Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (33): 5249-5255.doi: 10.12307/2023.750
Epidermal neural crest stem cells of hair follicles regulate the local expression of inflammatory factors after facial nerve injury
Tang Li, Pan Yao, Zhu Guochen
- Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Affiliated Wuxi No. 2 People’s Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Wuxi 214002, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2022-10-24Accepted:2022-12-09Online:2023-11-28Published:2023-03-29 -
Contact:Zhu Guochen, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Affiliated Wuxi No. 2 People’s Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Wuxi 214002, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Tang Li, Master candidate, Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Affiliated Wuxi No. 2 People’s Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Wuxi 214002, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:General Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81770990 (to ZGC); Social Development Key R&D Project of Jiangsu Provincial Science and Technology Department, No. BE2018628 (to ZGC); The 16th Batch of “Six Talent Peaks” High-Level Talents in Jiangsu Province, No. WSW-141 (to ZGC); Wuxi Science and Technology Bureau - Medical and Health Technology Project, No. Y20212003 (to ZGC); Precision Medicine Project of Wuxi Municipal Health Commission, No. J202002 (to ZGC)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tang Li, Pan Yao, Zhu Guochen. Epidermal neural crest stem cells of hair follicles regulate the local expression of inflammatory factors after facial nerve injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5249-5255.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
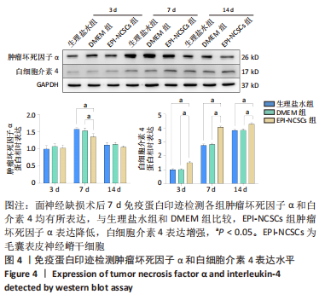
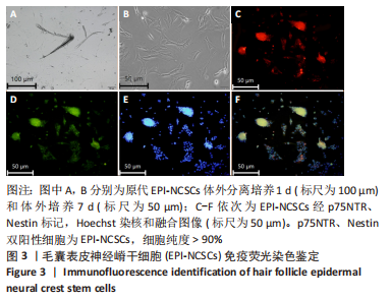
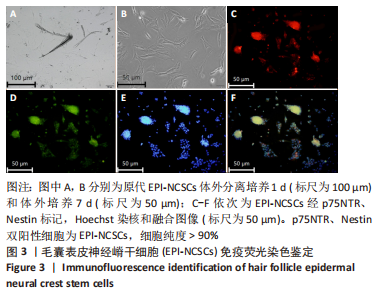
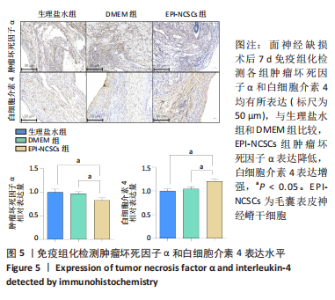
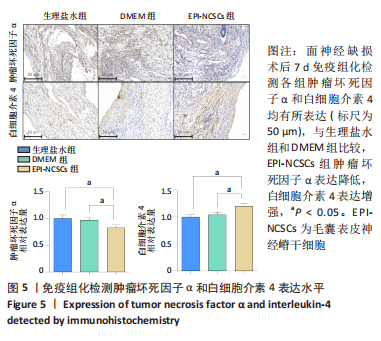
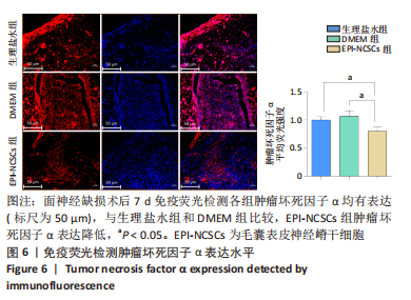
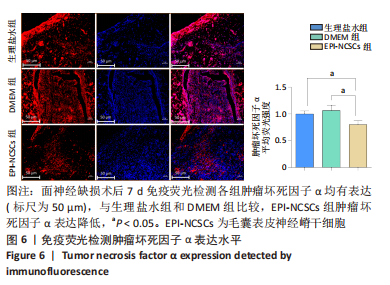
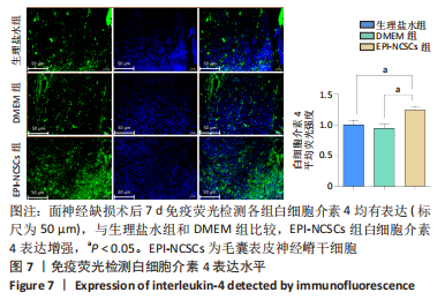
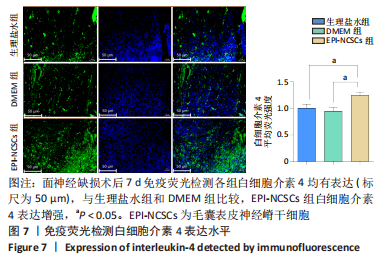
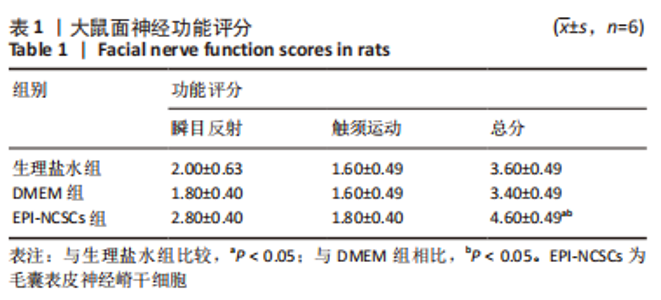
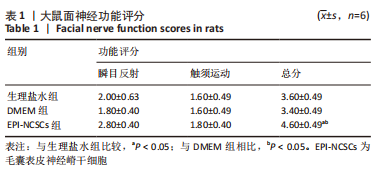
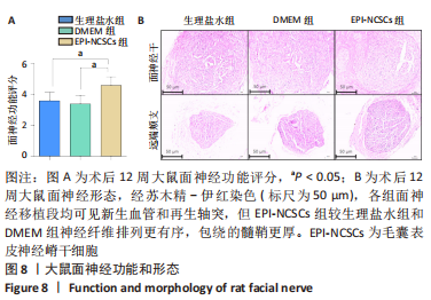
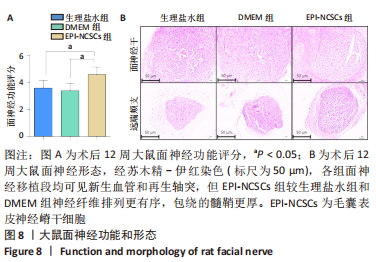
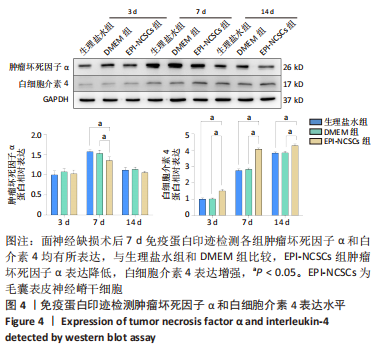
2.2 实验动物一般情况分析 实验选用SD大鼠 54 只,各时间节点所有大鼠均存活,一般状况可,无局部伤口感染,日常行为状态、活跃程度、饮食、睡眠、精神状态等均未见明显异常,排除躯体卷曲、震颤等颅内感染症状。 2.3 EPI-NCSCs 调节了肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素4的表达水平 2.3.1 免疫蛋白印迹检测结果 桥接后3,7,14 d测定相关细胞因子表达,以观察局部炎症微环境的变化。蛋白质印迹检测促炎细胞因子肿瘤坏死因子α和抗炎细胞因子白细胞介素4的表达水平如图4所示。在术后7 d,与生理盐水组和DMEM组相比,EPI-NCSCs 组的肿瘤坏死因子α表达水平显著降低(P < 0.05),而在术后3,14 d时未见显著性差异(P > 0.05);生理盐水组和DMEM组间比较在术后3,7,14 d都未见显著性差异(P > 0.05)。在术后3,7,14 d,EPI-NCSCs 组的白细胞介素4表达较生理盐水组和DMEM 组显著增高(P < 0.05),而生理盐水组和DMEM组间比较未见显著性差异(P > 0.05)。"
| [1] JAHROMI Z, MOHAMMADGHASEMI F, MOHARRAMI KF, et al. Cinnamaldehyde Enhanced Functional Recovery after Sciatic Nerve Crush Injury in Rats. Cells Tissues Organs. 2020;209(1):43-53. [2] GYÖRI E, PRZESTRZELSKI C, PONA I, et al. Quality of life and functional assessment of facial palsy patients: A questionnaire study. Int J Surg. 2018;55:92-97. [3] FLISS E, YANKO R, ZARETSKI A, et al. Facial Nerve Repair following Acute Nerve Injury. Arch Plast Surg. 2022;49(4):501-509. [4] KALINSKI AL, YOON C, HUFFMAN LD, et al. Analysis of the immune response to sciatic nerve injury identifies efferocytosis as a key mechanism of nerve debridement. Elife. 2020;9:e60223. [5] KWIECIEN JM, DABROWSKI W, DĄBROWSKA-BOUTA B, et al. Prolonged inflammation leads to ongoing damage after spinal cord injury. PLoS One. 2020;15(3):e0226584. [6] YUAN YS, YU F, ZHANG YJ, et al. Changes in proteins related to early nerve repair in a rat model of sciatic nerve injury. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(8):1622-1627. [7] XU M, CHENG Z, DING Z, et al. Resveratrol enhances IL-4 receptor-mediated anti-inflammatory effects in spinal cord and attenuates neuropathic pain following sciatic nerve injury. Mol Pain. 2018;14:1744806918767549. [8] 吴丽娜,范晓萌,武爽,等.人参皂苷Rg1调节氧化应激和炎症因子表达改善糖尿病大鼠周围神经损伤[J].中国免疫学杂志,2021,37(4):486-491. [9] ZHANG XM, ZENG LN, YANG WY, et al. Inhibition of LncRNA Vof-16 expression promotes nerve regeneration and functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(1):217-227. [10] CASADEI M, FIORE E, RUBIONE J, et al. IMT504 blocks allodynia in rats with spared nerve injury by promoting the migration of mesenchymal stem cells and by favoring an anti-inflammatory milieu at the injured nerve. Pain. 2022; 163(6):1114-1129. [11] MIRZAKHANI N, FARSHID AA, TAMADDONFARD E, et al. Carnosine improves functional recovery and structural regeneration after sciatic nerve crush injury in rats. Life Sci. 2018;215:22-30. [12] PAN D, SCHELLHARDT L, ACEVEDO-CINTRON JA, et al. IL-4 expressing cells are recruited to nerve after injury and promote regeneration. Exp Neurol. 2022; 347:113909. [13] DAINES JM, SCHELLHARDT L, WOOD MD. The Role of the IL-4 Signaling Pathway in Traumatic Nerve Injuries. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2021;35(5):431-443. [14] MATSUI Y, KADOYA K, NAGANO Y, et al. IL4 stimulated macrophages promote axon regeneration after peripheral nerve injury by secreting uPA to stimulate uPAR upregulated in injured axons. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022;79(6):289. [15] 陈达兵,杨婷.间充质干细胞移植后免疫重建和抗巨细胞病毒的免疫作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(25):4052-4057. [16] DENG W, ZHANG Y, WANG W, et al. Hair follicle-derived mesenchymal stem cells decrease alopecia areata mouse hair loss and reduce inflammation around the hair follicle. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):548. [17] NAIR S, ROCHA-FERREIRA E, FLEISS B, et al. Neuroprotection offered by mesenchymal stem cells in perinatal brain injury: Role of mitochondria, inflammation, and reactive oxygen species. J Neurochem. 2021;158(1):59-73. [18] YUAN Y, YUAN L, LI L, et al. Mitochondrial transfer from mesenchymal stem cells to macrophages restricts inflammation and alleviates kidney injury in diabetic nephropathy mice via PGC-1α activation. Stem Cells. 2021;39(7):913-928. [19] GE Y, ZHANG Y, TANG Q, et al. Mechanisms of the Immunomodulation Effects of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Facial Nerve Injury in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Stem Cells Dev. 2019;28(7):489-496. [20] PANDAMOOZ S, SALEHI MS, SAFARI A, et al. Enhancing the expression of neurotrophic factors in epidermal neural crest stem cells by valproic acid: A potential candidate for combinatorial treatment. Neurosci Lett. 2019;704:8-14. [21] SOTO J, DING X, WANG A, et al. Neural crest-like stem cells for tissue regeneration. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021;10(5):681-693. [22] DARADKA MH, BANI ISMAIL ZA, IRSHEID MA. Peripheral nerve regeneration: A comparative study of the effects of autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells, platelet-rich plasma, and lateral saphenous vein graft as a conduit in a dog model. Open Vet J. 2021;11(4):686-694. [23] BENSE F, MONTAVA M, DUCLOS C, et al. Syngeneic Transplantation of Rat Olfactory Stem Cells in a Vein Conduit Improves Facial Movements and Reduces Synkinesis after Facial Nerve Injury. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020;146(6):1295-1305. [24] ESAKI S, KATSUMI S, HAMAJIMA Y, et al. Transplantation of Olfactory Stem Cells with Biodegradable Hydrogel Accelerates Facial Nerve Regeneration After Crush Injury. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(2):169-178. [25] MOGHADASI BS, KOONTZ A, TSEROPOULOS G, et al. Neural crest stem cells from human epidermis of aged donors maintain their multipotency in vitro and in vivo. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):9750. [26] BAHARVAND Z, NABIUNI M, TAHMASEB M, et al. Investigating the synergic effects of valproic acid and crocin on BDNF and GDNF expression in epidermal neural crest stem cells. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2020;80(1):38-46. [27] WANG Y, LAI X, WU D, et al. Umbilical mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes facilitate spinal cord functional recovery through the miR-199a-3p/145-5p-mediated NGF/TrkA signaling pathway in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 202;12(1):117. [28] GAO Y, LI H, QIN C, et al. Embryonic stem cells-derived exosomes enhance retrodifferentiation of retinal Müller cells by delivering BDNF protein to activate Wnt pathway. Immunobiology. 2022;227(3):152211. [29] SALEHI MS, PANDAMOOZ S, SAFARI A, et al. Epidermal neural crest stem cell transplantation as a promising therapeutic strategy for ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2020;26(7):670-681. [30] KHAN J, WANG Q, REN Y, et al. Exercise induced hypoalgesia profile in rats is associated with IL-10 and IL-1 β levels and pain severity following nerve injury. Cytokine. 2021;143:155540. [31] HU Z, DENG N, LIU K, et al. CNTF-STAT3-IL-6 Axis Mediates Neuroinflammatory Cascade across Schwann Cell-Neuron-Microglia. Cell Rep. 2020;31(7):107657. [32] GALLEGUILLOS D, WANG Q, STEINBERG N, et al. Anti-inflammatory role of GM1 and other gangliosides on microglia. J Neuroinflammation. 2022;19(1):9. [33] LIM EF, HOGHOOGHI V, HAGEN KM, et al. Presence and activation of pro-inflammatory macrophages are associated with CRYAB expression in vitro and after peripheral nerve injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2021;18(1):82. [34] OLYMPIOU M, SARGIANNIDOU I, MARKOULLIS K, et al. Systemic inflammation disrupts oligodendrocyte gap junctions and induces ER stress in a model of CNS manifestations of X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2016;4(1):95. [35] LIU X, ZHANG Y, WANG Y, et al. Inflammatory Response to Spinal Cord Injury and Its Treatment. World Neurosurg. 2021;155:19-31. [36] SHIMADA N, SAKATA A, IGARASHI T, et al. M1 macrophage infiltration exacerbate muscle/bone atrophy after peripheral nerve injury. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):44. [37] 王海峰,丁宏霞,胡沣,等. 海水浸泡对大鼠坐骨神经损伤后促炎因子表达的影响及早期干预效果观察[J].解放军医学杂志,2015,40(10):788-793. [38] LUO H, BAO Z, ZHOU M, et al. Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury by inhibiting oxidative stress, neuronal apoptosis, and inflammation via activating the nuclear factor erythroid 2 related factor 2/heme oxygenase-1 signaling pathway. Neuroreport. 2022;33(11):451-462. [39] SIQUEIRA MIETTO B, KRONER A, GIROLAMI EI, et al. Role of IL-10 in Resolution of Inflammation and Functional Recovery after Peripheral Nerve Injury. J Neurosci. 2015;35(50):16431-16442. [40] CHEN P, PIAO X, BONALDO P. Role of macrophages in Wallerian degeneration and axonal regeneration after peripheral nerve injury. Acta Neuropathol. 2015; 130(5):605-618. [41] ZHANG F, MIAO Y, LIU Q, et al. Changes of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory macrophages after peripheral nerve injury. RSC Adv. 2020;10(64): 38767-38773. [42] LI Y, YAO D, ZHANG J, et al. The Effects of Epidermal Neural Crest Stem Cells on Local Inflammation Microenvironment in the Defected Sciatic Nerve of Rats. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017;10:133. [43] ARABPOUR M, SAGHAZADEH A, REZAEI N. Anti-inflammatory and M2 macrophage polarization-promoting effect of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;97:107823. [44] AL-GHADBAN S, BUNNELL BA. Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells: Immunomodulatory Effects and Therapeutic Potential. Physiology (Bethesda). 2020;35(2):125-133. [45] YU A, MAO L, ZHAO F, et al. Olfactory ensheathing cells transplantation attenuates chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induced cognitive dysfunction and brain damages by activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2018;10(10):3111-3121. [46] JACKSON JS, GOLDING JP, CHAPON C, et al. Homing of stem cells to sites of inflammatory brain injury after intracerebral and intravenous administration: a longitudinal imaging study. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2010;1(2):17. [47] ZHANG J, BULLER BA, ZHANG ZG, et al. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells promote remyelination and reduce neuroinflammation in the demyelinating central nervous system. Exp Neurol. 2022;347:113895. [48] WRIGHT AA, TODOROVIC M, MURTAZA M, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor and its binding partner HTRA1 are expressed by olfactory ensheathing cells. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2020;102:103450. [49] PAJER K, BELLÁK T, REDL H, et al. Neuroectodermal Stem Cells Grafted into the Injured Spinal Cord Induce Both Axonal Regeneration and Morphological Restoration via Multiple Mechanisms. J Neurotrauma. 2019;36(21):2977-2990. [50] MOGHADDAM A, CHILD C, BRUCKNER T, et al. Posttraumatic inflammation as a key to neuroregeneration after traumatic spinal cord injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(4):7900-7916. [51] RODRíGUEZ-FUENTES N, ALCáNTARA-QUINTANA LE, HERNáNDEZ-RAMíREZ DF, et al. Cytokines secretion from human mesenchymal stem cells induced by bovine bone matrix. Biomed Mater Eng. 2021;32(4):217-228. [52] NAKAZAKI M, MORITA T, LANKFORD KL, et al. Small extracellular vesicles released by infused mesenchymal stromal cells target M2 macrophages and promote TGF-β upregulation, microvascular stabilization and functional recovery in a rodent model of severe spinal cord injury. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10(11): e12137. [53] MOHANTY A, POLISETTI N, VEMUGANTI GK. Immunomodulatory properties of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Biosci. 2020;45:98. [54] DONG B, WANG C, ZHANG J, et al. Exosomes from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells attenuate the inflammation of severe steroid-resistant asthma by reshaping macrophage polarization. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):204. |
| [1] | Xu Cong, Zhao He, Sun Yan. Regeneration of facial nerve injury repaired by biomaterial nerve conduits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1089-1095. |
| [2] | Yan Le, Zhang Huiping, Dai Lintong. Mesenchymal stem cells for allergic rhinitis: a meta-analysis based on animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 977-984. |
| [3] | Li Long, Li Guangdi, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 751-757. |
| [4] | Zhang Huiyu, Yu Jingwen, Bai Zhenjun, Li Liang, Mu Bingtao, Zhang Jinfeng, Xie Jiawei. Triptolide protects damaged neurons by regulating microglial polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5342-5347. |
| [5] | Xie Na, Ma Run, Wang Lian, Shu Yuanhui, He Ping, Zhou Yan, Xiang Yining, Wang Yuping. Effect of formononetin on glucose oxidase-induced oxidative stress in rat hepatic stellate cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5309-5313. |
| [6] | Huang Jinsheng, Zhang Geyi, Li Senrui, Li Jiangnan, Lu Laijin, Zhou Nan. Lymphatic endothelial cells-derived exosomes promote axonal regeneration following peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5314-5319. |
| [7] | Feng Ruibing, Huang Yong, Hu Hao, Wu Gang, Duan Xiaofeng, Li Chaowen. Analgesic effect and mechanism of icariin in a rat model of post-traumatic knee arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(32): 5108-5113. |
| [8] | Yue Jing, Wang Shijun. Antiinflammatory and analgesic effects and mechanisms of coix seed and its components in adjuvant arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(26): 4187-4192. |
| [9] | Chen Zili, Cao Ning, Xu Meng, Jiang Yan, Ji Meichao, Zheng Yangyang, Yang Lili. Biological characteristics of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-primed human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(24): 3780-3787. |
| [10] | Liu Haichao, Wang Hao, Wang Shizhong, Lin Jianping, Jin Jing, Chen Shaoqing. Effects of point-pressing of the spleen meridian on inflammatory factors and calcium homeostasis in the skeletal muscle of acute blunt contusion rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3123-3128. |
| [11] | Xia Yu, Sun Jia, Qi Zhengyan, Ma Lin, Ma Wenqian, Niu Jianguo, Wen Yujun. Repair effect of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanospheres with sustained-release of neurotrophin-3 and ganglioside GD1a on spinal cord injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(16): 2518-2524. |
| [12] | Ying Chunmiao, Ma Yucheng, Fan Feiyan, Gao Chen, Wang Shaona, Yang Xing, Zhang Yunke. Action mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine to regulate neural stem cells in treatment of Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2385-2394. |
| [13] | Zhang Houjun, Jiang Shengyuan, Deng Bowen, Liu Gang, Bai Huizhong, Tao Jingwei, Fan Xiao, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Mechanism by which tetramethylpyrazine improves inflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(11): 1701-1707. |
| [14] | Zhang Chunli, Liu Jingchen, Zhou Wenjie, Yu Yongzhen, Tang Cuicui, Zou Xiulan, Zou Yuping. Protective effect of stem cells on retinal ganglion cell regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(10): 1593-1602. |
| [15] | Wang Xinxin, Wang Jingxin. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes in treatment of secondary lymphedema [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(10): 1603-1609. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||