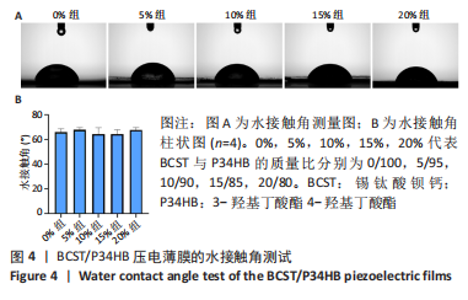
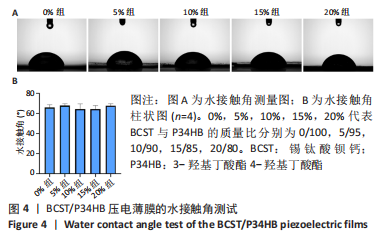
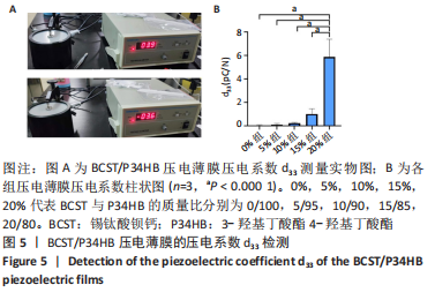
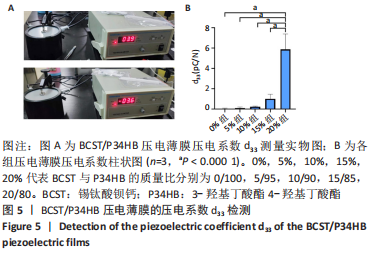
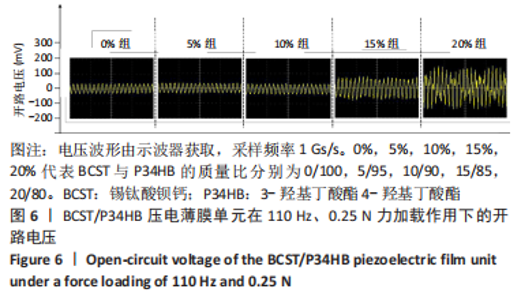
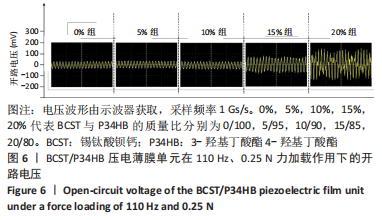
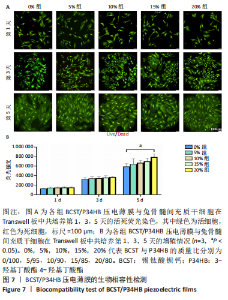
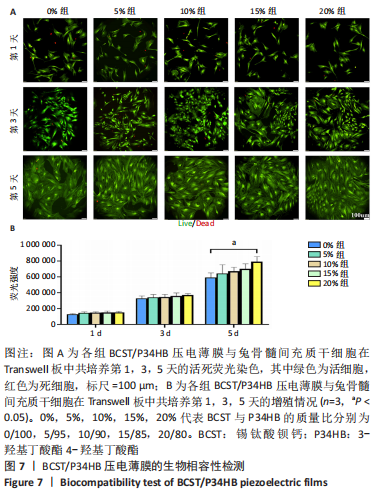
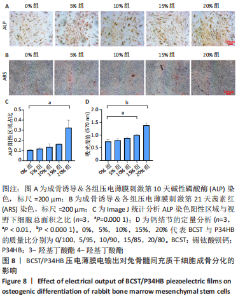
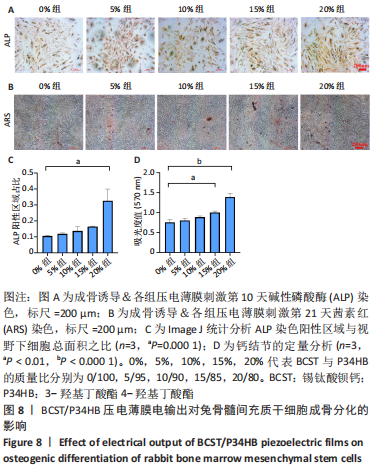
[1] 傅双庆,杜洁,贾新超,等.姜黄素生物可降解纳米胶囊制备综合实验设计[J].实验技术与管理,2022,39(6):30-33.
[2] KOURILOVA X, PERNICOVA I, SEDLAR K, et al. Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) by a thermophilic strain of Schlegelella thermodepolymerans from xylose rich substrates. Bioresour Technol. 2020;315:123885.
[3] 陈安琪,吴清霖,吴勇敏,等.PLA/PVP-GEL复合支架对MC3T3-E1细胞生物学行为的影响及成骨性能的初探[J].口腔生物医学, 2022,13(4):234-240.
[4] 刘鋆,杨龙,王伟宇,等.聚3-羟基丁酸酯4-羟基丁酸酯/聚乙二醇/氧化石墨烯组织工程支架的制备和性能评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(22):3466-3472.
[5] YANG L, ZHAO Y, CUI D, et al. Coaxial bioelectrospinning of P34HB/PVA microfibers biomimetic scaffolds with simultaneity cell-laden for improving bone regeneration. Materials & Design. 2022; 213:110349.
[6] SHAN J, WANG S, ZHOU F, et al. Designing New-Generation Piezoelectric Transducers by Embedding Superior Graphene-Based Thermal Regulators. Adv Mater. 2021;33(41):e2103141.
[7] DHALL A, ISLAM S, PARK M, et al. Bimodal Nanocomposite Platform with Antibiofilm and Self-Powering Functionalities for Biomedical Applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(34):40379-40391.
[8] ZHU P, CHEN Y, SHI J. Piezocatalytic Tumor Therapy by Ultrasound-Triggered and BaTiO3 -Mediated Piezoelectricity. Adv Mater. 2020; 32(29):e2001976.
[9] 梁帅博,袁涛,邱扬,等.钛酸钡介电调控提升纸基摩擦纳米发电机输出性能[J].物理学报,2022,71(7):306-315.
[10] SONG E, KIM DH, JEONG EJ, et al. Effects of particle size and polymorph type of TiO2 on the properties of BaTiO3 nanopowder prepared by solid-state reaction. Environ Res. 2021;202:111668.
[11] LI H, SONG H, LONG M, et al. Mortise-tenon joint structured hydrophobic surface-functionalized barium titanate/polyvinylidene fluoride nanocomposites for printed self-powered wearable sensors. Nanoscale. 2021;13(4):2542-2555.
[12] WANG P, TANG Q, ZHANG L, et al. Ultrasmall Barium Titanate Nanoparticles for Highly Efficient Hypoxic Tumor Therapy via Ultrasound Triggered Piezocatalysis and Water Splitting. ACS Nano. 2021;15(7):11326-11340.
[13] TANG Y, CHEN L, DUAN Z, et al. Graphene/barium titanate/polymethyl methacrylate bio-piezoelectric composites for biomedical application. Ceramics International. 2020;46(5):6567-6574.
[14] SODANO HA, INMAN DJ. A Review of Power Harvesting From Vibration Using Piezoelectric Materials. The Shock and Vibration Digest. 2004; 36:197-205.
[15] WU H, DONG H, TANG Z, et al. Electrical stimulation of piezoelectric BaTiO3 coated Ti6Al4V scaffolds promotes anti-inflammatory polarization of macrophages and bone repair via MAPK/JNK inhibition and OXPHOS activation. Biomaterials. 2023;293:121990.
[16] BASSETT CA, BECKER RO. Generation of electric potentials by bone in response to mechanical stress. Science. 1962;137(3535):1063-1064.
[17] 许言,李平,赖春花,等. 血管化骨再生中压电生物材料的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(7):1126-1132.
[18] WANG A, LIU Z, HU M, et al. Piezoelectric nanofibrous scaffolds as in vivo energy harvesters for modifying fibroblast alignment and proliferation in wound healing. Nano Energy. 2018;43:63-71.
[19] JIN F, LI T, YUAN T, et al. Physiologically Self-Regulated, Fully Implantable, Battery-Free System for Peripheral Nerve Restoration. Adv Mater. 2021;33(48):e2104175.
[20] LIU Y, DZIDOTOR G, LE TT, et al. Exercise-induced piezoelectric stimulation for cartilage regeneration in rabbits. Sci Transl Med. 2022; 14(627):eabi7282.
[21] WU C, TANG Y, ZHAO K , et al. Erbium-doped barium titanate/hydroxyapatite composites with enhanced piezoelectric and biological properties. Micro & Nano Letters. 2020;15(7):421-424.
[22] CAI K, JIAO Y, QUAN Q, et al. Improved activity of MC3T3-E1 cells by the exciting piezoelectric BaTiO3/TC4 using low-intensity pulsed ultrasound. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(11):4073-4082.
[23] ZHOU X, SHEN B, ZHAI J, et al. High Performance Generation of H2 O2 under Piezophototronic Effect with Multi-Layer In2 S3 Nanosheets Modified by Spherical ZnS and BaTiO3 Nanopiezoelectrics. Small Methods. 2021;5(6):e2100269.
[24] DONG Y, DONG S, LIU B, et al. 2D Piezoelectric Bi2 MoO6 Nanoribbons for GSH-Enhanced Sonodynamic Therapy. Adv Mater. 2021;33(51):e2106838.
[25] CHEN J, LI S, JIAO Y, et al. In Vitro Study on the Piezodynamic Therapy with a BaTiO3-Coating Titanium Scaffold under Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Stimulation.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(41): 49542-49555.
[26] GUO W, YANG Z, QIN X, et al. Fabrication and Characterization of the Core-Shell Structure of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-4-Hydroxybutyrate) Nanofiber Scaffolds. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:8868431.
[27] BUR AJ. Measurements of the dynamic piezoelectric properties of bone as a function of temperature and humidity. J Biomech. 1976;9(8):495-507.
[28] LIU X, MA J, WU X, et al. Polymeric Nanofibers with Ultrahigh Piezoelectricity via Self-Orientation of Nanocrystals. ACS Nano. 2017; 11(2):1901-1910.
[29] LEWIS JS, DOLGOVA NV, CHANCELLOR TJ, et al. The effect of cyclic mechanical strain on activation of dendritic cells cultured on adhesive substrates. Biomaterials. 2013;34(36):9063-9070.
[30] 姚雪容,任敏巧,郑萃,等.聚丙烯流延膜厚度对结晶取向及力学性能的影响[J].石油化工,2020,49(6):557-564.
[31] TANG Y, CHEN L, DUAN Z, et al. Enhanced compressive strengths and induced cell growth of 1-3-type BaTiO3/PMMA bio-piezoelectric composites. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;120:111699.
[32] 代香林,张文凤,姚喜军,等.钛酸钡/聚乳酸复合压电薄膜材料对MC3T3-E1细胞黏附、增殖和成骨分化能力的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(3):367-373.
[33] YAN H, LI L, WANG Z, et al. Mussel-Inspired Conducting Copolymer with Aniline Tetramer as Intelligent Biological Adhesive for Bone Tissue Engineering. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(1):634-646.
[34] LOUKIN SH, TENG J, KUNG C. A channelopathy mechanism revealed by direct calmodulin activation of TrpV4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(30):9400-9405.
[35] IKEDA F, NISHIMURA R, MATSUBARA T, et al. Activation of NFAT signal in vivo leads to osteopenia associated with increased osteoclastogenesis and bone-resorbing activity. J Immunol. 2006;177(4):2384-2390.
[36] YANAI R, TETSUO F, ITO S, et al. Extracellular calcium stimulates osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells by enhancing bone morphogenetic protein-2 expression. Cell Calcium. 2019;83:102058.
|