Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (32): 5108-5113.doi: 10.12307/2023.573
Previous Articles Next Articles
Analgesic effect and mechanism of icariin in a rat model of post-traumatic knee arthritis
Feng Ruibing1, Huang Yong1, 2, Hu Hao1, 2, Wu Gang1, 2, Duan Xiaofeng1, 2, Li Chaowen1, 2
- 1Department of Spine Surgery, Hubei Hospital of TCM, Wuhan 430074, Hubei Province, China; 2School of Health Sciences, Wuhan Sports University, Wuhan 430079, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2022-07-20Accepted:2022-09-19Online:2023-11-18Published:2023-03-22 -
Contact:Huang Yong, MD, Chief physician, Department of Spine Surgery, Hubei Hospital of TCM, Wuhan 430074, Hubei Province, China; School of Health Sciences, Wuhan Sports University, Wuhan 430079, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Feng Ruibing, MD, Attending physician, Department of Spine Surgery, Hubei Hospital of TCM, Wuhan 430074, Hubei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Feng Ruibing, Huang Yong, Hu Hao, Wu Gang, Duan Xiaofeng, Li Chaowen. Analgesic effect and mechanism of icariin in a rat model of post-traumatic knee arthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(32): 5108-5113.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
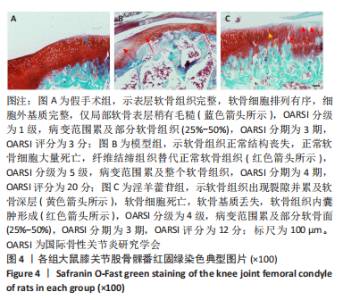
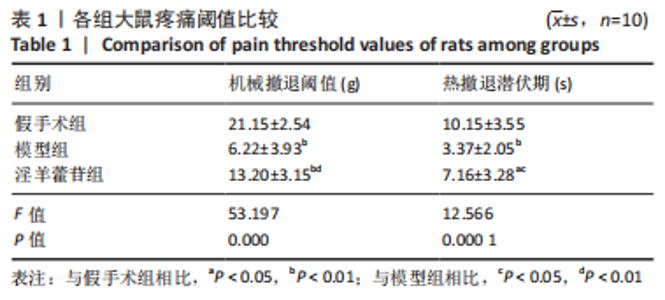
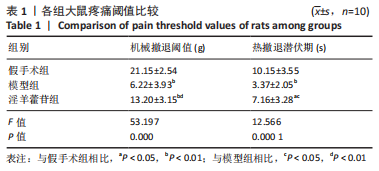
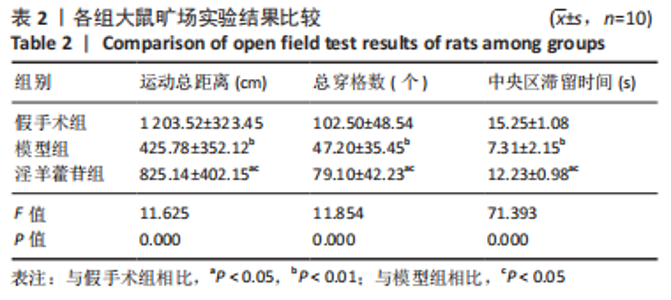
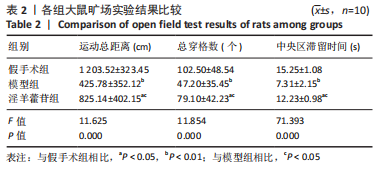
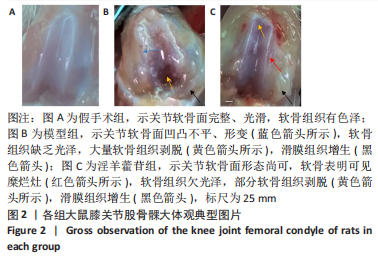
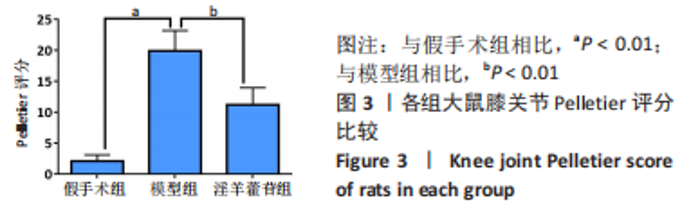
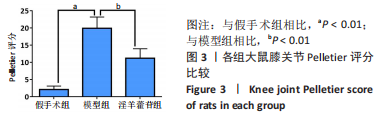
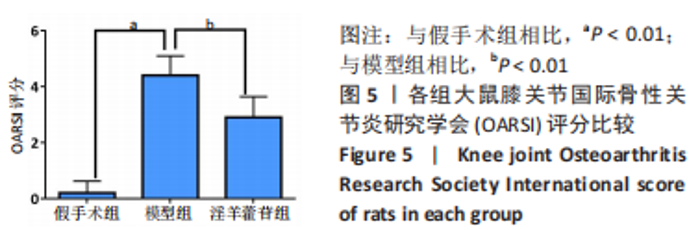
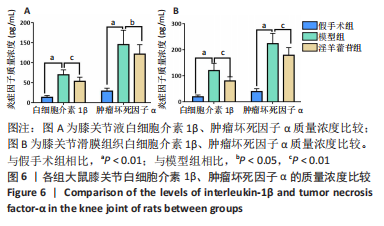
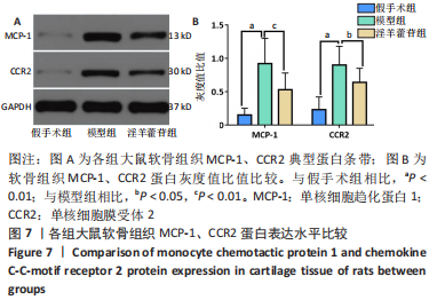
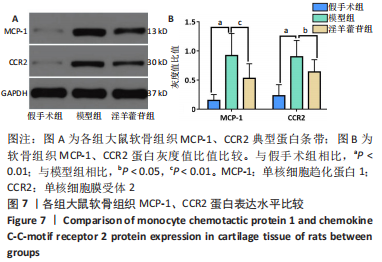
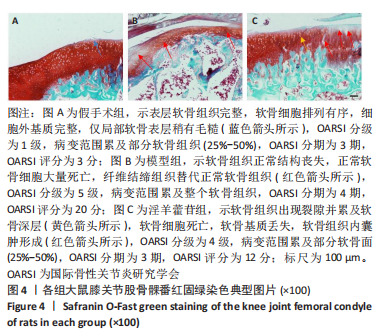
2.5 组织学检测与OARSI评分结果 假手术组关节软骨组织的表层软骨组织完整,软骨细胞排列有序,细胞外基质完整,多数仅软骨表层稍有毛糙(表层纤颤),OARSI分级多为一二级;而模型组多显示为软骨组织正常结构丧失,软骨组织形变,正常软骨细胞大量死亡,纤维结缔组织替代正常软骨组织,软骨内囊肿形成,软骨组织内出现裂隙并累及软骨深层,OARSI分级多为五六级,病变范围多累及整个软骨组织;淫羊藿苷组多显示为表层软骨不完整,软骨组织内出现裂隙,软骨细胞部分死亡,软骨内囊肿形成,但软骨组织形态仍正常,OARSI分级多为三四级,见图4。与假手术组相比,模型组OARSI评分显著升高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);而与模型组相比,淫羊藿苷组OARSI评分显著降低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图5。"
| [1] KHELLA CM, HORVATH JM, ASGARIAN R, et al. Anti-Inflammatory Therapeutic Approaches to Prevent or Delay Post-Traumatic Osteoarthritis (PTOA) of the Knee Joint with a Focus on Sustained Delivery Approaches. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(15):8005. [2] BANNURU RR,OSANI MC,VAYSBROT EE, et al. OARSI guidelines for the non-surgical management of knee, hip, and polyarticular osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(11):1578-1589. [3] MOBASHERI A, REGINSTER JY. Non-surgical management of knee osteoarthritis: comparison of ESCEO and OARSI 2019 guidelines. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021;17(1):59-66. [4] RAUSCH AK, NIEDERMANN K, BRAUN J ,et al. 2018 EULAR recommendations for physical activity in people with inflammatory arthritis and osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77(9):1251-1260. [5] RAVALLI S, SZYCHLINSKA MA, LEONARDI RM, et al. Recently highlighted nutraceuticals for preventive management of osteoarthritis. World J Orthop. 2018;9(11):255-261. [6] COMBLAIN F, SERISIER S, BARTHELEMY N, et al. Review of dietary supplements for the management of osteoarthritis in dogs in studies from 2004 to 2014. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2016;39(1):1-15. [7] LIU X, EYLES J, MCLACHLAN AJ, et al. Which supplements can I recommend to my osteoarthritis patients? .Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018; 57(suppl_4):iv75-iv87. [8] SETTON LA, ELLIOTT DM, MOW VC. Altered mechanics of cartilage with osteoarthritis: human osteoarthritis and an experimental model of joint degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1999;7(1):2-14. [9] TANG XF, LI XX, CHEN YH, et al. Combination of icariin and oleanolic acid attenuates in vivo and in vitro glucocorticoid resistance through protecting dexamethasone-induced glucocorticoid receptor impairment. RSC Advances. 2018;8(1):230-242. [10] 邹志余,周劲松,肖昆林,等.姜黄素对单碘乙酸诱导的膝骨关节炎大鼠的治疗作用[J]. 西安交通大学学报(医学版),2020,41(2): 299-303. [11] PRITZKER KP, GAY S, JIMENEZ SA, et al. Osteoarthritis cartilage histopathology: grading and staging. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006; 14(1):13-29. [12] CHEN M, GU X, XING D, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis in China (2019 edition). Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(19):1213. [13] O’NEILL TW, MCCABE PS, MCBETH J. Update on the epidemiology, risk factors and disease outcomes of osteoarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2018;32(2):312-326. [14] MI B, WANG J, LIU Y, et al. Icariin Activates Autophagy via Down-Regulation of the NF-κB Signaling-Mediated Apoptosis in Chondrocytes. Front Pharmacol. 2018;6(9):605. [15] LIU DH, WU PY, JIAO F, et al. Icariin inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis and angiogenesis by regulating the TDP-43 signaling pathway. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019;7(4):e00586. [16] LIU D, TANG W, ZHANG H, et al. Icariin protects rabbit BMSCs against OGD-induced apoptosis by inhibiting ERs-mediated autophagy via MAPK signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2020;15(253):117730. [17] TANG Y, LI Y, XIN D, et al. Icariin alleviates osteoarthritis by regulating autophagy of chondrocytes by mediating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):2984-2999. [18] WANG G, ZHANG L, SHEN H, et al. Up-regulation of long non-coding RNA CYTOR induced by icariin promotes the viability and inhibits the apoptosis of chondrocytes.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021; 21(1):152. [19] ZENG L, RONG XF, LI RH, et al. Icariin inhibits MMP‑1, MMP‑3 and MMP‑13 expression through MAPK pathways in IL‑1β‑stimulated SW1353 chondrosarcoma cells. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15(5):2853-2858. [20] ZUO S, ZOU W, WU RM, et al. Icariin Alleviates IL-1β-Induced Matrix Degradation By Activating The Nrf2/ARE Pathway In Human Chondrocytes. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;21(13):3949-3961. [21] 吴海,庞坚,陈博,等.膝骨关节炎患者焦虑与抑郁情绪的调查[J].中国医药导报,2018,15(15):47-50. [22] AHN H, WEAVER M, LYON D, et al. Depression and pain in Asian and white Americans with knee osteoarthritis. J Pain. 2017;18(10): 1229-1236. [23] WOODELL-MAY JE, SOMMERFELD SD. Role of Inflammation and the Immune System in the Progression of Osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(2):253-257. [24] LIEBERTHAL J, SAMBAMURTHY N, SCANZELLO CR. Inflammation in joint injury and post-traumatic osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(11):1825-1834. [25] WATT FE. Posttraumatic osteoarthritis: what have we learned to advance osteoarthritis? Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2021;33(1):74-83. [26] ROBINSON WH, LEPUS CM, WANG Q, et al. Low-grade inflammation as a key mediator of the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12:580-592. [27] SCANZELLO CR. Chemokines and inflammation in osteoarthritis: insights from patients and animal models. J Orthop Res. 2017;35:735-739. [28] TANG CH, HSU CJ, FONG YC. The CCL5/CCR5 axis promotes interleukin-6 production in human synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(1):3615-3624. [29] LIN YM, HSU CJ, LIAO YY, et al. The CCL2/CCR2 axis enhances vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in human synovial fibroblasts. PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e49999. [30] RAGHU H, LEPUS CM, WANG Q, et al. CCL2/CCR2, but not CCL5/CCR5, mediates monocyte recruitment, inflammation and cartilage destruction in osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(5):914-922. [31] BIANCONI V, SAHEBKAR A, ATKIN SL, et al. The regulation and importance of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. Curr Opin Hematol. 2018;25(1):44-51. [32] ZHANG K, LUO J. Role of MCP-1 and CCR2 in alcohol neurotoxicity. Pharmacol Res. 2019;139:360-366. |
| [1] | Li Chao, Zhang Peipei, Xu Mengting, Li Linlin, Ding Jiangtao, Liu Xihua, Bi Hongyan. Respiratory training improves morphological changes of the multifidus muscle in patients with chronic nonspecific lower back pain assessed by musculoskeletal ultrasound [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1417-1421. |
| [2] | Zhang Qiming, Bao Sairong, Shan Sharui, Zhong Zhiliang, Liu Chunlong. Effect of deep muscle stimulation on muscle tone and stiffness of erector spinaes in patients with chronic nonspecific low back pain: a digital muscle testing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1250-1256. |
| [3] | Qiao Luhui, Ma Ziyu, Guo Haoyu, Hou Yudong. Comparison of puerarin and icariin on the biological properties of mouse preosteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 872-877. |
| [4] | Li Long, Li Guangdi, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 751-757. |
| [5] | Xu Yangyang, He Peiliang, Meng Qingqi, Li Siming. A meta-analysis of the effects of continuous adductor canal block and continuous femoral nerve block on early activity after knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 640-645. |
| [6] | Chai Hao, Yang Deyong, Zhang Lei, Shu Li. 3D printing personalized osteotomy guide technology versus conventional total knee arthroplasty on the accuracy of lower limb force alignment: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 646-654. |
| [7] | Li Yaping, Liu Hong, Gao Zhen, Chen Xiaolin, Huang Wujie, Jiang Zheng. Three-dimensional motion analysis of lower limb biomechanical performance in Tai Chi practitioners accompanied by knee joint pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 520-526. |
| [8] | Wan Guoli, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan, Li Ang, Shi Xunda, Cai Yi. Retrospective analysis of the influencing factors of chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 558-564. |
| [9] | Zhang Xuebin, Ao Wenjun, Jiang Xin, Song Chenglin. Improvement of delayed-onset muscle soreness by pre-exercise whole-body vibration at 50 Hz [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(32): 5085-5090. |
| [10] | Zhu Hongliu, Wang Wei. Correlation analysis of low back pain in middle-aged and elderly people in China and construction of a linear graph prediction mode [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 4937-4942. |
| [11] | Zhou Jinyan, Zhong Yuanming, Li Zhifei, Xu Wei, Zhang Jiali, Liang Ziyang. Pressure biofeedback training for treating cervical spondylosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 5052-5057. |
| [12] | Bai Gaigai, Zhao Yujuan, Wei Jiakai, Huang Wendi, An Yao, Wang Zhi. Icariin improves pituitary development in hypothyroidism model rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(28): 4546-4553. |
| [13] | Luo Wei, Zhong Tao, Huang Zhirui, Gao Yan, Huang Zhen. Static balance and limits of stability in patients with chronic nonspecific low back pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4362-4366. |
| [14] | An Hepeng, Liu Zhenteng, Li Lixin, Xu Yafang, Fan Guofeng. Effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on neuronal activity, pain, and related cytokines in rats with lumbar spinal stenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(26): 4120-4125. |
| [15] | Yue Jing, Wang Shijun. Antiinflammatory and analgesic effects and mechanisms of coix seed and its components in adjuvant arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(26): 4187-4192. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||