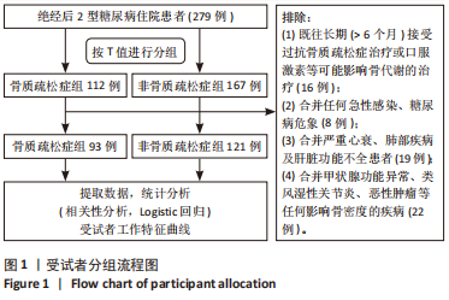
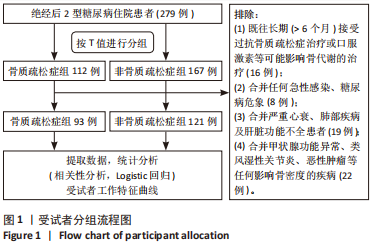
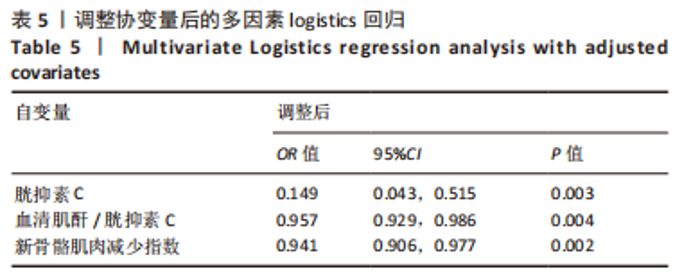
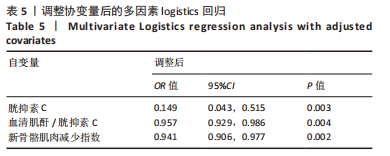
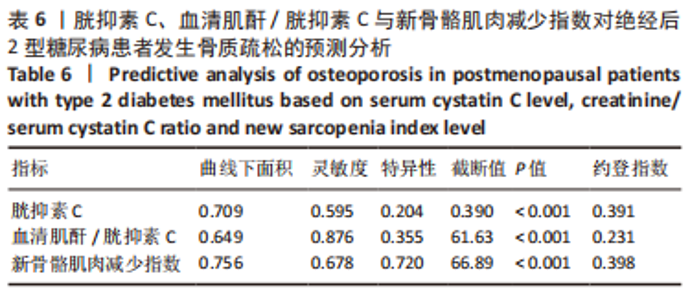
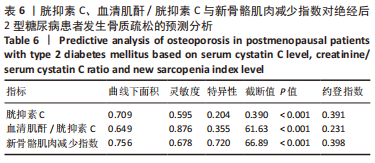
[1] UKON Y, MAKINO T, KODAMA J, et al. Molecular-Based Treatment Strategies for Osteoporosis: A Literature Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20(10):2557.
[2] RACHNER TD, KHOSLA S, HOFBAUER LC. Osteoporosis: now and the future. New Horizons. 2011;1276(377):87.
[3] OEI L, RIVADENEIRA F, ZILLIKENS MC, et al. Diabetes, Diabetic Complications, and Fracture Risk. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2015;13(2): 106-115.
[4] SHANBHOGUE VV, MITCHELL DM, ROSEN CJ, et al. Type 2 diabetes and the skeleton: new insights into sweet bones. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016;4(2):159-173.
[5] KASHANI KB, FRAZEE EN, KUKRÁLOVÁ L, et al. Evaluating Muscle Mass by Using Markers of Kidney Function. Crit Care Med. 2017;45(1): e23-e29.
[6] OSAKA T, HAMAGUCHI M, HASHIMOTO Y, et al. decreased the creatinine to cystatin c ratio is a surrogate marker of sarcopenia in patients with type 2. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018;139:52-58.
[7] LIEN YH. Looking for Sarcopenia Biomarkers. Am J Med. 2017;130(5): 502-503.
[8] FU X, TIAN Z, WEN S, et al. A new index based on serum creatinine and cystatin C is useful for assessing sarcopenia in patients with advanced cancer. Nutrition. 2021;82:111032.
[9] REISS J, IGLSEDER B, ALZNER R, et al. Sarcopenia and osteoporosis are interrelated in geriatric inpatients. Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2019;52(7): 688-693.
[10] EDWARDS MH, DENNISON EM, AIHIE SAYER A, et al. Osteoporosis and sarcopenia in older age. Bone. 2015;80:126-130.
[11] SUI SX, WILLIAMS LJ, HOLLOWAY-KEW KL, et al. Skeletal Muscle Health and Cognitive Function: A Narrative Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(1): 255.
[12] IKEDA K, HORIE-INOUE K, INOUE S. Functions of estrogen and estrogen receptor signaling on skeletal muscle. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2019;191:105375.
[13] 董旋, 高飞. 2型糖尿病病人血清Cys-C水平与骨质疏松症的相关性分析[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2019,17(16):2521-2524.
[14] 晏丕军, 欧阳芳, 马红艳,等. 2型糖尿病患者血清胱抑素C与骨质疏松的相关性[J]. 山西医科大学学报,2016,47(1):59-63.
[15] 董晓芬, 李香波, 吴震宇,等. 绝经后2型糖尿病合并骨质疏松症患者外周血NLR、PLR、Cys-C水平与骨密度的相关性分析[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志,2022,21(2):174-177.
[16] YOSHII I, CHIJIWA T, SAWADA N. Screening osteoporotic femoral neck without measuring bone mineral density with the use of tartrate resistant acid phosphatase-5b and serum-creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio in Japanese postmenopausal women. J Orthop Sci. 2020;25(4):671-676.
[17] TABARA Y, KOHARA K, OKADA Y, et al. Creatinine to Cystatin C Ratio as a Marker of Bone Property in Older Adults: The J-Shipp Study. J Nutr Health Aging. 2020;24(3):277-281.
[18] 熊丹, 刘丽君, 贺佩祥,等. 2型糖尿病患者内脏脂肪与骨密度及骨折风险的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2022,25(6):682-688.
[19] GENG Q, GAO H, YANG R, et al. Pyrroloquinoline Quinone Prevents Estrogen Deficiency-Induced Osteoporosis by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Osteocyte Senescence. Int J Biol Sci. 2019;15(1):58-68.
[20] ICONARU L, MOREAU M, KINNARD V, et al. Does the Prediction Accuracy of Osteoporotic Fractures by BMD and Clinical Risk Factors Vary With Fracture Site? JBMR Plus. 2019;3(12):e10238.
[21] 遇呈祥, 陈亮, 邓忠良. 骨密度对骨质疏松性骨折的判断价值[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2012,18(2):127-129.
[22] 戴小宇, 黄智慧, 王珂杰, 等. 血清钙磷乘积预测老年椎体压缩性骨折风险的意义[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(4):505-508.
[23] 朱秀洁, 王禹, 于同, 等. 血尿酸与骨密度相关性的研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2017,23(12):1664-1667.
[24] 王玲, 袁伟杰, 谷立杰, 等. 慢性肾脏病患者骨代谢与尿蛋白量的关系[J]. 中华肾脏病杂志,2010,26(9):667-670.
[25] KAJI H, YAMAUCHI M, YAMAGUCHI T, et al. Mild Renal Dysfunction Is a Risk Factor for a Decrease in Bone Mineral Density and Vertebral Fractures in Japanese Postmenopausal Women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95(10):4635-4642.
[26] KIM H, PARK IY, CHOI JM, et al. A Decline in Renal Function is Associated With Loss of Bone Mass in Korean Postmenopausal Women With Mild Renal Dysfunction. J Korean Med Sci. 2011;26(3):392.
[27] HSU C, CHEN L, CHEN K. Osteoporosis in Patients with Chronic Kidney Diseases: A Systemic Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(18):6846.
[28] CANNATA-ANDÍA JB, MARTÍN-CARRO B, MARTÍN-VÍRGALA J, et al. Chronic Kidney Disease—Mineral and Bone Disorders: Pathogenesis and Management. Calcif Tissue Int. 2021;108(4):410-422.
[29] SHIMADA T, HASEGAWA H, YAMAZAKI Y, et al. FGF-23 Is a Potent Regulator of Vitamin D Metabolism and Phosphate Homeostasis. J Bone Miner Res. 2004;19(3):429-435.
[30] RAMLI FF, CHIN K. A Review of the Potential Application of Osteocyte-Related Biomarkers, Fibroblast Growth Factor-23, Sclerostin, and Dickkopf-1 in Predicting Osteoporosis and Fractures. Diagnostics. 2020;10(3):145.
[31] HEERSPINK HJ, PERKINS BA, FITCHETT DH, et al. Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors in the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus: Cardiovascular and Kidney Effects, Potential Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications. Circulation. 2016;134(10):752-772.
[32] YANG J, ZHANG T, FENG D, et al. A new diagnostic index for sarcopenia and its association with short-term postoperative complications in patients undergoing surgery for colorectal cancer. Colorectal Dis. 2019; 21(5):538-547. |