Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (33): 5385-5393.doi: 10.12307/2023.687
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bidirectional interaction between inflammatory factors and dental pulp stem cells during bone regeneration
Xu Rongwei, Wang Hao, Fu Qiuyue, Lan Xingming, Yang Kun
- 遵义医科大学附属口腔医院牙周科,贵州省遵义市 563000
-
Received:2022-09-24Accepted:2022-10-12Online:2023-11-28Published:2023-03-30 -
Contact:Yang Kun, MD, Associate professor, Department of Periodontology, Hospital of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Xu Rongwei, Department of Periodontology, Hospital of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China Wang Hao, Department of Periodontology, Hospital of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Science and Technology Foundation of Guizhou Health Commission, No. gzwkj2022-169 (to YK); Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Fund Plan, No. [2020]1Y328 (to YK); Zunyi Science and Technology Plan Project, No. HZ(2021)302 (to YK)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Rongwei, Wang Hao, Fu Qiuyue, Lan Xingming, Yang Kun. Bidirectional interaction between inflammatory factors and dental pulp stem cells during bone regeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5385-5393.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
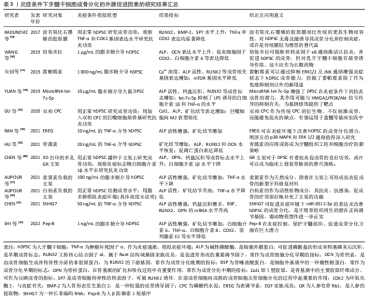
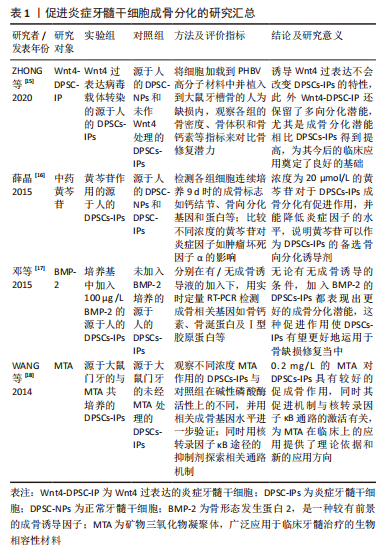
2.1 牙髓干细胞的特性 2.1.1 正常牙髓干细胞 牙髓干细胞是第一个明确的具有间充质特征和成骨分化潜能的牙源性间充质干细胞,起源于外胚层的神经嵴细胞[2,7]。目前首选酶消化法提取牙髓干细胞[8]。众所周知,在相应的诱导条件下,牙髓干细胞可分化为成牙本质细胞、神经细胞、成骨细胞等多种细胞类型,于牙髓再生、神经修复、组织工程以及转化医学等方面都具有应用价值[9]。其中在骨组织工程领域,研究者对牙髓干细胞的成骨分化潜能关注度很高,不少动物实验和体外实验都相继证明了牙髓干细胞胞外囊泡的促进成骨作用,以及细胞搭载的支架材料、注射凝胶、膜片等在骨再生治疗中的应用前景[6],尤其是针对相关支架的运用,有学者对近年来相关的临床前动物实验进行了回顾和Meta分析,肯定了牙髓干细胞的合成支架在治疗骨缺损中的有效性[10],说明牙髓干细胞成骨应用前景较为可观。与此同时,牙髓干细胞还具有免疫调节特性,它可以通过与T细胞等免疫细胞相互作用来调节免疫系统,还能分泌如白细胞介素6(interleukin-6,IL-6)、白细胞介素10(interleukin-10,IL-10),转化生长因子β(transforming growth factor-β,TGF-β)等抗炎因子,即使是已成骨分化的牙髓干细胞也有免疫调节能力[11],这一免疫特性对炎症反应乃至修复炎症性骨质缺损都有重大意义。 2.1.2 炎症牙髓干细胞 从炎症牙髓组织分离得到的牙髓干细胞为炎症牙髓干细胞(dental pulp stem cells from inflamed pulps,DPSCs-IPs),获取时也可以用酶消化法,且此法相比于生长法更有利于炎症牙髓干细胞成骨分化[12]。对于炎症牙髓干细胞的研究,最早可追溯至2010年学者第一次从患有不可逆性牙髓炎的恒牙牙髓中成功分离出干细胞,此后其相关的生物学特性等也逐渐被报道[13]。近年来的研究表明,炎症牙髓干细胞具有如免疫表型、集落形成能力、牙髓增殖再生、多向分化等牙源性间充质干细胞的典型特征[14],这使得长期被当成医疗废物扔弃的发炎的牙髓组织重获了临床应用价值,一些学者也针对如何人为地提高炎症牙髓干细胞的成骨潜力展开研究。例如由于Wnt信号通路在干细胞成骨分化过程中扮演了关键的角色,ZHONG等[15]构建了Wnt4过表达的炎症性牙髓干细胞(Wnt4-DPSC-IP)并用它治疗大鼠的牙槽骨缺损,发现其骨再生疗效优于一般的炎症牙髓干细胞,为推进日后炎症牙髓干细胞的应用提供了改进方案。类似的可以促进炎症牙髓干细胞成骨的还有中药黄芩苷[16]、人骨形态发生蛋白2(bone morphogenetic protein,BMP-2)[17]、矿物三氧化物凝聚体(mineral trioxide aggregate,MTA)等[18],详细的实验研究方法见表1。"

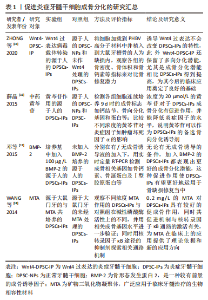
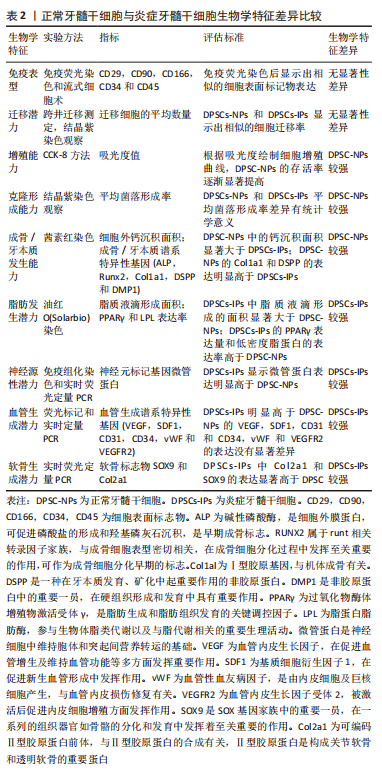
炎症牙髓干细胞也保留了一定的免疫调节特性,比如LEE等[19]发现炎症牙髓干细胞可以抑制巨噬细胞肿瘤坏死因子α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)的分泌,这种对巨噬细胞活化的免疫抑制作用可以避免过度炎症带来的损伤,同时吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶(indoleamine2,3-Dioxygenase,IDO)作为其中重要的介质,其表达水平在炎症牙髓干细胞中也较正常牙髓干细胞(dental pulp stem cells-normal pulps,DPSC-NPs)高。但是在最近的体外研究发现,炎症牙髓干细胞的IDO活性和对T细胞增殖的免疫调节能力却比正常牙髓干细胞要低[14],此发现与LEE等学者的报道产生矛盾,可靠的结果需日后在体内进一步验证和探索。当然,针对受损的免疫抑制能力的改善,SONODA等[20]发现干扰素γ(interferon-γ,IFN-γ)可以作为调节剂有效地提高炎症牙髓干细胞在体外的免疫抑制力。得益于自身的免疫特性,炎症牙髓干细胞可以释放一些炎症相关的细胞因子,值得注意的是,炎症牙髓干细胞表达的白细胞介素6水平高于正常牙髓干细胞,同时由于白细胞介素6的促进作用导致其成骨能力提高,该结果不仅说明了炎症牙髓干细胞较好的成骨潜力,同时也指明了白细胞介素6增强成骨的应用价值[21]。 2.1.3 正常牙髓干细胞对比炎症牙髓干细胞 近来有不少针对正常和炎症牙髓中牙髓干细胞的生物学特性做的对比研究,文章选取NIE等[22]较为全面可信的研究结果作为参考,总结了目前已知的两者差异,见表2。"
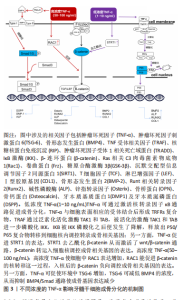
上述研究数据也有个别存在争议,如炎症牙髓干细胞的增殖速率和分化潜能,有人观察的结果是与正常牙髓干细胞相似[23],这些差异可能与炎症牙髓的状态、炎症来源、炎症强度和持续时间、分离培养方法以及个体之间遗传背景差异等众多因素有关,因此需要未来研究更大的样本量并控制相关因素来解释现下的矛盾之处。 从上述的特性和对比来看,正常牙髓干细胞和炎症牙髓干细胞都具有一定的免疫特性和成骨分化潜能,其他方向的分化潜能也各有强弱。正常牙髓干细胞的应用前景已被人们广泛认可,然而考虑到来源因素,炎症牙髓干细胞在临床上更易被获取应用,但是目前针对炎症性牙髓干细胞生物学特性的研究报道具有一定争议,相关的临床试验也较少,这些都是未来需要进一步研究的方向。 2.2 炎症因素对牙髓干细胞成骨分化的影响 炎症作为一把“双刃剑”,其诱导的损伤和修复往往不可分割[24]。牙髓组织常处于炎症环境中,使得牙髓干细胞的成骨分化能力也受此影响,比如除了众人熟知的牙髓炎以外,牙周炎也可以影响牙髓干细胞。据报道,患有侵袭性牙周炎的患者尽管牙周受损,但只要患牙内的牙髓活力尚未完全丧失,那么从中获取的牙髓干细胞就仍然保留有分化为成骨细胞表型的潜力[25],有研究近一步表明,这种成骨潜力不仅被保留,还由于促炎因子长期维持的炎症环境和应激反应蛋白的表达使得成骨分化潜能不减反增,这其中涉及到细胞骨架重塑的相关机制[26]。但是后来的研究得出,受牙周炎影响的牙髓干细胞成骨潜力没有改变,而软骨生成潜力、生长速度和迁移能力都降低[27]。由此看来,相关结论存在矛盾之处,牙周炎是一个复杂的且因人而异的炎症过程,针对牙周炎究竟对牙髓干细胞成骨分化造成何种影响,还需要更多样本量和更多牙周炎类型的实验去证实。尽管目前知晓的就炎症因素本身如何影响牙髓干细胞成骨的相关机制尚不全面,但是近来很多学者对一些外源性刺激因子如何介导并影响在炎症环境下牙髓干细胞的成骨分化进行了深入探索,包括各类介质、药物、生物材料、调控基因等。 2.2.1 促进成骨分化的炎症递质 炎症环境中存在很多炎症递质,它们是作用于牙髓干细胞成骨分化的重要媒介。白三烯B4(leukotriene B4,LTB4)是一种有效的炎症递质,属于中性粒细胞激活剂,它有刺激免疫反应、招募吞噬细胞、调节细胞因子等众多功能,研究发现白三烯B4能激活LTB4/BLT2机制来诱导牙髓干细胞产生矿化结节,还可通过Runt相关转录因子2(Runt-related transcription factor 2,RUNX2)和整合素结合唾液蛋白(integrinbinding sialoprotein,Ibsp)表达的增加促进细胞增殖和分化[28]。 白细胞介素10是一种抗炎因子,在炎症修复和骨骼稳态中起着关键作用,有研究表明白细胞介素10可激活牙髓干细胞中的氧化磷酸化过程(从糖酵解到氧化磷酸化),同时还能激活ERK/P-ERK/核转录因子κB通路,这些都与促进牙髓干细胞的成骨分化有关[29]。白细胞介素37作为炎症反应和免疫反应的天然抑制剂,与骨代谢相关的炎症因子存在一定联系,据报道[30],它可显著上调牙髓干细胞中牙本质涎磷蛋白(dentin sialophosphoprotein,DSPP)、Runt相关转录因子2、碱性磷酸酶和Osterix蛋白的蛋白质水平,这表明白细胞介素37能够正向诱导牙髓干细胞的成骨分化。 肿瘤坏死因子α是一种主要的促炎细胞因子,有研究表明肿瘤坏死因子α能刺激牙髓干细胞的成骨分化,此过程中,信号转导因子和转录激活因子3(signal transducer and activator of transcription 3,STAT3)在细胞核中表达增加,而在细胞质中表现出相反的现象,与此同时miR-21的表达增加与信号转导因子和转录激活因子3之间存在正反馈作用,二者共同促进了炎症微环境中牙髓干细胞的成骨分化[31]。肿瘤坏死因子α还可激活核转录因子κB通路来刺激牙髓干细胞成骨分化,当使用二硫氨基甲酸肽吡咯烷(核转录因子κB抑制剂)时,可以阻断肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的成骨分化[32]。然而有趣的发现是,低浓度肿瘤坏死因子α通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路促进人牙髓干细胞的成骨分化,而高浓度则会抑制成骨,此过程与调节因子NAD-依赖性去乙酰化酶(NAD-dependent deacetylase sirtuin-1,SIRT1)密切相 关[33],同时高浓度抑制成骨的潜在机制远不止于此。目前已知的肿瘤坏死因子α双重作用于牙髓干细胞成骨分化的机制见图3。"

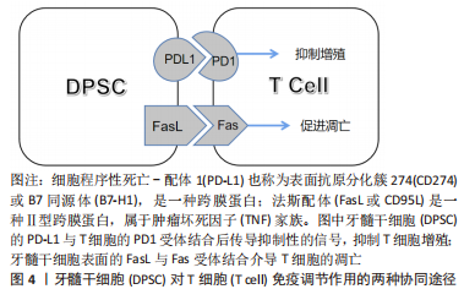
有学者发现,人β防御素1短基序Pep-B作为有抗炎和免疫调节特性的阳离子肽,对脂多糖模拟的炎症条件下的人牙髓干细胞有促进成骨作用[34],其过程抑制了核转录因子κB和P38丝裂原活化蛋白酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)途径介导的炎症的激活,说明人β防御素1短基序Pep-B有促进炎症环境下的人牙髓干细胞分化与成骨矿化的潜在价值。表皮调节素(epiregulin,EREG)是表皮生长因子家族成员,有学者证实表皮调节素在炎症环境下通过改善磷酸化MAPK和磷酸化的细胞外信号调节激酶(extracellular signal regulated kinases,ERK)的表达来调节MAPK信号通路,维持了人牙髓干细胞的成骨分化水平,增添了用生长因子调节牙髓干细胞于炎症中的成骨潜能的可行性[35]。 青蒿素作为熟知的抗疟疾药物,还能在缺氧和炎症环境下恢复牙髓干细胞的成骨分化能力,同时可以再次激活已失活的Wnt信号通路,具体机制与碳酸酐酶9的上调密切相关,该结果为青蒿素治疗牙髓干细胞奠定了重要基础[36]。姜黄素是一类抗炎抗菌的天然药剂,将其负载在支架上作用于炎症条件下的牙髓干细胞,不仅能发挥其抗炎抗菌的生物特性,还能诱导人牙髓干细胞的成骨矿化,这对于牙髓修复材料的开发提供了新思路[37]。人参皂苷Rb1(Ginsenoside Rb1,GR)是人参的提取物,常用于骨质缺损的修复,有学者将其负载于3D打印的陶瓷复合材料的支架上形成多孔GR支架,并将牙髓干细胞播种其上,植入于人造股骨缺损的兔模型中,发现GR支架不仅能够促进牙髓干细胞的增殖,还具有抑制炎症和促进骨修复的功效[38],类似的研究还有白杨素支架[39],这些都是药物和支架联合运用的良好成果。倍他米松作为糖皮质激素是一种常见的抗炎药物,有文献指出其可抑制核转录因子κB信号的激活帮助牙髓干细胞具有抗炎作用[40],还能在炎症条件下促进人牙髓干细胞成骨,但是需要强调的是,它对乳牙牙髓干细胞有诱导破骨的趋势,而对牙髓干细胞却没有此趋势,两者为何有此区别值得深入研究。雷帕霉素是一种新型大环内酯类免疫抑制剂,它除了抗免疫排斥反应之外,对牙髓干细胞炎症状态下的成骨也具有一定的促进作用,具体机制主要涉及ERK1/2及JNK通路的抑制等[41]。这些研究体现出用药物提高牙髓干细胞炎症下成骨的策略广受学者关注。 磷酸钙水泥作为牙科修复材料一直被不断地改良,有人构建出含有β-磷酸三钙(β-tricalcium phosphate,β-TCP)的新型双相磷酸钙骨水泥[42-43],相比传统的磷酸钙骨水泥,β-磷酸三钙可以使巨噬细胞向M2表型极化从而避免炎症,同时双相磷酸钙骨水泥更能促进人牙髓干细胞的分化与矿物沉积。胶原膜是治疗牙周和种植体周骨缺损、引导骨再生的重要材料,用能影响干细胞增殖分化的氧化石墨烯涂层可提高其生物性能,研究发现涂有氧化石墨烯的胶原膜对牙髓干细胞无细胞毒性,不仅促进人牙髓干细胞的成骨分化,还能控制肿瘤坏死因子α和环氧合酶2介导的炎症,相较于传统的胶原膜无疑是一次成功的修饰和改良[44]。 基因调控对于炎症环境中牙髓干细胞的成骨分化也值得探讨。据报道,SNHG7作为一种可以增强干细胞成骨分化的长非编码RNA,能促进炎症环境下miR-6512-3p的表达来改善人牙髓干细胞的成骨分化,这为牙髓干细胞成骨发掘了潜在的基因调节的靶点[45]。MicroRNA let-7c-5p作为一种内源性非编码调控因子,其对炎症环境下的牙髓干细胞也具有抗炎促成骨的积极作用等[46]。 2.2.3 抑制成骨分化 相较于促进因素,抑制牙髓干细胞炎症下成骨分化的外源性因素的研究较少。炎症过程被认为是牙本质-牙髓复合物愈合和再生的先决条件,早期炎症反应是牙髓细胞的保护机制[24]。然而有研究发现,长期接触促炎因子干扰素γ显著减弱了牙髓干细胞中碱性磷酸酶的活性(成骨标志),而当使用干扰素γ抑制剂预处理时碱性磷酸酶的活性得到了改善[47],这表明长期炎症会损害牙髓干细胞的成骨矿化能力。 肿瘤坏子因子α作为重要炎症递质之一,在低浓度时可以促进牙髓干细胞的成骨分化,在高浓度下则变为抑制作用[48]。FENG等[49]发现,肿瘤坏子因子α可以通过增加RAC1蛋白的表达发挥抑制作用。肿瘤坏死因子α刺激基因6(tumor necrosis factorαstimulated gene 6,TSG-6)的表达水平以及骨形态发生蛋白4/Smad通路也是潜在机制之一,肿瘤坏子因子α诱导TSG-6产生,当TSG-6的表达水平增加时,骨形态发生蛋白4/Smad信号通路相关蛋白质随之减少,成骨标志物的表达也减少,在TSG-6基因敲除后则相反,也就是说,高水平的肿瘤坏子因子α能促进TSG-6的表达来抑制牙髓干细胞的骨形态发生蛋白4 / Smad信号通路,并随之抑制其成骨分化[50]。 G蛋白信号转导激活因子(activators of G protein signaling 3,AGS3)与环磷腺苷效应元件结合蛋白(cAMP-response element binding protein,CREB)的磷酸化有关,它可以负向调控cAMP/PKA/CREB信号通路从而抑制在肿瘤坏死因子α影响下的牙髓干细胞的成骨分化[51],但相关机制局限于肿瘤坏死因子α介导的炎症条件,对于复杂的炎症环境来说略显片面。炎症环境中往往存在一些促进细胞凋亡的因子,B淋巴细胞瘤-2基因(B-cell lymphoma 2,Bcl-2),作为一种抗凋亡基因正好可以提高牙髓干细胞在炎症中的存活率,然而更重要的发现是Bcl-2基因在抗凋亡的同时还损害了牙髓干细胞的成骨分化潜力,这对未来Bcl-2基因的运用明显设限[52]。有些抑制因素的研究,虽未设有炎症前提,但其本身可以触发炎症因子的释放,比如樟脑醌作为一种用于牙科材料的聚合粘接光引发剂,有研究表明其可以诱导牙髓产生促炎因子以引发炎症,同时还能抑制牙髓干细胞的成骨分化,这也启示临床应避免含光引发剂的材料直接盖髓[53]。 总之,炎症因素对牙髓干细胞成骨分化具有双重作用,其中涉及了复杂的炎症递质、细胞因子和信号通路。早期炎症是牙髓干细胞的一种保护机制,可以促进牙髓干细胞成骨分化以抵御骨质破坏,但长期持续的、高强度的炎症则会抑制其成骨分化。近来的研究多集中于探索牙髓干细胞炎症环境下成骨的促进因素,尤其集中于非炎症介质的其他外源因子,由此看来,如何让牙髓干细胞在炎症条件下保持高效的成骨分化能力是当下的一大研究热点。 2.3 牙髓干细胞对炎症的作用 2.3.1 调节炎症的免疫活性 牙髓干细胞的免疫调节能力高度可塑,且由微环境中炎症递质的种类和浓度决定[54]。已有学者较为详细地阐述了口腔间充质干细胞对于炎症微环境的双重反应: 较低炎症水平下促进炎症产生和骨吸收,较高炎症水平则出现相反的现象,即抑制炎症产生和骨吸收,其过程涉及了肥大细胞、树突状细胞、自然杀伤细胞、巨噬细胞(M1和M2表型)、T细胞和B细胞等,干细胞还可以通过细胞间直接接触和微环境中可溶性的细胞因子发挥其免疫调节作用,包括转化生长因子β1、前列腺素E2、吲哚胺2,3-二加氧酶(IDO)、一氧化氮、白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6和白细胞介素10 [55]。不同的表面蛋白可存在不同的调节机制。程序性细胞死亡配体1(programmed death-ligand 1,PD-L1)是抑制免疫系统激活的重要蛋白,炎症微环境下牙髓干细胞的程序性细胞死亡配体1上调,其与程序性死亡受体PD1结合可调节T细胞反应来协调炎症,Fas / FasL途径也参与其中[56],两者的协同作用见图4。"
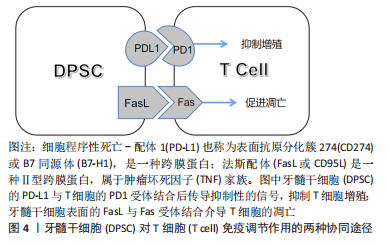
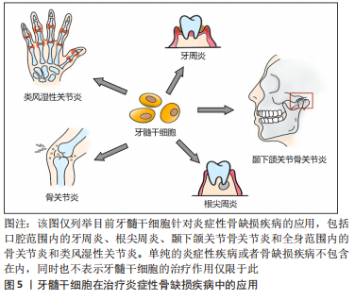
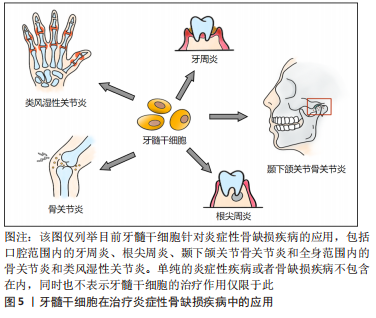
Fas配体(Fas ligand,FasL)是肿瘤坏死因子家族中的一种Ⅱ型跨膜蛋白,与Fas受体结合后可在许多细胞类型中诱导凋亡过程。牙髓干细胞可以表达Fas配体以诱导T细胞凋亡[57](目前只在骨髓间充质干细胞中报道过详细机制[58]),同时Fas/FasL通路还被证明有促进人牙髓干细胞软骨分化的作用[59]。由此可见,在炎症环境下牙髓干细胞的免疫调节机制极其复杂,不同免疫调节途径间存在串扰和协同作用,这些无疑是未来研究炎症调节机制的重要方向。 2.3.2 治疗口腔炎症 由于牙髓干细胞的免疫调节和抗炎潜力,将牙髓干细胞用于治疗炎症性疾病已经成为了一个新兴的、涵盖多学科的研究领域。在口腔范围内,牙髓干细胞的牙髓再生作用对不可逆性牙髓炎有着天然的治疗优势,已有临床试点研究展现出这种再生性治疗的可行性[60-61]。与此同时,牙髓干细胞的成骨分化潜能对于炎症性疾病导致的骨组织缺损的再生修复也值得关注,下文对将牙髓干细胞用于治疗口腔炎症性骨缺损的相关研究进展作总结。 牙髓治疗失败易造成根管内细菌感染,引发根尖周炎症而破坏根尖周骨组织,虽然根管治疗是目前普遍的治疗方案,但是再生性治疗更为理想。有学者通过回顾3份以注射性支架递送的、源于人第三磨牙的正常牙髓干细胞为治疗手段的根尖周病变病例,发现在牙髓干细胞的诱导下,患者不仅能形成成熟的根尖、愈合根尖周的大面积骨缺损,还在没有其他并发症的前提下比传统治疗方式更加省时[62]。这项结果为临床治疗方案提供了新思路,是牙髓干细胞运用的良好开端,但稍有不足的是缺乏了一些炎症水平变化的指标,因而无从知晓牙髓干细胞的免疫调节特性是否在此发挥作用。 牙周炎是龈下生物膜引起的炎症和免疫反应,会导致牙槽骨和牙周韧带的不可逆性破坏[63]。针对其治疗,相比于牙周膜干细胞来源有限、发炎时免疫调节能力受损的缺点[64],牙髓干细胞更具有应用价值。HU等[65]建立牙周炎猪模型,发现正常的人牙髓干细胞注射和人牙髓干细胞片植入治疗可诱导牙周组织再生,且人牙髓干细胞片疗效更佳。在临床应用中,也有学者用患者自体需拔除的牙的正常牙髓组织作为牙髓干细胞来源,对牙周骨缺陷的案例进行再生治疗,最终的骨增量结果也对牙髓干细胞的疗效给予了肯定[66]。当然,炎症牙髓干细胞作为临床上更易获取的一类干细胞,其对牙周炎所致骨缺损的修复作用也在逐渐被人们探索,比如同一个研究团队先后在临床牙周-牙髓病变患者和小猪标准牙周炎模型中,分别用人和猪自体的炎症牙髓干细胞和支架材料结合进行治疗,结果都显示出炎症牙髓干细胞成骨分化能力和良好的牙周骨质修复效果[67-68],为炎症牙髓干细胞未来应用于临床当中提供了证据。除了牙髓干细胞本身,还有研究表明牙髓干细胞分泌的外泌体也对牙周炎具有一定的治疗作用,实验中,牙髓干细胞来源的外泌体不仅可以加速牙周炎小鼠模型的牙槽骨愈合,还可以将巨噬细胞从促炎表型转化为抗炎表型以调节炎症反应,这种抗炎促成骨的双重作用为牙周炎的治疗提供了新方案[69]。 颞下颌关节骨关节炎(temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis,TMJOA)是口腔颌面部的一种常见的慢性炎症性退行性病变,严重炎症、进行性软骨和髁突骨骼破坏是TMJOA典型病理变化。目前其病因多样且机制未明,炎症因素和机械应力等都与它密切相关,而继发性炎症因素是疾病发生和进展的关键。由于目前对于此病多为药物治疗,虽能缓解症状但不能从根本上修复骨软骨缺损,因此近来不乏干细胞再生疗法的相关报道[70]。有动物实验(在大鼠关节腔内注射化学试剂建立TMJOA模型)发现正常人牙髓干细胞可以减少进行性TMJOA中肿瘤坏死因子α和干扰素γ的表达,并且可缓解痛觉过敏和滑膜炎症,减轻软骨基质降解,并诱导骨再生;由于调节炎症的转录激活因子1 (STAT1) 参与了TMJOA进展过程中基质金属蛋白酶的调节,体外研究中也发现牙髓干细胞可以有效抑制转录激活因子1的激活,导致基质金属蛋白酶3和基质金属蛋白酶13的下调,从而缓解炎症,这证实了牙髓干细胞对TMJOA的局部注射疗效[71]。另外,针对机械应力如颞下颌关节紊乱病导致的TMJOA,牙髓干细胞可以通过分泌一些如肝细胞生长因子等多种治疗因子,不仅能够减轻滑膜和颞肌的炎症,还能再生修复机械应力损伤的髁突软骨和软骨下骨质,由此看来,牙髓干细胞有望成为重度TMJOA患者的再生治疗方案[72]。 2.3.3 治疗全身炎症 不仅在口腔范围内,牙髓干细胞对全身炎性疾病也有极大的治疗价值。比如,作为备受关注且当下仍在传播的感染性肺部炎症——2019年新型冠状病毒病(Corona Virus Disease 2019,COVID-19),牙髓干细胞就被报道可作为其潜在的干细胞治疗策略[73]。诸如此类的研究还有很多[4],此处仅罗列可造成(软)骨破坏的全身炎症性疾病。 骨关节炎是一种伴有软骨丢失的退行性和炎性关节疾病,软骨的完全再生一直是治疗难点。而牙髓干细胞的软骨分化、免疫调节等特性对骨关节炎有着潜在治疗价值,诸多实验皆已证明其应用潜力[74]。深究其治疗机制,发现牙髓干细胞在体外可以通过抑制巨噬细胞的活化来减轻炎症,其中涉及了肝细胞生长因子、转化生长因子β1的分泌和MAPK信号的多条传导途径的失活;而在兔骨关节炎模型的体内实验也进一步印证了巨噬细胞被抑制的结果,同时还发现牙髓干细胞可以减轻软骨损伤和骨软骨病变,最终达到修复骨损伤和抗炎的疗效[75]。 类风湿性关节炎是可导致关节软骨和骨破坏的自身免疫性疾病,具有滑膜增生和慢性炎症的特点。研究类风湿性关节炎的小鼠模型[由胶原Ⅱ型抗体(CAIA)诱导]和来自人乳牙牙髓干细胞的培养基(SHED-CM)的学者发现,SHED-CM可以降低小鼠模型的促炎细胞因子的水平、抑制破骨细胞的形成和骨质破坏,并诱导抗炎M2型巨噬细胞的极化[76],说明在SHED-CM中存在乳牙牙髓干细胞分泌的因子,它们对类风湿性关节炎具有潜在的疗效。乳牙牙髓干细胞是牙髓干细胞的一种特殊类型,可以由此类推牙髓干细胞具有修复类风湿性关节炎的潜力。 综上,牙髓干细胞调节炎症的免疫活性机制还具有很大的研究空间,尤其针对不同调节途径之间的相互协同和串扰作用。牙髓干细胞的成骨分化协同抗炎潜能对于治疗炎症性骨缺损的意义重大,然而相关的临床应用研究却不是很多,见图5。"
| [1] XUE N, DING X, HUANG R, et al. Bone tissue engineering in the treatment of bone defects. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022;15(7):879. [2] ERCAL P, PEKOZER GG, KOSE GT. Dental stem cells in bone tissue engineering: current overview and challenges. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1107:113-127. [3] FAWZY EK, ELSALAWY R, IBRAHIM N, et al. The dental pulp stem/progenitor cells-mediated inflammatory-regenerative axis. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2019;25(5):445-460. [4] YAMADA Y, NAKAMURA-YAMADA S, KUSANO K, et al. Clinical potential and current progress of dental pulp stem cells for various systemic diseases in regenerative medicine: a concise review. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. doi: 10.3390/ijms20051132. [5] 刘雪梅,刘尧,陈旭.牙源性干细胞与炎症相互作用研究进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2015,8(1):52-55. [6] 魏代福,魏馨蕊,赵戬.与牙髓干细胞相关的骨组织工程研究进展[J].中国医学创新,2022,19(14):171-175. [7] HUANG X, LI Z, LIU A, et al. Microenvironment influences odontogenic mesenchymal stem cells mediated dental pulp regeneration. Front Physiol. 2021;12:656588. [8] PILBAUEROVÁ N, SOUKUP T, SUCHÁNKOVÁ KT, et al. Enzymatic isolation, amplification and characterization of dental pulp stem cells. Folia Biol (Praha). 2019;65(3):124-133. [9] NUTI N, CORALLO C, CHAN BM, et al. Multipotent differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells: a literature review. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2016;12(5):511-523. [10] LORUSSO F, INCHINGOLO F, DIPALMA G, et al. Synthetic scaffold/dental pulp stem cell (dpsc) tissue engineering constructs for bone defect treatment: an animal studies literature review. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. doi:10.3390/ijms21249765. [11] HOSSEIN-KHANNAZER N, HASHEMI SM, NAMAKI S, et al. Study of the immunomodulatory effects of osteogenic differentiated human dental pulp stem cells. Life Sci. 2019;216:111-118. [12] GOPINATH VK, SOUMYA S, JAYAKUMAR MN. Osteogenic and odontogenic differentiation potential of dental pulp stem cells isolated from inflamed dental pulp tissues (I-DPSCs) by two different methods. Acta Odontol Scand. 2020;78(4): 281-289. [13] 赵华翔,赵珊梅,辛欣,等.炎症牙髓干细胞:起步研究与未来发展[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(23):3756-3761. [14] INOSTROZA C, VEGA-LETTER AM, BRIZUELA C, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from human inflamed dental pulp exhibit impaired immunomodulatory capacity in vitro. J Endod. 2020;46(8):1091-1098. [15] ZHONG T, GAO Y, QIAO H, et al. Elevated osteogenic potential of stem cells from inflammatory dental pulp tissues by Wnt4 overexpression for treating bone defect in rats. Ann Palliat Med. 2020;9(5):2962-2969. [16] 薛晶.中药黄芩苷对炎症牙髓干细胞增殖及牙向/骨向分化的影响及机制研究[D].南京:南京医科大学,2015. [17] 邓云贞,李珏丹,魏虹,等.BMP-2促进人炎症牙髓干细胞骨向诱导分化的体外研究[J].口腔生物医学,2015,6(2):71-77. [18] WANG Y, YAN M, FAN Z, et al. Mineral trioxide aggregate enhances the odonto/osteogenic capacity of stem cells from inflammatory dental pulps via NF-κB pathway. Oral Dis. 2014;20(7):650-658. [19] LEE S, ZHANG QZ, KARABUCAK B, et al. DPSCs from inflamed pulp modulate macrophage function via the TNF-α/IDO Axis. J Dent Res. 2016;95(11):1274-1281. [20] SONODA S, YAMAZA H, MA L, et al. Interferon-gamma improves impaired dentinogenic and immunosuppressive functions of irreversible pulpitis-derived human dental pulp stem cells. Sci Rep. 2016;6:19286. [21] PARK YT, LEE SM, KOU X, et al. The role of interleukin 6 in osteogenic and neurogenic differentiation potentials of dental pulp stem cells. J Endod. 2019; 45(11):1342-1348. [22] NIE SC, YANG K, LUAN NN, et al. Unveiling the differences in biological properties of dental pulp stem cells from normal and inflamed pulp: a comprehensive comparative study. Med Sci Monit. 2022;28:e934511. [23] PEREIRA LO, RUBINI MR, SILVA JR, et al. Comparison of stem cell properties of cells isolated from normal and inflamed dental pulps. Int Endod J. 2012;45(12): 1080-1090. [24] COOPER PR, HOLDER MJ, SMITH AJ. Inflammation and regeneration in the dentin-pulp complex: a double-edged sword. J Endod. 2014;40(4 Suppl):S46-S51. [25] SUN HH, CHEN B, ZHU QL, et al. Investigation of dental pulp stem cells isolated from discarded human teeth extracted due to aggressive periodontitis. Biomaterials. 2014;35(35):9459-9472. [26] TOMASELLO L, MAUCERI R, COPPOLA A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from inflamed dental pulpal and gingival tissue: a potential application for bone formation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):179. [27] FAGEEH HN. Preliminary evaluation of proliferation, wound healing properties, osteogenic and chondrogenic potential of dental pulp stem cells obtained from healthy and periodontitis affected teeth. Cells. 2021. doi:10.3390/cells10082118. [28] DA SF, DE CAMPOS CLG, DE OLIVEIRA F, et al. Leukotriene B(4) loaded in microspheres regulate the expression of genes related to odontoblastic differentiation and biomineralization by dental pulp stem cells. BMC Oral Health. 2022;22(1):45. [29] YUAN L, YOU H, QIN N, et al. Interleukin-10 modulates the metabolism and osteogenesis of human dental pulp stem cells. Cell Reprogram. 2021;23(5):270-276. [30] LI N, YAN M, CHEN Y, et al. Extracellular IL-37 promotes osteogenic and odontogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells via autophagy. Exp Cell Res. 2021;407(1):112780. [31] XU K, XIAO J, ZHENG K, et al. MiR-21/STAT3 signal is involved in odontoblast differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells mediated by TNF-α. Cell Reprogram. 2018;20(2):107-116. [32] FENG X, FENG G, XING J, et al. TNF-α triggers osteogenic difion of human dental pulp stem cells via the NF-κB signalling pathway. Cell Biol Int. 2013;37(12):1267-1275. [33] FENG G, ZHENG K, SONG D, et al. SIRT1 was involved in TNF-α-promoted osteogenic differentiation of human DPSCs through Wnt/β-catenin signal. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2016;52(10):1001-1011. [34] SHI J, HU Z, ZHOU Y, et al. Therapeutic potential of synthetic human β-defensin 1 short motif pep-B on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human dental pulp stem cells. Mediators Inflamm. 2022;2022:6141967. [35] RAN R, YANG H, CAO Y, et al. Depletion of EREG enhances the osteo/dentinogenic differentiation ability of dental pulp stem cells via the p38 MAPK and Erk pathways in an inflammatory microenvironment. BMC Oral Health. 2021;21(1):314. [36] HU HM, MAO MH, HU YH, et al. Artemisinin protects DPSC from hypoxia and TNF-α mediated osteogenesis impairments through CA9 and Wnt signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2021;277:119471. [37] ALIPOUR M, FADAKAR S, AGHAZADEH M, et al. Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of curcumin-loaded endodontic reparative material. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2021;35(9):e22854. [38] CHEN CY, SHIE MY, LEE AK, et al. 3D-printed ginsenoside rb1-loaded mesoporous calcium silicate/calcium sulfate scaffolds for inflammation inhibition and bone regeneration. Biomedicines. 2021;9(8):907. [39] ALIPOUR M, POUYA B, AGHAZADEH Z, et al. The antimicrobial, antioxidative, and anti-inflammatory effects of polycaprolactone/gelatin scaffolds containing chrysin for regenerative endodontic purposes. Stem Cells Int. 2021;2021:3828777. [40] WANG D, ZHU NX, QIN M, et al. Betamethasone suppresses the inflammatory response in LPS-stimulated dental pulp cells through inhibition of NF-κB. Arch Oral Biol. 2019;98:156-163. [41] 朱钊,宋佳欣,单兆臣.雷帕霉素在炎症状态下对牙髓干细胞分化能力的影响研究[J].北京口腔医学,2019,27(4):186-190. [42] GU Y, XIE X, ZHUANG R, et al. A biphasic calcium phosphate cement enhances dentin regeneration by dental pulp stem cells and promotes macrophages M2 phenotype in vitro. Tissue Eng Part A. 2021;27(17-18): 1113-1127. [43] GU Y, ZHUANG R, XIE X, et al. Osteogenic stimulation of human dental pulp stem cells with self-setting biphasic calcium phosphate cement. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020;108(4):1669-1678. [44] RADUNOVIC M, DE COLLI M, DE MARCO P, et al. Graphene oxide enrichment of collagen membranes improves DPSCs differentiation and controls inflammation occurrence. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(8):2312-2320. [45] CHEN W. SNHG7 promotes the osteo/dentinogenic differentiation ability of human dental pulp stem cells by interacting with hsa-miR-6512-3p in an inflammatory microenvironment. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;581:46-52. [46] YUAN H, ZHAO H, WANG J, et al. MicroRNA let-7c-5p promotes osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells by inhibiting lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation via HMGA2/PI3K/Akt signal blockade. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2019;46(4):389-397. [47] STROJNY C, BOYLE M, BARTHOLOMEW A, et al. Interferon gamma-treated dental pulp stem cells promote human mesenchymal stem cell migration in vitro. J Endod. 2015;41(8):1259-1264. [48] QIN Z, FANG Z, ZHAO L, et al. High dose of TNF-α suppressed osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J Mol Histol. 2015;46(4-5):409-420. [49] FENG G, SHEN Q, LIAN M, et al. RAC1 regulate tumor necrosis factor-α-mediated impaired osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells. Dev Growth Differ. 2015;57(7):497-506. [50] WANG Y, YUAN S, SUN J, et al. Inhibitory effect of the TSG-6 on the BMP-4/Smad signaling pathway and odonto/osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;128:110266. [51] XING J, LIAN M, SHEN Q, et al. AGS3 is involved in TNF-αmedicated osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells. Differentiation. 2015;89(5):128-136. [52] HENG B C, YE X, LIU Y, et al. Effects of recombinant overexpression of bcl2 on the proliferation, apoptosis, and osteogenic/odontogenic differentiation potential of dental pulp stem cells. J Endod. 2016;42(4): 575-583. [53] KIM RH, WILLIAMS DW, BAE S, et al. Camphorquinone inhibits odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp cells and triggers release of inflammatory cytokines. J Endod. 2013;39(1):57-61. [54] WANG Y, CHEN X, CAO W, et al. Plasticity of mesenchymal stem cells in immunomodulation:pathological and therapeutic implications. Nat Immunol. 2014;15(11):1009-1016. [55] ZHOU LL, LIU W, WU YM, et al. Oral mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells:the immunomodulatory masters. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:1327405. [56] DI TINCO R, BERTANI G, PISCIOTTA A, et al. Role of PD-L1 in licensing immunoregulatory function of dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):598. [57] ZHAO Y, WANG L, JIN Y, et al. Fas ligand regulates the immunomodulatory properties of dental pulp stem cells. J Dent Res. 2012;91(10):948-954. [58] AKIYAMA K, CHEN C, WANG D, et al. Mesenchymal-stem-cell-induced immunoregulation involves FAS-ligand-/FAS-mediated T cell apoptosis. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;10(5):544-555. [59] PISCIOTTA A, BERTANI G, BERTONI L, et al. Modulation of cell death and promotion of chondrogenic differentiation by Fas/FasL in human dental pulp stem cells (hDPSCs). Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:279. [60] MEZA G, URREJOLA D, SAINT J N, et al. Personalized cell therapy for pulpitis using autologous dental pulp stem cells and leukocyte platelet-rich fibrin: a case report. J Endod. 2019;45(2):144-149. [61] NAKASHIMA M, IOHARA K, MURAKAMI M, et al. Pulp regeneration by transplantation of dental pulp stem cells in pulpitis: a pilot clinical study. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):61. [62] SHIEHZADEH V, AGHMASHEH F, SHIEHZADEH F, et al. Healing of large periapical lesions following delivery of dental stem cells with an injectable scaffold: new method and three case reports. Indian J Dent Res. 2014;25(2):248-253. [63] KWON T, LAMSTER IB, LEVIN L. Current concepts in the management of periodontitis. Int Dent J. 2021;71(6):462-476. [64] LIU D, XU J, LIU O, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from inflamed periodontal ligaments exhibit impaired immunomodulation. J Clin Periodontol. 2012;39(12):1174-1182. [65] HU J, CAO Y, XIE Y, et al. Periodontal regeneration in swine after cell injection and cell sheet transplantation of human dental pulp stem cells following good manufacturing practice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):130. [66] AIMETTI M, FERRAROTTI F, GAMBA M N, et al. Regenerative treatment of periodontal intrabony defects using autologous dental pulp stem cells: a 1-year follow-up case series. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2018;38(1):51-58. [67] LI Y, ZHAO S, NAN X, et al. Repair of human periodontal bone defects by autologous grafting stem cells derived from inflammatory dental pulp tissues. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):141. [68] LI Y, NAN X, ZHONG TY, et al. Treatment of periodontal bone defects with stem cells from inflammatory dental pulp tissues in miniature swine. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;16(2):191-200. [69] SHEN Z, KUANG S, ZHANG Y, et al. Chitosan hydrogel incorporated with dental pulp stem cell-derived exosomes alleviates periodontitis in mice via a macrophage-dependent mechanism. Bioact Mater. 2020;5(4):1113-1126. [70] ZHAO Y, XIE L. An update on mesenchymal stem cell-centered therapies in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Stem Cells Int. 2021;2021:6619527. [71] CUI S J, ZHANG T, FU Y, et al. DPSCs attenuate experimental progressive tmj arthritis by inhibiting the STAT1 pathway. J Dent Res. 2020;99(4):446-455. [72] NOGASAWARA N, KANK F, HASHIMOTO N, et al. Factors secreted from dental pulp stem cells show multifaceted benefits for treating experimental temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(6): 831-841. [73] ZAYED M, IOHARA K. Immunomodulation and regeneration properties of dental pulp stem cells: a potential therapy to treat coronavirus disease 2019. Cell Transplant. 2020;29:2138944793. [74] FERNANDES TL, CORTEZ D SJ, FRISENE I, et al. Systematic review of human dental pulp stem cells for cartilage regeneration. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2020;26(1):1-12. [75] LI PL, WANG YX, ZHAO ZD, et al. Clinical-grade human dental pulp stem cells suppressed the activation of osteoarthritic macrophages and attenuated cartilaginous damage in a rabbit osteoarthritis model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021; 12(1):260. [76] ISHIKAWA J, TAKAHASHI N, MATSUMOTO T, et al. Factors secreted from dental pulp stem cells show multifaceted benefits for treating experimental rheumatoid arthritis. Bone. 2016;83:210-219. |
| [1] | Fang Xingyan, Tian Zhenli, Zhao Zheyi, Wen Ping, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and sphingosine kinases 1/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling axis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | Nong Fuxiang, Jiang Zhixiong, Li Yinghao, Xu Wencong, Shi Zhilan, Luo Hui, Zhang Qinglang, Zhong Shuang, Tang Meiwen. Bone cement augmented proximal femoral nail antirotation for type A3.3 intertrochanteric femoral fracturalysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10. |
| [3] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-8. |
| [4] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [5] | Cai Zhihao, Xie Zhaoyong. Femoral neck anteversion measurement assessment: how to establish a unified method and standard [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1448-1454. |
| [6] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [7] | Tang Liang, Li Xiheng, Niu Ruijuan, Li Xinyue, Zou Xinying, Mao Tianjiao, Li Jiang. Naringin regulates the function of RAW264.7 macrophages to affect the osteogenic differentiation of MC-3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1205-1210. |
| [8] | Yang Jiujie, Li Zhi, Wang Shujie, Tian Ye, Zhao Wei. Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring of functional changes following durotomy with decompression for acute spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1232-1236. |
| [9] | Yang Zhishan, Tang Zhenglong. YAP/TAZ, a core factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, is involved in bone formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| [10] | Wang Ji, Zhang Min, Yang Zhongya, Zhang Long. A review of physical activity intervention in type 2 diabetes mellitus with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1272-1277. |
| [11] | Song Hehua, Wei Zairong. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: research and therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1278-1285. |
| [12] | Nie Chenchen, Su Kaiqi, Gao Jing, Fan Yongfu, Ruan Xiaodi, Yuan Jie, Duan Zhaoyuan, Feng Xiaodong. The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| [13] | Liang Jiaqi, Liu Hengxu, Yang Jinxin, Yang Yi, Deng Xuhui, Tan Mingjian, Luo Jiong. Health benefit relationship between exercise and intestinal bacteria [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1292-1299. |
| [14] | Gao Yu, Han Jiahui, Ge Xin. Immunoinflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [15] | Xu Xingxing, Wen Chaoju, Meng Maohua, Wang Qinying, Chen Jingqiao, Dong Qiang. Carbon nanomaterials in oral implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1062-1070. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||