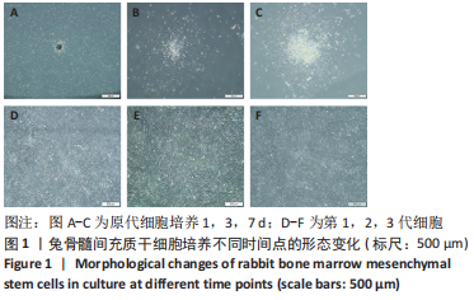
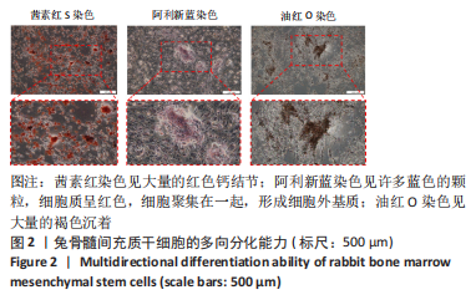
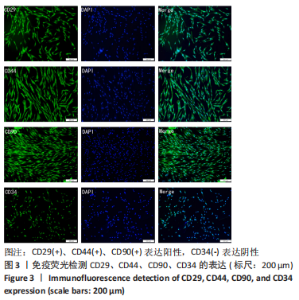
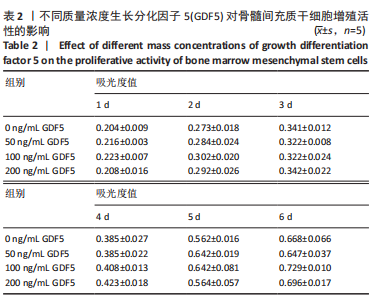
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (13): 1976-1982.doi: 10.12307/2024.126
Previous Articles Next Articles
Chondrogenic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced by growth differentiation factor 5
Li Feifei, Wang Buyu, Yang Zhihang, Dong Xiaoyu, Deng Jiang
- Third Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University (First People’s Hospital of Zunyi), Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2023-02-28Accepted:2023-04-04Online:2024-05-08Published:2023-08-28 -
Contact:Deng Jiang, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Third Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University (First People’s Hospital of Zunyi), Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Li Feifei, Master candidate, Physician, Third Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University (First People’s Hospital of Zunyi), Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81660367 (to DJ); Guizhou Provincial Health Commission Science and Technology Fund, No. gzwkj 2021-236 (to DJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Feifei, Wang Buyu, Yang Zhihang, Dong Xiaoyu, Deng Jiang. Chondrogenic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced by growth differentiation factor 5[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(13): 1976-1982.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
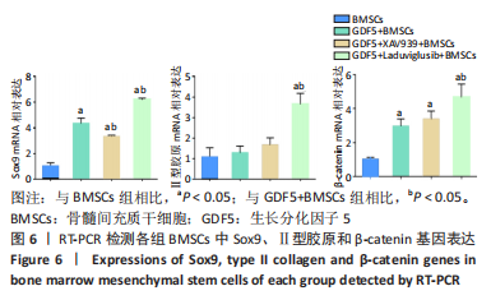
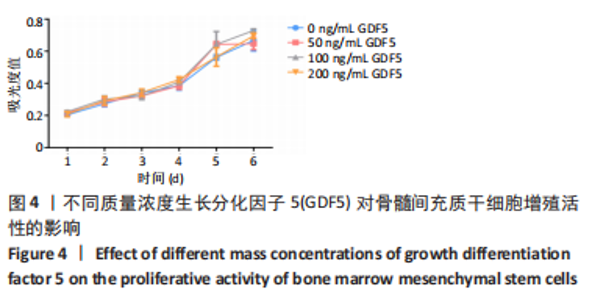
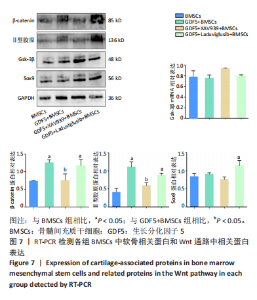
2.6 GDF5诱导BMSCs成软骨分化的机制研究 2.6.1 RT-PCR检测软骨相关基因Ⅱ型胶原、Sox9和Wnt通路中β-catenin的表达 与BMSCs组比较,GDF5+BMSCs组、GDF5+Laduviglusib+BMSCs组、GDF5+XAV939+BMSCs组Sox9和β-catenin表达上调(P < 0.05),GDF5+Laduviglusib+BMSCs组Ⅱ型胶原表达上调(P < 0.05)。与GDF5+BMSCs组比较,GDF5+Laduviglusib+BMSCs组Ⅱ型胶原、Sox9和β-catenin表达上调(P < 0.05),GDF5+XAV939+BMSCs组Sox9的表达下调(P < 0.05),见图6。"

| [1] JANG S, LEE K, JU JH. Recent Updates of Diagnosis, Pathophysiology, and Treatment on Osteoarthritis of the Knee. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2619. [2] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019; 393(10182):1745-1759. [3] GEYER M, SCHÖNFELD C. Novel Insights into the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2018;14(2):98-107. [4] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2):293-311. [5] LANGER R, VACANTI J. Advances in tissue engineering. J Pediatr Surg. 2016;51(1):8-12. [6] LIU C, TSAI AL, LI PC, et al. Endothelial differentiation of bone marrow mesenchyme stem cells applicable to hypoxia and increased migration through Akt and NFκB signals. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):29. [7] YAN H, YU C. Repair of full-thickness cartilage defects with cells of different origin in a rabbit model. Arthroscopy. 2007;23(2):178-187. [8] SUN W, GREGORY DA, TOMEH MA, et al. Silk Fibroin as a Functional Biomaterial for Tissue Engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(3):1499. [9] WANG D, JIANG X, LU A, et al. BMP14 induces tenogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Exp Ther Med. 2018; 16(2):1165-1174. [10] BUXTON P, EDWARDS C, ARCHER CW, et al. Growth/differentiation factor-5 (GDF-5) and skeletal development. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001; 83-A Suppl 1(Pt 1):S23-30. [11] CUI Y, YAO M, LIU Y, et al. Effects of cartilage-derived morphogenetic protein 1 (CDMP1) transgenic mesenchymal stem cell sheets in repairing rabbit cartilage defects. Genet Mol Res. 2016;15(2). doi: 10.4238/gmr.15028058. [12] YANG Z, GAO XJ, ZHAO X. CDMP1 promotes type II collagen and aggrecan synthesis of nucleus pulposus cell via the mediation of ALK6. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(21):10975-10983. [13] MANG T, KLEINSCHMIDT-DÖRR K, PLOEGER F, et al. The GDF-5 mutant M1673 exerts robust anabolic and anti-catabolic effects in chondrocytes. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(13):7141-7150. [14] LE MAITRE CL, FREEMONT AJ, HOYLAND JA. Expression of cartilage-derived morphogenetic protein in human intervertebral discs and its effect on matrix synthesis in degenerate human nucleus pulposus cells. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(5):R137. [15] LUO XW, LIU K, CHEN Z, et al. Adenovirus-mediated GDF-5 promotes the extracellular matrix expression in degenerative nucleus pulposus cells. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2016;17(1):30-42. [16] HASENBEIN I, SACHSE A, HORTSCHANSKY P, et al. Single Application of Low-Dose, Hydroxyapatite-Bound BMP-2 or GDF-5 Induces Long-Term Bone Formation and Biomechanical Stabilization of a Bone Defect in a Senile Sheep Lumbar Osteopenia Model. Biomedicines. 2022;10(2):513. [17] BUNGARTZ M, KUNISCH E, MAENZ S, et al. GDF5 significantly augments the bone formation induced by an injectable, PLGA fiber-reinforced, brushite-forming cement in a sheep defect model of lumbar osteopenia. Spine J. 2017;17(11):1685-1698. [18] HU A, XING R, JIANG L, et al. Thermosensitive hydrogels loaded with human-induced pluripotent stem cells overexpressing growth differentiation factor-5 ameliorate intervertebral disc degeneration in rats. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020;108(5):2005-2016. [19] FENG C, LIU H, YANG Y, et al. Growth and differentiation factor-5 contributes to the structural and functional maintenance of the intervertebral disc. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35(1):1-16. [20] FITZGERALD MJ, MUSTAPICH T, LIANG H, et al. Tendon Transection Healing Can Be Improved With Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Cultured With Growth Differentiation Factor 5 and Platelet-Derived Growth Factor. Hand (N Y). 2023;18(3):436-445. [21] FONT TELLADO S, CHIERA S, BONANI W, et al. Heparin functionalization increases retention of TGF-β2 and GDF5 on biphasic silk fibroin scaffolds for tendon/ligament-to-bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2018;72:150-166. [22] GOULDING SR, ANANTHA J, COLLINS LM, et al. Growth differentiation factor 5: a neurotrophic factor with neuroprotective potential in Parkinson’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(1):38-44. [23] WU H, LI J, XU D, et al. Growth Differentiation Factor 5 Improves Neurogenesis and Functional Recovery in Adult Mouse Hippocampus Following Traumatic Brain Injury. Front Neurol. 2018;9:592. [24] ZHOU S, EID K, GLOWACKI J. Cooperation between TGF-beta and Wnt pathways during chondrocyte and adipocyte differentiation of human marrow stromal cells. J Bone Miner Res. 2004;19(3):463-470. [25] COLEMAN CM, VAUGHAN EE, BROWE DC, et al. Growth differentiation factor-5 enhances in vitro mesenchymal stromal cell chondrogenesis and hypertrophy. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(13):1968-1976. [26] YU F, LIAN R, LIU L, et al. Biomimetic Hydroxyapatite Nanorods Promote Bone Regeneration via Accelerating Osteogenesis of BMSCs through T Cell-Derived IL-22. ACS Nano. 2022;16(1):755-770. [27] JIN L, LI X. Growth differentiation factor 5 regulation in bone regeneration. Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(19):3364-3373. [28] CIARDULLI MC, MARINO L, LAMPARELLI EP, et al. Dose-Response Tendon-Specific Markers Induction by Growth Differentiation Factor-5 in Human Bone Marrow and Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(16):5905. [29] KAKUDO N, WANG YB, MIYAKE S, et al. Analysis of osteochondro-induction using growth and differentiation factor-5 in rat muscle. Life Sci. 2007;81(2):137-143. [30] 杨亚军. CDMP1诱导ADSCs修复软骨损伤的实验研究[D].西安:第四军医大学,2008. [31] 刘振宁,韩长旭,赵敏.生长分化因子5诱导脂肪干细胞复合Ⅰ型胶原支架成软骨细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(19): 2999-3004. [32] 许鹏,许珂,张银刚,等.人生长分化因子5重组质粒转染大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞体外成软骨观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016, 31(9):952-954. [33] HUANG P, YAN R, ZHANG X, et al. Activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway for disease therapy: Challenges and opportunities. Pharmacol Ther. 2019;196:79-90. [34] DESHMUKH V, HU H, BARROGA C, et al. A small-molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway (SM04690) as a potential disease modifying agent for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(1):18-27. [35] ZHU M, CHEN M, ZUSCIK M, et al. Inhibition of beta-catenin signaling in articular chondrocytes results in articular cartilage destruction. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(7):2053-2064. [36] YAO Q, WU X, TAO C, et al. Osteoarthritis: pathogenic signaling pathways and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023; 8(1):56. [37] LU K, MA F, YI D, et al. Molecular signaling in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. 2021;32:21-27. [38] XIA C, WANG P, FANG L, et al. Activation of β-catenin in Col2-expressing chondrocytes leads to osteoarthritis-like defects in hip joint. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(10):18535-18543. [39] ZHOU Y, WANG T, HAMILTON JL, et al. Wnt/β-catenin Signaling in Osteoarthritis and in Other Forms of Arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2017;19(9):53. [40] LI W, XIONG Y, CHEN W, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling may induce senescence of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2020; 20(3):2631-2638. [41] YUAN X, LIU H, HUANG H, et al. The Key Role of Canonical Wnt/β-catenin Signaling in Cartilage Chondrocytes. Curr Drug Targets. 2016;17(4): 475-484. [42] BAGHABAN ESLAMINEJAD M, FALLAH N. Small Molecule-BIO Accelerates and Enhances Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell in Vitro Chondrogenesis. Iran J Med Sci. 2014;39(2):107-116. [43] HAN C, REN Y, JIA Y, et al. The effective mode of growth and differentiation factor-5 in promoting the chondrogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stromal cells. Cell Tissue Bank. 2016;17(1):105-115. [44] VENKATESAN JK, EKICI M, MADRY H, et al. SOX9 gene transfer via safe, stable, replication-defective recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors as a novel, powerful tool to enhance the chondrogenic potential of human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2012;3(3):22. |
| [1] | Yang Yifeng, Huang Jian, Ye Nan, Wang Lin. Ischemia-reperfusion injury in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 955-960. |
| [2] | Liu Anhong, Cai Mengmeng, Han Xiao, Wang Zhanhui. Research status on element selection of medical magnesium alloy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 777-782. |
| [3] | Shen Feiyan, Yao Jixiang, Su Shanshan, Zhao Zhongmin, Tang Weidong. Knockdown of circRNA WD repeat containing protein 1 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of chondrocytes in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 499-504. |
| [4] | Qiao Hujun, Wang Guoxiang. Evaluation of rat osteoarthritis chondrocyte models induced by interleukin-1beta [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 516-521. |
| [5] | Liu Luxing, Di Mingyuan, Yang Qiang. Signaling pathways in the mechanism underlying active ingredients of Chinese medicine in the treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 609-614. |
| [6] | Zhu Zhiqi, Yuan Sijie, Zhang Zilin, Ji Shijie, Meng Mingsong, Yan Anming, Han Jing. Mechanism underlying the effect of Liuwei Dihuang Pill on osteolysis and osteogenesis induced by titanium particles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 392-397. |
| [7] | Yin Linwei, Huang Xiarong, Qu Mengjian, Yang Lu, Wang Jinling, Jia Feiyang, Liao Yang, Zhou Jun. Effects of treadmill exercise on osteoporosis and wnt/beta-catenin signal pathway in aged rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 231-236. |
| [8] | Zhao Kui, Pan Runsang, Lan Fengjun, Deng Jin, Chen Houping. Molecular mechanisms of autophagy-apoptosis interactions in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(18): 2912-2917. |
| [9] | Zhang Shasha, Wang Na, Li Yongjun. Grape seed extract inhibits apoptosis of rat growth plate chondrocytes and promotes tibial bone growth [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(16): 2494-2499. |
| [10] | Gao Zhengang, Zhang Xiaoyun, Jiang Wen. Mechanism of ferroptosis in osteoarthritis and its traditional Chinese medicine interventions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2242-2247. |
| [11] | Wen Tinghao, Li Yuandi, He Keke, Song Wenqian, Wang Xianbin, Gao Jie, Su Min, Hu Rong. Wnt signaling pathway is involved in differentiation of embryonic stem cells into thymic epithelial progenitor cells together with autoimmune regulators [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(13): 1996-2001. |
| [12] | Fan Zhihong, Zhang Xian, Li Chao. Wnt signaling pathway in intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(12): 1950-1955. |
| [13] | Yuan Changshen, Liao Shuning, Li Zhe, Guan Yanbing, Wu Siping, Hu Qi, Mei Qijie, Duan Kan. N6-methyladenosine related regulatory factors in osteoarthritis: bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(11): 1724-1729. |
| [14] | Sun Kexin, Zeng Jinshi, Li Jia, Jiang Haiyue, Liu Xia. Mechanical stimulation enhances matrix formation of three-dimensional bioprinted cartilage constructs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [15] | Shen Feiyan, Yao Jixiang, Su Shanshan, Zhao Zhongmin, Tang Weidong. Knockdown of circRNA WD repeat containing protein 1 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of chondrocytes in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-6. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||