Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (27): 4393-4400.doi: 10.12307/2023.388
Previous Articles Next Articles
Research status and progress of establishment and validation of finite element model of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis
Peng Lu1, 2, Duan Zhili1, 2, Li Zhenyu3, 4, Li Junhui5, Li Yunhong4, Wang Song1, 6, Liu Weiqiang1, 2, 6
- 1Shenzhen International Graduate School, Tsinghua University, Shenzhen 518055, China; 2Department of Mechanical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China; 3Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital, Shenzhen 518037, China; 4Shenzhen Aonuo Medical Technology Company, Shenzhen 518107, China; 5Luoyang Orthopedic Hospital of Henan Province (Orthopedic Hospital of Henan Province), Zhengzhou 450002, China; 6Biomechanics and Biotechnology Lab, Research Institute of Tsinghua University in Shenzhen, Shenzhen 518057, China
-
Received:2022-05-27Accepted:2022-07-14Online:2023-09-28Published:2022-11-08 -
Contact:Wang Song, PhD, Shenzhen International Graduate School, Tsinghua University, Shenzhen 518055, Guangdong Province, China; Biomechanics and Biotechnology Lab, Research Institute of Tsinghua University in Shenzhen, Shenzhen 518057, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Peng Lu, Master candidate, Shenzhen International Graduate School, Tsinghua University, Shenzhen 518055, Guangdong Province, China; Department of Mechanical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. 2020B1515120082 (to WS); Shenzhen Natural Science Foundation, No. JCYJ20190807144001746 (to WS)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Peng Lu, Duan Zhili, Li Zhenyu, Li Junhui, Li Yunhong, Wang Song, Liu Weiqiang. Research status and progress of establishment and validation of finite element model of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4393-4400.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
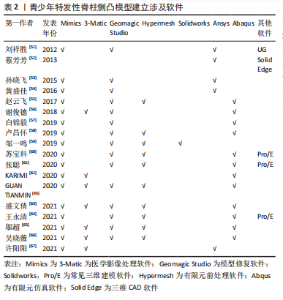
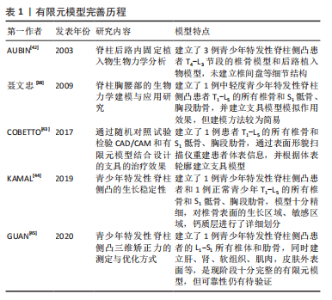
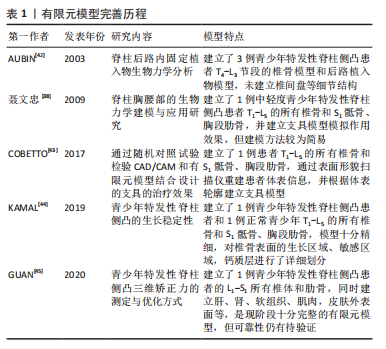
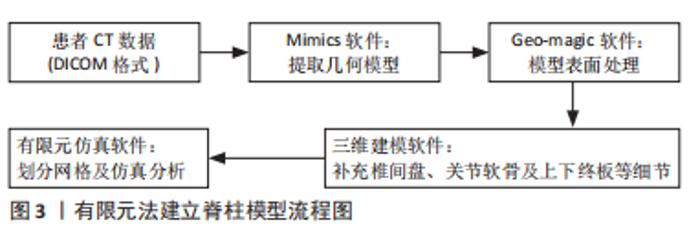
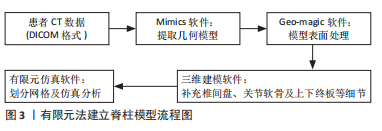
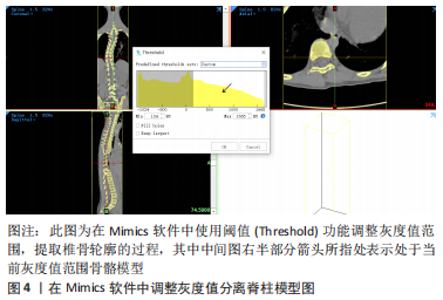
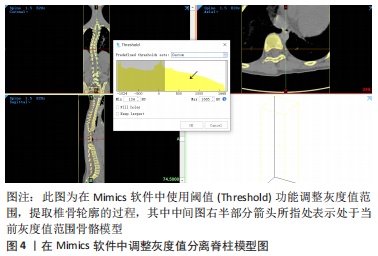
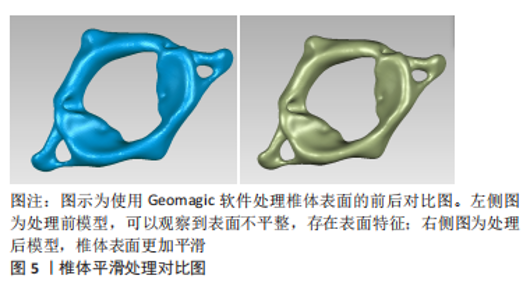
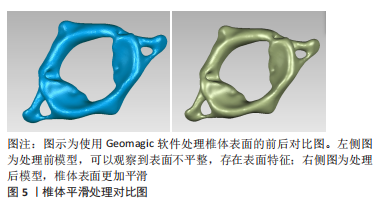
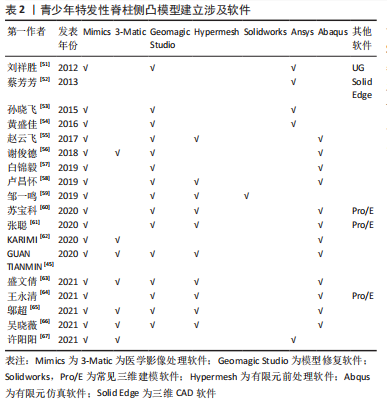
常见的建模方法是通过人体影像学数据,利用三维重建软件重建脊柱三维模型。CT扫描图像是构建有限元三维模型的常用方法,能够将骨骼与软组织鲜明分离,但全脊柱CT扫描是在仰卧位或俯卧位下进行,因此建立的模型也应是卧位模型,同时辐射剂量较大,这些局限限制了CT图像扫描的应用。X射线作为诊断脊柱侧凸的常用手段,辐射剂量较小,但成像效果也相对较差,单视图X射线图像无法准确地反映脊柱的几何学形态,具有多平面自校准的X射线的EOS成像系统获取椎骨模型在降低对患者身体损害的同时能较好地兼顾图像清晰度,有着广泛的应用[46-50]。模型建立和分析过程主要包括医学影像处理、三维建模、模型修复、有限元前处理、有限元模型建立验证和仿真(材料赋值、网格划分及接触模式选择等)等几个步骤,根据开展有限元建模研究的流程顺序,该综述内容主要分为软件选择、椎骨建立、椎间盘建立、韧带建立和躯干建立几个部分,其中软件选择部分介绍了影像处理、三维建模、模型修复、有限元前处理及有限元模型建立的相关软件,椎骨建立、椎间盘建立、韧带建立和躯干建立几个部分按照解剖结构不同分别介绍相应子模型的材料赋值、网格划分及接触模式等建模细节[51-67]。 2.1.1 软件选择 常见期刊文献中缺少对建模过程的详细描述,文章参考了众多硕博论文,就如何建立青少年特发性脊柱侧凸有限元模型进行详细综述。文章总结了以往相关文献中涉及的软件[51-67],见表2。"
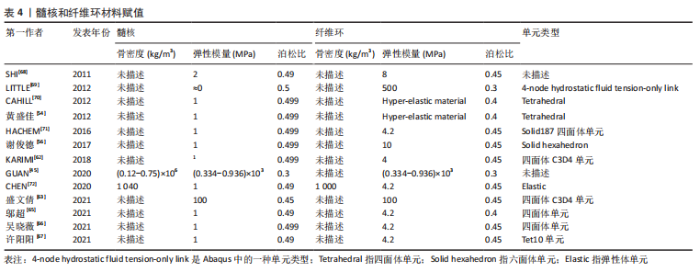
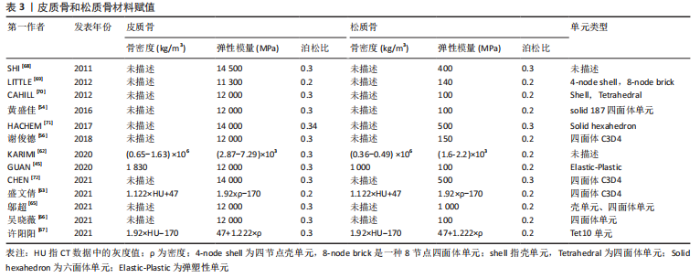
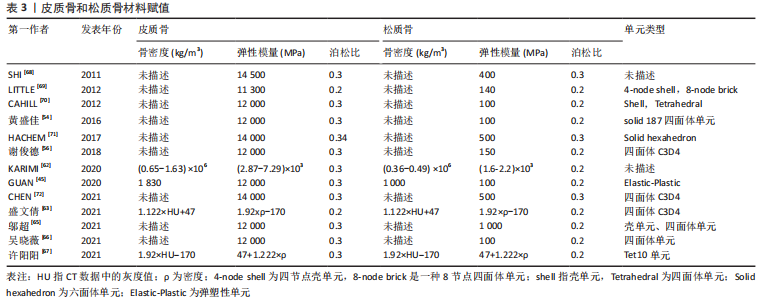
总之,学者们对皮质骨、松质骨的弹性模量、泊松比赋值较为统一,一般情况下认为皮质骨的弹性模量为12 000 MPa,泊松比为0.3,松质骨的弹性模量为100 MPa,泊松比为0.2。但是不同研究中皮质骨和松质骨的网格单元类型有所差异,四面体单元网格在体现模型几何形状和真实性的同时可以减少网格划分难度,但皮质骨采用壳单元、松质骨采用四面体单元可以更好地反映不同部位的形状特征及重要性。 有限元模型建立过程中材料赋值只能是均一的,但脊柱侧凸的出现说明身体两侧各个结构属性并不是完全对称的,且椎骨的不同节段之间也有所区别,这就决定了有限元模型与实体差异必然存在。为了减少其中误差,一些学者根据放射性影像中的灰度值判断对应区域的骨骼密度,通过骨密度和弹性模量之间的经验公式为材料赋值,但不同文献中使用的经验公式各不相同,目前还未形成统一标准。因此,常规椎骨的皮质骨和松质骨材料赋值已形成较为统一的认知,但针对青少年特发性脊柱侧凸模型的椎骨材料的差异性仍有待深入研究,尤其是不同节段和不对称结构材料的差异性。 2.1.3 椎间盘模型建立方法 根据脊柱解剖结构可知,椎骨之间是由椎间盘连接在一起,且由于椎间盘的灰度值与周围组织区分度并不明显,无法直接从CT图像中进行分离,需要通过椎骨模型对椎间盘进行模拟重建。不同文献中椎间盘建立方式大同小异,具体方法为提取椎体上、下表面,建立相应圆柱体;采用布尔运算,得到了椎间盘三维模型,这样生成的椎间盘和椎骨有较好贴合性,更符合人体椎间盘几何形状。一般认为髓核和纤维环的面积比例约为6∶4。弹性模量和泊松比赋值见表4。"
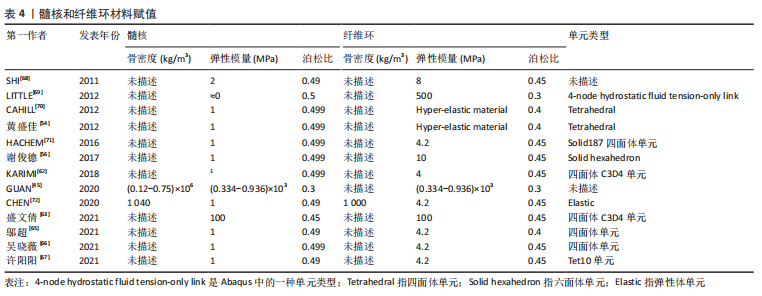
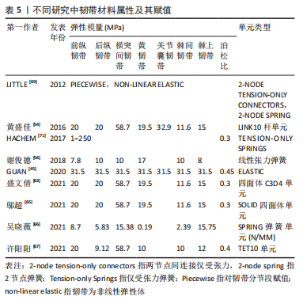
文章总结发现,不同文献中关于髓核和纤维环材料赋值数值相差不大。但在网格划分上有所区别,一些学者采用四面体网格划分纤维环和髓核,也有学者用六面体网格单元构建髓核和纤维环。例如,李劲松等[25]对比了四面体单元建立椎体,六面体单元建立椎间盘;六面体建立椎体和椎间盘;四面体单元建立椎体和椎间盘3种不同建模方式,认为采用四面体单元构建椎体和六面体单元构建椎间盘结构的有限元模型模拟人体脊柱运动单元生物力学特性效果较优。因此,目前椎间盘的模型建立主要通过布尔运算获得,且髓核和纤维环材料赋值数值相差不大,其主要区别在于不同的网格划分,网格结构不同也会导致其生物力学特征具有差异性。考虑到椎间盘的复杂解剖结构以及黏弹性材料属性,未来在椎间盘的建立方面应更多开展髓核纤维环精细结构建模,不同材料属性尤其是黏弹性材料特征的赋予等方面研究。 2.1.4 韧带模型构建方法 韧带的添加可以显著提升模型的精细化程度以及结果可信度。脊柱有限元模型中添加的韧带有6种,包括棘间韧带、棘上韧带、横突韧带、黄韧带、前纵韧带和后纵韧带,部分文献中也可见添加关节囊韧带。不同文献对韧带单元定义有所区别。由于定义方式不同,文献中对韧带材料特性选取也各不相同。一般将韧带定义为弹簧单元时会赋予刚度值,将韧带定义为杆、四面体单元和缆绳单元时一般赋予弹性模量、泊松比和横截面积。即使对韧带的单元定义相同,材料赋值也存在细微差别。文章汇总了不同文献的韧带单元类型以及各参数和数值情况[45,54,56,62-63,65-67,69],见表5。"
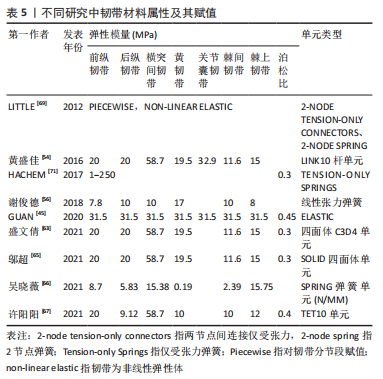
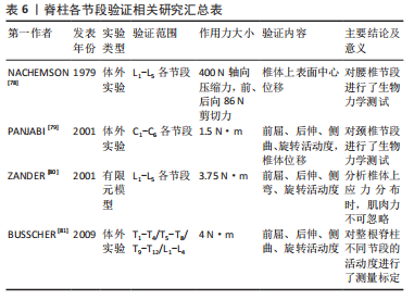
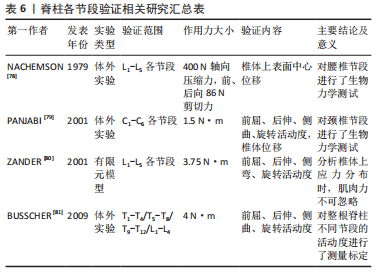
从表5中可知,盛文倩[63]利用solid四面体单元表示韧带,将在Mimics里面建好的模型导入3-matic软件,根据解剖学知识确定脊柱韧带附着点;在合适的区域划线模拟韧带的轮廓,然后将曲线闭合;生成一个表面,向内或向外平移表面1 mm 来模拟韧带的厚度;用Loft指令将2个面生成一个实体模型,生成的模型用布尔运算减去与椎体多余的重叠部分从而建立完整的韧带模型,通过材料赋值将韧带与椎骨等进行区分。而有研究认为韧带主要施加张力,支撑力可以忽略,采用缆绳单元定义韧带[67,73];黄盛佳等[54]认为韧带既会受压,也会受到拉力,采用杆单元定义韧带属性;HACHEM等[71]和吴晓薇等[66]用弹簧单元代替韧带,较好地模拟了脊柱变形时韧带的形变情况;也有研究提出用ANSYS中的Link10单元模拟韧带[38],进行生物力学分析。 因此,弹簧单元有自成体系的赋值方法,以刚度为参考标准,区别于其他材料以弹性模量和横截面积为标准。除此之外,杆单元的弹性模量赋值与四面体单元、缆绳单元和Link10单元有显著区别,这可能是为了杆单元模拟的韧带具有一定可压缩特性,所以其后纵韧带、棘间韧带、棘间韧带的弹性模量较大。对于四面体单元、缆绳单元和Link 10单元,它们的前纵韧带、后纵韧带、黄韧带、棘间韧带和棘上韧带的弹性模量数值较统一。因此,韧带单元类型和材料属性的选择会引起较大的结果差异,未来关于韧带建模的材料和网格划分属性仍有待系统深入对比。 2.1.5 躯干模型建立方法 躯干模型的建立可以提高有限元研究的精度。由于支具作用力直接施加在患者皮肤表面,进而传递到肋骨和椎骨,因此探究支具对躯干的作用区域和作用力分布对于支具设计、调整和治疗效果认定具有重要意义。20世纪90年代初,光学技术被应用于躯干模型建立中,研究人员利用可见光或紫外线对患者所处空间和患者自身进行扫描[74],通过集成了结构化投影仪和CCD相机的三维光学数字转化仪,获得躯干表面的几何形状。PAZOS等[75]用四台三维光学数字转化仪,对人体躯干连续投射黑白窄条纹图案,在4-6 s内就获得了躯干模型。有研究比较了手臂轻微外展于身体双侧和手掌贴于颈部双侧的不同姿势下躯干模型获取质量,发现前者的躯干图像无遮挡,质量更高[76]。也有学者提出根据椎体的位置逆向推断躯干模型[77],由于CT数据是在仰卧位获得的,而表面形貌扫描仪获得的躯干模型是站立位模型,这种方法从某种程度来具有更高精度。综上,采用扫描方式建立躯干模型是目前研究的主流,但其网格划分、材料赋值等内容较复杂,目前的研究仍较少涉及。 2.2 青少年特发性脊柱侧凸有限元模型验证方式 有限元模型的可靠性和真实性一直是值得商榷的问题,分析结果的正确与否取决于模型是否合理,能否反映青少年特发性脊柱侧凸的脊柱生物力学特性。常见的模型验证方法包括几何形态验证、与已有文献对比及实验验证等方法。模型验证的方法并不单一,多数文献都会采用多种方法从不同角度论证模型的有效性。 2.2.1 几何形态验证 几何验证是最常见的模型验证方法,其内容是将三维模型与患者原始CT图像作比较。该方法直观、方便,几乎所有文献在模型建立完成后均会采用该种方法判断模型是否合理。例如,盛文倩[63]将建立的有限元模型与原始仰卧位的X射线图像比较,发现有限元模型的几何形状与患者的医学图像基本相似,模型的Cobb角和影像学图像的Cobb角仅相差0.46°。邬超等[65]将优化后的模型与临床站立位的X射线图像对比,测量胸弯、腰弯Cobb角和各椎体到骶骨中线的距离,发现模型与X射线图像的误差在要求范围内。通过分析相关研究发现,Cobb角、腰椎前凸角、胸椎后凸角、各椎体质心相对骶骨中线的偏移距离是较为常见的几何验证中的比较参数。 2.2.2 文献结果验证 与已经发表的权威文献对比也是验证模型有效性的方式之一。由于青少年特发性脊柱侧凸建模涉及到T1-S的整段脊柱,目前关于整段脊柱的模型分析较少,且各模型病变位置不同,直接比较缺乏可行性。常用的验证模型方法是选择结构正常的节段,施加不同作用力,观察不同工况下脊柱活动度活动如与椎体位移是否与既有文献报道相仿[78-81],见表6。"

2.2.3 实验结果验证 实验验证有限元结果是最可靠的验证方式,一般是通过实际治疗效果与有限元分析结果对比来评估一致性。例如,VERGARI等[82]建立了42例青少年特发性脊柱侧凸患者的有限元模型,通过在胸腔上安放软圆柱形压力垫和在对关键椎施加位移的方法模拟支具的作用,与支具实际治疗效果对比,通过比较T1-T12后凸角、L1-L5前凸角、Cobb角、顶椎旋转角度及肋骨隆起6个参数在有限元模拟下和实际治疗时的均方根误差,发现模拟的均方根误差在容许范围内,进而验证了模型的有效性。 2.3 青少年特发性脊柱侧凸有限元模型的不足与发展方向 如今,青少年特发性脊柱侧凸有限元模型及其生物力学分析已被广泛地应用于青少年特发性脊柱侧凸的手术治疗、非手术治疗和病因研究3大方面[83],不仅可为治疗方案设计提供科学依据,也可对治疗结果进行科学预测。随着计算机性能的提升,有限元模型的精确程度也越来越高,模型可靠性也随之提升,模拟结果更加趋向于实际情况。但有限元模型本身就是对人体的一种以简化,和实际情况必然存在差异,当前有限元分析在材料赋值、结构设计及网格划分等方面还未形成统一标准,不同研究中采用不同的建模方式,相互之间并不互通,为形成可信结论埋下隐患。由于青少年特发性脊柱侧凸病情复杂,目前仍有多种疾病情况没有研究,未形成系统的模型库。针对患者的个性化建模费时费力,在临床治疗中难以普及,种种因素制约了有限元方法的发展。 因此,未来青少年特发性脊柱侧凸有限元模型的发展方向主要是:①有限元模型的精准化,既包括几何结构的精准也包括力学方案的精准,只有将有限元模型误差控制在一定范围内,其分析结果才具有可信度,才能有效为临床医生、支具设计师等相关人员提供治疗方案参考依据。根据前文建模文献分析可知,椎间盘、韧带和躯干等模型的结构、材料属性、网格划分等均有待深入对比分析。②有限元模型的标准化,包括不同软件之间对比依据、材料赋值、网格划分等方面,均需要建立相应的标准。③有限元模型的个性化,个性化既体现在个体差异性,也体现在要针对不同青少年特发性脊柱侧凸分型,建立相应的具有代表性的有限元模型数据库。"

| [1] GOHARI E, HAGHPANAHI M, PARNIANPOUR M, et al. Numerical analysis (finite element method) of brace effects on the adolescent idiopatic scolosis during 24 hours. Biomed Eng. 2014;26(3):1450046. [2] LI QY, ZHONG GB, LIU ZD, et al. Effect of asymmetric tension on biomechanics and metabolism of vertebral epiphyseal plate in a rodent model of scoliosis. Orthop Surg. 2017;9(3):311-318. [3] AROEIRA RMC, PERTENCE AEM, KEMMOKU DT, et al. The effect of hypokyphosis on the biomechanical behavior of the adolescent thoracic spine. J Braz Soc Mech Sci. 2018;40(3):1-10. [4] DUPUIS S, FORTIN C, CAOUETTE C, et al. Global postural re-education in pediatric idiopathic scoliosis: a biomechanical modeling and analysis of curve reduction during active and assisted self-correction. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):200. [5] ZHANG Q, CHON T, ZHANG Y, et al. Finite element analysis of the lumbar spine in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis subjected to different loads. Comput Biol Med. 2021;136:104745. [6] LALONDE NM, VILLEMURE I, PANNETIER R, et al. Biomechanical modeling of the lateral decubitus posture during corrective scoliosis surgery. Clin Biomech. 2010;25(6):510-516. [7] DRISCOLL M, MAC-THIONG J-M, LABELLE H, et al. Development of a detailed volumetric finite element model of the spine to simulate surgical correction of spinal deformities. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:931741. [8] ZHANG H, HU X, WANG Y, et al. Use of finite element analysis of a Lenke type 5 adolescent idiopathic scoliosis case to assess possible surgical outcomes. Comput Aided Surg. 2013;18(3-4):84-92. [9] RIGO MD, VILLAGRASA M, GALLO D. A specific scoliosis classification correlating with brace treatment:description and reliability. Scoliosis. 2010;5(1):1. [10] KING HA, MOE JH, BRADFORD DS, et al. The selection of fusion levels in thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983;65(9):1302-1313. [11] BERTEAU JP, PITHIOUX M, MESURE S, et al. Beyond the classic correction system: a numerical nonrigid approach to the scoliosis brace. Spine J. 2011; 11(5):424-431. [12] PÉRIÉ D, AUBIN CE, LACROIX M, et al. Personalized biomechanical modeling of boston brace treatment in idiopathic scoliosis. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2002;91:393-396. [13] CLIN J, AUBIN C E, PARENT S, et al. Biomechanical modeling of brace design. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2006;123:255-260. [14] FORTIN D, CHERIET F, BEAUSéJOUR M, et al. A 3D visualization tool for the design and customization of spinal braces. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2007; 31(8):614-624. [15] CLIN J, AUBIN CE, LABELLE H. Virtual prototyping of a brace design for the correction of scoliotic deformities. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2007;45(5):467-473. [16] CLIN J, AUBIN CE, PARENT S, et al. Comparison of the biomechanical 3D efficiency of different brace designs for the treatment of scoliosis using a finite element model. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(7):1169-1178. [17] VERGARI C, CHEN Z, ROBICHON L, et al. Towards a predictive simulation of brace action in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2021;24(8):874-882. [18] AULISA AG, MASTANTUONI G, LAINERI M, et al. Brace technology thematic series:the progressive action short brace (PASB). Scoliosis. 2012;7(1):6. [19] AULISA AG, GUZZANTI V, FALCIGLIA F, et al. Lyon bracing in adolescent females with thoracic idiopathic scoliosis: a prospective study based on SRS and SOSORT criteria. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16(1):316. [20] KUROKI H. Brace treatment for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Clin Med. 2018;7(6):136. [21] KAELIN AJ. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis:indications for bracing and conservative treatments. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(2):28. [22] WEISS HR, LAY M, SEIBEL S, et al. Is it possible to improve treatment safety in the brace treatment of scoliosis patients by using standardized CAD algorithms? Orthopade. 2021;50(6):435-445. [23] SATTOUT A, CLIN J, COBETTO N, et al. Biomechanical assessment of providence nighttime brace for the treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine Deform. 2016;4(4):253-260. [24] MARTINO J, AUBIN CE, LABELLE H, et al. Biomechanical analysis of vertebral derotation techniques for the surgical correction of thoracic scoliosis. Spine. 2013;38(2):E73-E83. [25] 李劲松.有限元法模拟特发性脊柱侧凸后路矫形及内固定应力分析研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2013. [26] PéRIé D, AUBIN CE, PETIT Y, et al. Boston brace correction in idiopathic scoliosis: a biomechanical study. Spine. 2003;28(15):1672-1677. [27] GUY A, LABELLE H, BARCHI S, et al. Braces designed using cad/cam combined or not with finite element modeling lead to effective treatment and quality of life after 2 years a randomized controlled trial. Spine. 2021; 46(1):9-16. [28] BREKELMANS WA, POORT HW, SLOOFF TJ. A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts. Acta Orthop Scand. 1972;43(5):301-317. [29] SCHULTZ AB, BELYTSCHKO TB, ANDRIACCHI TP, et al. Analog studies of forces in the human spine:mechanical properties and motion segment behavior. J Biomech. 1973;6(4):373-383. [30] LIU YK, RAY G, HIRSCH C. The resistance of the lumbar spine to direct shear. Orthop Clin North Am. 1975;6(1):33-49. [31] ANDRIACCHI TP, SCHULTZ AB, BELYTSCHKO TB, et al. Milwaukee brace correction of idiopathic scoliosis. A biomechanical analysis and a restrospective study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976;58(6):806-815. [32] VIVIANI GR, GHISTA DN, LOZADA PJ, et al. Biomechanical analysis and simulation of scoliosis surgical correction. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986;(208):40-47. [33] 戴力扬,屠开元,徐印坎,等.椎间盘退变腰椎活动节段力学模型的研究[J].第二军医大学学报,1989,15(1):480. [34] STOKES IA, LAIBLE JP. Three-dimensional osseo-ligamentous model of the thorax representing initiation of scoliosis by asymmetric growth. J Biomech. 1990;23(6):589-595. [35] BOZIC KJ, KEYAK JH, SKINNER HB, et al. Three-dimensional finite element modeling of a cervical vertebra: an investigation of burst fracture mechanism. J Spinal Disord. 1994;7(2):102-110. [36] 王哲.青少年特发性脊柱侧凸的生物力学研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2007. [37] 汪正宇,刘祖德,王哲,等.脊柱侧凸有限元模型的建立和参数优化[J].北京生物医学工程,2008,27(1):28-32. [38] 聂文忠.脊柱胸腰部的生物力学建模与应用研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2009. [39] 唐明星. Lenke1A-型青少年特发性脊柱侧凸有限元模型建立及其生物力学研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2009. [40] CLIN J, AUBIN CÉ, PARENT S, et al. Biomechanical modeling of brace treatment of scoliosis:effects of gravitational loads. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2011;49(7):743-753. [41] DESBIENS-BLAIS F, CLIN J, PARENT S, et al. New brace design combining CAD/CAM and biomechanical simulation for the treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Clin Biomech. 2012;27(10):999-1005. [42] AUBIN CE, PETIT Y, STOKES IA, et al. Biomechanical modeling of posterior instrumentation of the scoliotic spine. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2003;6(1):27-32. [43] COBETTO N, AUBIN CÉ, PARENT S, et al. 3D correction of AIS in braces designed using CAD/CAM and FEM: a randomized controlled trial. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2017;12(1):1-8. [44] KAMAL Z, ROUHI G, ARJMAND N, et al. A stability-based model of a growing spine with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a combination of musculoskeletal and finite element approaches. Med Eng Phys. 2019;64:46-55. [45] GUAN T, ZHANG Y, ANWAR A, et al. Determination of three-dimensional corrective force in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis and biomechanical finite element analysis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:963. [46] HENAO J, AUBIN CÉ, LABELLE H, et al. Patient-specific finite element model of the spine and spinal cord to assess the neurological impact of scoliosis correction:preliminary application on two cases with and without intraoperative neurological complications. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2016;19(8):901-910. [47] AUBIN CÉ, CLIN J, RAWLINSON J. Biomechanical simulations of costo-vertebral and anterior vertebral body tethers for the fusionless treatment of pediatric scoliosis. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(1):254-264. [48] PEA R, DANSEREAU J, CAOUETTE C, et al. Computer-assisted design and finite element simulation of braces for the treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis using a coronal plane radiograph and surface topography. Clin Biomech. 2018;54:86-91. [49] BIDARI S, KAMYAB M, GHANDHARI H, et al. Efficacy of computer-aided design and manufacturing versus computer-aided design and finite element modeling technologies in brace management of idiopathic scoliosis: a narrative review. Asian Spine J. 2021;15(2):271-282. [50] VERGARI C, GAUME M, PERSOHN S, et al. From in vitro evaluation of a finite element model of the spine to in silico comparison of spine instrumentations. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021;123:104797. [51] 刘祥胜.Lenke 2型特发性脊柱侧凸有限元建模及三维矫形手术的有限元模拟研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2012. [52] 蔡芳芳,孙东明,解京明,等.L1-L5段腰椎简化模型的建立及其有效性验证[J].第二军医大学学报,2013,34(12):1384-1386. [53] 孙晓飞.重度青少年特发性脊柱侧凸主胸弯节段柔韧性评估及有限元分析[D].上海:第二军医大学,2015. [54] 黄盛佳,霍洪军,杨学军,等.PUMCⅡd1型青少年特发性脊柱侧凸后路三维矫形手术有限元研究[J].国际骨科学杂志,2016,37(1):46-52. [55] 赵云飞.力学性能优化的青少年特发性脊柱侧凸三维有限元模型建立及置钉策略的生物力学和临床回顾研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2017. [56] 谢俊德,张顺心,李晔,等.青少年特发性侧凸脊柱的动态特性[J].医用生物力学,2018,33(4):312-319. [57] 白锦毅.人体动态生物力学优化的Lenke 1型青少年特发性脊柱侧凸仿真三维有限元模型的建立[D].上海:中国人民解放军海军军医大学, 2019. [58] 卢昌怀,刘志军,晏峻峰,等.Lenke 1AN型青少年特发性脊柱侧凸不同置棒顺序矫形的有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(19):1780-1784. [59] 邹一鸣.青少年特发性脊柱侧凸手术置钉策略优化的生物力学研究[D].上海:中国人民解放军海军军医大学,2019. [60] 苏宝科.青少年特发性脊柱侧凸Lenke5型胸腰段矫形后有限元分析[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古医科大学,2020. [61] 张聪,赵岩,杜小宇,等.青少年特发性脊柱侧凸腰主弯患者腰椎-骨盆的生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(8):1155-1161. [62] KARIMI MT, RABCZUK T, POURABBAS B. Evaluation of the efficiency of various force configurations on scoliotic, lordotic and kyphotic curves in the subjects with scoliosis. Spine Deform. 2020;8(3):361-367. [63] 盛文倩.个性化脊柱侧凸的有限元建模和分析[D].太原:太原理工大学, 2021. [64] 王永清,苏宝科,王威,等.青少年特发性脊柱侧凸Lenke5型胸腰段后路矫形后钛棒有限元分析[J].中国当代医药,2021,28(6):4-7,16,241-242. [65] 邬超,高明杰,王建忠,等.有限元法分析Lenke 3型青少年特发性脊柱侧凸胸-腰椎的应力及位移变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(33): 5273-5280. [66] 吴晓薇.轻度青少年特发性脊柱侧凸的三维有限元模型构建及有效性验证[D].广州:南方医科大学,2021. [67] 许阳阳,李筱贺,李志军,等. Lenke 1型青少年特发性脊柱侧凸与正常脊柱有限元模型建立与分析[J].解剖学杂志,2021,44(2):140-146. [68] SHI L, WANG D, DRISCOLL M, et al. Biomechanical analysis and modeling of different vertebral growth patterns in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis and healthy subjects. Scoliosis. 2011;6:11. [69] LITTLE JP, ADAM C. Towards determining soft tissue properties for modelling spine surgery:current progress and challenges. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2012; 50(2):199-209. [70] CAHILL PJ, WANG W, ASGHAR J, et al. The use of a transition rod may prevent proximal junctional kyphosis in the thoracic spine after scoliosis surgery a finite element analysis. Spine. 2012;37(12):E687-695. [71] HACHEM B, AUBIN C-E, PARENT S. Porcine spine finite element model: a complementary tool to experimental scoliosis fusionless instrumentation. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(6):1610-1617. [72] CHEN K, ZHAO J, ZHAO Y, et al. A finite element analysis of different pedicle screw placement strategies for treatment of Lenke 1 adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: which is better?. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2021; 24(3):270-277. [73] 李文成.脊柱矫正力的计算与分析[D].大连:大连交通大学,2018. [74] JAREMKO JL, PONCET P, RONSKY J, et al. Estimation of spinal deformity in scoliosis from torso surface cross sections. Spine. 2001;26(14):1583-1591. [75] PAZOS V, CHERIET F, SONG L, et al. Accuracy assessment of human trunk surface 3D reconstructions from an optical digitising system. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2005;43(1):11-15. [76] PAZOS V, CHERIET F, DANSERAU J, et al. Reliability of trunk shape measurements based on 3-D surface reconstructions. Eur Spine J. 2007; 16(11):1882-1891. [77] HUI C, PIAO J, WONG M S, et al. Study of textile fabric materials used in spinal braces for scoliosis. J Med Biol Eng. 2020;40:356-371. [78] NACHEMSON AL, SCHULTZ AB, BERKSON MH. Mechanical properties of human lumbar spine motion segments. Influence of age, sex, disc level, and degeneration. Spine. 1979;4(1):1-8. [79] PANJABI MM, CHEN NC, SHIN EK, et al. The cortical shell architecture of human cervical vertebral bodies. Spine. 2001;26(22):2478-2484. [80] ZANDER T, ROHLMANN A, CALISSE J, et al. Estimation of muscle forces in the lumbar spine during upper-body inclination. Clin Biomech. 2001;16:S73-S80. [81] BUSSCHER I, VAN DIEËN JH, KINGMA I, et al. Biomechanical characteristics of different regions of the human spine: an in vitro study on multilevel spinal segments. Spine. 2009;34(26):2858-2864. [82] VERGARI C, RIBES G, AUBERT B, et al. Evaluation of a patient-specific finite-element model to simulate conservative treatment in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine Deform. 2015;3(1):4-11. [83] GOULD SL, CRISTOFOLINI L, DAVICO G, et al. Computational modelling of the scoliotic spine: a literature review. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng. 2021;37(10):e3503. |
| [1] | Zhong Yizheng, Huang Peizhen, Cai Qunbin, Zheng Liqin, He Xingpeng, Dong Hang. Microstructural indexes that determine the trabecular bone maximum stress of micro-finite element models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1313-1318. |
| [2] | Wu Taoguang, Nie Shaobo, Chen Hua, Zhu Zhengguo, Qi Lin, Tang Peifu. Biomechanical characteristics of a new multi-dimensional cross locking plate in the treatment of subtrochanteric nonunion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1330-1334. |
| [3] | Peng Zhixin, Yan Wengang, Wang Kun, Zhang Zhenjiang. Finite element analysis and structural optimization design of 3D printed forearm braces [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1340-1345. |
| [4] | Liu Jinyu, Zhang Hanshuo, Cui Hongpeng, Pan Lingzhi, Zhao Boran, Li Fei, Ding Yu. Finite element biomechanical analysis of minimally invasive treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy and accurate exercise rehabilitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1359-1364. |
| [5] | Wen Xinghua, Ding Huanwen, Cheng Kai, Yan Xiaonan, Peng Yuanhao, Wang Yuning, Liu Kang, Zhang Huiwu. Three-dimensional finite element model analysis of intramedullary nailing fixation design for large femoral defects in Beagle dogs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1371-1376. |
| [6] | Liu Jiaxin, Jia Peng, Men Yutao, Liu Lu, Wang Yeming, Ye Jinduo. Design and optimization of bone trabecular structure with triply periodic minimal surfaces [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 992-997. |
| [7] | Guo Tingting, Xie Hong, Xu Guanghua. Finite element analysis of elastic ankle brace performance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1031-1037. |
| [8] | Li Huiqin, Wang Chunjuan, Wang Yu, Wang Weifeng, Chen Dinggen, Li Na. Clear aligner orthodontic therapy of rotated mandibular teeth with different shapes: a three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1050-1054. |
| [9] | Song Jian, Zhao Lei, Liu Aishi. Construction and application of myocardial ischemia model in miniature pigs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 772-778. |
| [10] | Liu Qinghua, Cai Yongqiang, Jin Feng, Yu Jinghong, Wang Haiyan, Zhang Yunfeng, Wang Lidong, Li Jiawei, Wang Xing, He Yujie, Dai Lina, Wang Jianzhong, Wu Chao, Tong Ling, Kang Zhijie, Li Zhijun, Li Xiaohe. Finite element model of the 12-year-old child whole cervical spine: establishment and validity verification based on CT data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 500-504. |
| [11] | Li Yaping, Liu Hong, Gao Zhen, Chen Xiaolin, Huang Wujie, Jiang Zheng. Three-dimensional motion analysis of lower limb biomechanical performance in Tai Chi practitioners accompanied by knee joint pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 520-526. |
| [12] | Li Shihao, Li Qi, Li Zhen, Zhang Yuanyuan, Liu Miaomiao, Ouyang Yi, Xu Weiguo. Plantar pressure and gait analysis in patients with anterior cruciate ligament injury and reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 626-631. |
| [13] | Zhan Yi, Wang Biao, Ma Yuli, He Simin, Sun Honghui, Hao Dingjun. Biomechanical comparison between a novel bone cement screw system and common surgical methods for the treatment of Kummell’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 385-390. |
| [14] | Lu Hui, Wu Qimei, Liu Rong. Finite element analysis and application of unilateral and bilateral bone-filling mesh container in treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 391-397. |
| [15] | Tang Zhi, Lang Lei, Wang Renyuan, Gu Song. Construction of finite element model of hallux valgus foot and biomechanical analysis of the first metatarsophalangeal joint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4283-4290. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||