Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (33): 5394-5403.doi: 10.12307/2023.711
Previous Articles Next Articles
Pretreatment methods improve the role of exosomes in spinal cord injury
Zhou Heshan1, Tan Longwang2, Liu Chuang1, Zhang Chi1
- 1Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang 712000, Shaanxi Province, China; 2Department of Spinal Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang 712000, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2022-10-09Accepted:2022-11-21Online:2023-11-28Published:2023-03-31 -
Contact:Tan Longwang, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Spinal Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang 712000, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Zhou Heshan, Master candidate, Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang 712000, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81774349 (to TLW)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Heshan, Tan Longwang, Liu Chuang, Zhang Chi. Pretreatment methods improve the role of exosomes in spinal cord injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5394-5403.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
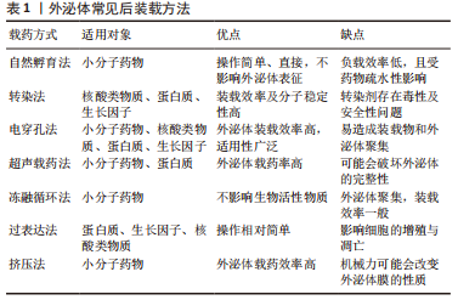
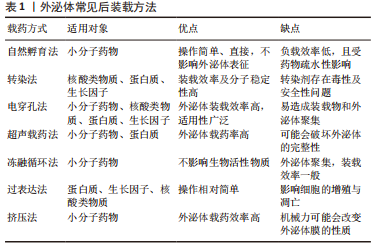
2.1 外泌体及外泌体在脊髓损伤中的应用概述 细胞外囊泡是真核细胞在其生命周期内产生的具有磷脂双分子层的纳米级颗粒,早期细胞外囊泡被认为是细胞废弃物,近年来随着研究的不断深入,细胞外囊泡的功能逐渐被人们所发掘[11]。根据细胞外囊泡的大小、形成方式的不同,细胞外囊泡通常被分为以下3种亚型:①微囊泡:由细胞膜直接萌发并释放到细胞外空间;大小为100-1 000 nm;②外泌体:外泌体的形成是一个复杂的动态过程,细胞通过质膜内陷形成早期内吞体,进而形成晚期内吞体,经过细胞膜向内出芽,在内吞体转运复合物及相关蛋白的调控下,构成包含多个腔内囊泡的多囊泡小体,多囊泡小体与细胞膜融合并释放到细胞外的物质就是外泌体;大小为30-100 nm,外泌体可以通过内吞作用或配体受体结合等方式被其他细胞所摄取;③凋亡小体:由凋亡细胞产生,是凋亡过程的产物,直径为1 000-5 000 nm[12-13]。 外泌体含有多种生物活性物质,如蛋白质(跨膜转运相关蛋白、热休克蛋白和TSPAN 蛋白超家族等)、脂类(胆固醇、双甘酯和鞘磷脂等)、核酸(DNA,miRNA,lncRNA,mRNA和tRNA等)等[14],因其来源及分泌机制不同,其表面标记物也有所差异,在不同的病理情况下,其标志物会发生显著变化,据此可以用于疾病的诊断[15]。外泌体来源广泛,易于收集,且与源性细胞功能类似,因此在多种疾病中展现出良好的治疗作用。外泌体具备双层磷脂膜结构,能够在循环中保持稳定,内部负载物质不会轻易降解,且其活性在适当条件下能够长期保持不变,这是促使外泌体实现临床转化的重要前提[16]。外泌体作为细胞外囊泡的最小亚型,具有良好的通过性(可跨越血-组织屏障),免疫排斥风险低,细胞靶向性强,故以外泌体为载体的药物递送系统在多个领域得到广泛研究[17]。目前外泌体常见分离和纯化方法主要包括以下几种:超速离心法(金标准)、密度梯度离心法、超滤法、聚合物沉淀法、免疫磁珠法及试剂盒提取法等[18]。高纯度和高质量的外泌体是实验开展的前提和基础,而不同的提取方法各具优缺点,研究者们要根据研究场景的不同,选取恰当的分离方法,确保后续实验的顺利开展。 由于外泌体具备以上诸多优势,近年来人们逐渐开始发掘其在脊髓损伤修复领域的作用,目前已经开展了多项关于外泌体治疗脊髓损伤的临床前研究,并在动物模型上验证了这一结果。WANG等[19]对脊髓损伤大鼠尾静脉注射间充质干细胞和等量同细胞源性的外泌体,发现二者均可降低神经胶质纤维酸性蛋白的表达,抑制A1星形胶质细胞的比例,从而发挥对脊髓损伤的神经保护作用;同时,间充质干细胞外泌体在病变部位被检测出,而损伤部位未检测到间充质干细胞,但两种方式发挥了相同的治疗效果,这至少证明在静脉给药方式下,间充质干细胞的增殖分化能力不是介导脊髓损伤治疗作用的主要机制,其发挥治疗作用可能来自于旁分泌所产生的外泌体,但不排除间充质干细胞中其他组分参与了治疗过程。其他研究者在类似的实验中取得了同样的结果,在损伤部位只检测到了静脉输注的间充质干细胞外泌体,间充质干细胞被发现可在肺部停留约2 d,但二者均可特异性靶向损伤部位的M2型巨噬细胞,从而发挥对脊髓损伤的治疗作用[20]。 根源于细胞疗法的外泌体疗法,已经在多项研究中被证明具有与细胞移植相同的疗效,且具备强搭载性及低免疫原性等诸多优势[21]。未经预处理的天然外泌体主要继承了原代细胞生物学特性,如周细胞产生的外泌体更容易被内皮细胞摄取,可显著改善损伤状态下的内皮屏障功能,恢复血脊髓屏障的完整性[22]。根据治疗目的,选择适当来源的亲代细胞是决定外泌体疗效的重要前提。因此,来源于不同种类细胞的外泌体,可通过抑制炎症反应、减少细胞凋亡、保持血脊髓屏障的完整性、抑制胶质瘢痕的形成、促进轴突再生、血管生成及神经保护等机制治疗脊髓损伤[23]。 外泌体作为近年来的研究热点,在中枢神经系统疾病中应用前景广阔,虽然在基础实验中证明了外泌体对脊髓损伤的治疗作用,但关于其治疗机制有待深入研究,只有进一步明确脊髓损伤的分子靶点,才能对脊髓损伤做到针对性治疗。研究者们要根据外泌体的特性,选择最适合的给药方式、给药途径和给药剂量,在起到治疗效果的同时避免副反应的发生;天然外泌体发挥着细胞间信号通讯的功能,可以利用外泌体判断脊髓损伤的损伤程度和预后,继而予以精准干预。外泌体的分离、纯化与储存技术尚需更多探索,并制定相应规范化标准,推动外泌体产业迅速走上正轨。 2.2 外泌体的预处理方法及在脊髓损伤中的应用 常规外泌体在脊髓损伤领域研究愈发深入的同时,研究者们也发现治疗过程中存在的一些缺点。①在现有研究中,外泌体一般通过尾静脉注射给药,也有鼻腔给药的案例[24],外泌体经过体内循环后,相当一部分会被其他靶器官或细胞所摄入,从而无法到达损伤部位发挥治疗效果。相关研究证明了早期局部注射外泌体可以控制急性期炎症,但是药效无法长期维持[25],脊髓损伤次级阶段的级联反应会继续发生,但多次局部给药会导致新的二次伤害,其利弊有待进一步研究。②常规环境产生的外泌体,在脊髓损伤后氧化应激和离子失衡的微环境下,活性可能受到抑制,无法充分发挥治疗效果。③外泌体含有丰富的核酸类物质,这是其在治疗过程发挥作用的主要成分,母本细胞在分泌组装过程往往不具备特异性,但是脊髓损伤过程中主要机制是特定的,常规外泌体因为具备治疗作用的活性物质含量低,常需高剂量才能取得治疗效果,但是,大剂量外泌体是否会带来新的不良反应,其安全性有待进一步研究。④脊髓损伤是一个多细胞、多分子共同致病的过程,单细胞外泌体可以精准调控某一通路,但无法针对脊髓损伤起到全面、显著的疗效。 正是因为治疗过程中存在上述问题,各种预处理手段也就应运而生,预处理外泌体是指在外泌体培养及制备过程中,通过对亲代细胞或天然外泌体加以干预,进一步优化外泌体功能和疗效的方法[26]。常见预处理方法有特殊微环境下的预培养、药物或核酸类物质的预搭载、水凝胶等生物材料的预联合,通过这些方法,可以有效提高外泌体的稳定性、治疗的靶向性、全面性及降低发生不良反应的可能性。 2.2.1 外泌体的预培养 在培养细胞收集外泌体的过程中,对源性细胞进行干预,即为外泌体的预培养,主要包括改变源性细胞的培养方式及培养环境,根据培养条件的不同,细胞所分泌外泌体的生理功能也会有所差异,通过选择适当的培养条件,可以增强外泌体的生理活性和相关特性,有效改善其在不同疾病中的疗效。 (1)三维培养外泌体:当前外泌体来源细胞的培养方式可分为二维培养和三维培养,二维培养即通过培养基在平面上单层培养细胞的传统方式,三维培养为通过生物材料构建类似于机体的微环境,进行细胞培养[27]。相较于二维培养,三维培养所构建的仿生环境可以使细胞表型更具生理相关性,能加强细胞间的相互作用,维持细胞形态,并进一步提高所分泌外泌体的数量与质量,最大限度发挥外泌体的功效[28]。但是,三维培养也存在一定的局限性,如水凝胶等材料中培养产生的外泌体,在提取收集上存在一定难度,可能会部分残留在材料中。三维培养产生的外泌体已经被证明在抗炎、抑制凋亡、神经再生等方面比二维培养更具优势[29]。HAN等[30]选择细胞相容性较好的甲基丙烯酰明胶水凝胶,模拟骨髓间充质干细胞的自然生长环境,对细胞进行三维培养并提取外泌体,发现三维培养的骨髓间充质干细胞干性标志物SOX2及Nanog的表达明显高于二维培养的细胞,显示出更强的细胞干性和治疗潜力。相较于二维培养外泌体,三维培养收集的外泌体中含有更多与中枢神经系统生长发育相关的蛋白质和miRNAs;在体内外脊髓损伤实验中,三维培养外泌体比二维培养抗炎作用更强,且可以促进小胶质细胞/巨噬细胞向M2型极化,并阻止星形胶质细胞的大量聚集,显示出比二维培养外泌体更优越的神经保护作用。 三维培养可以提供更真实的生理微环境,不管是天然衍生材料还是人工合成材料,均能通过细胞-基质黏附及细胞动态反馈调节细胞的命运,从而影响外泌体的产生和功能。但支架材料本身所含有小分子物质也会被外泌体所摄取,其可能会干预后续研究的结果,目前技术手段无法对外泌体进一步纯化,尚需开展相关实验以明确影响[31]。三维培养外泌体在脊髓损伤领域表现出良好的特性,且作为基本预处理措施,不会影响外泌体的深度优化,研究者们应改进外泌体的收集提纯技术,减少其他成分对外泌体的干扰,明确二维、三维培养间的差异变化,避免在运用中带来未知的不良反应。 (2)低氧预处理外泌体:脊髓损伤后,局部会处于氧化应激、炎症等状态,天然外泌体在损伤环境下活性可能受到影响,而在模拟损伤局部状态条件下,可显著提高细胞的生存能力,从而增强其在疾病中的治疗作用,细胞旁分泌产生的外泌体会继承亲代细胞的这一特性。目前在脊髓损伤领域针对外泌体的培养环境预适应,主要以对间充质干细胞的低氧预适应为主。氧浓度在间充质干细胞增殖、分化过程中很重要,在体外进行细胞培养时,空气中氧浓度为21%,但是人体内氧含量较低,一般在2%-8%,在细胞培养时进行低氧预适应,模拟脊髓损伤时病变部位的缺氧微环境,可以促进外泌体的分泌,调节miRNAs的表达,增强外泌体在脊髓损伤模型中的生物学功能和活性。LIU等[32]分别在常氧和低氧环境下培养并分离了骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体,发现在低氧条件下外泌体分泌量明显增加,其蛋白浓度显著高于常氧条件外泌体,且低氧条件下产生的外泌体存在更多差异表达的miRNAs,相较于常氧外泌体,更容易被小胶质细胞摄取,并可通过抑制TLR4通路的激活,促进小胶质细胞从M1型向M2型极化,显著抑制脊髓损伤后神经炎症,促进小鼠功能行为的恢复。LIANG等[33]也对低氧预处理脂肪间充质干细胞外泌体治疗脊髓损伤大鼠的机制进行了研究,低氧环境和常氧环境产生的脂肪间充质干细胞外泌体在形状、大小、标志蛋白上未见明显差异,这说明低氧预处理不会改变外泌体的基本形态和特征,主要是蛋白质及核酸等活性物质发生改变。通过体外构建神经元氧糖剥夺再灌注模型,发现低氧预处理外泌体治疗组细胞死亡数量明显低于常氧外泌体组,能更大程度减少神经元凋亡;在脊髓损伤大鼠体内实验表明,低氧预处理的脂肪间充质干细胞外泌体可以促进大鼠后肢功能恢复,减少脊髓空洞形成,并通过miR-499-5P负调控JNK3/c-jun凋亡信号通路抑制神经细胞凋亡。 在一项涉及到低氧预处理时间的研究中,发现分别进行 15 min和3 h的低氧预处理,对外泌体的影响无明显差异[34]。一般认为,长时间的低氧预处理对治疗更有效,短时间低氧环境缺乏相关文献,因此,在研究低氧预处理的时候,应考虑到不同时长所带来的影响,进一步优化预培养条件。 低氧预处理对于改善外泌体功能是一种简单有效的方法,可以显著提高外泌体治疗脊髓损伤的作用。但在低氧预处理过程中,不同的氧气浓度及处理时间是否会改变源性细胞的表型,从而影响所分泌外泌体的成分,还缺乏相关实验论证。并且,当前研究以低氧预处理为主,脊髓损伤后局部还会表现出强烈炎症、缺血及离子失衡等,构造相应微环境条件刺激下产生的外泌体,是否能改善疗效,目前暂无报道,KONG等[35]在实验中发现来源于脊髓损伤大鼠脑脊液的外泌体在体外可以促进神经元细胞增殖,而正常脑脊液外泌体无这一特征,但并未开展体内实验及挖掘相关分子机制,故模拟外部刺激的预处理方式在脊髓损伤中的作用还需进一步开展相关研究。 对源性细胞进行预培养,改变其培养方式和培养环境,是外泌体预处理的一项基本措施,常规外泌体培养方式产量低、耗时长,且间充质干细胞等无法无限制增殖,三维培养通过构建中空细胞生物反应器或球形支架等,可以促进细胞间相互作用,产生机械刺激,并促进细胞增殖和外泌体分泌,不仅有效提高外泌体产量,还能增强外泌体的生物活性,因此,构建先进的外泌体培养系统对于高质量大规模的外泌体生产是非常有必要的。调整外泌体培养过程中的氧含量,营造类似机体内部的低氧微环境,可以促使外泌体的生物活性物质发生改变,形成多个差异表达的内部成分,从而发挥积极的治疗作用,但过长的干预时间及过低的氧浓度,可能会抑制细胞活力,带来负面影响。同时,用凝血酶、过氧化氢及脂多糖等材料刺激亲代细胞,也可以提高外泌体的产量,丰富其内容物,但这些物质可能造成不健康的外泌体产生,利用生物刺激改变培养环境的外泌体预处理方法,相较于传统方式,能降低成本、提高产量,但可能导致的不良后果亦需重视。 2.2.2 外泌体的物质预搭载 外泌体具备典型的磷脂双分子层结构,可以保护其在循环中的稳定性,外泌体的生物学起源为内源性细胞因子的搭载提供了机会,且含有多种特定的膜蛋白,可以穿透生物屏障,靶向到损伤部位,是良好的药物运载与递送系统,可运送核酸、中药成分及化学药物等多种物质,有广阔的研究前景[36]。 外泌体药物预搭载最关键环节是在保证外泌体结构完整性的同时,不影响药物活性,将药物高效率的装载到外泌体上。目前外泌体预搭载方式可大致分为前装载与后装载两类。前装载是指将预载物质与亲代细胞进行共同培养,使药物能被亲代细胞充分摄取或转染亲代细胞,然后分泌出含有此种物质的外泌体,前装载不会影响外泌体的完整性,但载药率偏低。后装载是指收集到外泌体后,通过各种方法使药物载入外泌体中。常见后装载方法有自然孵育法、电穿孔法、冻融循环法、超声载药法、挤压法和化学共轭法等,后装载提高了外泌体载药效率,但某些方法可能会破坏外泌体膜完整性,影响药物活性[37-38]。不同载药方式各有利弊,适用对象也各不相同,现将常见后装载方法进行归纳,见表1。"
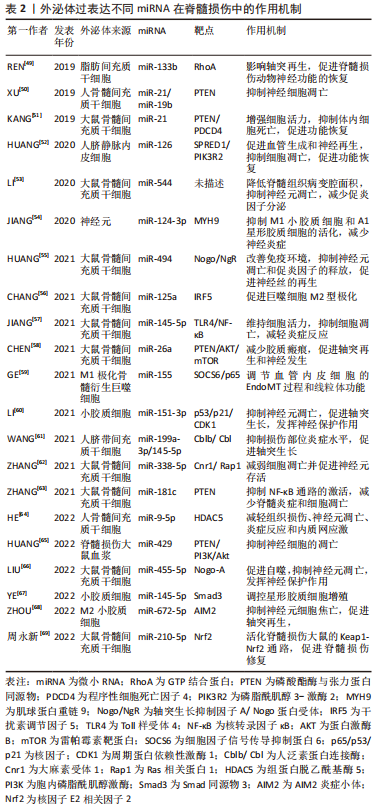
目前在外泌体治疗脊髓损伤领域,关于外泌体搭载中药成分或化学药物的研究较少,一般通过对源性细胞转染非编码RNA,收集高表达某种非编码RNA或基因的外泌体,从而达到对脊髓损伤靶点的精准干预。 (1)外泌体预载药物 预载小分子中药提取物:外泌体自身具备对脊髓损伤的治疗效果,其作为天然的物质递送载体,还可以穿透血脊髓屏障,将药物运送至损伤部位,从而实现对脊髓损伤的双重干预。白藜芦醇在脊髓损伤后可以激活自噬、促进神经修复,但受到血脑屏障的限制,导致脊髓药物浓度偏低,因此可以利用外泌体预载白藜芦醇[39],并将其输送至损伤部位。采用前装载的方式,将小胶质细胞与白藜芦醇共培养,收集含有白藜芦醇的小胶质细胞外泌体,相较于血浆游离白藜芦醇,白藜芦醇-外泌体的降解时间显著延长,具有更好的药物稳定性和局部疗效,在脊髓损伤中,白藜芦醇-外泌体表现出比游离白藜芦醇更强的自噬激活和神经元存活作用,在大鼠运动功能的改善方面具备明显优势。GAO等[40]探究了M2型巨噬细胞外泌体预载小檗碱的药物递送体系对脊髓损伤的治疗作用,收集巨噬细胞外泌体后,通过超声载药法将小檗碱预载到外泌体中,并对载药体系进行鉴定,发现小檗碱-外泌体性能稳定,载药率明显高于自然孵育法,超声载药法没有破坏外泌体的表面特征,小檗碱-外泌体的缓释作用进一步延长了药物的循环时间。在脊髓损伤体内外实验中,相较于单纯外泌体和小檗碱治疗组,小檗碱-外泌体实现了损伤部位的高浓度蓄积,能更好地诱导M2型巨噬细胞极化,抑制炎症因子表达,减少神经细胞凋亡,促进大鼠运动功能恢复。 预载化学药物:芬戈莫德(FTY720)是一种免疫抑制剂,研究证明FTY720在脊髓损伤的修复中有积极效果,但全身应用可能会导致粒细胞减少等不良反应,因此,实现FTY720的精准递送可以在避免不良反应的同时发挥对脊髓损伤的治疗效果。CHEN等[41]通过超声循环法将FTY720预载入收集好的神经干细胞外泌体中,FTY720与神经干细胞外泌体共培养60 min后,外泌体载药量达到最大。将载FTY720的神经干细胞外泌体尾静脉注射给脊髓损伤大鼠,发现可以维持神经元细胞的形态,保护内皮屏障,减少细胞凋亡,并缓解脊髓水肿,从而达到改善脊髓损伤后功能和行为的目的。相较于单纯应用FTY720,通过预处理方法构建的外泌体递送体系,不仅取得了更好的疗效,还避免了FTY720所带来的不良反应。 构建基于外泌体的药物递送体系,在诸多领域得到了充分的研究,尤其是肿瘤化疗药物的靶向递送及跨越血脑屏障的中枢神经系统药物递送[42],不仅可以避免药物所带来的全身不良反应,还可以穿透生物膜,使药物直达病所。外泌体的药物预搭载在治疗脊髓损伤过程中展现出了良好的效果,研究者们在选择外泌体和搭载药物时也要考虑其各自特性,实现最优组合,如上文中M2型巨噬细胞外泌体具备天然的炎症靶向性,而小檗碱在脊髓损伤中抗炎作用同样得到了验证,二者结合,可以做到对炎性细胞的精准干预[40]。此外,诸多中药成分在脊髓损伤中的作用已经得到验证,如川芎嗪、芍药苷和槲皮素等[43],外泌体联合中药成分递送体系的构建,可以为脊髓损伤的治疗开辟一条新的路径。 (2)外泌体预载核酸类物质:随着高通量测序技术的发展,核酸类物质在脊髓损伤中的作用愈发受到重视,如非编码RNA和小干扰RNA(small interference RNA,siRNA),非编码RNA主要包括微小RNA(micro RNA,miRNA)、环状RNA(circular RNA,circRNA)及长链非编码RNA(long non-coding RNA,lncRNA)等,非编码RNA不参与蛋白编码,在调节基因表达过程中发挥重要作用,siRNA能够抑制mRNA翻译,起到基因沉默的作用。研究发现,脊髓损伤后出现多种非编码RNA的差异表达,并在不同病理阶段呈现出不同的变化特征[44]。非编码RNA能参与脊髓损伤后免疫调节、细胞凋亡及神经再生等多种机制,是具备治疗潜力的全新靶点[45]。外泌体含有丰富的生物活性物质,如miRNA,circRNA和lncRNA等,能介导细胞间信息传递,调节受体细胞内基因水平的表达。源性细胞通过预先转染特定的非编码RNA模拟物,进而分泌出高含量特定非编码RNA的外泌体,进一步改善外泌体在脊髓损伤中的治疗作用[46]。外泌体不仅可以过表达自身含有的核酸物质,也能将外源性基因药物转运至损伤部位。 预载微小RNA:目前,在关于外泌体的预处理措施研究中,绝大多数通过高表达某种miRNA来实现在脊髓损伤中的疗效优化,主要涉及的miRNA为miR-29b,miR-133b及miR-145-5p等。Kang等[47]通过实验探究了骨髓、牙髓、DPC12、胚胎、脂肪及神经上皮不同来源干细胞外泌体对脊髓损伤的治疗作用,发现对脊髓损伤的恢复均有疗效,在针对H2O2诱导的细胞凋亡体外实验时,各组不同程度抑制了细胞凋亡,而神经上皮干细胞外泌体效果最强。上述6组干细胞外泌体中,神经上皮干细胞外泌体呈现出最高的miR-29b表达,用miR-29b模拟物预转染神经上皮干细胞收集到的过表达miR-29b外泌体,在脊髓损伤大鼠中的治疗效果最强,其可能是通过抑制PTEN和caspase-3的表达起到抑制细胞凋亡和促进轴突再生的作用。在类似实验中,经过miR-29b质粒预转染的骨髓间充质干细胞分泌的外泌体对脊髓损伤大鼠有修复作用,且效果强于单纯外泌体或转染miR-29b的骨髓间充质干细胞[48],主要通过调节神经丝蛋白200、生长相关蛋白43和神经胶质纤维酸性蛋白等神经再生相关蛋白的表达发挥治疗作用。 外泌体预载miRNA在脊髓损伤中得到了最广泛的研究[49-69],现将外泌体过表达特定miRNA治疗脊髓损伤的机制归纳如下,见表2。"
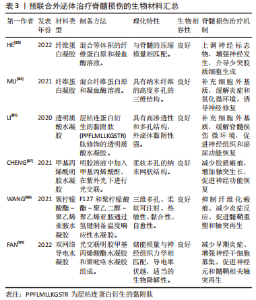
预载lncRNA:lncRNA是长度超过200个核苷酸的非编码转录本,可以作为miRNA的竞争内源性RNA,其异常表达与脊髓损伤的发生发展密切相关。LIU等[70]研究了lncRNA结构家族蛋白2(tectonic family member 2,TCTN2)预修饰的间充质干细胞的外泌体对脊髓损伤的治疗作用,利用TCTN2的高表达载体预先转染骨髓间充质干细胞,然后收集含有TCTN2的外泌体,外泌体表征及标志蛋白未发生改变,TCTN2高表达。体外细胞实验发现,TCTN2外泌体通过 miR-329-3p抑制神经元凋亡、炎症和氧化应激,主要靶向IGF1R表达来实现。同时,TCTN2外泌体在脊髓损伤大鼠体内通过调节miR-329-3p/IGF1R轴改善脊髓损伤后功能恢复,miR-329-3p过表达会减弱TCTN2外泌体的神经保护作用。 预载circRNA:circRNA是一类具有环状结构的非编码RNA,可以抑制miRNA与靶点的结合,从而发挥miRNA“海绵”作用。目前关于circRNA在脊髓损伤中的研究较少,尚需进一步探究circRNA在脊髓损伤中的作用机制。TIAN等[71]发现circZFHX3在脊髓损伤动物模型中下调,并参与了炎症反应过程。将circZFHX3过表达载体预导入骨髓间充质干细胞后,收集过表达circZFHX3的外泌体(Exo-circZFHX3),在脂多糖诱导的BV-2细胞损伤中,Exo-circZFHX3可以通过海绵化 miR-16-5p调节IGF-1的表达,从而提高细胞活力,抑制细胞凋亡、炎症反应和氧化应激,Exo-circZFHX3尾静脉注射给脊髓损伤小鼠后,病变体积缩小,运动功能明显改善,而来自未经预修饰细胞的外泌体仅达到上述部分治疗效果,同时,Exo-circZFHX3可能不是脊髓损伤中circZFHX3的惟一机制。 预载小干扰RNA(siRNA):siRNA可以选择性靶向致病基因,在脊髓损伤领域有广阔前景。但siRNA存在传递效率低、性质不稳定、易刺激免疫系统等问题,因此选择合适的递送载体至关重要,外泌体具备低免疫原性、良好穿透性及循环稳定性等优势,是siRNA递送的可靠载体。HUANG等[72]应用骨髓间充质干细胞来源的外泌体作为搭载siRNA的载体,构建了能特异性沉默损伤部位结缔组织生长因子基因的siRNA,通过电穿孔的方式进行预装载,制备出可以用于脊髓损伤精确治疗的外泌体siRNA。表征鉴定显示预载siRNA不影响外泌体的特性,在电穿孔装载过程中,不同参数会显著影响负载效率,包封好的外泌体能阻止siRNA在体液中的降解。体外研究显示,外泌体siRNA能有效抑制星形胶质细胞中结缔组织生长因子基因的表达,刺激受损脊髓神经营养因子和抗炎因子的分泌,此外,外泌体siRNA在脊髓损伤环境中可以抑制神经元凋亡,促进M2型巨噬细胞极化,但与正常外泌体组无显著差异,说明抗凋亡和抗炎作用主要来自于外泌体。脊髓损伤大鼠尾静脉注射外泌体siRNA后,主要富集在肝、肺及损伤脊髓部位,检测显示外泌体对靶器官无明显毒副反应。外泌体siRNA能有效抑制结缔组织生长因子 mRNA的表达,从而弱化星形胶质细胞增生,减少胶质瘢痕的产生,为神经轴突的再生创造条件,促进脊髓损伤大鼠运动功能的显著恢复。 细胞转染技术作为基因治疗的一种方式,当前发展较为成熟,在多个领域均得到了认可。通过转染技术使外泌体过表达核酸类物质,可以使目的基因持续作用于损伤部位,促进脊髓损伤后的功能恢复,而导入外源性基因的关键在于载体的选择,目前研究以腺病毒和脂质体为主,但其安全性和转染率有待进一步提高,且均以单一RNA为主,虽然外泌体预载核酸类物质还存在相关问题,但其拥有广阔应用前景,脊髓损伤后非编码RNA广泛差异表达,通过外泌体预载非编码RNA和siRNA,可以在充分发挥天然外泌体对脊髓损伤治疗效果的前提下,进一步实现对脊髓损伤相应靶点的精确干预。 (3)外泌体预载蛋白质:外泌体不仅可以预载药物及核酸类物质,还可以预载蛋白质类药物,进一步改善天然外泌体对脊髓损伤的治疗作用。G蛋白偶联受体激酶相互作用蛋白1(G protein coupled receptor kinase interacting protein 1,GIT1)是一种多功能多结构域支架蛋白,在细胞迁移和细胞骨架形成过程中发挥重要作用。LUO等[73]利用高表达GIT1的重组腺病毒转染骨髓间充质干细胞,并成功分离高表达GIT1的骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体(Exo-GIT1),发现Exo-GIT1可以防止GLU诱导的神经元凋亡和兴奋性毒性,促进轴突再生和抑制体内胶质瘢痕形成,对受损脊髓具有显著的保护作用,其机制可能是通过激活PI3K/AKT信号通路来实现的,相较于天然外泌体,Exo-GIT1在血管生成和神经元保护中发挥了关键作用。 JIA等[74]通过实验证明了过表达刺猬因子蛋白(Sonic Hedgehog,Shh)的骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体(Exo-Shh)可以激活Shh信号通路,抑制胶质瘢痕形成,促进轴突和髓鞘的再生,修复受损神经元,从而达到改善脊髓损伤大鼠运动功能的目的。而在另一项对照实验中,给脊髓损伤大鼠脊髓注射用于沉默Shh的shRNA Shh-腺相关病毒(sh-Shh-AAV),并予以骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体治疗,在Shh沉默的大鼠体内,外泌体对脊髓损伤未起到治疗效果,在不注射sh-Shh-AAV的脊髓损伤大鼠体内,外泌体发挥了显著治疗效果[75],这表明Shh的存在是外泌体治疗脊髓损伤的必要因素,因此,预搭载Shh的外泌体可能在脊髓损伤中取得更好的治疗效果。 蛋白质类药物在脊髓损伤中发挥了重要作用,但其分子质量大、体内稳定性差,限制其进一步应用。外泌体预载蛋白质可以在保持生物稳定性的同时,实现靶向给药。目前研究主要为外泌体预载不同蛋白质,利用外泌体的受体-配体结合机制,实现药物的精准靶向给药,减少对非靶器官的不良反应,可能是未来的一个研究方向。 (4)外泌体预载生长因子:生长因子是一种多肽类物质,可以调节细胞的生长、增殖过程,对脊髓损伤后的神经修复及血管再生具有重要作用。生长因子基因治疗在脊髓损伤中得到了较多研究,通过构建生长因子的基因载体,并利用载体转染受体细胞,作用于损伤局部,使生长因子可以在机体内持续表达,充分发挥对脊髓损伤的治疗作用,其中神经生长因子、血管内皮生长因子和脑源性神经生长因子等研究较为成熟[76]。细胞旁分泌产生的外泌体,同样会高表达预转染亲代细胞的生长因子,在治疗脊髓损伤的同时避免细胞移植的弊端。 LI等[77]制备了片状骨髓间充质干细胞,相较于非片状骨髓间充质干细胞,能更好地促进神经元轴突再生。构建过表达神经生长因子的慢病毒载体,并转染骨髓间充质干细胞片材,得到预载神经生长因子的骨髓间充质干细胞片外泌体,可以传递神经生长因子刺激神经干细胞分化为神经元细胞和轴突再生,最终促进脊髓损伤小鼠的功能恢复。在另外一项关于外泌体预载血管内皮生长因子A治疗脊髓损伤的研究中,使用shRNA删除神经干细胞中的血管内皮生长因子A,得到沉默血管内皮生长因子A的神经干细胞外泌体,体内外实验发现神经干细胞外泌体可将血管内皮生长因子A导入脊髓微血管内皮细胞,改善其血管生成活性,促进脊髓损伤后小鼠神经功能的恢复,但神经干细胞外泌体对血管生成的影响并不因为沉默血管内皮生长因子A而完全消除,其他分子在调节血管生成中也发挥一定作用[78]。 生长因子在神经组织的修复中发挥着重要作用,但其半衰期短,稳定性差,通过构建外泌体预载生长因子的递送体系,可以实现生长因子在体内的稳定释放,从而最大限度地发挥修复作用。外泌体预载生长因子治疗脊髓损伤仍处在探索阶段,目前主要通过基因修饰源性细胞,得到过表达特定生长因子的外泌体,转染率无法得到保证,且过表达载体的构建技术还不完善,但不可否认,这将是未来外泌体治疗脊髓损伤的一条重要途径。 外泌体封装药物所构建的物质递送体系,可以将小分子药物、核酸类物质、蛋白质及生长因子等物质搭载到外泌体中,在当前得到了最广泛和深入的研究,相较于传统的脂质体、聚合物囊泡等药物递送方式,来自于细胞或体液的天然外泌体成分,有着无与伦比的优势,极低的免疫原性避免了细胞毒性,血液循环稳定性获得较长半衰期,独特的膜结构可以穿透血脑屏障,源于生物的纳米颗粒易于被靶细胞摄取等,可以将负载的物质输送到损伤部位,从而更好地发挥治疗效果。但外泌体的靶向性有待进一步提高,化学键合修饰或基因工程修饰,可能是增强其靶向递送、避免副反应的有效方法,同时,如何调控药物的释放率,避免其短时聚集,也是未来研究的重点。 2.2.3 生物材料的预联合 目前外泌体常见的给药方式包括3种:静脉给药、局部注射和鼻腔给药。静脉注射的外泌体会在循环中被其他细胞所摄取,从而导致生物活性因子广泛扩散,产生不可忽视的副反应。鼻腔给药基于较明确的鼻-脑通路,但吸收率无法保证,且可能会使药物绕过脾脏等靶器官,影响疗效。局部注射的外泌体会在损伤部位短期蓄积,但保留率较低,重复注射会导致二次损伤。因此,通过工程化手段,将外泌体和生物材料相结合,开发一种更有效的外泌体输送方法,以实现外泌体持续、稳定的释放,在当前尤为重要[79]。 生物材料与细胞及药物等相结合,为脊髓损伤的修复提供了新方向。水凝胶作为生物材料的一类,已被广泛用作负载生长因子和细胞移植的载体,常用水凝胶可分为天然生物材料水凝胶、合成类水凝胶、自组装肽水凝胶等几类[80]。水凝胶与外泌体相结合,具备以下诸多优势:①水凝胶具备良好的生物相容性,可以发挥载体作用,负载外泌体到达损伤部位,降低外泌体的清除率;②水凝胶可以填补脊髓损伤后形成的空腔,恢复神经传导的内源性电信号;③水凝胶能补充损伤部位的细胞外基质,利于脊髓组织的再生和外泌体的输送;④水凝胶可以缓释外泌体,实现外泌体在病变部位的稳定递送,保持应激环境下外泌体的活性和生物功能[81-82]。故水凝胶与外泌体的预联合在脊髓损伤领域具有良好的应用前景。 (1)天然生物材料水凝胶:天然生物材料水凝胶包括胶原蛋白、纤维蛋白、明胶、壳聚糖、透明质酸及海藻酸盐等,具有生物相容性好,易于降解,可构成细胞外基质等优点。 纤维蛋白凝胶:纤维蛋白凝胶已被批准用于临床实践,具有可控的生物降解特性,其降解产物能促进细胞增殖,调节细胞黏附。HE等[83]通过混合等体积的纤维蛋白原和凝血酶制备纤维蛋白凝胶 (fibrin gel,FG),将过表达神经生长因子诱导蛋白(nerve growth factor inducible,VGF)的骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体掺入纤维蛋白凝胶(FG-Exo),移植到脊髓损伤部位进行外泌体递送,FG-Exo具备适合细胞浸润和迁移的多孔微结构,与脊髓组织的压缩模量相匹配,可以以液体形式注入并原位固化,填充病变部位,Gel-Exo在体内外均可促进少突胶质细胞的形成,并改善脊髓横断小鼠的运动功能。MU等[84]使用纤维蛋白凝胶封装人脐带间充质干细胞外泌体,对脊髓横断大鼠急性损伤阶段进行紧急治疗,可以为病变部位细胞外基质的损伤提供即时补充及完成外泌体的递送,此外泌体能缓解脊髓损伤大鼠氧化应激和炎症反应,促进神经组织再生,显著改善泌尿系统功能。 透明质酸水凝胶:透明质酸是细胞外基质的组成成分之一,脊髓组织的再生和外泌体的有效输送都需要补充细胞外基质。LI等[85]利用层粘连蛋白衍生的黏附肽(PPFLMLLKGSTR)对透明质酸水凝胶进行了修饰,得到可以高度保留外泌体的黏附性水凝胶(PGel),然后用PGel包裹人胎盘间充质干细胞外泌体(Exo-PGel),Exo-PGel在体外被证明具有模拟细胞外基质和持续释放外泌体的能力,在严重的大鼠大跨度脊髓横断模型中,Exo-PGel能使外泌体有效整合到大鼠脊髓中,并减轻炎症和氧化应激反应,获得显著的神经恢复和泌尿功能改善。在该团队的另一项研究中,收集缺氧预处理的人脐静脉内皮细胞源性外泌体,并使用PGel将缺氧预处理外泌体递送到脊髓病变处,外泌体在PGel中均匀分布,低氧预处理可以增加外泌体中缺氧诱导因子1α的表达,促进受体内皮细胞的血管化,局部植入负载缺氧预处理外泌体的PGel,可以有效促进脊髓横断大鼠病变部位的血管和神经再生[86]。 (2)人工合成水凝胶:人工合成水凝胶的材料来源十分广泛,常见的包括聚乳酸、聚乙二醇、聚己内酯、导电生物材料等,具备优越的可塑性,可根据需求对结构、强度、降解率及相关特性等进行精确调整。 甲基丙烯酰明胶水凝胶(gelatin methacryloyl,GelMA):甲基丙烯酰明胶水凝胶具有光交联特性及可控的力学和降解性能,在组织再生及脊髓损伤领域得到了广泛应用,通过制备3D GelMA用作移植的外泌体递送系统[87],收集骨髓间充质干细胞源性外泌体并将其负载到水凝胶上(GelMA-Exo),以微创注射将其输送到损伤部位,GelMA-Exo能填补脊髓空洞,实现外泌体的长期缓释,在体外可以促进神经干细胞的存活和神经分化,在脊髓损伤大鼠模型中,减少了胶质瘢痕的形成,增加了轴突生长,可有效促进脊髓损伤后神经功能恢复。 聚柠檬酸酯-聚乙烯亚胺水凝胶:WANG等[88]发现柠檬酸基聚合物具有生物相容性高、生物降解可控等优点,开发了一种可以在局部持续和稳定递送外泌体的热敏型可注射聚柠檬酸酯-聚乙烯亚胺水凝胶(polycitrate-polyethyleneimine hydrogel,FE),用于负载间充质干细胞外泌体(FE@Exo)治疗脊髓损伤,FE水凝胶表现出3D多孔形态并带有正电荷,为外泌体提供了负载空间和静电相互作用,FE@Exo具备热敏性、可注射性、自愈性和黏合性,其降解产物对脊髓损伤大鼠组织器官无毒副反应,细胞相容性良好,在脊髓损伤大鼠体内,FE@Exo在损伤部位对外泌体的保存和控释长达 56 d,可以通过调节局部微环境减轻炎症反应,抑制胶质瘢痕形成,促进髓鞘重塑和轴突再生,从而达到脊髓损伤后高效的组织修复和运动功能恢复。 导电水凝胶:导电水凝胶拥有类似组织的柔软性,还具备与神经系统相似的电传输特性,是一类有广阔应用前景的水凝胶材料。FAN等[89]开发了由光交联GelMA水凝胶和聚吡咯 (Polypyrrole,PPy) 水凝胶组成的双网络导电水凝胶(GMP),骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体通过可逆的非共价结合固定在GMP网络中,这种结合方式不会影响外泌体的结构和活性,形成GM/PPy/Exo水凝胶(GMPE),GMPE具有出色的生物黏附性,使用GMPE桥接横断脊髓时,可以部分恢复内源性电信号传输,GMPE水凝胶在脊髓损伤部位释放负载的外泌体可长达14 d。单纯使用不预载外泌体的GMP治疗脊髓损伤,可能会加重损伤部位的炎症反应,将GMPE水凝胶移植到脊髓损伤小鼠损伤部位,GMPE通过核转录因子κB通路调节小胶质细胞由M1向M2型极化,还能增强神经干细胞的神经元和少突胶质细胞分化,并激活PTEN/PI3K/AKT/mTOR通路促进轴突生长,共同促进脊髓半切小鼠的运动功能恢复。 水凝胶作为一种生物材料,自身可以对脊髓损伤发挥一定的治疗作用,如壳聚糖水凝胶能促进神经元分化和轴突生长,且水凝胶材料具备良好的生物相容性及机械特性,能填补脊髓损伤后细胞外基质的缺损,为外泌体的递送和细胞的黏附、生长提供必要的物质基础,外泌体联合水凝胶材料所构建的新型药物递送系统,不仅可以提高外泌体在损伤部位的保留率,还能实现外泌体的长期稳定递送,从而持续发挥外泌体的生物学功能,因此,基于组织工程技术,实现生物材料与外泌体的预联合是一种有前途的 脊髓损伤 治疗策略。现将外泌体联合生物材料治疗脊髓损伤的相关实验加以汇总,见表3。"
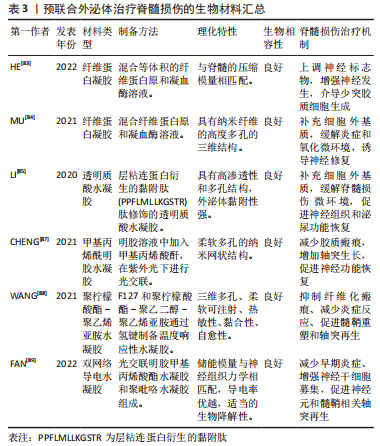

外泌体与生物材料的预联合,是当前组织工程技术成熟后产生的新发展方向,水凝胶等生物材料本身可以填补脊髓损伤后损伤的细胞外基质,为细胞提供黏附和生长的物质基础,一定程度上促进脊髓损伤的修复。将水凝胶与外泌体结合后,可以构建为新的外泌体负载系统,实现外泌体的靶向递送和超长时间缓释,持续作用于损伤部位并发挥治疗作用。此种预处理方法的关键在于水凝胶材料的制备,天然生物材料和人工材料各有利弊,天然材料生物相容性好,降解产物安全无毒,但存在可塑性差,机械强度不足及结构不稳定等缺点;人工合成材料具备优越的可塑性,机械模量和降解率可调节,但有细胞亲和力较差,降解产物可能会产生不良反应等弊端。故探寻综合两者优点的全新复合材料可能会是上述问题的最佳解决方案。 2.3 脊髓损伤领域外泌体常见的预处理措施总结 文章将脊髓损伤领域外泌体常见的预处理措施归纳为3类: 2.3.1 外泌体的预培养:包括三维培养和低氧预处理,三维培养为构建中空纤维生物反应器或球形支架等,模拟细胞的机体内生存环境,可以促进细胞增殖和外泌体分泌,不仅有效提高外泌体产量,还能增强外泌体的生物活性,在脊髓损伤中,展现出比二维培养外泌体更优越的神经保护作用。三维培养的主要问题在于培养基质的构建与外泌体的收集,安全性良好。低氧预处理即模拟机体低氧环境培养细胞,并收集此状态下产生的外泌体,能促使外泌体的内在成分差异表达,增强外泌体的生物学功能和活性,可以抑制脊髓损伤大鼠的神经炎症,减少神经元凋亡,但其内在活性物质不可控,可能会带来未知的副反应。 2.3.2 外泌体的预搭载:通过前装载及后装载的方式,将小分子药物、核酸类物质、蛋白质及生长因子等物质搭载到外泌体中,可以延长药物在体内的半衰期,实现药物的精准干预和稳定释放。小分子药物包括中药提取物及化学药物,可以避免其带来的全身不良反应,促使药物直达病所,在脊髓损伤大鼠体内,能抑制炎症因子表达,减少神经细胞凋亡。但载药的外泌体可能在非靶器官蓄积,导致生物毒性。核酸类物质包括非编码RNA和小干扰RNA,主要利用转染或过表达的方法进行转载,通过靶标分析工具,找到显著差异表达的RNA,并加以干预,可以实现对脊髓损伤损伤的精准治疗。根据负载非编码RNA和小干扰RNA的不同,在细胞凋亡、氧化应激及轴突再生等多个方面发挥对脊髓损伤的治疗作用,其安全问题主要为转染试剂存在毒性残留可能。蛋白质和生长因子除转染和过表达方式外,针对分子质量较大的,也可利用蛋白融合表达或相互作用进行转运,在脊髓损伤后血管生成和神经元保护中发挥着关键作用,但可能会影响外泌体表面膜蛋白的性质,存在一定的安全隐患。 2.3.3 外泌体与生物材料的预联合:将外泌体和生物材料相结合,构建出一种可以持续、稳定释放外泌体的新体系,同时发挥生物材料本身的修复填充作用。纤维蛋白、透明质酸等天然生物材料水凝胶,可以有效补充细胞外基质,填充病变部位,缓解脊髓损伤大鼠氧化应激和炎症反应,促进血管和神经再生,但天然材料机械强度不足,结构不稳定,无法实现外泌体的长期释放,在对急性损伤阶段进行紧急治疗时可发挥显著优势,但其快速分解可能导致外泌体蓄积,无法持续发挥修复作用。甲基丙烯酰明胶水凝胶、聚柠檬酸酯-聚乙烯亚胺水凝胶、聚吡咯双网络导电水凝胶并非单纯的人工合成水凝胶,均为复合型生物合成材料,一定程度上兼顾了生物相容性与脊髓力学特性,并可具备注射性、导电性等其他特性,可以实现搭载外泌体在损伤部位的超长周期释放,在脊髓损伤模型中,可填补脊髓空洞,减少胶质瘢痕,促进轴突再生,并恢复内源性电信号传输。实验中回馈细胞相容性良好,无毒副反应,主要问题在于材料的制备存在较大难度,其降解产物是否会带来不良反应尚无长期数据。 上述预处理措施均存在两面性,在带来良好治疗效果的同时,也不可避免存在一些弊端,但正因为如此,研究者们才要积极探索,解决上述问题,促进预处理外泌体的临床转化。"

| [1] ANJUM A, YAZID MD, FAUZI DAUD M, et al. Spinal cord injury: pathophysiology, multimolecular interactions, and underlying recovery mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7533. [2] QUADRI SA, FAROOQUI M, IKRAM A, et al. Recent update on basic mechanisms of spinal cord injury. Neurosurg Rev. 2020;43(2):425-441. [3] ROUANET C, REGES D, ROCHA E, et al. Traumatic spinal cord injury: current concepts and treatment update. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2017;75(6):387-393. [4] ZHANG Y, AL MAMUN A, YUAN Y, et al. Acute spinal cord injury: pathophysiology and pharmacological intervention (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(6):12056. [5] ASSINCK P, DUNCAN GJ, HILTON BJ, et al. Cell transplantation therapy for spinal cord injury. Nat Neurosci. 2017;20(5):637-647. [6] COFANO F, BOIDO M, MONTICELLI M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells for spinal cord injury: current options, limitations, and future of cell therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(11):2698. [7] GHAFOURI-FARD S, NIAZI V, HUSSEN BM, et al. The emerging role of exosomes in the treatment of human disorders with a special focus on mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9: 653296. [8] LIU WZ, MA ZJ, LI JR, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: therapeutic opportunities and challenges for spinal cord injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):102. [9] KHALATBARY AR. Stem cell-derived exosomes as a cell free therapy against spinal cord injury. Tissue Cell. 2021;71:101559. [10] PAN Z, SUN W, CHEN Y, et al. Extracellular vesicles in tissue engineering: biology and engineered strategy. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;e2201384. [11] KIM GU, SUNG SE, KANG KK, et al. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells (mscs) and msc-derived extracellular vesicles for the treatment of spinal cord injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(24):13672. [12] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Sci. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977. [13] ZHANG Y, BI J, HUANG J, et al. Exosome: a review of its classification, isolation techniques, storage, diagnostic and targeted therapy applications. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:6917-6934. [14] TSIAPALIS D, O’DRISCOLL L. Mesenchymal stem cell derived extracellular vesicles for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications. Cells. 2020;9(4):991. [15] BARILE L, VASSALLI G. Exosomes: therapy delivery tools and biomarkers of diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 2017;174:63-78. [16] MA ZJ, YANG JJ, LU YB, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: toward cell-free therapeutic strategies in regenerative medicine. World J Stem Cells. 2020;12(8):814-840. [17] FAMILTSEVA A, JEREMIC N, TYAGI SC. Exosomes: cell-created drug delivery systems. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019;459(1-2):1-6. [18] ALZHRANI GN, ALANAZI ST, ALSHARIF SY, et al. Exosomes: isolation, characterization, and biomedical applications. Cell Biol Int. 2021;45(9):1807-1831. [19] WANG L, PEI S, HAN L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes reduce a1 astrocytes via downregulation of phosphorylated NFκB P65 subunit in spinal cord injury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(4):1535-1559. [20] LANKFORD KL, ARROYO EJ, NAZIMEK K, et al. Intravenously delivered mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes target M2-type macrophages in the injured spinal cord. PLoS One. 2018;13(1):e0190358. [21] ZHAO T, SUN F, LIU J, et al. Emerging role of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in regenerative medicine. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;14(6):482-494. [22] YUAN X, WU Q, WANG P, et al. Exosomes derived from pericytes improve microcirculation and protect blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury in mice. Front Neurosci. 2019;13:319. [23] REN Z, QI Y, SUN S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: hope for spinal cord injury repair. Stem Cells Dev. 2020;29(23):1467-1478. [24] WANG X, ZHAI WT, ZHU JH, et al. Treatment of the bone marrow stromal stem cell supernatant by nasal administration-a new approach to EAE therapy. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):11. [25] ROMANELLI P, BIELER L, SCHARLER C, et al. Extracellular vesicles can deliver anti-inflammatory and anti-scarring activities of mesenchymal stromal cells after spinal cord injury. Front Neurol. 2019;10:1225. [26] HERTEL FC, SILVA ASD, SABINO AP, et al. Preconditioning methods to improve mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles in bone regeneration-a systematic review. Biology (Basel). 2022;11(5):733. [27] YU W, LI S, GUAN X, et al. Higher yield and enhanced therapeutic effects of exosomes derived from MSCs in hydrogel-assisted 3D culture system for bone regeneration. Biomater Adv. 2022; 133:112646. [28] FARUQU FN, LIAM-OR R, ZHOU S, et al. Defined serum-free three-dimensional culture of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells yields exosomes that promote fibroblast proliferation and migration in vitro. FASEB J. 2021;35(1):e21206. [29] ZHANG Y, CHOPP M, ZHANG ZG, et al. Systemic administration of cell-free exosomes generated by human bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured under 2D and 3D conditions improves functional recovery in rats after traumatic brain injury. Neurochem Int. 2017;111:69-81. [30] HAN M, YANG H, LU X, et al. Three-dimensional-cultured msc-derived exosome-hydrogel hybrid microneedle array patch for spinal cord repair. Nano Lett. 2022;22(15):6391-6401. [31] ABDOLLAHI S. Extracellular vesicles from organoids and 3D culture systems. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2021;118(3):1029-1049. [32] LIU W, RONG Y, WANG J, et al. Exosome-shuttled miR-216a-5p from hypoxic preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells repair traumatic spinal cord injury by shifting microglial M1/M2 polarization. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):47. [33] LIANG Y, WU JH, ZHU JH, et al. Exosomes secreted by hypoxia-pre-conditioned adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells reduce neuronal apoptosis in rats with spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2022;39(9-10):701-714. [34] LI L, MU J, ZHANG Y, et al. Stimulation by exosomes from hypoxia preconditioned human umbilical vein endothelial cells facilitates mesenchymal stem cells angiogenic function for spinal cord repair. ACS Nano. 2022;16(7):10811-10823. [35] KONG FL, WANG XP, LI YN, et al. The role of exosomes derived from cerebrospinal fluid of spinal cord injury in neuron proliferation in vitro. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(1):200-205. [36] PATIL SM, SAWANT SS, KUNDA NK. Exosomes as drug delivery systems: a brief overview and progress update. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2020;154:259-269. [37] MEHRYAB F, RABBANI S, SHAHHOSSEINI S, et al. Exosomes as a next-generation drug delivery system: An update on drug loading approaches, characterization, and clinical application challenges. Acta Biomater. 2020;113:42-62. [38] SUN Y, LIU G, ZHANG K, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes for drug delivery. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):561. [39] FAN Y, LI Y, HUANG S, et al. Resveratrol-primed exosomes strongly promote the recovery of motor function in SCI rats by activating autophagy and inhibiting apoptosis via the PI3K signaling pathway. Neurosci Lett. 2020;736:135262. [40] GAO ZS, ZHANG CJ, XIA N, et al. Berberine-loaded M2 macrophage-derived exosomes for spinal cord injury therapy. Acta Biomater. 2021;126:211-223. [41] CHEN J, ZHANG C, LI S, et al. Exosomes derived from nerve stem cells loaded with fty720 promote the recovery after spinal cord injury in rats by PTEN/AKT signal pathway. J Immunol Res. 2021;2021:8100298. [42] 邢昊楠,陆梅,刘瑛琪,等.基于外泌体的抗肿瘤药物靶向递送的研究进展[J].药学学报, 2022,57(1):150-158,277. [43] LU Y, YANG J, WANG X, et al. Research progress in use of traditional Chinese medicine for treatment of spinal cord injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;127:110136. [44] DING SQ, CHEN YQ, CHEN J, et al. Serum exosomal microRNA transcriptome profiling in subacute spinal cord injured rats. Genomics. 2020;112(6):5086-5100. [45] LI P, JIA Y, TANG W, et al. Roles of non-coding RNAs in central nervous system axon regeneration. Front Neurosci. 2021;15:630633. [46] YANG ZL, RAO J, LIN FB, et al. The role of exosomes and exosomal noncoding rnas from different cell sources in spinal cord injury. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022;16:882306. [47] KANG J, ZHANG C, ZHI Z, et al. Stem-like cells of various origins showed therapeutic effect to improve the recovery of spinal cord injury. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2020;48(1):627-638. [48] YU T, ZHAO C, HOU S, et al. Exosomes secreted from miRNA-29b-modified mesenchymal stem cells repaired spinal cord injury in rats. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2019;52(12):e8735. [49] REN ZW, ZHOU JG, XIONG ZK, et al. Effect of exosomes derived from MiR-133b-modified ADSCs on the recovery of neurological function after SCI. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(1):52-60. [50] XU G, AO R, ZHI Z, et al. miR-21 and miR-19b delivered by hMSC-derived EVs regulate the apoptosis and differentiation of neurons in patients with spinal cord injury. J Cell Physiol. 2019; 234(7):10205-10217. [51] KANG J, LI Z, ZHI Z, et al. MiR-21 derived from the exosomes of MSCs regulates the death and differentiation of neurons in patients with spinal cord injury. Gene Ther. 2019;26(12):491-503. [52] HUANG JH, XU Y, YIN XM, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-126-modified MSCs promote angiogenesis and neurogenesis and attenuate apoptosis after spinal cord injury in rats. Neuroscience. 2020;424:133-145. [53] LI C, LI X, ZHAO B, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-544-modified mesenchymal stem cells promote recovery after spinal cord injury. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2020;126(4):369-375. [54] JIANG D, GONG F, GE X, et al. Neuron-derived exosomes-transmitted miR-124-3p protect traumatically injured spinal cord by suppressing the activation of neurotoxic microglia and astrocytes. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020;18(1):105. [55] HUANG W, LIN M, YANG C, et al. Rat bone mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes loaded with mir-494 promoting neurofilament regeneration and behavioral function recovery after spinal cord injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:1634917. [56] CHANG Q, HAO Y, WANG Y, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-125a promotes M2 macrophage polarization in spinal cord injury by downregulating IRF5. Brain Res Bull. 2021;170:199-210. [57] JIANG Z, ZHANG J. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes containing miR-145-5p reduce inflammation in spinal cord injury by regulating the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell Cycle. 2021;20(10):993-1009. [58] CHEN Y, TIAN Z, HE L, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-26a-modified MSCs promote axonal regeneration via the PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway following spinal cord injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):224. [59] GE X, TANG P, RONG Y, et al. Exosomal miR-155 from M1-polarized macrophages promotes EndoMT and impairs mitochondrial function via activating NF-κB signaling pathway in vascular endothelial cells after traumatic spinal cord injury. Redox Biol. 2021;41(101932. [60] LI C, QIN T, LIU Y, et al. Microglia-derived exosomal microRNA-151-3p enhances functional healing after spinal cord injury by attenuating neuronal apoptosis via regulating the p53/p21/CDK1 signaling pathway. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:783017. [61] WANG Y, LAI X, WU D, et al. Umbilical mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes facilitate spinal cord functional recovery through the miR-199a-3p/145-5p-mediated NGF/TrkA signaling pathway in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):117. [62] ZHANG A, BAI Z, YI W, et al. Overexpression of miR-338-5p in exosomes derived from mesenchymal stromal cells provides neuroprotective effects by the Cnr1/Rap1/Akt pathway after spinal cord injury in rats. Neurosci Lett. 2021;761:136124. [63] ZHANG M, WANG L, HUANG S, et al. Exosomes with high level of miR-181c from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit inflammation and apoptosis to alleviate spinal cord injury. J Mol Histol. 2021;52(2):301-311. [64] HE X, ZHANG J, GUO Y, et al. Exosomal miR-9-5p derived from BMSCs alleviates apoptosis, inflammation and endoplasmic reticulum stress in spinal cord injury by regulating the HDAC5/FGF2 axis. Mol Immunol. 2022;145:97-108. [65] HUANG J, WU C, XU G, et al. The decreased expression of miR-429 in plasma exosomes after spinal cord injury inhibits neuronal apoptosis by mediating the PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway. Ann Transl Med. 2022;10(1):6. [66] LIU B, ZHENG W, DAI L, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomal miR-455-5p protects against spinal cord ischemia reperfusion injury. Tissue Cell. 2022;74:101678. [67] YE Y, HAO J, HONG Z, et al. Downregulation of microRNA-145-5p in activated microglial exosomes promotes astrocyte proliferation by removal of Smad3 inhibition. Neurochem Res. 2022;47(2):382-393. [68] ZHOU Z, LI C, BAO T, et al. Exosome-shuttled miR-672-5p from anti-inflammatory microglia repair traumatic spinal cord injury by inhibiting AIM2/ASC/Caspase-1 signaling pathway mediated neuronal pyroptosis. J Neurotrauma. 2022;39(15-16):1057-1074. [69] 周永新,翟文静,贾志强,等.miR-210-5p修饰间充质干细胞源外泌体促进大鼠脊髓损伤修复的机制 [J].实用医学杂志,2022,38(6):711-714. [70] LIU J, LIN M, QIAO F, et al. Exosomes derived from lncRNA TCTN2-modified mesenchymal stem cells improve spinal cord injury by miR-329-3p/IGF1R axis. J Mol Neurosci. 2022;72(3):482-495. [71] TIAN F, YANG J, XIA R. Exosomes secreted from circZFHX3-modified mesenchymal stem cells repaired spinal cord injury through mir-16-5p/IGF-1 in mice. Neurochem Res. 2022;47(7):2076-2089. [72] HUANG W, QU M, LI L, et al. SiRNA in MSC-derived exosomes silences CTGF gene for locomotor recovery in spinal cord injury rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):334. [73] LUO Y, XU T, LIU W, et al. Exosomes derived from GIT1-overexpressing bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote traumatic spinal cord injury recovery in a rat model. Int J Neurosci. 2021;131(2):170-182. [74] JIA Y, LU T, CHEN Q, et al. Exosomes secreted from sonic hedgehog-modified bone mesenchymal stem cells facilitate the repair of rat spinal cord injuries. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2021;163(8):2297-2306. [75] JIA Y, YANG J, LU T, et al. Repair of spinal cord injury in rats via exosomes from bone mesenchymal stem cells requires sonic hedgehog. Regen Ther. 2021;18:309-315. [76] 高钰,龚芷宁,郭宇恬,等.水凝胶结合生长因子在脊髓损伤修复中的作用 [J].中华实验外科杂志,2022,39(7):1413-1418. [77] LI S, LIAO X, HE Y, et al. Exosomes derived from NGF-overexpressing bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell sheet promote spinal cord injury repair in a mouse model. Neurochem Int. 2022;157:105339. [78] ZHONG D, CAO Y, LI C J, et al. Neural stem cell-derived exosomes facilitate spinal cord functional recovery after injury by promoting angiogenesis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020;245(1):54-65. [79] WANG X, BOTCHWAY BOA, ZHANG Y, et al. Combinational treatment of bioscaffolds and extracellular vesicles in spinal cord injury. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019;12:81. [80] 赵兴昌,宋世强,何峰,等.生物材料支架在治疗脊髓损伤中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(28):4562-4568. [81] SILVA D, SOUSA RA, SALGADO AJ. Hydrogels as delivery systems for spinal cord injury regeneration. Mater Today Bio. 2021;9:100093. [82] PISHAVAR E, LUO H, NASERIFAR M, et al. Advanced hydrogels as exosome delivery systems for osteogenic differentiation of mscs: application in bone regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(12):6203. [83] HE X, YANG L, DONG K, et al. Biocompatible exosome-modified fibrin gel accelerates the recovery of spinal cord injury by VGF-mediated oligodendrogenesis. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):360. [84] MU J, WU J, CAO J, et al. Rapid and effective treatment of traumatic spinal cord injury using stem cell derived exosomes. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2021;16(6):806-815. [85] LI L, ZHANG Y, MU J, et al. Transplantation of human mesenchymal stem-cell-derived exosomes immobilized in an adhesive hydrogel for effective treatment of spinal cord injury. Nano Lett. 2020;20(6):4298-4305. [86] MU J, LI L, WU J, et al. Hypoxia-stimulated mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes loaded by adhesive hydrogel for effective angiogenic treatment of spinal cord injury. Biomater Sci. 2022;10(7):1803-1811. [87] CHENG J, CHEN Z, LIU C, et al. Bone mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome-loaded injectable hydrogel for minimally invasive treatment of spinal cord injury. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2021; 16(18):1567-1579. [88] WANG C, WANG M, XIA K, et al. A bioactive injectable self-healing anti-inflammatory hydrogel with ultralong extracellular vesicles release synergistically enhances motor functional recovery of spinal cord injury. Bioactive Materials. 2021;6(8):2523-2534. [89] FAN L, LIU C, CHEN X, et al. Exosomes-loaded electroconductive hydrogel synergistically promotes tissue repair after spinal cord injury via immunoregulation and enhancement of myelinated axon growth. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(13):e2105586. [90] PAN D, LIU W, ZHU S, et al. Potential of different cells-derived exosomal microRNA cargos for treating spinal cord injury. J Orthop Translat. 2021;31:33-40. [91] JI W, JIANG W, LI M, et al. miR-21 deficiency contributes to the impaired protective effects of obese rat mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes against spinal cord injury. Biochimie. 2019;167:171-178. |
| [1] | Sun Kexin, Zeng Jinshi, Li Jia, Jiang Haiyue, Liu Xia. Mechanical stimulation enhances matrix formation of three-dimensional bioprinted cartilage constructs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | Nong Fuxiang, Jiang Zhixiong, Li Yinghao, Xu Wencong, Shi Zhilan, Luo Hui, Zhang Qinglang, Zhong Shuang, Tang Meiwen. Bone cement augmented proximal femoral nail antirotation for type A3.3 intertrochanteric femoral fracturalysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10. |
| [3] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-8. |
| [4] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [5] | Yang Jiujie, Li Zhi, Wang Shujie, Tian Ye, Zhao Wei. Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring of functional changes following durotomy with decompression for acute spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1232-1236. |
| [6] | Nie Chenchen, Su Kaiqi, Gao Jing, Fan Yongfu, Ruan Xiaodi, Yuan Jie, Duan Zhaoyuan, Feng Xiaodong. The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| [7] | Liu Xiaolin, Mu Xinyue, Ma Ziyu, Liu Shutai, Wang Wenlong, Han Xiaoqian, Dong Zhiheng. Effect of hydrogel-loaded simvastatin microspheres on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 998-1003. |
| [8] | Xu Xingxing, Wen Chaoju, Meng Maohua, Wang Qinying, Chen Jingqiao, Dong Qiang. Carbon nanomaterials in oral implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1062-1070. |
| [9] | Yang Yitian, Wang Lu, Yao Wei, Zhao Bin. Application of the interaction between biological scaffolds and macrophages in bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1071-1079. |
| [10] | Li Cheng, Zheng Guoshuang, Kuai Xiandong, Yu Weiting. Alginate scaffold in articular cartilage repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1080-1088. |
| [11] | Shi Yehong, Wang Cheng, Chen Shijiu. Early thrombosis and prevention of small-diameter blood vessel prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1110-1116. |
| [12] | Tang Haotian, Liao Rongdong, Tian Jing. Application and design of piezoelectric materials for bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1117-1125. |
| [13] | Xu Yan, Li Ping, Lai Chunhua, Zhu Peijun, Yang Shuo, Xu Shulan. Piezoelectric materials for vascularized bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1126-1132. |
| [14] | Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 840-845. |
| [15] | Li Xinyue, Li Xiheng, Mao Tianjiao, Tang Liang, Li Jiang. Three-dimensional culture affects morphology, activity and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 846-852. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||