[1] CLOUET J, FUSELLIER M, CAMUS A, et al. Intervertebral disc regeneration: From cell therapy to the development of novel bioinspired endogenous repair strategies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;146:306-324.
[2] HENRY N, CLOUET J, LE BIDEAU J, et al. Innovative strategies for intervertebral disc regenerative medicine: From cell therapies to multiscale delivery systems. Biotechnol Adv. 2018;36(1):281-294.
[3] SAMPARA P, BANALA RR, VEMURI SK, et al. Understanding the molecular biology of intervertebral disc degeneration and potential gene therapy strategies for regeneration: a review. Gene Ther. 2018;25(2):67-82.
[4] VAN UDEN S, SILVA-CORREIA J, OLIVEIRA JM, et al. Current strategies for treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration:substitution and regeneration possibilities. Biomater Res. 2017;21:22.
[5] CHOU FC, CHEN HY, KUO CC, et al. Role of Galectins in Tumors and in Clinical Immunotherapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(2):430.
[6] SEROPIAN IM, GONZÁLEZ GE, MALLER SM, et al. Galectin-1 as an Emerging Mediator of Cardiovascular Inflammation: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities. Mediators Inflamm. 2018;2018:8696543.
[7] ITO K, STANNARD K, GABUTERO E, et al. Galectin-1 as a potent target for cancer therapy: role in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012;31(3-4):763-778.
[8] BLANCHARD H, BUM-ERDENE K, BOHARI MH, et al. Galectin-1 inhibitors and their potential therapeutic applications: a patent review. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2016;26(5):537-554.
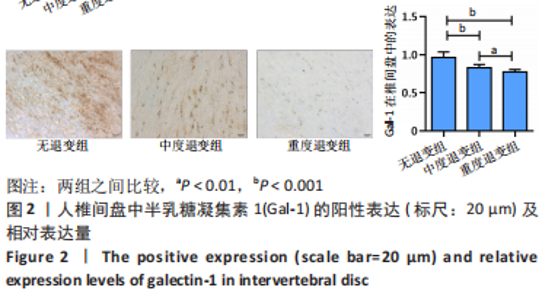
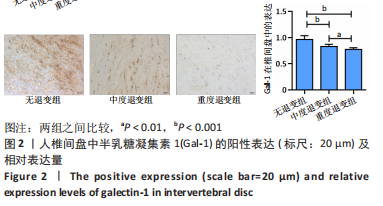
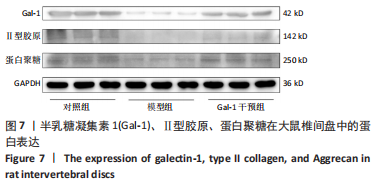
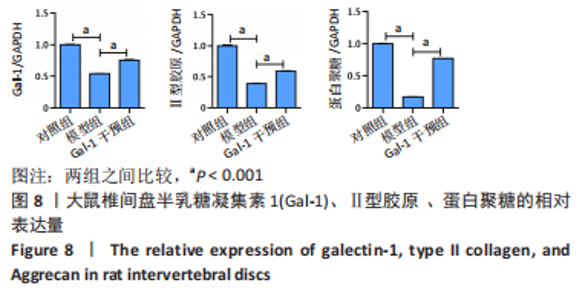
[9] JING L, SO S, LIM SW, et al. Differential expression of galectin-1 and its interactions with cells and laminins in the intervertebral disc. J Orthop Res. 2012;30(12): 1923-1931.
[10] MURPHY J, MCLOUGHLIN E, DAVIES AM, et al. Is T9-11 the true thoracolumbar transition zone? J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020;11(5):891-895.
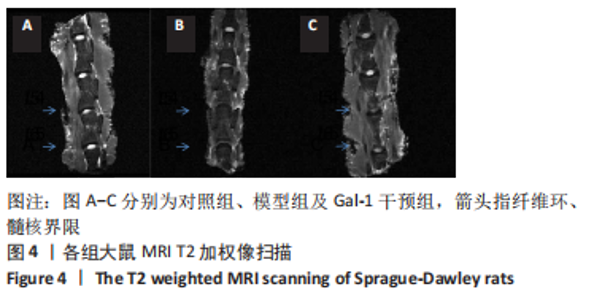
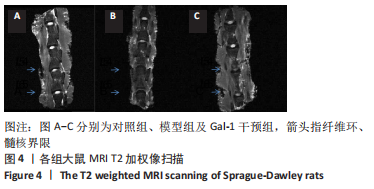
[11] HAN B, ZHU K, LI FC, et al. A simple disc degeneration model induced by percutaneous needle puncture in the rat tail. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(1):1925-1934.
[12] VERGROESEN PP, KINGMA I, EMANUEL KS, et al. Mechanics and biology in intervertebral disc degeneration: a vicious circle. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015; 23(7):1057-1070.
[13] KADOW T, SOWA G, VO N, et al. Molecular basis of intervertebral disc degeneration and herniations: what are the important translational questions? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(6):1903-1912.
[14] MARSICH E, MOZETIC P, ORTOLANI F, et al. Galectin-1 in cartilage: expression, influence on chondrocyte growth and interaction with ECM components. Matrix Biol. 2008;27:513-525.
[15] SUNDBLAD V, MOROSI LG, GEFFNER JR, et al. Galectin-1: A Jack-of-All-Trades in the Resolution of Acute and Chronic Inflammation. J Immunol. 2017;199(11): 3721-3730.
[16] BATZKE K, BÜCHEL G, HANSEN W, et al. TrkB-Target Galectin-1 Impairs Immune Activation and Radiation Responses in Neuroblastoma: Implications for Tumour Therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(3):718.
[17] WILLEMS N, TELLEGEN AR, BERGKNUT N, et al. Inflammatory profiles in canine intervertebral disc degeneration. BMC Vet Res. 2016;12:10.
[18] GU SX, LI X, HAMILTON JL, et al. MicroRNA-146a reduces IL-1 dependent inflammatory responses in the intervertebral disc. Gene. 2015;555(2):80-87.
[19] AL-OBAIDI N, MOHAN S, LIANG S, et al. Galectin-1 is a new fibrosis protein in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. FASEB J. 2019;33(1):373-387.
[20] PEINTNER L, VENKATRAMAN A, WAELDIN A, et al. Loss of PKD1/polycystin-1 impairs lysosomal activity in a CAPN (calpain)-dependent manner. Autophagy. 2021;17(9):2384-2400.
[21] MAEDA N, KAWADA N, SEKI S, et al. Stimulation of proliferation of rat hepatic stellate cells by galectin-1 and galectin-3 through different intracellular signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(21):18938-18944. |