Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (2): 263-266.doi: 10.12307/2023.895
Previous Articles Next Articles
A systematic review of mouse model construction for sarcopenia
Xie Peng1, Zhang Jiang2, Deng Xiaolei2, Wei Bo2, Hou Decai2
- 1Liaoning University of Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110032, Liaoning Province, China; 2Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning University of Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110847, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2022-11-22Accepted:2023-01-18Online:2024-01-18Published:2023-06-30 -
Contact:Hou Decai, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Chief physician, Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning University of Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110847, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Xie Peng, Master candidate, Liaoning University of Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110032, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:Science and Technology Research Project of Liaoning Provincial Department of Education, No. L202043 (to HDC); Seedling Breeding Project of the Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning University of Chinese Medicine, No. YM202029 (to ZJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xie Peng, Zhang Jiang, Deng Xiaolei, Wei Bo, Hou Decai. A systematic review of mouse model construction for sarcopenia[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 263-266.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

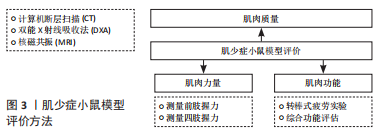
2.1.1 肌肉质量评估 指南建议应首先评估肌肉质量,在临床上常用方法有计算机断层扫描(CT)、核磁共振(MRI)、双能X射线吸收法以及生物电阻抗分析法等。其中CT和MRI是测量骨骼肌质量最直接、准确的方法,这一点也同样适用小鼠[5]。PASETTO等[6]还开发了一种基于micro-CT而不使用对比剂的非侵入性程序,该程序可广泛用于以肌肉萎缩为特征的疾病模型。小鼠也可以在麻醉后放置在双能X射线吸收法扫描平台上,用双能X射线吸收法测量它们的脂肪和肌肉质量[7]。 2.1.2 肌肉力量评估 2019年欧洲老年人肌肉减少症工作组将肌力减退视为肌少症的重要特征,认为肌力是目前最可靠的测量指标[1]。对于肌少症小鼠模型,前肢握力的测量较为简便,可作为评估的首选方法。测试前,使小鼠适应握力仪10 min,将小鼠前肢置于握力仪的传感横杆上,前肢抓住横杆,水平向后拖动小鼠尾部直至前肢松开,握力仪会自动记录小鼠抓杆过程中的最大握力。重复测量数次,记录最大值或平均值作为小鼠前肢握力[8-9]。除了前肢的力量外,还可以测量小鼠四肢的握力。王雅兰等[10]将小鼠放在测力计上,使其四爪全部抓住网格,然后缓慢向后拖动小鼠,直至其失去握力,实验过程中小鼠保持水平姿势,重复进行5次同样的操作,记录数据,取3次较大抓力的平均值作为此小鼠的抓力值。 2.1.3 肌肉功能评估 肌少症患者对肌肉功能的评估往往以步速评估来实现[11],步速是指以日常步调步行3-6 m所需的时间,该方法较为简便,可行性高。对于小鼠,也可以采用步速评估,但所用的方法不同,通常采用转棒式疲劳实验间接反映小鼠的步数[10]。除了简单评价肌肉功能外,还可以采用多种组合综合评价肌肉功能,如LIU等[12]通过握力、步行速度、体力活动和耐力对肌肉功能进行了综合评估。GRABER等[13]开发了一套针对肌少症综合功能评估的组合。 2.2 肌少症小鼠模型建造方式 2.2.1 衰老模型 鉴于衰老是肌少症的高危因素,衰老小鼠模型已被广泛用于肌少症的研究。通常采用自然衰老、高脂饮食诱导的衰老和加速衰老3种小鼠模型。 (1)自然衰老模型:由于自然衰老小鼠模型能够最大程度地再现衰老过程,因此可能最适合用于衰老相关肌少症的研究。KIM等[14]发现18月龄小鼠的握力、肌肉质量和肌肉体积明显低于10周龄小鼠,表明该模型中存在肌少症。FUJII等[15]通过研究发现25月龄大的小鼠是研究肌少症的合理模型。 (2)高脂饮食诱导模型:由于自然衰老小鼠模型的建立需要大量时间且费用较高,越来越多的研究者选择其他造模方法来缩短肌少症的建模时间。研究发现高脂饮食是肌少症的重要危险因素,长期高脂饮食的老年患者相比同龄人,其肌肉质量和肌肉力量明显下降[16]。LEE等[17]在高脂饮食诱导的肥胖小鼠模型中,发现肥胖小鼠肌肉间脂肪堆积增加,肌肉质量减少。HU等[18]发现在高脂喂养小鼠模型中,不仅干细胞的再生能力下降,而且肌细胞分化为肌纤维的过程也遭到破坏。尽管高脂饮食加速小鼠衰老的研究较少,但由于高脂饮食可以导致肌少症,同时导致肥胖,因此高脂饮食诱导的衰老小鼠模型是肌少症伴肥胖模型的理想选择。 (3)加速衰老小鼠:加速衰老小鼠(senaging-accelerated mouse,SAM)是通过亲本AKR/J小鼠重复选择性近交建立的动物衰老模型,包括具有正常衰老的抗衰老自交系(SAMR)以及具有加速衰老和衰老相关病理的衰老倾向自交系(SAMP)[19]。与SAMR相比,SAMP表现出更快的衰老过程和更短的寿命,并且更早表现出与年龄相关的病理进展,这与人类的老年病较类似[20]。其中SAMP8是研究肌少症最常用的加速衰老小鼠模型,相比于SAMP6和SAMR1小鼠模型,SAMP8小鼠肌肉衰老的典型特征出现在相对年轻的年龄,几乎是其他模型的2倍,且肌肉萎缩以Ⅱ型肌纤维为主,这一点与人类肌少症患者骨骼肌变化相一致,因此SAMP8小鼠是研究肌少症较为理想的动物模型[20-22]。 2.2.2 肌肉萎缩模型 小鼠肌肉萎缩诱导指通过外科手术法或制动法诱导小鼠骨骼肌发生失用性萎缩,最终导致肌少症。手术方法主要通过切断胫神经或坐骨神经使肌肉失去神经支配而导致骨骼肌失用性萎缩,失神经动物模型已被广泛应用于肌少症的研究[23]。制动法通过限制小鼠肢体活动从而导致肌肉失用性萎缩,包括后肢悬吊法和关节位置固定法[24]。 (1)手术法:骨骼肌的生长、发育和正常功能依赖于运动神经的支配和调节,创伤性周围神经损伤、药物干预、衰老等因素都可以引起的骨骼肌失神经支配从而导致肌肉功能降低,造成肌肉萎缩。ZHAO等[25] 通过切除12周龄小鼠左后肢0.5-1.0 cm的坐骨神经,诱导小鼠骨骼肌出现失用性萎缩。NAGPAL等[26]同样用切断小鼠胫神经的方式制造出肌少症的模型,并分别探究神经支配肌肉萎缩的短期和长期过程。然而由于失神经小鼠模型的建立需要精确的手术操作,难度较大且较耗费时间,因此失神经大鼠模型更为常用。 (2)后肢悬吊法:后肢悬吊法最初设计是用于研究宇航员对失重或低重力条件的骨骼肌肉反应,此后被广泛用作肌肉消耗模型,模拟肌肉消耗性疾病、制动、卧床和固定等[27]。后肢悬吊法是一种较为常用的小鼠肌少症模型制作方法,已被证明会限制肌肉生长,并导致后肢肌肉质量、球蛋白含量的显著下降。尤其在那些主要由Ⅰ型纤维组成的肌肉中,这种肌肉质量的损失更为广泛[28-30]。ANDERSON等[31]将小鼠后肢悬吊18 d后,发现后肢肌肉的收缩张力和质量都明显降低;同时,他们发现硝酸异山梨酯可治疗肌肉萎缩及代谢变化,防止失用,并能预防老年性肌少症。后肢悬吊法小鼠模型作为一种与运动无关的肌少症模型,对于骨骼肌老化的研究具有重要意义,可视为老年肌少症的有效模型。 (3)关节位置固定法:关节位置固定法是研究肌少症常用的模型,因为它可以模拟骨折后石膏固定导致的失用性肌肉萎缩。用石膏绷带或螺旋线包裹腿部,限制小鼠关节从而造成小鼠肌肉的失用性萎缩,导致小鼠肌肉质量和肌肉力量的降低,建立小鼠肌少症模型。同时,关节固定方式也有许多不同种类,BURKS等[32]使用外科缝合钉将后肢的腹侧部分固定到腿的远端部分。也有研究将小鼠髋关节、膝关节和踝关节以最大屈曲固定到背部皮肤来进行小鼠肌少症的造模[33]。虽然制动模型可模拟长期卧床肌少症患者疾病的发生和发展,但其骨骼肌衰减的特征与老年人并不一致,这一点可能限制此模型的进一步应用。 2.2.3 试剂注射模型 试剂注射诱导是一种较为常见的肌少症动物造模方法,操作方法也较为简单,只需将试剂直接注射或灌注到待诱导的小鼠模型中,这些试剂在小鼠体内经历一系列复杂的过程,最终会诱导肌少症。较为常用的注射用试剂是地塞米松和肉毒毒素A。 (1)注射地塞米松:地塞米松是一种合成的糖皮质激素,具有抗炎、抗过敏和抗休克的作用,但是,长期注射地塞米松可引起不良反应,例如体质量增加、肌肉萎缩以及脂肪向心性积聚堆积等[34]。鲁飞翔等[35]向小鼠皮下注射地塞米松,观察10-19 d,发现小鼠的肌肉质量和功能明显下降。同样,王月兵等[36]分别对8-10周龄小鼠和六七月龄小鼠注射地塞米松试剂,观察19 d,结果发现8-10周龄小鼠相比于六七月龄小鼠,肌肉质量明显下降,因此认为六七月龄小鼠相于8-10周龄小鼠更适合作为肌少症模型。有研究表明地塞米松诱导的肌肉萎缩主要是由Ⅱ型肌纤维减少引起的,这与衰老引起的肌肉萎缩一致[37]。虽然注射地塞米松能够降低小鼠的肌肉质量和肌力,但小鼠的年龄、给药剂量、给药天数等其他影响因素还需进一步研究。 (2)注射肉毒毒素A:皮下注射肉毒毒素A也被用于建立衰老肌少症小鼠模型。肉毒毒素A是一种高分子蛋白毒素,注射后肉毒毒素A作用于神经肌肉接头突触间隙中,阻断乙酰胆碱的运转、融合和释放,导致肌肉麻痹,从而造成肌肉的快速丢失[38]。MANSKE等[39]向小鼠注射肉毒毒素A后,发现小鼠的肌肉质量和肌肉横截面积都大幅下降,肌肉表现出快速萎缩,甚至骨小梁和皮质骨也明显减少。但应注意的是注射肉毒毒素A会导致骨质的流失,这与老年性肌少症较为不同,故此种造模方式的可行性还需进一步研究。 2.2.4 转基因模型 许多转基因小鼠模型也被应用于肌少症的研究。使用较多的转基因小鼠可分为3类,分别为基因敲除小鼠模型、基因过表达小鼠模型以及线粒体DNA(mitochondrial DNA,mtDNA)突变小鼠模型。 (1)基因敲除模型:基因敲除动物模型是指运用基因工程技术将目的基因敲除,或用其他相似的基因替换目的基因而得到的动物模型[40]。抗炎细胞因子白细胞介素10的缺失,可促进核因子κB炎症递质的过表达,从而导致虚弱、肌无力、炎症、身体功能下降等特征。KO等[41]在白细胞介素10敲除小鼠模型中发现骨骼肌中ATP合成率较低,线粒体受损,导致肌肉萎缩,因此白细胞介素10敲除小鼠模型可用于研究炎症条件下肌少症的发病机制。另外一种常见的是敲除超氧化物歧化酶1(superoxide dismutase 1,SOD1)小鼠模型,SOD1是生物内源性抗氧化剂,可清除体内超氧阴离子自由基,从而减轻细胞损伤,对维持细胞膜的结构和功能起重要作用[42]。JANG等[43]敲除小鼠SOD1后发现小鼠表现出高水平的氧化损伤以及肌肉加速老化的特征,并表现出神经肌肉接头的虚弱和破坏。同时有研究表明CuZnSOD可以逆转SOD1敲除小鼠骨骼肌中自由基的产生,防止肌肉萎缩[44]。 (2)基因过表达模型:有研究发现某些炎症因子如肿瘤坏死因子α、转化生长因子β、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β等在骨骼肌过多积累可引起肌肉萎缩,从而导致肌少症[45]。LI等[46]研究发现通过阻止骨骼肌中的TRAF6信号转导,能够抑制肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的蛋白水解,从而治疗与年龄和类风湿性关节炎相关的肌少症。Wnt/β-catenin信号通路可促进衰老,并可抑制肌肉细胞再生能力,(Pro)肾素受体[(P) RR]是Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的激活物,骨骼肌中(P)RR过表达可激活Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路,从而阻碍成肌细胞融合,导致骨骼肌生长迟缓[24]。有研究发现,(P)RR转基因小鼠会出现早期死亡,以及表现出肌肉萎缩伴肌少症的特征,可作为肌少症的一种造模方式[47]。 (3)mtDNA突变模型:mtDNA突变被认为是导致线粒体功能障碍的原因之一。研究表明mtDNA突变可能是由于活性氧对mtDNA的氧化损伤造成的,随着突变的积累线粒体呼吸链功能会进一步损坏,并产生更多的突变和活性氧,加速细胞衰老进程[48]。有研究人员利用基因敲入技术建立mtDNA突变型小鼠模型,结果发现这些小鼠产生明显早衰表现,如体质量降低、骨质疏松、肌纤维溶解、心肌炎和肌少症[49-50]。目前对于mtDNA突变的研究大多是在动物模型中进行的,对人类肌少症患者的mtDNA突变研究尚不多见,仅有少数学者研究探讨了mtDNA缺失与肌少症的关系[51]。"

| [1] SAYER AA, CRUZ-JENTOFT A. Sarcopenia definition, diagnosis and treatment: consensus is growing. Age Ageing. 2022;51(10):afac220. [2] 彭洪俊,曾羿.肌肉减少症和骨关节炎相关性研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2022,36(12):1549-1557. [3] 杜娟,杨玲,黄乙欢,等.肌肉减少症治疗研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2022,42(2): 506-511. [4] 李含笑,姬笑颜,张欣怡,等.肌少症动物模型的研究进展[J].实验动物科学,2022, 39(1):74-77. [5] XIE WQ, XIAO GL, FAN YB, et al. Sarcopenic obesity: research advances in pathogenesis and diagnostic criteria. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2021;33(2):247-252. [6] PASETTO L, OLIVARI D, NARDO G, et al. Micro-computed tomography for non-invasive evaluation of muscle atrophy in mouse models of disease. PloS One. 2018;13(5):e0198089. [7] HALLDORSDOTTIR S, CARMODY J, BOOZER CN, et al. Reproducibility and accuracy of body composition assessments in mice by dual energy x-ray absorptiometry and time domain nuclear magnetic resonance. Int J Body Compos Res. 2009;7(4):147-154. [8] CHANG YC, CHEN YT, LIU HW, et al. Oligonol Alleviates Sarcopenia by Regulation of Signaling Pathways Involved in Protein Turnover and Mitochondrial Quality. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2019;63(10):e1801102. [9] CAMPOS F, ABRIGO J, AGUIRRE F, et al. Sarcopenia in a mice model of chronic liver disease: role of the ubiquitin-proteasome system and oxidative stress. Pflugers Arch. 2018;470(10):1503-1519. [10] 王雅兰,吕欣,葛宝金,等.快速老化小鼠红细胞和肌肉功能的增龄性变化及相关性研究[J].重庆医学,2020,49(9):1377-1380+1386. [11] 王坤,罗炯,刘立,等.老年人肌少症的成因、评估及应对[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(11):1767-1773. [12] LIU H, GRABER TG, FERGUSON-STEGALL L, et al. Clinically relevant frailty index for mice. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2014;69(12):1485-1491. [13] GRABER TG, MAROTO R, FRY CS, et al. Measuring Exercise Capacity and Physical Function in Adult and Older Mice. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2021;76(5):819-824. [14] KIM C, HWANG JK. The 5,7-Dimethoxyflavone Suppresses Sarcopenia by Regulating Protein Turnover and Mitochondria Biogenesis-Related Pathways. Nutrients. 2020;12(4):1079. [15] FUJII C, MIYASHITA K, MITSUISHI M, et al. Treatment of sarcopenia and glucose intolerance through mitochondrial activation by 5-aminolevulinic acid. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):4013. [16] 张静,李维辛.老年人糖尿病相关性肌少症发病机制与防治[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2021,14(6):681-687. [17] LEE SR, KHAMOUI AV, JO E, et al. Effects of chronic high-fat feeding on skeletal muscle mass and function in middle-aged mice. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2015;27(4):403-411. [18] HU Z, WANG H, LEE IH, et al. PTEN inhibition improves muscle regeneration in mice fed a high-fat diet. Diabetes. 2010;59(6):1312-1320. [19] GUO AY, LEUNG KS, SIU PM, et al. Muscle mass, structural and functional investigations of senescence-accelerated mouse P8 (SAMP8). Exp Anim. 2015;64(4):425-433. [20] 张红佳,刘强和,王杰.快速老化小鼠听功能及耳蜗组织中p-ERK1/2的增龄性变化[J]. 听力学及言语疾病杂志,2015(5):510-514. [21] KRISHNAN VS, WHITE Z, MCMAHON CD, et al. A Neurogenic Perspective of Sarcopenia: Time Course Study of Sciatic Nerves From Aging Mice. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2016;75(5):464-478. [22] HUANG Y, WU B, SHEN D, et al. Ferroptosis in a sarcopenia model of senescence accelerated mouse prone 8 (SAMP8). Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(1):151-162. [23] 王世杨,孙慧哲,颜南,等.被动训练促进失神经肌萎缩模型大鼠骨骼肌结构和功能的恢复[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(32):5138-5144. [24] 周晓宁,袁帅,赵启,等.肌少症造模方法的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022, 28(9):1365-1368. [25] ZHAO J, TIAN Z, KADOMATSU T, et al. Age-dependent increase in angiopoietin-like protein 2 accelerates skeletal muscle loss in mice. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(5):1596-1609. [26] NAGPAL P, PLANT PJ, CORREA J, et al. The ubiquitin ligase Nedd4-1 participates in denervation-induced skeletal muscle atrophy in mice. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e46427. [27] 李聪,高泽林,方碧青,等.肌少症动物模型的研究进展[J].中国实验动物学报, 2021,29(1):85-90. [28] PALUS S, SPRINGER JI, DOEHNER W, et al. Models of sarcopenia: Short review. Int J Cardiol. 2017;238:19-21. [29] BAEK KW, JUNG YK, KIM JS, et al. Rodent Model of Muscular Atrophy for Sarcopenia Study. J Bone Metab. 2020;27(2):97-110. [30] 王岩,马剑雄,董本超.肌肉减少症动物模型的研究进展[J].中华老年医学杂志, 2021,40(8):962-966. [31] ANDERSON JE, ZHU A, MIZUNO TM. Nitric oxide treatment attenuates muscle atrophy during hind limb suspension in mice. Free Radic Biol Med. 2018;115:458-470. [32] BURKS TN, ANDRES-MATEOS E, MARX R, et al. Losartan restores skeletal muscle remodeling and protects against disuse atrophy in sarcopenia. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3(82):82ra37. [33] YOU JS, ANDERSON GB, DOOLEY MS, et al. The role of mTOR signaling in the regulation of protein synthesis and muscle mass during immobilization in mice. Dis Model Mech. 2015;8(9):1059-1069. [34] 耿洪伟. 地塞米松通过miR-322增强对肌肉萎缩的诱导作用[D].长春:吉林大学,2020. [35] 鲁飞翔,李军,周仙杰,等.地塞米松致小鼠肌肉衰减综合征模型建立[J].中国老年学杂志,2016,36(22):5542-5544. [36] 王月兵,刘庆春,鲁飞翔,等.地塞米松对小鼠体成分的影响[J].武警医学,2017, 28(11):1093-1095+1099. [37] CLEGG A, HASSAN-SMITH Z. Frailty and the endocrine system. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6(9):743-752. [38] THOMSEN JS, CHRISTENSEN LL, VEGGER JB, et al. Loss of bone strength is dependent on skeletal site in disuse osteoporosis in rats. Calcif Tissue Int. 2012;90(4):294-306. [39] MANSKE SL, BOYD SK, ZERNICKE RF. Vertical ground reaction forces diminish in mice after botulinum toxin injection. J Biomech. 2011;44(4):637-643. [40] 方磊,乔立超,顾一帆,等.克罗恩病大小鼠动物模型研究进展[J].中国实验动物学报,2020,28(5):688-694. [41] KO F, ABADIR P, MARX R, et al. Impaired mitochondrial degradation by autophagy in the skeletal muscle of the aged female interleukin 10 null mouse. Exp Gerontol. 2016;73:23-27. [42] 饶丽莎,许珊珊,黄田盛,等.杉木Cu/Zn-SOD基因克隆、序列特征及组织特异性表达[J].西北林学院学报,2018,33(2):75-82. [43] JANG YC, LUSTGARTEN MS, LIU Y, et al. Increased superoxide in vivo accelerates age-associated muscle atrophy through mitochondrial dysfunction and neuromuscular junction degeneration. FASEB J. 2010;24(5):1376-1390. [44] AHN B, SMITH N, SAUNDERS D, et al. Using MRI to measure in vivo free radical production and perfusion dynamics in a mouse model of elevated oxidative stress and neurogenic atrophy. Redox Biol. 2019;26:101308. [45] 李梦俊,张晓荣,高艳萍.炎症反应与肌肉减少症[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2020,13(4):367-373. [46] LI J, YI X, YAO Z, et al. TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 6 Mediates TNFα-Induced Skeletal Muscle Atrophy in Mice During Aging. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(8):1535-1548. [47] YOSHIDA N, ENDO J, KINOUCHI K, et al. (Pro)renin receptor accelerates development of sarcopenia via activation of Wnt/YAP signaling axis. Aging Cell. 2019;18(5):e12991. [48] 梅雯,熊伟,赵一.哺乳动物线粒体DNA转录调节因子研究进展[J].生物技术, 2022,32(4):506-512. [49] JOSEPH AM, ADHIHETTY PJ, WAWRZYNIAK NR, et al. Dysregulation of mitochondrial quality control processes contribute to sarcopenia in a mouse model of premature aging. PLoS One. 2013;8(7):e69327. [50] XIAO B, CUI Y, WANG Y, et al. Parkin-mediated mitochondrial quality control protects against aluminum-induced liver damage in mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 2021;156:112485. [51] HERBST A, LEE CC, VANDIVER AR, et al. Mitochondrial DNA deletion mutations increase exponentially with age in human skeletal muscle. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2021;33(7):1811-1820. [52] KIM IY, SHIN JH, SEONG JK. Mouse phenogenomics, toolbox for functional annotation of human genome. BMB Rep. 2010;43(2):79-90. [53] BARRETO G, HUANG TT, GIFFARD RG. Age-related defects in sensorimotor activity, spatial learning, and memory in C57BL/6 mice. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2010;22(3):214-219. [54] ZHU M, SHEN W, LI J, et al. AMPK Activator O304 Protects Against Kidney Aging Through Promoting Energy Metabolism and Autophagy. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:836496. [55] DUTTA S, SENGUPTA P. Men and mice: Relating their ages. Life Sci. 2016;152: 244-248. [56] MITCHELL SJ, SCHEIBYE-KNUDSEN M, LONGO DL, et al. Animal models of aging research: implications for human aging and age-related diseases. Annu Rev Anim Biosci. 2015;3:283-303. [57] RYDELL-TÖRMÄNEN K, JOHNSON JR. The Applicability of Mouse Models to the Study of Human Disease. Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1940:3-22. [58] SCHIAFFINO S, REGGIANI C. Fiber types in mammalian skeletal muscles. Physiol Rev. 2011;91(4):1447-1531. [59] PARKS RJ, FARES E, MACDONALD JK, et al. A procedure for creating a frailty index based on deficit accumulation in aging mice. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2012;67(3):217-227. |
| [1] | Wang Jingfeng, Wen Dengtai, Wang Shijie, Gao Yinghui. Atg-mediated autophagy, exercise and skeletal muscle aging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 295-301. |
| [2] | Long Yi, Yang Jiaming, Ye Hua, Zhong Yanbiao, Wang Maoyuan. Extracellular vesicles in sarcopenic obesity: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 315-320. |
| [3] | Cheng Haotian, Zhao Xiaofeng, Lu Xiangdong, Zhao Yibo, Fan Zhifeng, Qi Detai, Wang Xiaonan, Zhou Runtian, Jin Xinjie, Zhao Bin. Single-cell RNA sequencing and the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 93-99. |
| [4] | Ma Suilu, He Zhijun, Liu Tao, Li Yan, He Yuanxu, He Bo, Wang Weiwei, Wei Xiaotao. Traditional Chinese medicine monomer in the prevention and treatment of flap necrosis by regulating “autophagy” [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 153-158. |
| [5] | Wang Ji, Zhang Min, Yang Zhongya, Zhang Long. A review of physical activity intervention in type 2 diabetes mellitus with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1272-1277. |
| [6] | Song Hehua, Wei Zairong. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: research and therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1278-1285. |
| [7] | Song Jian, Zhao Lei, Liu Aishi. Construction and application of myocardial ischemia model in miniature pigs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 772-778. |
| [8] | Meng Meng, Hu Guanyu, Wu Xingquan, Cong Deyu. Effects of skeletal muscle massage on skeletal muscle function and conversion of skeletal muscle fiber types in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(35): 5628-5633. |
| [9] | Gu Peng, Pu Bin, Chen Junbang, Yue Dan, Xin Qiao, Zeng Zhanpeng, Zheng Xiaohui. Correlation between new sarcopenia index and bone mineral density in postmenopausal patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 5009-5014. |
| [10] | Peng Lu, Duan Zhili, Li Zhenyu, Li Junhui, Li Yunhong, Wang Song, Liu Weiqiang. Research status and progress of establishment and validation of finite element model of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4393-4400. |
| [11] | Zhou Jing, Wu Xiaoxiao, Liu Wan, Wei Meng, Wu Miao, Zheng Lan. Modulatory effect of leptin on the effector cells of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(26): 4231-4238. |
| [12] | Zhao Yongjun, Wang Wei, Bai Tao, Li Jianying. Exercise intervention strategies for frailty syndrome in the elderly [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(26): 4246-4253. |
| [13] | Zhang Jian, Lin Jianping, Zhou Gang, Wang Benchao, Wu Yongchang. Etiological analysis of discoid meniscus based on whole exome sequencing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 192-199. |
| [14] | Li Mingxiu, Wang Xuan, Yang Jie, Li Yi. An osteoarthritis model in vitro: characteristics and new design idea [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 300-306. |
| [15] | Tang Yujing, Lan Fengjun, Li Guangdi, Wang Jian, Liu Riguang. Role of calcium ions in the pathogenesis of chronic fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(17): 2745-2753. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||