Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (32): 5137-5143.doi: 10.12307/2023.577
Previous Articles Next Articles
Huangqi Guizhi Wuwu Decoction attenuates mitochondrial damage and oxidative stress in intervertebral disc endplate chondrocytes
Dong Jiaan1, Liu Ruyin2, Yue Zongjin2, Xu Xiangyang2, Wang Zhengzhen1
- 1College of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; 2Department of Spine, Henan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Second Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
-
Online:2023-11-18Published:2023-03-23 -
Contact:Liu Ruyin, Master, Chief physician, Department of Spine, Henan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Second Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Dong Jiaan, Master candidate, College of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the Special Fund of Traditional Chinese Medicine Research of Henan Province in 2022, No. 2022ZY1092 (to LRY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Dong Jiaan, Liu Ruyin, Yue Zongjin, Xu Xiangyang, Wang Zhengzhen. Huangqi Guizhi Wuwu Decoction attenuates mitochondrial damage and oxidative stress in intervertebral disc endplate chondrocytes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(32): 5137-5143.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
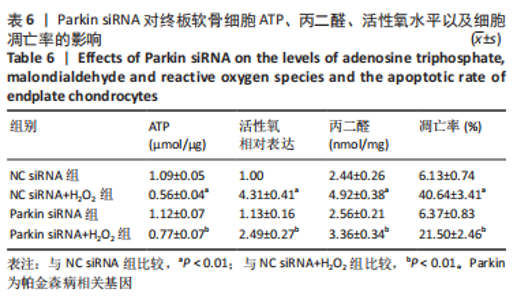
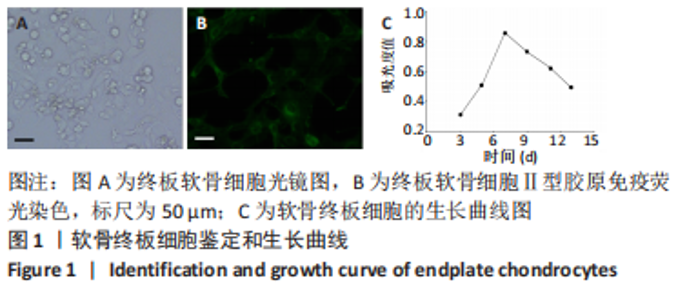
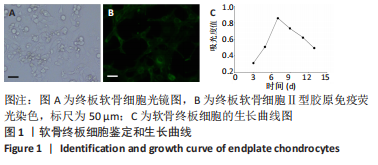
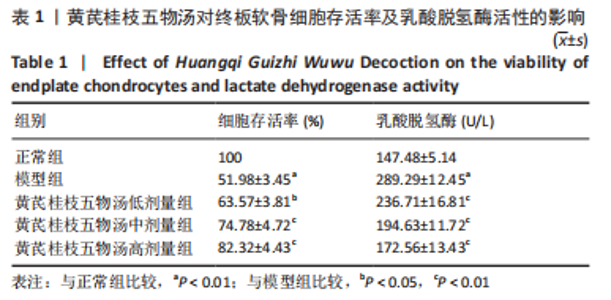
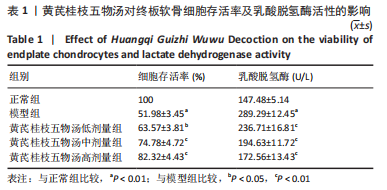
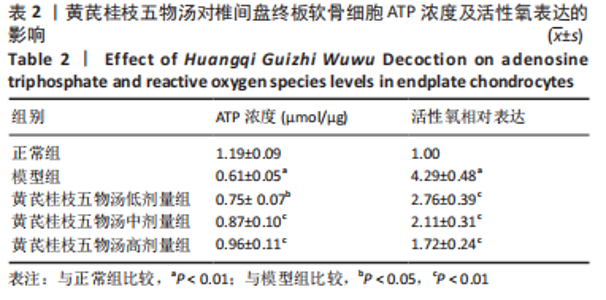
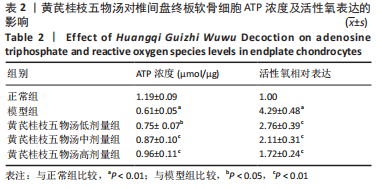
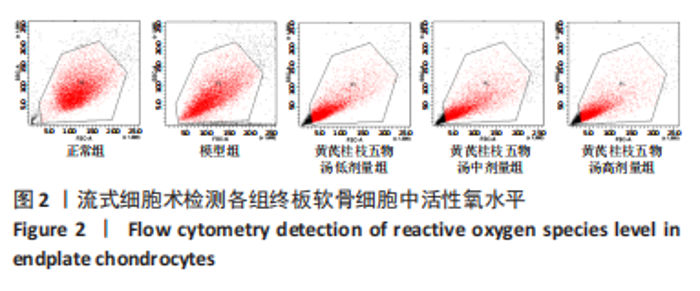
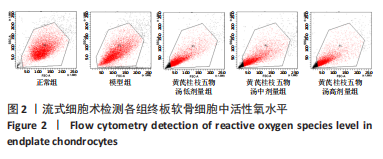
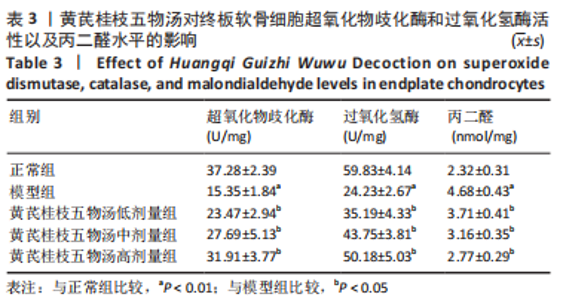
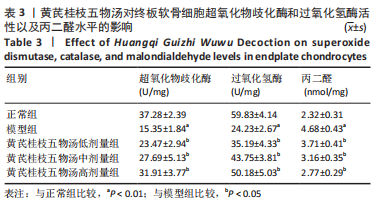
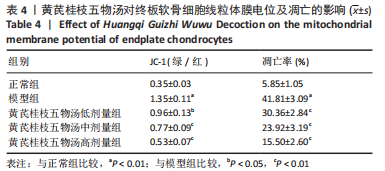
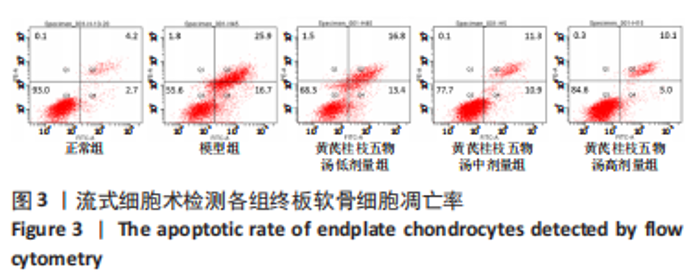
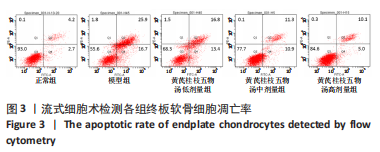
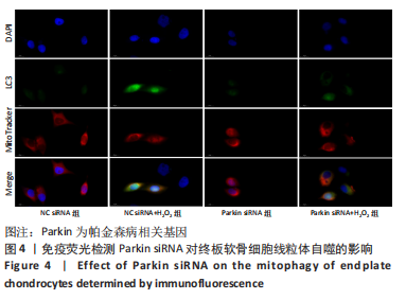
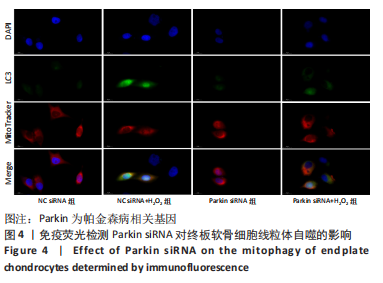
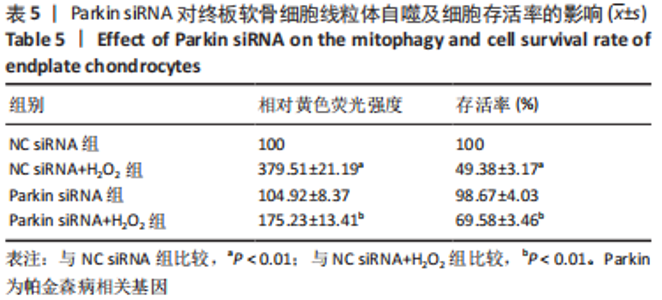
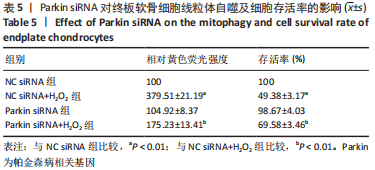
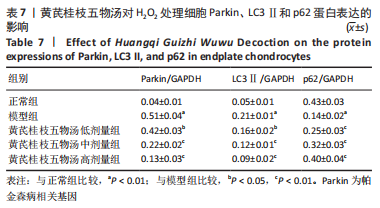
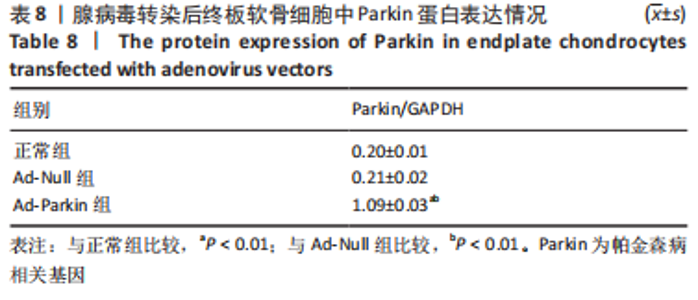
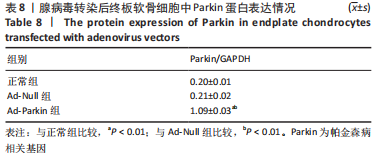
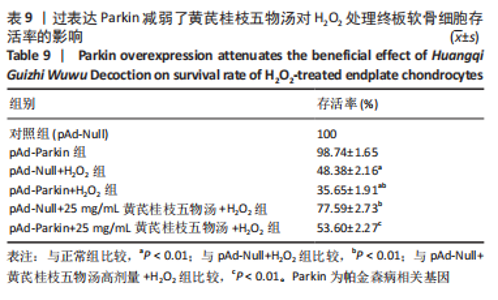
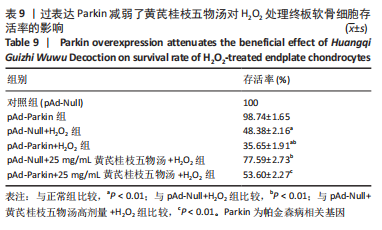
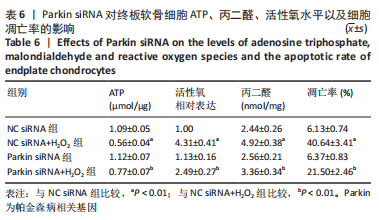
2.9 Parkin siRNA对H2O2处理细胞存活率的影响 与NC siRNA+H2O2组比较,Parkin siRNA+H2O2组细胞存活率显著升高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01),结果如表5所示。 2.10 Parkin siRNA对H2O2处理细胞ATP、丙二醛和活性氧水平以及细胞凋亡率的影响 与NC siRNA+H2O2组比较,Parkin siRNA+H2O2组细胞ATP浓度显著升高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01);而Parkin siRNA+H2O2组细胞活性氧、丙二醛水平以及细胞凋亡率与NC siRNA+H2O2组相比显著降低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01),结果如表6所示。"
| [1] NICK KN, CANDIDO KD, VLAEYEN J, et al. Low back pain. Lancet (London, England). 2021;398(10294):78-92. [2] KIRNAZ S, CAPADONA C, WONG T, et al. Fundamentals of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. World Neurosurg. 2022;157:264-273. [3] KAMALI A, ZIADLOU R, LANG G, et al. Small molecule-based treatment approaches for intervertebral disc degeneration: Current options and future directions. Theranostics. 2021;11(1):27-47. [4] CAZZANELLI P, WUERTZ-KOZAK K. MicroRNAs in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration, Apoptosis, Inflammation, and Mechanobiology. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(10):3601. [5] ASHINSKY BG, BONNEVIE ED, MANDALAPU SA, et al. Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Is Associated With Aberrant Endplate Remodeling and Reduced Small Molecule Transport. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(8):1572-1581. [6] 陈胜, 陈明珏, 林嗣雄, 等. 线粒体功能障碍在椎间盘退变中的作用[J]. 生物骨科材料与临床研究,2021,18(3):1-5. [7] 刘祺, 杨舟, 朱青安. 氧化应激与椎间盘退变的研究进展[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2020,38(3):363-366. [8] JIANG Z, WEI L, ZENG Q, et al. High glucose-induced excessive reactive oxygen species promote apoptosis through mitochondrial damage in rat cartilage endplate cells. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(9):2476-2483. [9] HE F, GAI J, WANG J, et al. Atrial natriuretic peptide protects vertebral endplate chondrocytes against H2O2 induced apoptosis and oxidative stress through activation of the Nrf2/HO1 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2021;24(5):754. [10] 李泽君, 呼丹, 熊克朝, 等. 活性氧与线粒体损伤研究概述 [J]. 中南药学, 2014,12(10):989-993. [11] LIANG K, SLA B, JLAB C, et al. Parkin and Nrf2 prevent oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in intervertebral endplate chondrocytes via inducing mitophagy and anti-oxidant defenses - ScienceDirect. Life Sci. 2020;243:117244. [12] SUNDE RA, THOMPSON KM, FRITSCHE KL, et al. Minimum Selenium Requirements Increase When Repleting Second-Generation Selenium-Deficient Rats but Are Not Further Altered by Vitamin E Deficiency. Biol Trace Element Res. 2016;177(1):139-147. [13] 陈科, 吕小华, 林健静, 等. 自噬在大鼠椎间盘软骨终板退变中的作用[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2021,14(7):632-637. [14] 李文超, 林一峰, 沈国喜, 等. 软骨终板细胞凋亡的影响因素及其调控途径的研究进展[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2019,27(4):85-88. [15] 陈舰舰, 周临东, 谢林. 基于“肝主筋”理论治疗椎间盘退变探讨[J]. 浙江中医药大学学报,2013,37(6):832-834. [16] 李杰辉, 雒晓东. 基于黄煌医案的黄芪桂枝五物汤方证研究[J]. 中医杂志, 2017,58(3):215-217. [17] 李鑫, 曹建中, 满荣勇, 等. 黄芪桂枝五物汤治疗类风湿关节炎的研究进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2021,27(6):176-181. [18] 方颖, 王亚东, 周雯, 等. 黄芪桂枝五物汤对糖尿病周围神经病变大鼠模型AGEs/RAGE/NF-κB信号通路的影响[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2020,26(13):52-58. [19] 邓博文, 李筱叶, 蒋昇源, 等.黄芪桂枝五物汤对颈椎病和焦虑症“异病同治”作用机制的网络药理学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(23):3650-3656. [20] 唐晓栋, 樊成虎. 黄芪桂枝五物汤治疗脊髓型颈椎病27例[J]. 现代中医药, 2013,33(3):41-42. [21] 李园琦, 林海, 罗红蓉, 等. 线粒体自噬与骨髓间充质干细胞成软骨分化的关联[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(31):4954-4960. [22] 靳晓飞, 高维娟. PINK1/Parkin介导线粒体自噬对缺血性脑卒中作用的研究进展[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2020,40(11):2447-2451. [23] 林祎嘉, 程丽珍, 苗雅. 线粒体自噬异常在阿尔茨海默病中的作用及机制研究综述[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版),2022,42(3):387-392. [24] LAN T, ZHENG YC, LI ND, et al. CRISPR/dCas9-Mediated Parkin Inhibition Impairs Mitophagy and Aggravates Apoptosis of Rat Nucleus Pulposus Cells Under Oxidative Stress. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;15(8):674632. [25] ZHU HL, SHI XT, XU XF, et al. Environmental cadmium exposure induces fetal growth restriction via triggering PERK-regulated mitophagy in placental trophoblasts. Environ Int. 2021;147:106319. |
| [1] | Fang Xingyan, Tian Zhenli, Zhao Zheyi, Wen Ping, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and sphingosine kinases 1/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling axis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-8. |
| [3] | Cao Sheng, Kong Lingwei, Xu Kun, Sun Zhijie. Correlation of cervical sagittal force line parameters with degenerative segment and Pfirrmann classification in patients with cervical intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1319-1324. |
| [4] | You Zhengqiu, Zhang Zhongzu, Wang Qunbo. Early symptomatic intervertebral disc pseudocysts after discectomy detected on MRI [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1403-1409. |
| [5] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [6] | Nie Chenchen, Su Kaiqi, Gao Jing, Fan Yongfu, Ruan Xiaodi, Yuan Jie, Duan Zhaoyuan, Feng Xiaodong. The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| [7] | Liang Jiaqi, Liu Hengxu, Yang Jinxin, Yang Yi, Deng Xuhui, Tan Mingjian, Luo Jiong. Health benefit relationship between exercise and intestinal bacteria [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1292-1299. |
| [8] | Ruan Ling, Wang Guanghua, Wu Rongping, Jin Zhan, Lyu Zhenqing, Zhang Nan, Li Shoubang. Correlation between exercise intensity and lipid metabolism disorder and oxidative stress in a high-diet rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1149-1155. |
| [9] | Lian Shilin, Zhang Yan, Jiang Qiang, Zhang Hanshuo, Li Tusheng, Ding Yu. Interventional effects of whole blood and platelet-rich plasma with different preparation methods on nucleus pulposus cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1199-1204. |
| [10] | Tian Qinyu, Tian Xinggui, Tian Zhuang, Sui Xiang, Liu Shuyun, Lu Xiaobo, Guo Quanyi. Protection of manganese oxide nanoparticles for bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell spreading against oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 821-826. |
| [11] | Li Zhichao, Tan Guoqing, Su Hui, Xu Zhanwang, Xue Haipeng. Regulatory role of non-coding RNAs as potential therapeutic targets in spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 758-764. |
| [12] | He Qi, Pan Zhaofeng, Chen Baihao, Yang Junzheng, Li Shaocong, Zeng Jiaxu, Zhou Chi, Wang Haibin. Establishment of chondrocyte model of iron overload and the mechanism of injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(32): 5126-5132. |
| [13] | Jiang Shengyuan, Zhang Yaqi, Bi Jingxin, Zhang Chengfei, Zhang Qiue, Mu Xiaohong, Bai Huizhong, Zuo Xinwei, Liu Tonghua, Qin Lingling. Tangbikang reduces sciatic nerve oxidative stress injury in a rat model of diabetic peripheral neuropathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(32): 5162-5167. |
| [14] | Yang Chaoqiang, Zhang Hulin, Wang Xiaomin, Wang Liang, Wang Yican. Prevention and treatment of bone-related diseases by regulating macrophages with Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 5064-5070. |
| [15] | Liu Xin, Sun Tianze, Zhang Jing, Zhang Wentao, Li Zhonghai. Research and advance in intervertebral disc annulus fibrosus repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 5078-5084. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||