Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (33): 5277-5282.doi: 10.12307/2023.754
Previous Articles Next Articles
Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells with chondromodulin-1 overexpression affect the proliferation of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis
Wu Zhiwen1, Shen Enpu1, Li Beibei1, Liu Danping1, Qi Hui2
- 1First Affiliated Hospital of Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121000, Liaoning Province, China; 2Beijing Institute of Trauma Orthopedics, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, Beijing 100035, China
-
Received:2022-11-09Accepted:2022-12-12Online:2023-11-28Published:2023-03-29 -
Contact:Liu Danping, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, First Affiliated Hospital of Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121000, Liaoning Province, China Qi Hui, PhD, Assistant researcher, Beijing Institute of Trauma Orthopedics, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, Beijing 100035, China -
About author:Wu Zhiwen, Master candidate, First Affiliated Hospital of Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121000, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81572140 (to LDP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Zhiwen, Shen Enpu, Li Beibei, Liu Danping, Qi Hui. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells with chondromodulin-1 overexpression affect the proliferation of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5277-5282.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
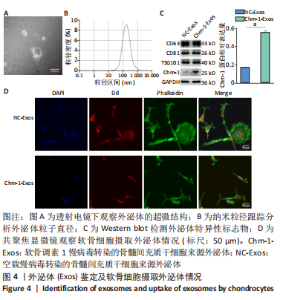
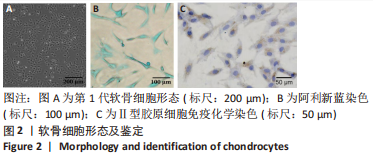
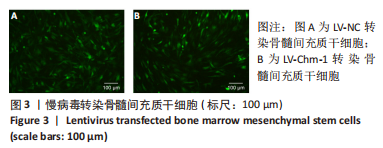
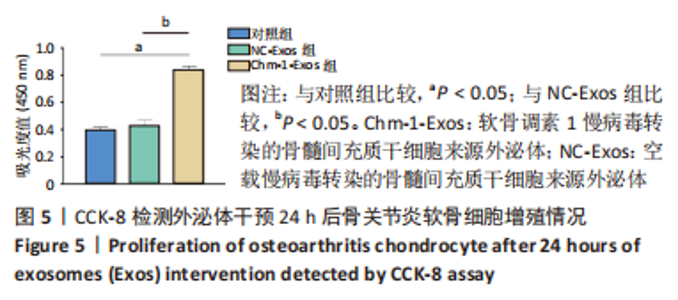
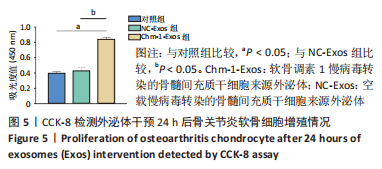
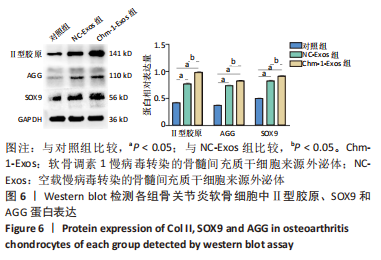
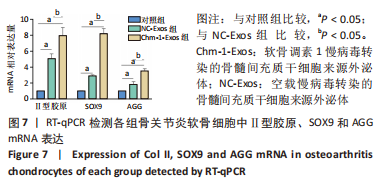
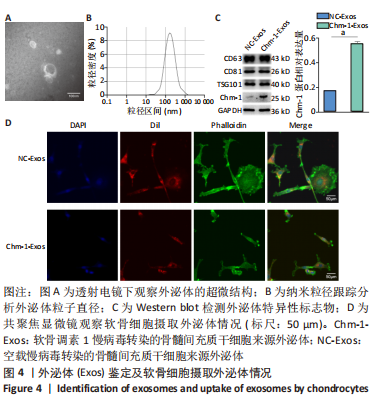
2.4 BMSCs来源Exos的分离培养及鉴定结果 透射电镜观察可见Exos呈圆形,见图4A;纳米粒径分析Exos直径在40-150 nm之间,见图4B;Western blot结果显示Exos特异标志物CD63、CD81、TSG101的表达呈阳性,Chm-1在Chm-1-Exos中高表达,见图4C。以上结果证实经过超速离心法提取的物质分别为NC-Exos和Chm-1-Exos。 2.5 软骨细胞摄取Exos情况 NC-Exos和Chm-1-Exos被DiI标记为红色,细胞核被DAPI标记为蓝色,细胞骨架被Phalloidin 标记为绿色,共聚焦显微镜下可见NC-Exos和Chm-1-Exos均可以被骨关节炎软骨细胞摄取并在细胞核周围区域聚集,见图4D。 "
| [1] GLYN-JONES S, PALMER AJ, AGRICOLA R, et al. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2015;386(9991):376-387. [2] DWIVEDI G, FLAMAN L, ALAYBEYOGLU B, et al. Inflammatory cytokines and mechanical injury induce post-traumatic osteoarthritis-like changes in a human cartilage-bone-synovium microphysiological system. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022;24(1):198. [3] VARGAS NEGRÍN F, MEDINA ABELLÁN MD, HERMOSA HERNÁN JC, et al. Treatment of patients with osteoarthritis. Aten Primaria. 2014;46 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):39-61. [4] HUSSAIN SM, NEILLY DW, BALIGA S, et al. Knee osteoarthritis: a review of management options. Scott Med J. 2016;61(1):7-16. [5] KATZ JN, ARANT KR, LOESER RF. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review. JAMA. 2021;325(6):568-578. [6] ZHANG R, MA J, HAN J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell related therapies for cartilage lesions and osteoarthritis. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(10): 6275-6289. [7] YU M, WANG D, CHEN X, et al. BMSCs-derived Mitochondria Improve Osteoarthritis by Ameliorating Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Promoting Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Chondrocytes. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022;18(8):3092-3111. [8] JEVOTOVSKY DS, ALFONSO AR, EINHORN TA, et al. Osteoarthritis and stem cell therapy in humans: a systematic review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(6):711-729. [9] GAO Q, WANG L, WANG S, et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Identification, Classification, and Differentiation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;9:787118. [10] ZHUANG J, HANG R, SUN R, et al. Multifunctional exosomes derived from bone marrow stem cells for fulfilled osseointegration. Front Chem. 2022;10:984131. [11] HE L, HE T, XING J, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes protect cartilage damage and relieve knee osteoarthritis pain in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):276. [12] HA DH, KIM HK, LEE J, et al. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell-Derived Exosomes for Immunomodulatory Therapeutics and Skin Regeneration. Cells. 2020;9(5):1157. [13] MAQSOOD M, KANG M, WU X, et al. Adult mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes: Sources, characteristics, and application in regenerative medicine. Life Sci. 2020;256:118002. [14] CETIN Z, ILKER SAYGILI E, YILMAZ M. Crosstalk between CML cells with HUVECS and BMSCs through CML derived exosomes. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2021;26(3):444-467. [15] ZHAO X, WU D, MA X, et al. Exosomes as drug carriers for cancer therapy and challenges regarding exosome uptake. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;128:110237. [16] XU M, FENG T, LIU B, et al. Engineered exosomes: desirable target-tracking characteristics for cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative disease therapies. Theranostics. 2021;11(18):8926-8944. [17] LUAN X, SANSANAPHONGPRICHA K, MYERS I, et al. Engineering exosomes as refined biological nanoplatforms for drug delivery. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017;38(6):754-763. [18] ZHU S, QIU H, BENNETT S, et al. Chondromodulin-1 in health, osteoarthritis, cancer, and heart disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76(22): 4493-4502. [19] SUZUKI F. Roles of cartilage matrix proteins, chondromodulin-I and -II, in endochondral bone formation: a review. Connect Tissue Res. 1996; 35(1-4):303-307. [20] HIRAKI Y, SHUKUNAMI C. Chondromodulin-I as a novel cartilage-specific growth-modulating factor. Pediatr Nephrol. 2000;14(7):602-605. [21] ZHU Y, ZHANG Y, LIU Y, et al. The influence of Chm-I knockout on ectopic cartilage regeneration and homeostasis maintenance. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21(3-4):782-792. [22] HAYAMI T, FUNAKI H, YAOEDA K, et al. Expression of the cartilage derived anti-angiogenic factor chondromodulin-I decreases in the early stage of experimental osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 2003;30(10): 2207-2217. [23] YUE F, JOHKURA K, TOMOTSUNE D, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells as an inducer for cardiomyocyte differentiation from mouse embryonic stem cells. Ann Anat. 2010;192(5):314-321. [24] KARIM A, HALL AC. Chondrocyte Morphology in Stiff and Soft Agarose Gels and the Influence of Fetal Calf Serum. J Cell Physiol. 2017;232(5): 1041-1052. [25] WANG BW, JIANG Y, YAO ZL, et al. Aucubin Protects Chondrocytes Against IL-1β-Induced Apoptosis In Vitro And Inhibits Osteoarthritis In Mice Model. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13:3529-3538. [26] JIANG Y, TUAN RS. Origin and function of cartilage stem/progenitor cells in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(4):206-212. [27] LOESER RF, COLLINS JA, DIEKMAN BO. Ageing and the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(7):412-420. [28] GRÄSSEL S, MUSCHTER D. Recent advances in the treatment of osteoarthritis. F1000Res. 2020;9:F1000 Faculty Rev-325. [29] MIANEHSAZ E, MIRZAEI HR, Mahjoubin-Tehran M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: a new therapeutic approach to osteoarthritis? Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):340. [30] ZHANG S, TEO KYW, CHUAH SJ, et al. MSC exosomes alleviate temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis by attenuating inflammation and restoring matrix homeostasis. Biomaterials. 2019;200:35-47. [31] QIU B, XU X, YI P, et al. Curcumin reinforces MSC-derived exosomes in attenuating osteoarthritis via modulating the miR-124/NF-kB and miR-143/ROCK1/TLR9 signalling pathways. J Cell Mol Med. 2020; 24(18):10855-10865. [32] TAO SC, YUAN T, ZHANG YL, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-140-5p-overexpressing human synovial mesenchymal stem cells enhance cartilage tissue regeneration and prevent osteoarthritis of the knee in a rat model. Theranostics. 2017;7(1):180-195. [33] ZHANG Y, BI J, HUANG J, et al. Exosome: A Review of Its Classification, Isolation Techniques, Storage, Diagnostic and Targeted Therapy Applications. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:6917-6934. [34] WAN Z, DONG Y, WEI M, et al. Exosomes in Tumor Immunotherapy: Mediator, Drug Carrier, and Prognostic Biomarker. Adv Biosyst. 2020; 4(11):e2000061. [35] KAHROBA H, HEJAZI MS, SAMADI N. Exosomes: from carcinogenesis and metastasis to diagnosis and treatment of gastric cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76(9):1747-1758. [36] YIN L, LIU X, SHAO X, et al. The role of exosomes in lung cancer metastasis and clinical applications: an updated review. J Transl Med. 2021;19(1):312. [37] NIE H, XIE X, ZHANG D, et al. Use of lung-specific exosomes for miRNA-126 delivery in non-small cell lung cancer. Nanoscale. 2020; 12(2):877-887. [38] XU H, XU B. BMSC-Derived Exosomes Ameliorate Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting Pyroptosis of Cartilage via Delivering miR-326 Targeting HDAC3 and STAT1//NF-κB p65 to Chondrocytes. Mediators Inflamm. 2021;2021:9972805. [39] SHUKUNAMI C, OSHIMA Y, HIRAKI Y. Chondromodulin-I and tenomodulin: a new class of tissue-specific angiogenesis inhibitors found in hypovascular connective tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;333(2):299-307. [40] SHUKUNAMI C, HIRAKI Y. Role of cartilage-derived anti-angiogenic factor, chondromodulin-I, during endochondral bone formation. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2001;9 Suppl A:S91-101. [41] YOSHIOKA M, YUASA S, MATSUMURA K, et al. Chondromodulin-I maintains cardiac valvular function by preventing angiogenesis. Nat Med. 2006;12(10):1151-1159. [42] DENG B, CHEN C, GONG X, et al. Chondromodulin‑I expression and correlation with angiogenesis in human osteoarthritic cartilage. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(2):2142-2148. [43] FANG W, FRIIS TE, LONG X, et al. Expression of chondromodulin-1 in the temporomandibular joint condylar cartilage and disc. J Oral Pathol Med. 2010;39(4):356-360. |
| [1] | Sun Kexin, Zeng Jinshi, Li Jia, Jiang Haiyue, Liu Xia. Mechanical stimulation enhances matrix formation of three-dimensional bioprinted cartilage constructs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | Nong Fuxiang, Jiang Zhixiong, Li Yinghao, Xu Wencong, Shi Zhilan, Luo Hui, Zhang Qinglang, Zhong Shuang, Tang Meiwen. Bone cement augmented proximal femoral nail antirotation for type A3.3 intertrochanteric femoral fracturalysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10. |
| [3] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Zhu Guangyu, Wang Rongtian, Wang Jian, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Changes of lower limb force line and knee function after high tibial osteotomy in osteoporotic medial ventricular knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [4] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [5] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [6] | Huang Linke, Wei Linhua, Jiang Jie, Liu Qian, Chen Weiwei. Effects of estrogen combined with treadmill exercise on bone mass and articular cartilage in ovariectomized mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [7] | Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 840-845. |
| [8] | Long Yanming, Xie Mengsheng, Huang Jiajie, Xue Wenli, Rong Hui, Li Xiaojie. Casein kinase 2-interaction protein-1 regulates the osteogenic ability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in osteoporosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 878-882. |
| [9] | Li Qicheng, Deng Jin, Fu Xiaoyang, Han Na. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on hypoxia-treated myoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 853-859. |
| [10] | Wang Min, Yin Xiushan, Wang Yingxi, Zhang Yan, Zhao Long, Xia Shuyue. Inhalation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviates inflammatory injury in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 827-834. |
| [11] | Zhang Houjun, Deng Bowen, Jiang Shengyuan, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Proteomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid exosomes derived from cerebral palsy children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 903-908. |
| [12] | Gao Ting, Ma Xiaohong, Li Xiaorong. Extraction and identification of exosomes from three different sources of ovarian granulosa cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 860-865. |
| [13] | Yuan Bo, Xie Lide, Fu Xiumei. Schwann cell-derived exosomes promote the repair and regeneration of injured peripheral nerves [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 935-940. |
| [14] | Xu Qijing, Yang Yichun, Lei Wei, Yang Ying, Yu Jiang, Xia Tingting, Zhang Meng, Zhang Tao, Zhang Qian. Advances and problems in cell-free treatment of diabetic skin chronic wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 962-969. |
| [15] | Chen Guanting, Zhang Linqi, Li Qingru. Meta-analysis of the value of exosomal miRNA for the diagnosis of chronic kidney disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 970-976. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||