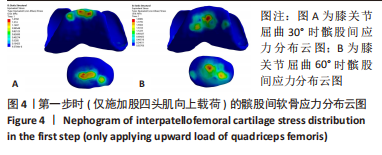
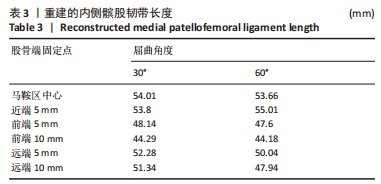
2.1 模型验证 首先是对不同屈曲角度时MPFL的长度进行验证,根据MPFL的等长性,膝关节不同屈曲角度时MPFL长度一般相差小于5 mm[24-25],即可视为具有等长性。MPFL长度见表3。数据显示,构建的MPFL除远端固定点有一定差异外,其他位置长度相差不大,而远端各固定点构建的MPFL长度相差也小于5 mm,因此可以将膝关节不同屈曲角度构建的MPFL视作具有等长性。其次是对髌股间应力位置的验证,对第一步只施加了股四头肌向上载荷的髌股间应力位置进行验证,膝关节屈曲30°与60°时,其髌股间应力接触位置见图4,屈曲30°时,此时髌骨未完全进入股骨滑车,因此髌骨软骨应力主要集中于中下部分,而股骨软骨应力主要集中在其最上部分;屈曲60°时,此时髌骨已基本进入股骨滑车中,此时髌骨软骨上的应力主要集中在中间区域,而股骨软骨上的应力主要集中在滑车中间靠内侧,结果符合正常髌股间的应力接触位置[26-27]。"
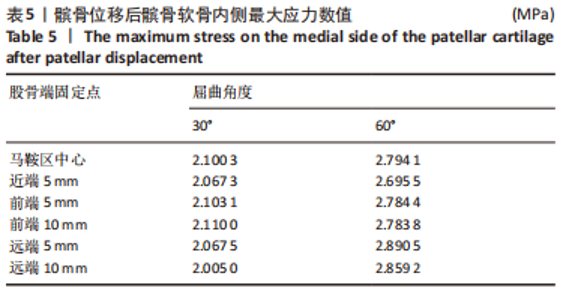
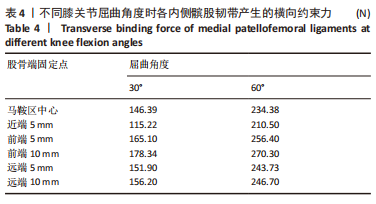
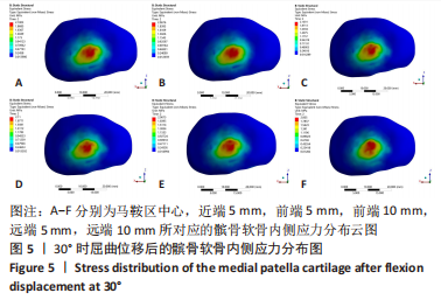
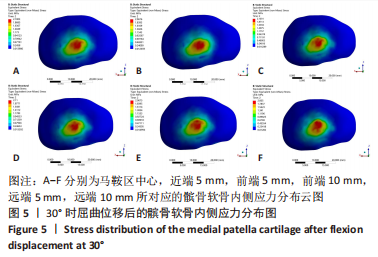
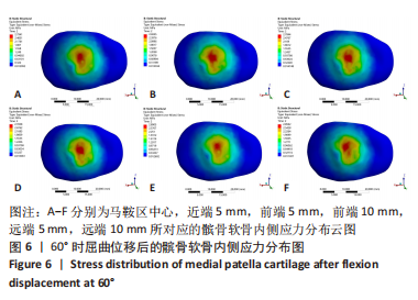
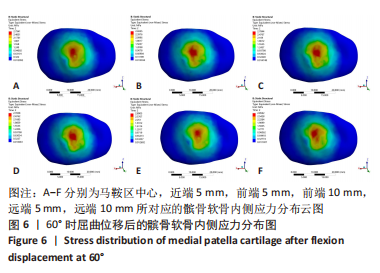
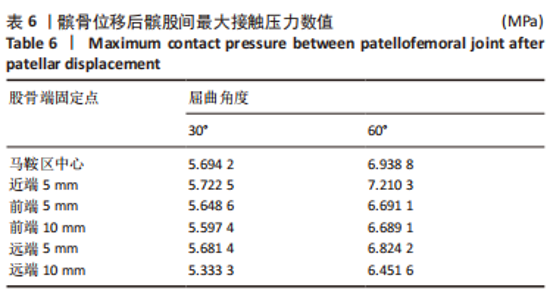
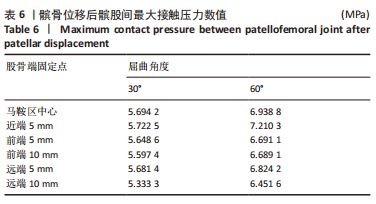
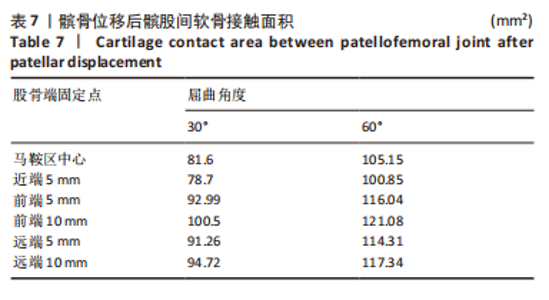
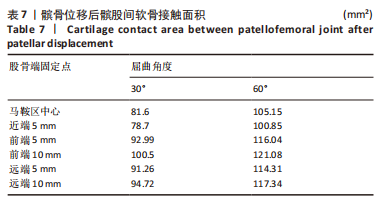
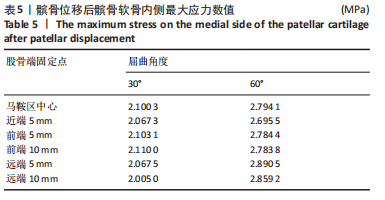
当膝关节屈曲60°时,各点构建的MPFL对髌骨的横向约束力数值在210.5-270.3 N之间,其最大值与最小值所在位置与30°时相同,且横向约束力的增加与减小趋势也与30°时相似。 2.3 位移后的髌股间应力及接触压力与接触面积 在对股四头肌上端面施加载荷后,将髌骨向膝关节外侧施加一个10 mm的位移,由ANSYS软件计算得出髌骨软骨内侧的最大应力数值,见表5。屈曲30°,60°的髌骨软骨内侧应力分布云图,见图5,6。屈曲30°时,应力分布主要集中在髌骨软骨的中下部,数值在2.005-2.103 1 MPa之间,而屈曲60°时,其应力分布主要集中在膑骨软骨的中间部分,数值在2.695 5-2.890 5 MPa之间。"
| [1] CLARK D, METCALFE A, WOGAN C, et al. Adolescent patellar instability: current concepts review. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B(2):159-170. [2] 王婧娟,那玉岩,任逸众,等.磁共振成像评估初次髌骨脱位导致内侧髌股韧带不同部位损伤与脱位复发风险关联的Meta分析[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2021,10(11):828-833. [3] 刘丽思,袁慧书.MRI对复发性髌骨脱位内侧髌股韧带重建术疗效的评估价值[J].临床放射学杂志,2020,39(8):1592-1596. [4] SANCHIS-ALFONSO V, GINOVART G, ALASTRUEY-LÓPEZ D, et al. Evaluation of Patellar Contact Pressure Changes after Static versus Dynamic Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstructions Using a Finite Element Model. J Clin Med. 2019;8(12):2093. [5] AFRAMIAN A, SMITH TO, TENNENT TD, et al. Origin and insertion of the medial patellofemoral ligament: a systematic review of anatomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(12):3755-3772. [6] ZHANG X, XIE G, ZHANG C, et al. Comparation and evaluation of the accuracy of the sulcus localization method to establish the medial patellofemoral ligament femoral tunnel: a cadaveric and clinical study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):53. [7] CHEN J, HAN K, JIANG J, et al. Radiographic Reference Points Do Not Ensure Anatomic Femoral Fixation Sites in Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction: A Quantified Anatomic Localization Method Based on the Saddle Sulcus. Am J Sports Med. 2021;49(2):435-441. [8] HOUDEK CG, ESQUIVEL AO, CRACCHIOLO AM, et al. A Biomechanical Comparison of Isometric and Anatomic Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction. J Knee Surg. 2016;29(6):522-526. [9] SANCHIS-ALFONSO V, RAMIREZ-FUENTES C, MONTESINOS-BERRY E, et al. Femoral insertion site of the graft used to replace the medial patellofemoral ligament influences the ligament dynamic changes during knee flexion and the clinical outcome. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(8):2433-2441. [10] DE ABREU-E-SILVA GM, BUARQUE FAR, DIAS TS, et al. Anatomical femoral tunnel positioning in the medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction: is the free-hand technique accurate? Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(15):924. [11] 林潮盛,刘雨微,朱伟民,等.内侧髌股韧带重建:移植物单双束选择、髌骨及股骨插入点的固定技术[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(26):4217-4222. [12] 张艳,李彦林,刘德健,等.内侧髌股韧带重建术中股骨隧道定位点研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(2):258-264. [13] 韩明展.自体腓骨长肌腱与半腱肌腱重建内侧髌股韧带的疗效分析[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2022. [14] HINCKEL BB, GOBBI RG, DEMANGE MK, et al. Medial Patellofemoral Ligament, Medial Patellotibial Ligament, and Medial Patellomeniscal Ligament: Anatomic, Histologic, Radiographic, and Biomechanical Study. Arthroscopy. 2017;33(10):1862-1873. [15] LAPRADE MD, KALLENBACH SL, AMAN ZS, et al. Biomechanical Evaluation of the Medial Stabilizers of the Patella. Am J Sports Med. 2018;46(7):1575-1582. [16] MESFAR W, SHIRAZI-ADL A. Biomechanics of the knee joint in flexion under various quadriceps forces. Knee. 2005;12(6):424-434. [17] STÄUBLI HU, SCHATZMANN L, BRUNNER P, et al. Mechanical tensile properties of the quadriceps tendon and patellar ligament in young adults. Am J Sports Med. 1999;27(1):27-34. [18] HAUT DONAHUE TL, HOWELL SM, HULL ML, et al. A biomechanical evaluation of anterior and posterior tibialis tendons as suitable single-loop anterior cruciate ligament grafts. Arthroscopy. 2002;18(6):589-597. [19] 葛永军,宣勇,穆帅,等.膝关节盘状半月板有限元模型的构建及生物力学分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(22):2071-2075. [20] 张吉超,董万鹏,董跃福,等.膝关节有限元模型参数设置[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(30):4781-4786. [21] BLACK SR, MEYERS KN, NGUYEN JT, et al. Comparison of Ligament Isometry and Patellofemoral Contact Pressures for Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction Techniques in Skeletally Immature Patients. Am J Sports Med. 2020;48(14):3557-3565. [22] FITZPATRICK CK, BALDWIN MA, RULLKOETTER PJ. Computationally efficient finite element evaluation of natural patellofemoral mechanics. J Biomech Eng. 2010;132(12):121013. [23] SMITH MK, WERNER BC, DIDUCH DR. Avoiding Complications with MPFL Reconstruction. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2018;11(2):241-252. [24] PÉREZ-PRIETO D, CAPURRO B, GELBER PE, et al. The anatomy and isometry of a quasi-anatomical reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017; 25(8):2420-2423. [25] 刘敏,蔡春元,杨国敬,等.MPFL重建术中股骨隧道定位对移植物等距特性的影响[J].医用生物力学,2010,25(5):385-388. [26] 白玉龙,范振华,陈世益.髌股关节接触面及应力分布的研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,1992(4):222-225. [27] 辛雨佳.髌下脂肪垫切除对股关节压力影响的有限元分析[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古医科大学,2020. [28] 郑雷,都基权,朱玲玲,等.分析比较急性髌骨外侧脱位与膝关节多发韧带损伤后内侧髌股韧带损伤的特点[J].武警医学,2021,32(7): 568-572. [29] 胡俊娇,林琦婷,汪飞,等.髌骨一过性外侧脱位MRI表现[J].中国医学影像技术,2020,36(6):945-947. [30] DEVRIES WATSON NA, DUCHMAN KR, et al. A Finite Element Analysis of Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction. Iowa Orthop J. 2015;35:13-19. [31] DUCHMAN KR, DEVRIES NA, MCCARTHY MA, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction. Iowa Orthop J. 2013;33:64-69. [32] TANAKA MJ, CHAHLA J, FARR J 2ND, et al. Recognition of evolving medial patellofemoral anatomy provides insight for reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(8):2537-2550. [33] PATEL NK, DE SA D, VASWANI R, et al. Knee Flexion Angle During Graft Fixation for Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction: A Systematic Review of Outcomes and Complications. Arthroscopy. 2019;35(6):1893-1904. |
| [1] | Wang Juan, Wang Guanglan, Zuo Huiwu. Efficacy of exercise therapy in the treatment of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction patients: #br# a network meta-analysis #br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1714-1726. |
| [2] | Li Shuai, Liu Hua, Shang Yonghui, Liu Yicong, Zhao Qihang, Liu Wen. Stress distribution on the maxilla when wearing the Twin-block appliance for Class II malocclusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 881-887. |
| [3] | Zhou Zonghao, Luo Siyang, Chen Jiawen, Chen Guangneng, Feng Hongchao. Finite element analysis of bioabsorbable plates versus miniature titanium plates in mandibular fracture fixation in different bone qualities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 818-826. |
| [4] | Chen Yilong, Zhang Xu, Li Hong. Mechanical analysis of fiber post combined with different crown restorations for endodontically treated non-carious cervical lesions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 866-871. |
| [5] | He Kai, Xing Wenhua, Liu Shengxiang, Bai Xianming, Zhou Chen, Gao Xu, Qiao Yu, He Qiang, Gao Zhiyu, Guo Zhen, Bao Aruhan, Li Chade. Constructing a model of degenerative scoliosis using finite element method: biomechanical analysis in etiology and treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 572-578. |
| [6] | Su Dejun, Dong Wanpeng, Dong Yuefu, Zhang Jichao, Zhang Zhen. Design of asymmetric prosthesis and mechanical analysis of total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 510-516. |
| [7] | Wang X, Wang Hm, Chen Sh, Feng Tx, Bu Hm, Zhu Lg, Chen Dd, Wei X. Stress and morphological characteristics of intervertebral foramen of cervical rotation-traction manipulation for treating cervical spondylotic radiculopathy: a three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 441-447. |
| [8] | Zhao Yuxin, Liang Liang, Jin Feng, Xu Yangyang, Kang Zhijie, Fang Yuan, He Yujie, Wang Xing, Wang Haiyan, Li Xiaohe. Establishment and stress analysis of a finite element model for adolescent cervical disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 448-454. |
| [9] | Li Zhenggang, Shang Xuehong, Wu Zhang, Li Hong, Sun Chaojun, Chen Huadong, Sun Zhe, Yang Yi. Finite element analysis of three internal fixation modalities for treatment of Pauwels type III femoral neck fractures under different loading conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 455-463. |
| [10] | Liu Mengfei, Chen Gang, Shi Yihan, Zeng Lin, Jiang Kan, Yilihamujiang•Wusiman. Finite element analysis of optimization of femoral prosthesis implantation position in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in osteoporotic patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 464-470. |
| [11] | Mawulanjiang · Abudurenmu, Zilalai · Julaiti, Baibujiafu · Yelisi, Gulizainu · Yibulayin, Nijiati · Tuerxun. Stress analysis of angled abutments of maxillary central incisor implant crown in different implant spacing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3351-3359. |
| [12] | Cao Yilin, Wang Xinyu, Zhuang Yan, Wang Yaru Jiang Zhixiu, Liu Danyu, Men Jiuxu, Ding Yuansheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of three-dimensional printed personalized orthodontic appliances for vertical movement of single teeth [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3360-3368. |
| [13] | Chen Wenhan, Men Jie, Yang Wei, Zhao Xiaoyu. Effect of vibration therapy combined with suspension training on movement and knee joint function after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2225-2230. |
| [14] | Bao Xiong, Wu Xiao, Tang Xijie, Zhang Yougao, Cai Jinkui, Li Zhanghua. A finite element analysis of different bone cement injection volumes and distribution patterns in bilateral percutaneous vertebral augmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2006-2014. |
| [15] | Chen Guangneng, Luo Siyang, Wang Mei, Ye Bin, Chen Jiawen, Liu Yin, Zuo Yuwen, He Xianyu, Shen Jiajin, Ma Minxian. Finite element analysis of various root shield thicknesses in maxillary central incisor socket-shield technique [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2052-2060. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||