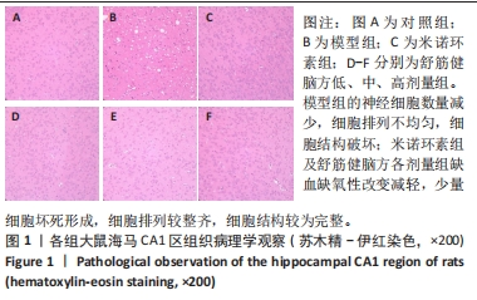
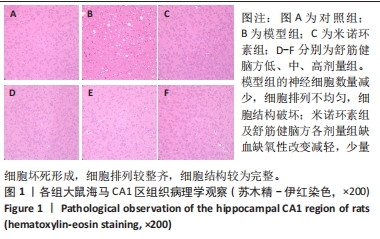
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (28): 4477-4483.doi: 10.12307/2024.395
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of Shujin Jiannao Prescription on cell apoptosis in rats with hypoxic-ischemic brain injury
Jiang Yu1, Xu Lin1, Zhao Yalin2, Liu Gang1, Zhang Yaqi1, Bai Huizhong1, Ren Jingpei1, Zeng Jie3, Mu Xiaohong1
- 1Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100007, China; 2Fengtai Rehabilitation Hospital of Beijing Municipality, Beijing 100161, China; 3Chongqing Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Chongqing 400011, China
-
Received:2023-05-30Accepted:2023-07-04Online:2024-10-08Published:2023-11-27 -
Contact:Mu Xiaohong, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100007, China -
About author:Jiang Yu, Master candidate, Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100007, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Beijing (General Program), No. 7222281 (to MXH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jiang Yu, Xu Lin, Zhao Yalin, Liu Gang, Zhang Yaqi, Bai Huizhong, Ren Jingpei, Zeng Jie, Mu Xiaohong. Effects of Shujin Jiannao Prescription on cell apoptosis in rats with hypoxic-ischemic brain injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4477-4483.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
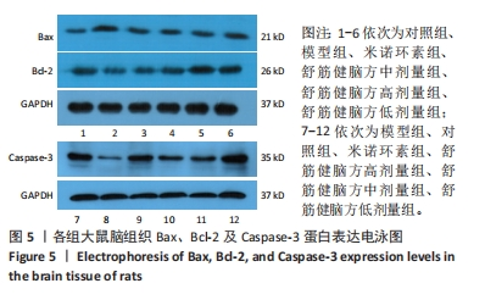
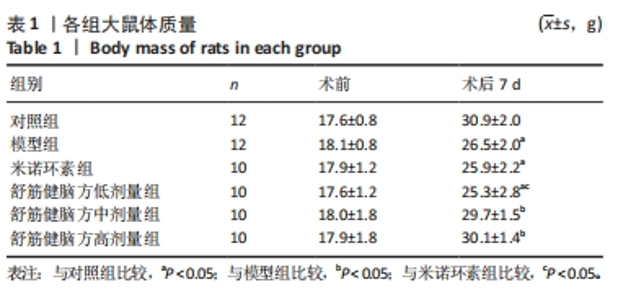
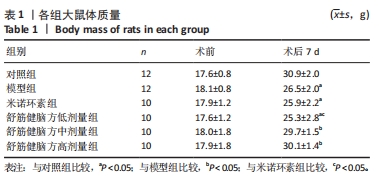
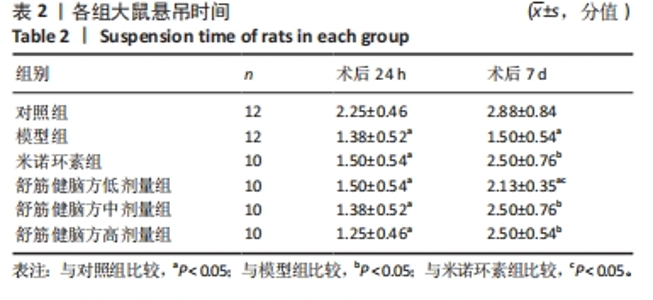
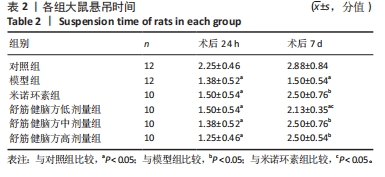
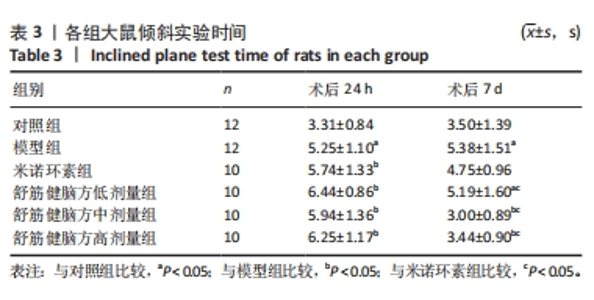
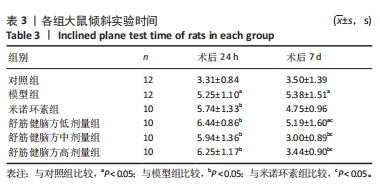
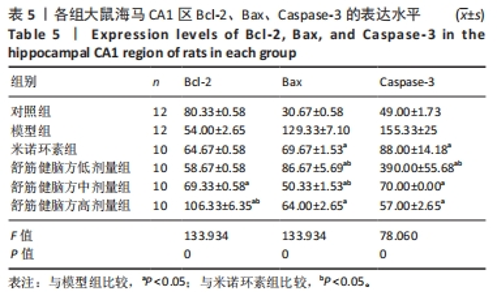
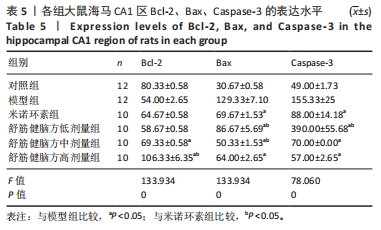
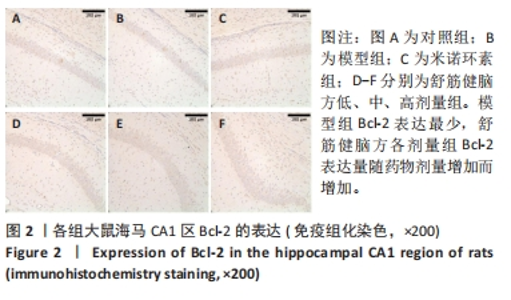
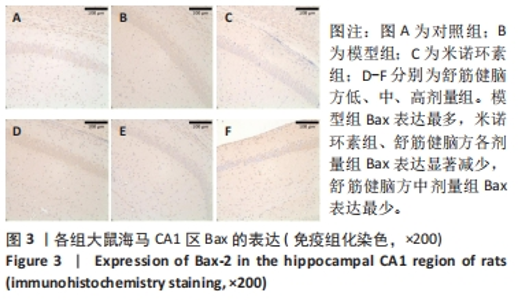
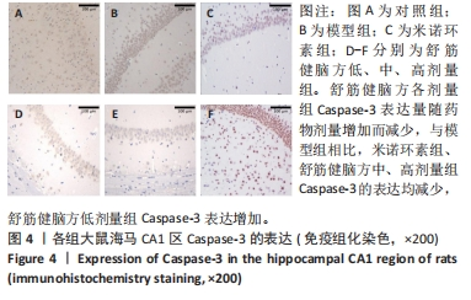
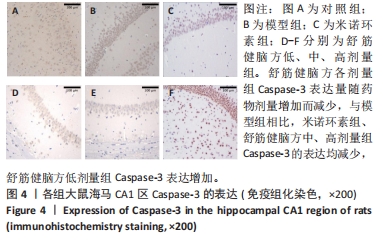
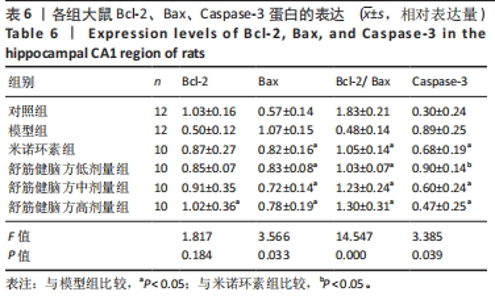
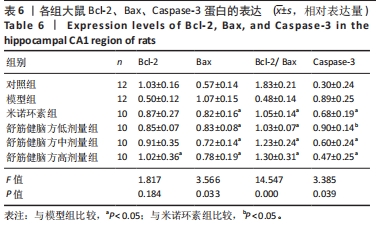
2.5.1 Bcl-2的表达 结果显示,模型组Bcl-2表达最少,舒筋健脑方高剂量组Bcl-2表达最多,舒筋健脑方各剂量组Bcl-2表达量随药物剂量增加而增加;与模型组相比,舒筋健脑方中、高剂量组Bcl-2表达显著增加(P < 0.05);与米诺环素组相比,舒筋健脑方高剂量Bcl-2表达显著增加(P < 0.05)。 2.5.2 Bax的表达 结果显示,模型组Bax表达最多,舒筋健脑方中剂量组Bax表达最少;与模型组相比,米诺环素组、舒筋健脑方低、中和高剂量组Bax表达显著减少(P < 0.05);与米诺环素组相比,舒筋健脑方低剂量Bax表达显著增加,舒筋健脑方中剂量Bax表达显著减少(P < 0.05)。 2.5.3 Caspase-3的表达 结果显示,舒筋健脑方低剂量组Caspase-3表达最多,舒筋健脑方高剂量组Caspase-3表达最少,舒筋健脑方各剂量组表达量随药物剂量增加而减少;与模型组相比,米诺环素组、舒筋健脑方各剂量组的Caspase-3表达均有显著性意义(P < 0.05);与米诺环素组相比,舒筋健脑方低剂量组Caspase-3表达显著增加(P < 0.05)。 2.6 Western blot检测各组大鼠海马CA1区Bcl-2、Bax、Caspase-3蛋白的表达 见图5,表6。"
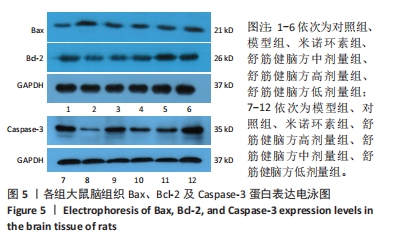

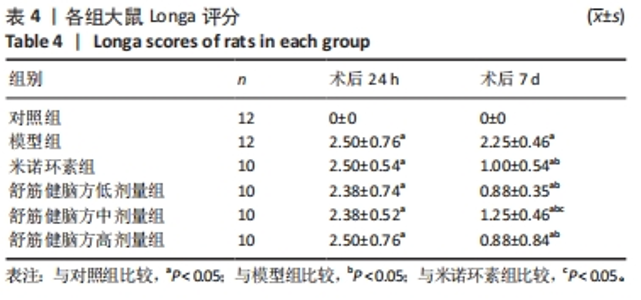
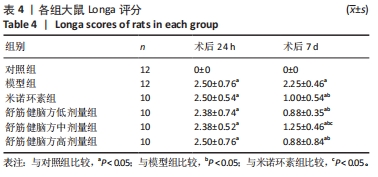
2.6.1 Bcl-2蛋白表达 结果显示,模型组表达少,对照组表达最多,舒筋健脑方各剂量组蛋白的表达量随着药物的剂量成正比;与模型组相比,舒筋健脑方高剂量组蛋白表达显著减少(P < 0.05)。 2.6.2 Bax蛋白表达 结果显示,模型组表达最多,对照组表达最少;与模型组相比,米诺环素组、舒筋健脑方各剂量组表达显著减少(P < 0.05)。 2.6.3 Bcl-2/Bax的比值 模型组Bcl-2/Bax的比值显著低于其他各组(P < 0.05),其中舒筋健脑方各剂量组的比值与药物的剂量成正比。 2.6.4 Caspase-3蛋白表达 结果显示,舒筋健脑方低剂量组表达最多,对照组表达最少;与模型组相比,舒筋健脑方高剂量组蛋白表达显著减少(P < 0.05);与米诺环素组相比,舒筋健脑方低剂量组蛋白表达显著增加(P < 0.05)。"

| [1] 汪乐, 徐林, 刘港, 等. 脑性瘫痪儿童选择性脊神经后根切断术的荟萃分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(15):1372-1376. [2] SADOWSKA M, SARECKA-HUJAR B, KOPYTA I. Cerebral Palsy: Current Opinions on Definition, Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Classification and Treatment Options. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2020;16:1505-1518. [3] SOLEVÅG AL, SCHMÖLZER GM, CHEUNG PY. Novel interventions to reduce oxidative-stress related brain injury in neonatal asphyxia.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;142:113-122. [4] WU YW, COMSTOCK BA, GONZALEZ FF, et al. Trial of Erythropoietin for Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy in Newborns. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(2):148-159. [5] PEDROZA-GARCÍA KA, CALDERÓN-VALLEJO D, QUINTANAR JL. Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy: Perspectives of Neuroprotective and Neuroregenerative Treatments. Neuropediatrics. 2022;53(6): 402-417. [6] 于嘉祥, 张瀚文, 王列, 等. 益糖康通过抑制AGE/RAGE信号通路改善骨骼肌细胞凋亡的机制 [J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2023,29(13): 54-64. [7] 赵亚林. 舒筋健脑方对脑瘫患者认知功能影响及机制研究[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2021. [8] 曾杰. 舒筋健脑方应用于痉挛型脑瘫术后康复的临床疗效和实验研究[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2021. [9] CAI Q, ZHANG X, SHEN L, et al. The protective effect of MiR-27a on the neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy by targeting FOXO1 in rats.Transl Pediatr. 2022;11(7):1199-1208. [10] 闵颖俊, 赵俊雄, 彭行, 等. 小胶质细胞参与新生儿缺氧缺血性脑损伤所致突触异常的研究 [J]. 中国病理生理杂志,2021,37(3):385-392. [11] 黄倩茹, 萨喆燕, 潘晓华, 等. 电针“长强”穴对缺血缺氧脑损伤大鼠行为学的影响[J]. 中国中医药现代远程教育,2018,16(7):91-93. [12] YI CA, JIANG YH, WANG Y, et al. Black Bamboo Rhizome Extract Improves Cognitive Dysfunction by Upregulating the Expression of Hippocampal BDNF and CREB in Rats with Cerebral Ischaemia-Reperfusion Injury. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2021;17:2257-2267. [13] 张宏, 王旭昀, 刘美奇,等. 中药含药血清实验动物灌胃给药剂量探讨[J].吉林中医药,2015,35(6):623-625. [14] 曾杰, 赵亚林, 徐林, 等. 基于“五迟五硬”探讨益肾健脾调肝法治疗痉挛型脑瘫的思路[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2020,35(10):5071-5073. [15] JOHNSON KJ, MOY B, RENSING N, et al. Functional neuropathology of neonatal hypoxia-ischemia by single-mouse longitudinal electroencephalography. Epilepsia. 2022;63(12):3037-3050. [16] XING Z, ZHEN T, JIE F, et al. Early Toll-like receptor 4 inhibition improves immune dysfunction in the hippocampus after hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Int J Med Sci. 2022;19(1):142-151. [17] LI LY, WANG Q, DENG L, et al. Chlorogenic acid alleviates hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal mice. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(3):568-576. [18] WANG M, RONG Y, LUO L. Neuroprotective effects of icariin in neonatal hypoxia-ischemic brain damage via its anti-apoptotic property. Childs Nerv Syst. 2021;37(1):39-46. [19] PENNY TR, PHAM Y, SUTHERLAND AE, et al. Optimization of behavioral testing in a long-term rat model of hypoxic ischemic brain injury. Behav Brain Res. 2021;409:113322. [20] LAWLESS S, BERGOLD PJ. Better together? Treating traumatic brain injury with minocycline plus N-acetylcysteine. Neural Regen Res. 2022; 17(12):2589-2592. [21] 赵黎阳, 刘扬, 张昕, 等. 米诺环素治疗急性脑卒中效果的meta分析[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版),2020,55(3):390-396. [22] LIU H, CHEN S, GUO C, et al. Astragalus Polysaccharide Protects Neurons and Stabilizes Mitochondrial in a Mouse Model of Parkinson Disease. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:5192-5199. [23] CHENG CY, KAO ST, LEE YC. Angelica sinensis extract protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury in the hippocampus by activating p38 MAPK-mediated p90RSK/p-Bad and p90RSK/CREB/BDNF signaling after transient global cerebral ischemia in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;252:112612. [24] 陈梦宇, 杜杰, 肖骋. 杜仲叶提取物通过上调miR-140-5p减轻缺血/再灌注引起的神经细胞损伤[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2023,43(7): 1735-1739. [25] 章喻, 张孙正远, 王利波, 等. 牛膝-杜仲成分组合干预糖皮质激素性骨质疏松模型小鼠的研究 [J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(5): 643-647. [26] SPITZ A Z, GAVATHIOTIS E. Physiological and pharmacological modulation of BAX. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2022;43(3):206-220. [27] LI Z, XIAO G, WANG H, et al. A preparation of Ginkgo biloba L. leaves extract inhibits the apoptosis of hippocampal neurons in post-stroke mice via regulating the expression of Bax/Bcl-2 and Caspase-3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;280:114481. [28] SARIĆ N, HASHIMOTO-TORII K, JEVTOVIĆ-TODOROVIĆ V, et al. Nonapoptotic caspases in neural development and in anesthesia-induced neurotoxicity. Trends Neurosci. 2022;45(6):446-458. [29] ABBASLOO E, AMIRESMAILI S, SHIRAZPOUR S, et al. Satureja khuzistanica Jamzad essential oil and pure carvacrol attenuate TBI-induced inflammation and apoptosis via NF-κB and caspase-3 regulation in the male rat brain. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):4780. [30] ORZALLI MH, PROCHERA A, PAYNE L, et al. Virus-mediated inactivation of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members promotes Gasdermin-E-dependent pyroptosis in barrier epithelial cells. Immunity. 2021;54(7):1447-1462. [31] 刘红淼, 李艳玲, 刘欢, 等. 通窍活血汤对血管性痴呆大鼠学习记忆及海马PI3K/Akt信号通路的影响[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2023.doi: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20230907. [32] 夏金言, 李钻芳, 杨嘉誉, 等. 电针百会、神庭对大脑中动脉栓塞大鼠学习记忆功能和前额叶皮层GABA_A受体及PSD-95表达的影响[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2023,38(6):730-736. |
| [1] | Chen Mengmeng, Bao Li, Chen Hao, Jia Pu, Feng Fei, Shi Guan, Tang Hai. Biomechanical characteristics of a novel interspinous distraction fusion device BacFuse for the repair of lumbar degenerative disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1325-1329. |
| [2] | Min Meipeng, Wu Jin, URBA RAFI, Zhang Wenjie, Gao Jia, Wang Yunhua, He Bin, Fan Lei. Role and significance of artificial intelligence preoperative planning in total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1372-1377. |
| [3] | Wang Menghan, Qi Han, Zhang Yuan, Chen Yanzhi. Three kinds of 3D printed models assisted in treatment of Robinson type II B2 clavicle fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1403-1408. |
| [4] | Feng Tianxiao, Bu Hanmei, Wang Xu, Zhu Liguo, Wei Xu. Interpretation of key points of International Framework for Examination of the Cervical Region for potential of vascular pathologies of the neck prior to Orthopaedic Manual Therapy (OMT) Intervention: International IFOMPT Cervical Framework [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1420-1425. |
| [5] | Yu Weijie, Liu Aifeng, Chen Jixin, Guo Tianci, Jia Yizhen, Feng Huichuan, Yang Jialin. Advantages and application strategies of machine learning in diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1426-1435. |
| [6] | Weng Rui, Lin Dongxin, Guo Haiwei, Zhang Wensheng, Song Yuke, Lin Hongheng, Li Wenchao, Ye Linqiang. Abnormal types of intervertebral disc structure and related mechanical loading with biomechanical factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1436-1442. |
| [7] | Yang Yufang, Yang Zhishan, Duan Mianmian, Liu Yiheng, Tang Zhenglong, Wang Yu. Application and prospects of erythropoietin in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1443-1449. |
| [8] | Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [9] | Yue Yun, Wang Peipei, Yuan Zhaohe, He Shengcun, Jia Xusheng, Liu Qian, Li Zhantao, Fu Huiling, Song Fei, Jia Menghui. Effects of croton cream on JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1186-1192. |
| [10] | Zhao Garida, Ren Yizhong, Han Changxu, Kong Lingyue, Jia Yanbo. Mechanism of Mongolian Medicine Erden-uril on osteoarthritis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1193-1199. |
| [11] | Liu Xin, Hu Man, Zhao Wenjie, Zhang Yu, Meng Bo, Yang Sheng, Peng Qing, Zhang Liang, Wang Jingcheng. Cadmium promotes senescence of annulus fibrosus cells via activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1217-1222. |
| [12] | Ruan Rong, Lou Xujia, Jin Qiguan, Zhang Libing, Xu Shang, Hu Yulong. Effect of resveratrol on gluconeogenesis in exercise-induced fatigue rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1229-1234. |
| [13] | Zuo Xinwei, Liu Gang, Bai Huizhong, Xu Lin, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Hu Chuanyu, Mu Xiaohong. Relationship between lumbar spine development and hip development in children with spastic cerebral palsy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1247-1252. |
| [14] | Zhang Xihui, Li Zhengrong, Li Shineng, Xing Zengyu, Wang Jiao. Effect of rehabilitation training guided by Pro-kin balance system on proprioception and balance function of the affected knee after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1259-1264. |
| [15] | Qi Xue, Li Jiahui, Zhu Yuanfeng, Yu Lu, Wang Peng. Abnormal modification of alpha-synuclein and its mechanism in Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1301-1306. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||