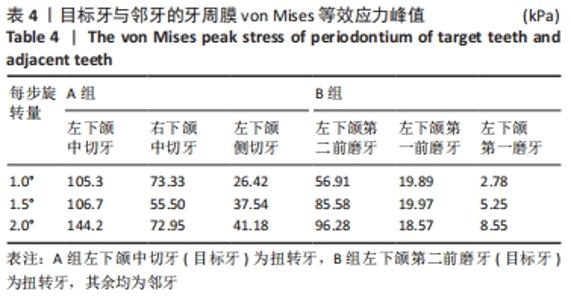
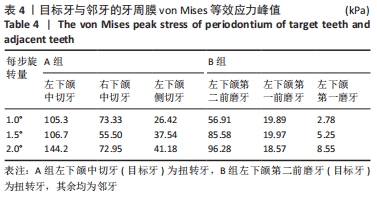
[1] 段银钟,陈华,张巧余.牙齿扭转畸形的调查及原因分析[J].口腔正畸学,1996(3):111-112.
[2] HAOUILI N, KRAVITZ ND, VAID NR, et al. Has Invisalign improved? A prospective follow-up study on the efficacy of tooth movement with Invisalign. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2020;158(3): 420-425.
[3] LOMBARDO L, ARREGHINI A, RAMINA F, et al. Predictability of orthodontic movement with orthodontic aligners: a retrospective study. Prog Orthod. 2017;18(1):35.
[4] KRAVITZ ND, KUSNOTO B, BEGOLE E, et al. How well does Invisalign work? A prospective clinical study evaluating the efficacy of tooth movement with Invisalign. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009; 135(1):27-35.
[5] SIMON M, KEILIG L, SCHWARZE J, et al. Treatment outcome and efficacy of an aligner technique--regarding incisor torque, premolar derotation and molar distalization. BMC Oral Health. 2014;14:68.
[6] CORTONA A, ROSSINI G, PARRINI S, et al. Clear aligner orthodontic therapy of rotated mandibular round-shaped teeth: A finite element study. Angle Orthod. 2020;90(2):247-254.
[7] WANG CY, SU MZ, CHANG HH, et al. Tension-compression viscoelastic behaviors of the periodontal ligament. J Formos Med Assoc. 2012; 111(9):471-481.
[8] GOMEZ JP, PENA FM, MARTINEZ V, et al. Initial force systems during bodily tooth movement with plastic aligners and composite attachments: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. Angle Orthod. 2015;85(3):454-460.
[9] KIM W, HONG K, LIM D, et al. Optimal Position of Attachment for Removable Thermoplastic Aligner on the Lower Canine Using Finite Element Analysis. Materials. 2020;13(15):3369.
[10] SINGH JR, KAMBALYAL P, JAIN M, et al. Revolution in Orthodontics: Finite element analysis. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2016;6(2): 110-114.
[11] JIANG T, WU RY, WANG JK, et al. Clear aligners for maxillary anterior en masse retraction: a 3D finite element study. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1): 10156.
[12] 白煜,李晨,曹猛,等.无托槽隐形矫治器联合微种植钉内收上前牙的三维有限元分析[J].中华口腔正畸学杂志,2020,27(1):21-26.
[13] 蔡永清,杨晓翔,何炳蔚.无托槽隐形矫治器各参数对尖牙压低移动治疗的影响[J].医用生物力学,2017,32(1):60-65.
[14] ALAIDROUS M, FINKELMAN M, KUDARA Y, et al. Influence of zirconia crown artifacts on cone beam computed tomography scans and image superimposition of tomographic image and tooth surface scan: An in vitro study. J Prosthet Dent. 2021;125(4):681-684.
[15] BIAO Y, KIM D, HWANG H, et al. Effect of artifact area on cone beam computed tomography scans when integrated with intraoral scans. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2021;131(4):468-474.
[16] 王勇.口内数字印模技术[J].口腔医学,2015(9):705-709,743.
[17] BARONE S, PAOLI A, RAZIONALE AV, et al. Computational design and engineering of polymeric orthodontic aligners Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng. 2017;33(8):e2839.
[18] 高洁.无托槽隐形矫治器圆锥形前磨牙旋转移动的三维有限元分析[D].兰州:兰州大学,2020.
[19] 潘婷婷,房兵.无托槽隐形矫治效能影响因素的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2015,42(3):364-366.
[20] LEE BW. Relationship between Tooth-Movement Rate and Estimated Pressure Applied. J Dent Res. 1965;44(5):1053.
[21] KRAVITZ ND, KUSNOTO B, AGRAN B, et al. Influence of attachments and interproximal reduction on the accuracy of canine rotation with Invisalign. A prospective clinical study. Angle Orthod. 2008;78(4):682-687.
|