Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (26): 4214-4222.doi: 10.12307/2023.530
Previous Articles Next Articles
Activation of cannabinoid receptors promotes periodontal healing by regulating periodontal inflammation and bone remodeling
Zhao Yuan, Zhai Haoyan, Liu Chunyan
- Department of Orthodontics, School and Hospital of Stomatology, Hebei Medical University, Hebei Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Hebei Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2022-08-05Accepted:2022-09-21Online:2023-09-18Published:2023-01-28 -
Contact:Liu Chunyan, MD, Associate chief physician, Associate professor, Department of Orthodontics, School and Hospital of Stomatology, Hebei Medical University, Hebei Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Hebei Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Zhao Yuan, Master candidate, Department of Orthodontics, School and Hospital of Stomatology, Hebei Medical University, Hebei Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Hebei Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:Hebei Provincial Key R&D Program, No. 21377715D (to LCY [project participant]); Hebei Provincial Government Supported Project of Training Excellent Talents in Clinical Medicine, No. 361029 (to LCY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhao Yuan, Zhai Haoyan, Liu Chunyan. Activation of cannabinoid receptors promotes periodontal healing by regulating periodontal inflammation and bone remodeling[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(26): 4214-4222.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

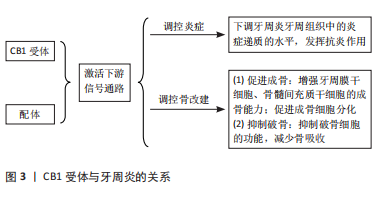
2.1 CB1受体和牙周炎的关系 2.1.1 CB1受体和牙周组织炎症的关系 CB1受体与配体结合后,可通过下调牙周组织中的炎症递质水平调控牙周炎。有研究表明,CB1受体在发炎组织的愈合中具有调节作用[40]。 KONERMANN等[41]研究表明,CB1受体与配体结合后可导致牙周组织的炎症减少。CP55940是CB1受体的激动剂,它通过激活CB1受体促进人牙龈成纤维细胞的伤口愈合[42]。虽然CB1受体在牙周组织中表达较少,但可以通过介导抗炎相关细胞途径参与对炎症反应的保护作用[37]。OSSOLA等[38]应用CB1受体选择性激动剂甲酰胺于大鼠牙周炎实验模型中,发现甲酰胺可减少牙槽骨丢失和炎症参数。AEA可以减少牙周炎牙龈组织中肿瘤坏死因子α的产生,使用CB1受体拮抗剂AM251可以减弱AEA的作用[43]。AEA剂量依赖性地减少脂多糖诱导的人牙龈成纤维细胞中白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8和单核细胞趋化蛋白1(MCP-1)的产生。此外,通过预处理大麻素CB1和CB2受体的有效和选择性拮抗剂,即AM251和SR144528,AEA的作用减弱,表明大麻素受体参与介导AEA诱导的人牙龈成纤维细胞抗炎作用[37]。过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体(peroxisome proliferator-activated Receptors,PPAR)是核激素受体家族中的配体激活受体[44]。在炎症反应中,PPAR-γ抑制炎症信号通路和炎症递质的产生[45]。PPAR-γ的激活,通常与CB1受体的激活相结合,可以介导大麻素的抗炎,镇痛,代谢,神经保护,抗肿瘤和心血管作用[46]。 CB1受体在牙周组织中表达较少,但可以通过介导一些细胞途径激活机体的一系列抗炎反应,减少牙周组织中炎症递质的产生,进而减少牙槽骨吸收。但是由于分布在牙周组织中的主要为CB2受体,所以在牙周炎的发生发展过程中CB2受体发挥主要的炎症调控作用。 2.1.2 CB1受体和牙槽骨骨改建的关系 CB1受体参与骨组织中的骨骼调节和骨代谢。据报道,在大鼠牙周炎模型中,使用CB1受体特异性激动剂AEA类似物治疗可显著减轻牙槽骨的丢失[38]。OSSOLA等[38]应用CB1受体选择性激动剂甲酰胺于大鼠牙周炎实验模型中,发现甲酰胺可减少牙槽骨丢失和炎症参数。 CB1受体主要通过影响成骨细胞的分化调控牙槽骨骨改建。YAN等[47]研究了CB1受体拮抗剂AM251在炎症环境中抑制牙周膜干细胞(PDLSCs)中的成牙/成骨分化能力。CB1受体在小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化过程中被激活,CB1受体增强骨髓间充质干细胞的早期成骨能力并影响其在急性应激期间的存活率[48-49]。一项研究报道,CB1受体调节小鼠的骨髓间充质干细胞迁移/归巢,且骨髓间充质干细胞功能可以通过CB1受体特异性激动剂ACEA增强,并被CB1特异性拮抗剂AM281削弱[50]。PPAR可以调节骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化,由于PPAR-γ的激活通常与CB1受体的激活相结合,所以CB1受体一定程度上也可以促进成骨细胞的形成[51]。 CB1受体可以促进炎症状态下牙周膜细胞的成骨能力,促进成骨细胞的形成,减少骨丢失。但是,CB1受体在牙周组织中少有分布,牙周组织中成骨细胞、破骨细胞、骨细胞分布的主要为CB2受体,所以CB2受体在牙周炎骨改建中似乎发挥更为明显的作用。CB1受体与牙周炎的关系见图3,CB1受体炎症环境下参与牙周组织再生的机制仍有待进一步研究。"
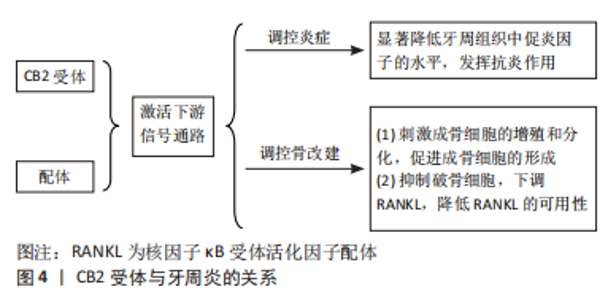
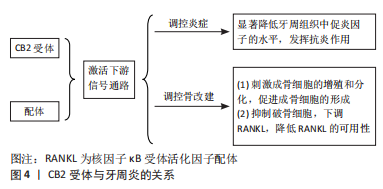
2.2 CB2受体和牙周炎的关系 大麻素可有效抑制体外白细胞和急性炎症动物模型中的免疫和炎症功能,例如肺、心肌、血管、牙周、神经、肝脏、胰腺和关节炎炎症模型,其中非精神活性大麻素受体CB2受体正在成为大麻素调节炎症的关键靶标[52]。CB2受体可能在骨代谢和炎症中发挥重要作用[53]。牙周炎中关于CB1和CB2基因表达的研究显示,CB2受体在牙龈组织中显著表达,而CB1受体无明显表达[13]。因此,大多数关于炎症性疾病中大麻素受体的研究仅限于CB2受体及其激动剂,CB2受体可能与牙周炎的关系更为密切。 2.2.1 CB2受体牙周组织炎症的关系 CB2受体在抗炎途径激活和免疫抑制作用方面发挥重要作用[54]。CB2受体激动剂HU-308和反向激动剂SMM-189在原代人牙周膜成纤维细胞(human periodontal ligament Fibroblasts,HPDLF)中表现出抗炎活性[55]。另有研究表明, CB2受体反向激动剂SMM-189可以显著抑制促炎细胞因子干扰素γ、白细胞介素6和白细胞介素12 p70(IL-12p70)的产生[56-57]。AEA可以减少牙周炎牙龈组织中肿瘤坏死因子α的产生,使用CB2受体拮抗剂AM630可以减弱AEA的作用[43]。有研究报道,牙周术后患者的炎症牙龈成纤维细胞中CB2受体的表达升高,这与龈沟液(gingival crevicular fluid,GCF)中的AEA和2-AG的上调有关[40],这表明牙周手术后内源性大麻素的增加可能促进牙龈成纤维细胞的增殖,有利于炎症愈合。 CB2受体与配体结合,可降低牙周组织的促炎细胞因子水平,发挥显著的抗炎作用。ABIDI等[59]研究发现CB2受体配体抑制促炎细胞因子/趋化因子的产生,并通过减少牙周组织破坏和牙槽骨吸收来减轻炎症,其中选择性CB2受体反向激动剂SMM-189对细胞因子、趋化因子和血管标记物的抑制程度大于激动剂HU-308,表明CB2受体反向激动剂可以作为治疗牙周炎症的新方法。ABIDI等[29]首次研究证明CB2受体反向激动剂是开发牙周炎新治疗干预的可行候选者。研究结果显示,与AEA和HU-308相比,SMM-189在抑制白细胞介素6和单核细胞趋化蛋白1(MCP-1,与慢性牙周炎相关的促炎标志物)表达方面的活性显示出更好的抗炎作用或免疫抑制作用。在用牙龈卟啉单胞菌脂多糖所诱导形成的炎症中,人牙周膜成纤维细胞中白细胞介素1、 肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6和单核细胞趋化蛋白1的产生被CB2受体激动剂和反向激动剂抑制[55]。OSSOLA等[60]在患有牙周病的大鼠中使用了CB2受体激动剂HU-308,结果表明牙周组织中炎症递质的量减少,证明CB2信号参与了牙周损伤的控制。一些研究表明,电针治疗通过激活CB2受体降低牙周促炎递质的表达[61-62]。 研究表明CB2受体可以显著降低牙周组织中促炎因子的水平从而发挥其抗炎作用,用CB2受体配体治疗牙周炎在很大程度上尚未探索,并且仍有待确定哪一类配体,即激动剂或反向激动剂,在牙周炎中产生最佳的抗炎活性[63]。 2.2.2 CB2受体和牙周炎牙槽骨骨改建的关系 CB2受体激活与成骨分化和矿化增加相关,它将刺激成骨细胞分化,并减轻破骨细胞的生成,这表明CB2受体信号通过直接作用于骨细胞,同时通过抑制促吸收细胞因子的表达来阻断骨丢失[64-65]。 有研究表明,在成骨细胞、骨细胞和破骨细胞中有CB2受体的表达,而CB1受体的表达非常低或未观察到[66]。CB2受体在维持骨量方面发挥重要作用,一方面是刺激基质细胞/成骨细胞,此外是通过抑制破骨细胞,降低核因子κB受体活化因子配体(receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand,RANKL)的可用性。RANKL是一种关键的破骨细胞生成因子[67-68],对破骨细胞前体细胞的完全分化至关重要,在牙周骨吸收中起关键作用[69]。至于CB1受体,已经证明中枢CB1受体刺激可能导致由肾上腺素能系统调节的外周骨形成[70]。 一直以来,已经证明CB2受体在成骨过程中发挥重要作用。体外研究表明,CB2受体刺激通过增加Runx2、骨涎蛋白、骨保护素(OPG)、碱性磷酸酶和骨钙素等成骨因子对成骨细胞增殖和功能产生积极影响[64]。根据研究,Schmuhl等[71]报道,CB2受体拮抗剂AM630抑制大麻二酚诱导的脂肪来源的间充质干细胞迁移和成骨细胞分化。QIAN等[72]证明,CB2受体的激活能够增强牙周膜细胞的成骨分化,HU-308上调成骨相关蛋白(OPG)基因表达,而下调RANKL基因,导致OPG/RANKL比值升高,并且HU-308使牙周膜细胞矿化加速。 CB2受体可以抑制破骨细胞的功能,减少牙槽骨骨丢失。牙周炎大鼠施加大麻二酚刺激后的牙槽骨丢失减少,RANKL/RANK的激活剂表达降低[73]。OSSOLA等[60]的研究结果表明HU-308可以明显减少牙槽骨丢失和牙龈组织中的炎症递质,在没有治疗的情况下,脂多糖诱导的牙周炎会增加牙槽骨丢失;使用HU-308治疗后,牙龈炎症参数的衰减导致骨代谢正常化。 由于牙周组织中CB2受体分布明显多于CB1受体,上述多项研究说明CB2受体及其激动剂可以有效减少牙周炎过程中牙槽骨的丢失,所以牙周炎时CB2受体与配体结合后,可以刺激成骨细胞分化,促进成骨细胞的形成,抑制破骨细胞的骨吸收,进而减少炎症过程中牙槽骨丢失。CB2受体与牙周炎关系见图4。"
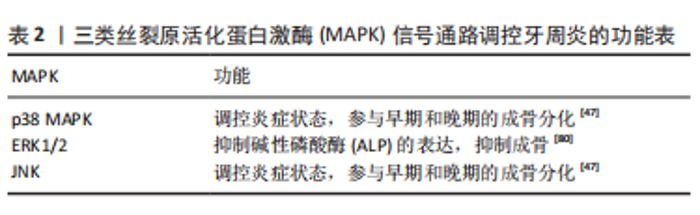
虽然OSSOLA等[60]认为CB2受体激动剂HU-308在脂多糖诱导的大鼠口腔炎症模型中具有骨保护作用,但其他研究表明,大麻素可能同样使动物易患破坏性牙周病。例如:与结扎的牙齿每天暴露于大麻烟雾中仅8 min的啮齿动物比,结扎的未暴露动物发生更广泛的骨损失[74];在大麻烟雾暴露的动物中,植入物周围的骨愈合减少也被证明[75];频繁使用大麻可能会导致更严重的牙周炎[76]。这些矛盾的结论可能是由于缺乏大麻素对牙周组织的基本生物学效应的了解。 2.3 大麻素受体调控骨改建的相关信号通路 大麻素通过与特定受体CB1和CB2结合,以激活下游信号通路,来实现其功能[77]。下面介绍涉及较多的两种信号通路。 2.3.1 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen activated protein kinase,MAPK)信号通路 MAPK由一系列高度同源的蛋白激酶组成,有助于将细胞外的信号传递到细胞内,并参与p38 MAPK、c-Jun 氨基末端激酶(c-Jun Nterminal kinase,JNK)和细胞外信号调节蛋白激酶1/2(extracellular signal regulated protein kinase1 /2,ERK1 /2)信号通路[78-79],它们都可调控牙周炎,见表2。三者与牙周膜干细胞增殖分化密切相关。CB1受体可以激活MAPK信号通路,包括p38 MAPK,JNK和Erk1/2途径,从而进一步调节细胞增殖、存活和分化[42,81]。 P38 MAPK和JNK信号通路在牙周膜干细胞中用低强度脉冲超声处理后被激活,p38 MAPK特异性抑制剂SB203580和JNK特异性抑制剂SP600125可以调节低强度脉冲超声刺激的牙周膜干细胞增殖[82]。Erk1/2与牙周膜干细胞增殖、分化也有密切关系[83-84]。"
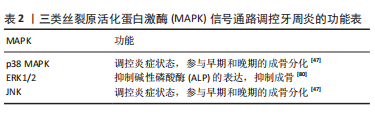

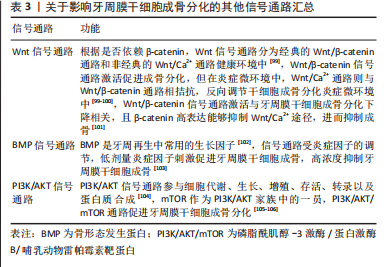
MAPK信号通路在人类脂肪来源的干细胞成骨中是必需的[85]。CB1受体主要是通过激活p38 MAPK和JNK信号通路,抑制了Erk1/2信号通路影响牙周膜干细胞和骨髓间充质干细胞的功能和分化,从而调控牙周炎的炎症水平和骨量。YAN等[47]研究发现,CB1受体激活了P38 MAPK和JNK信号,抑制了牙周膜干细胞中的Erk1/2和PPAR-γ信号,并可激活肿瘤坏死因子α和干扰素γ刺激抑制的p38 MAPK和JNK信号,PPAR-γ表达增加,但炎症条件下磷酸化的Erk1/2水平没有变化,炎症条件下该过程可能独立于Erk1/2。所以CB1受体可激活牙周膜干细胞的成骨/牙本质分化潜力并上调了肿瘤坏死因子α或干扰素γ刺激的牙周膜干细胞的成骨/牙本质分化潜力。所以,CB1受体通过p38 MAPK和JNK信号通路挽救受损牙周膜干细胞的功能,而不是通过Erk1/2信号通路。p38 MAPK和JNK是成骨分化的积极调节因子[86-87]。PPAR-γ是成骨分化的负调节因子,PPAR-γ的抑制导致成骨增强[88-89]。YAN等[90]进一步在CB1受体对于间充质干细胞功能的机制方面进行研究,发现CB1受体激活了骨髓间充质干细胞中的p38 MAPK和JNK信号通路并抑制了Erk1/2信号通路,证明CB1受体在间充质干细胞功能调控和牙周组织再生中的潜在作用,为炎症条件下的骨组织再生提供了新的作用靶点。 所以CB1受体可以通过不同的机制挽救牙周膜干细胞的增殖和成骨/成牙分化能力,p38 MAPK和JNK信号通路似乎对于炎症抑制时的CB1受体激活的牙周膜干细胞的增殖和成骨/牙分化潜力更为重要。 CB2受体主要是通过激活ERK1/2、抑制p38信号通路,增加牙周成骨相关基因的表达,同时影响牙周组织中细胞的功能,调控牙周组织的炎症。据报道,大麻素通过激活p-ERK、p-p38和Akt积极调节牙龈成纤维细胞[40],而在单核细胞中也可以看到细胞特异性差异,例如p-ERK和Akt被激活,而不是p-p38[91]。在体外模型中,CB2受体激动剂抑制cAMP的产生,这已被证明会导致ERK的磷酸化[91-93]。选择性CB2受体拮抗剂AM630抑制大麻二酚诱导的MAPK信号通路,大麻二酚通过炎症微环境中的p38-MAPK信号通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[94]。所以,大麻二酚通过结合CB2受体干预p38 MAPK,并增加了炎症环境中成骨相关mRNA和蛋白的表达水平。大麻素可以通过CB2依赖的方式促进牙周膜成纤维细胞的黏附和迁移,这些是通过涉及ERK1/2激活和p38抑制的MAPK信号级联的FAK激活介导的[5]。特异性阻断CB2受体可消除大麻素对这些细胞活性的影响。研究表明Δ-9-四氢大麻酚(THC,一种可以从植物中提取的大麻素)通过结合CB1/CB2受体增加FAK磷酸化,并启动MAPK下游信号转导通路,激活ERK1/2,抑制p38信号通路,促进牙周组织中细胞的黏附和迁移[5]。CB2受体拮抗剂AM630特异性阻断CB2后,细胞信号传导显著减弱。CB1受体拮抗剂AM251选择性阻断CB1后,FAK磷酸化很少被抑制,所以CB2受体在激活MAPK信号通路方面起决定性作用。当CB1和CB2受体同时被阻断后,THC几乎不能传导细胞信号,二者表现为协同作用。白细胞介素1β刺激的人牙周膜成纤维细胞对p-JNK没有任何影响,而仅用CB2受体配体SMM-189(反向激动剂)治疗显著上调p-JNK活性。SMM-189对p-JNK的这种独特作用可能负责控制在创伤愈合(组织修复和细胞迁移)以及胶原蛋白生物合成和基质收缩中必不可少的成纤维细胞功能[59]。SMM-189治疗可通过增强p-JNK来缓解,从而改善整体牙周健康。 2.3.2 核因子κB(Nuclear Factor-κB,NF-κB)信号通路 NF-κB激活对破骨细胞形成和功能具有关键作用,大麻素和受体结合后,可以抑制NF-κB信号通路的激活,进而减少破骨细胞的形成,减少牙周炎过程中的骨吸收。ZHU等[95]发现JWH133(CB2受体激动剂)对NF-κB信号通路具有抑制作用。LIU等[96]研究发现JZL184 抑制RANKL诱导的NF-κB通路激活。此外,JZL184处理明显抑制NF-κB信号通路中p65、IκBα和IKKβ的磷酸化。MAGL敲低可抑制RANKL诱导的NF-κB和MAPK激活,降低 MAGL可抑制p65、Akt和IκB-α的磷酸化。因此在牙周炎状态下,CB2受体激活可通过抑制NF-κB信号通路抑制破骨细胞的形成和分化,减少牙槽骨的吸收。NAKAJIMA等[37]研究证明了AEA对细菌脂多糖和其他炎性细胞因子(包括单核细胞趋化蛋白1、白细胞介素8和白细胞介素1)刺激的成纤维细胞中NF-κB表达的抑制作用,所以阿难酰胺Anandamide(AEA)抑制由NF-κB途径引发的主要炎症途径。据报道,大麻素可抑制NF-κB激活,并减少NF-kB靶基因肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6的上调[97]。两种CB2受体配体显著降低了p-NF-kB,并且在整个研究过程中一直受到抑制[59]。据报道,p-ERK的增加可能通过抑制血管内皮细胞中NF-κB的激活发挥抗炎活性[98]。所以,抑制NF-κB信号通路的激活可以激发抗炎活性。 由于NF-κB信号通路与骨吸收和炎症形成有关,所以抑制NF-κB信号通路可以减少牙周炎过程中牙槽骨的吸收,促进炎症愈合。炎症反应涉及细胞外到细胞内的信号传递,即信号级联反应。牙周炎还涉及到其他信号通路,但是由于与大麻素受体有关的研究相对较少,并没有展开论述,其他信号通路见表3。信号通路间关系交错纵横,同一种反应会影响不同的通路,不同的反应也会涉及同一种通路参与,所以炎症和GPCRs之间关系复杂。总之,大麻素受体作为GPCRs可以促进成骨细胞的分化和矿化,同时减少破骨细胞的数量和活性,以及可发挥抗炎活性,进而减少炎症过程中牙槽骨吸收。"
| [1] MECHOULAM R. The Pharmacohistory of Cannabis sativa, in Cannabis as Therapeutic Agent. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA:1986. [2] JONES É, VLACHOU S. A Critical Review of the Role of the Cannabinoid Compounds Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and Cannabidiol (CBD) and their Combination in Multiple Sclerosis Treatment. Molecules. 2020; 25(21):4930. [3] PERTWEE RG, HOWLETT AC, ABOOD ME, et al. International union of basic and clinical pharmacology. LXXIX. Cannabinoid receptors and their ligands: Beyond CB1and CB2. Pharmacol Rev. 2010;62:588-631. [4] ZOU S, KUMAR U. Cannabinoid Receptors and the Endocannabinoid System: Signaling and Function in the Central Nervous System. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(3):833. [5] LIU C, QI X, ALHABEIL J, et al. Activation of cannabinoid receptors promote periodontal cell adhesion and migration. J Clin Periodontol. 2019;46(12):1264-1272. [6] LU HC, MACKIE K. Review of the Endocannabinoid System. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2021;6(6):607-615. [7] JOSEF S, ZDENĚK L, SIMONA M, et al. Endocannabinoids. Ceska Gynekol. 2021;86(6):414-420. [8] AIZPURUA-OLAIZOLA O, ELEZGARAI I, RICO-BARRIO I, et al. Targeting the endocannabinoid system: future therapeutic strategies. Drug Discov Today. 2017;22(1):105-110. [9] PROSPÉRO-GARCÍA O, RUIZ CONTRERAS AE, ORTEGA GÓMEZ A, et al. Grupo de Neurociencias de la Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México. Endocannabinoids as Therapeutic Targets. Arch Med Res. 2019;50(8): 518-526. [10] IANNOTTI FA, DI MARZO V. The gut microbiome, endocannabinoids and metabolic disorders. J Endocrinol. 2021;248(2):R83-R97. [11] DIPATRIZIO NV. Endocannabinoids and the Gut-Brain Control of Food Intake and Obesity. Nutrients. 2021;13(4):1214. [12] PACHER P, KOGAN NM, MECHOULAM R. Beyond THC and Endocannabinoids. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2020;60:637-659. [13] ATAEI A, RAHIM REZAEE SA, MOEINTAGHAVI A, et al. Evaluation of cannabinoid receptors type 1-2 in periodontitis patients. Clin Exp Dent Res. 2022 Jun 19. doi: 10.1002/cre2.608. [14] YE L, CAO Z, WANG W, et al. New Insights in Cannabinoid Receptor Structure and Signaling. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2019;12(3):239-248. [15] MUNRO S, THOMAS KL, ABU-SHAAR M. Molecular characterization of a peripheral receptor for cannabinoids. Nature. 1993;365:61-65 . [16] MACCARRONE M, BAB R, BIRO T, et al. Endocannabinoid signaling at the periphery: 50 years after thc. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2015;36:277-296. [17] IZZO AA, SHARKEY KA. Cannabinoids and the gut: New developments and emerging concepts. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010;126:21-38. [18] MONTECUCCO F, DI MARZO V. At the heart of the matter: The endocannabinoid system in cardiovascular function and dysfunction. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012;33:331-340. [19] LAPRAIRIE RB, BAGHER AM, DENOVAN-WRIGHT EM. Cannabinoid receptor ligand bias: implications in the central nervous system. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2017;32:32-43. [20] LI X, SHEN L, HUA T, et al. Structural and Functional Insights into Cannabinoid Receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2020;41(9):665-677. [21] ALVES LCV, LISBOA MRP, DA SILVEIRA HF, et al. Electroacupuncture increases immunoexpression of CB1 and CB2 receptors in experimental model of inflammatory bone loss. Bone. 2019;127:59-66. [22] LISBOA SF, GOMES FV, GUIMARAES FS, et al. Microglial Cells as a Link between Cannabinoids and the Immune Hypothesis of Psychiatric Disorders. Front Neurol. 2016;7:5. [23] STEMPEL AV, STUMPF A, ZHANG HY, et al.Cannabinoid Type 2 Receptors Mediate a Cell Type-Specific Plasticity in the Hippocampus. Neuron. 2016; 90(4):795-809. [24] APOSTU D, LUCACIU O, MESTER A, et al.Cannabinoids and bone regeneration. Drug Metab Rev. 2019;51(1):65-75. [25] NAGOOR MEERAN MF, SHARMA C, GOYAL SN, et al. CB2 receptor-selective agonists as candidates for targeting infection, inflammation, and immunity in SARS-CoV-2 infections. Drug Dev Res. 2021;82(1):7-11. [26] KOMOROWSKA-MÜLLER JA, SCHMÖLE AC. CB2 Receptor in Microglia: The Guardian of Self-Control. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;22(1):19. [27] CABAÑERO D, MARTÍN-GARCÍA E, MALDONADO R. The CB2 cannabinoid receptor as a therapeutic target in the central nervous system. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2021;25(8):659-676. [28] KILARU A, CHAPMAN KD. The endocannabinoid system. Essays Biochem. 2020;64(3):485-499. [29] ABIDI AH, PRESLEY CS, DABBOUS M, et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of cannabinoid receptor 2 ligands in primary hPDL fibroblasts. Arch Oral Biol. 2018;87:79-85. [30] SAWZDARGO M, NGUYEN T, LEE DK, et al. Identification and cloning of three novel human G protein-coupled receptor genes GPR52, PsiGPR53 and GPR55: GPR55 is extensively expressed in human brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1999;64(2):193-198. [31] MOSCA MG, MANGINI M, CIOFFI S, et al. Peptide targeting of lysophosphatidylinositol-sensing GPR55 for osteoclastogenesis tuning. Cell Commun Signal. 2021;19(1):48. [32] NISHIMURA H, KAWASAKI M, TSUKAMOTO M, et ,al .Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 and 4 double knockout leads to increased bone mass in mice. Bone Rep. 2020;12:100268. [33] SANTAMARIA-JR M, BAGNE L, ZANIBONI E, et al. Diabetes mellitus and periodontitis: Inflammatory response in orthodontic tooth movement. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2020;23(1):27-34. [34] SUN X, GAO J, MENG X, et al. Polarized Macrophages in Periodontitis: Characteristics, Function, and Molecular Signaling. Front Immunol. 2021; 12:763334. [35] PAN W, WANG Q, CHEN Q. The cytokine network involved in the host immune response to periodontitis. Int J Oral Sci. 2019;11(3):30. [36] JEAN-GILLES L, BRAITCH M, LATIF ML, et al. Effects of pro-inflammatory cytokines on cannabinoid cb1 and cb2 receptors in immune cells. Acta Physiol. 2015;214(1):63-74. [37] NAKAJIMA Y, FURUICHI Y, BISWAS KK, et al. Endocannabinoid, anandamide in gingival tissue regulates the periodontal inflammation through NF-kappaB pathway inhibition. FEBS Lett. 2006;580(2):613-619. [38] OSSOLA CA, SURKIN PN, PUGNALONI A, et al. Long-term treatment with methanandamide attenuates LPS-induced periodontitis in rats. Inflamm Res. 2012;61(9):941-948. [39] KREITZER FR, STELLA N. The therapeutic potential of novel cannabinoid receptors. Pharmacol Ther. 2009;122(2):83-96. [40] KOZONO S, MATSUYAMA T, BIWASA KK, et al. Involvement of the endocannabinoid system in periodontal healing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;394(4):928‐933. [41] KONERMANN A, JÄGER A, HELD S, et al.In vivo and in vitro identification of endocannabinoid signaling in periodontal tissues and their potential role in local pathophysiology. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2017;37(8):1511‐1520. [42] GRUDEN G, BARUTTA F, KUNOS G, et al. Role of the endocannabinoid system in diabetes and diabetic complications. Br J Pharmacol. 2016; 173(7):1116‐1127. [43] RETTORI E, DE LAURENTIIS A, ZORRILLA ZUBILETE M, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of the endocannabinoid anandamide in experimental periodontitis and stress in the rat. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2012;19(5):293-303. [44] LI M, PASCUAL G, GLASS CK. Peroxisome proliferator‐activated receptor gamma‐dependent repression of the inducible nitric oxide synthase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20(13):4699‐4707. [45] STARK JM, COQUET JM, TIBBITT CA. The Role of PPAR-γ in Allergic Disease. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2021;21(11):45. [46] O’SULLIVAN SE. An update on PPAR activation by cannabinoids. Br J Pharmacol. 2016;173(12):1899‐1910. [47] YAN W, CAO Y, YANG H, et al. CB1 enhanced the osteo/dentinogenic differentiation ability of periodontal ligament stem cells via p38 MAPK and JNK in an inflammatory environment. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(6):e12691. [48] GOWRAN A, MCKAYED K, CAMPBELL VA. The cannabinoid receptor type 1 is essential for mesenchymal stem cell survival and differentiation: implications for bone health. Stem Cells Int. 2013;2013:796715. [49] ROSSI F, TORTORA C, PUNZO F, et al. The endocannabinoid/endovanilloid system in bone: from osteoporosis to osteosarcoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20(8):E1919. [50] WANG L, YANG L, TIAN L, et al. Cannabinoid receptor 1 mediates homing of bone marrow‐derived mesenchymal stem cells triggered by chronic liver injury. J Cell Physiol. 2017;232(1):110‐121. [51] HONG JH, HWANG ES, MCMANUS MT, et al. TAZ, a transcriptional modulator of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Science. 2005;309(5737): 1074‐1078. [52] ASHTON JC. Cannabinoids for the treatment of inflammation. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2007;8(5):373-384. [53] HU SJ, CHENG G, ZHOU H, et al. Identification of Novel Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor Agonists from Botanical Compounds and Preliminary Evaluation of Their Anti-Osteoporotic Effects. Molecules. 2022;27(3):702. [54] DI MARZO V, BIFULCO M, DE PETROCELLIS L. The endocannabinoid system and its therapeutic exploitation. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3(9):771-784. [55] HAN S, THATTE J, BUZARD DJ, et al. Therapeutic utility of cannabinoid receptor type 2 (cb(2)) selective agonists. J Med Chem. 2013;56(21):8224-8256. [56] PRESLEY C, ABIDI A, SURYAWANSHI S, et al.Preclinical evaluation of SMM-189, a cannabinoid receptor 2-specific inverse agonist. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2015;3(4):e00159. [57] REINER A, HELDT SA, PRESLEY CS, et al. Motor, visual and emotional deficits in mice after closed-head mild traumatic brain injury are alleviated by the novel CB2 inverse agonist SMM-189. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;16(1):758-787. [58] KOZONO S, MATSUYAMA T, BIWASA KK, et al. Involvement of the endocannabinoid system in periodontal healing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;394(4):928-933. [59] ABIDI AH, ALGHAMDI SS, DABBOUS MK, et al. Cannabinoid type-2 receptor agonist, inverse agonist, and anandamide regulation of inflammatory responses in IL-1β stimulated primary human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. J Periodontal Res. 2020;55(5):762-783. [60] OSSOLA CA, SURKIN PN, MOHN CE, et al. Anti-inflammatory and osteoprotective effects of cannabinoid-2 receptor agonist HU-308 in a rat model of lipopolysaccharide-induced periodontitis. J Periodontol. 2016; 87:725-734. [61] GONDIM DV, ARAÚJO JC, CAVALCANTE AL, et al. CB1 and CB2 contribute to antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of electroacupuncture on experimental arthritis of the rat temporomandibular joint. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012;90:1479-1489. [62] SU TF, ZHAO YQ, ZHANG LH, et al.Electroacupuncture reduces the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in inflamed skin tissues through activation of cannabinoid CB2 receptors. Eur J Pain 2012;16:624-635. [63] KLEIN TW. Cannabinoid-based drugs as anti-inflammatory therapeutics. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5(5):400-411. [64] SUN YX, XU AH, YANG Y, et al. Activation of cannabinoid receptor 2 enhances osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:874982. [65] FUKUDA S, KOHSAKA H, TAKAYASU A, et al. Cannabinoid receptor 2 as a potential therapeutic target in rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Musculoskel Dis. 2014;15:275. [66] BAB I, ZIMMER A. Cannabinoid receptors and the regulation of bone mass. Br J Pharmacol. 2008;15:182-188. [67] OFEK O, KARSAK M, LECLERC N, et al. Peripheral cannabinoid receptor, CB2, regulates bone mass. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:696-701. [68] BOYLE WJ, SIMONET WS, LACEY DL. Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 2003;423:337-342. [69] NAGASAWA T, KIJI M, YASHIRO R, et al. Roles of receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL) and osteoprotegerin in periodontal health and disease. Periodontol 2000. 2007;43:65-84. [70] TAM J, OFEK O, FRIDE E, et al. Involvement of neuronal cannabinoid receptor CB1 in regulation of bone mass and bone remodeling. Mol Pharmacol. 2006;70:786-792. [71] SCHMUHL E, RAMER R, SALAMON A, et al. Increase of mesenchymal stem cell migration by cannabidiol via activation of p42/44 MAPK. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014;87(3):489-501. [72] QIAN H, ZHAO Y, PENG Y, et al. Activation of cannabinoid receptor CB2 regulates osteogenic and osteoclastogenic gene expression in human periodontal ligament cells. J Periodontal Res. 2010;45:504-511. [73] JIRASEK P, JUSKU A, SIMANEK V, et al. Cannabidiol and periodontal inflammatory disease: A critical assessment. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2022;166(2):155-160. [74] NOGUEIRA-FILHO GR, TODESCAN S, SHAH A, et al. Impact of Cannabis sativa (marijuana) smoke on alveolar bone loss: a histometric study in rats. J Periodontol. 2011;82:1602-1607. [75] NOGUEIRA-FILHO GR, CADIDE T, ROSA BT, et al. Cannabis sativa smoke inhalation decreases bone filling around titanium implants: a histomorphometric study in rats. Implant Dent. 2008;17: 461-470. [76] SHARIFF JA, AHLUWALIA KP, PAPAPANOU PN. Relationship Between Frequent Recreational Cannabis (Marijuana and Hashish) Use and Periodontitis in Adults in the United States: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011 to 2012. J Periodontol. 2017;88(3):273-280. [77] PERTWEE RG. The diverse CB1 and CB2 receptor pharmacology of three plant cannabinoids: delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol and delta9-tetrahydrocannabivarin. Br J Pharmacol. 2008;153(2):199-215. [78] PATIL CS, KIRKWOOD KL. p38 MAPK signaling in oral‐related diseases. J Dent Res. 2007;86(9):812‐825. [79] BLÜTHGEN N, LEGEWIE S. Systems analysis of MAPK signal transduction. Essays Biochem. 2008;45:95‐107. [80] ZHAO Y, GAO J, ZHANG Y, et al. Cyclosporine A Promotes Bone Remodeling in LPS-Related Inflammation via Inhibiting ROS /ERK Signaling: Studies In Vivo and In Vitro. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:8836599. [81] GALVE‐ROPERH I, CHIURCHIÙ V, DÍAZ‐ALONSO J, et al. Cannabinoid receptor signaling in progenitor/stem cell proliferation and differentiation. Prog Lipid Res. 2013;52(4):633‐650. [82] GAO Q, WALMSLEY AD, COOPER PR, et al. Ultrasound stimulation of different dental stem cell populations: role of mitogen‐activated protein kinase signaling. J Endod. 2016;42(3):425‐431. [83] YU Y, MU J, FAN Z, et al. Insulin‐like growth factor 1 enhances the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells via ERK and JNK MAPK pathways. Histochem Cell Biol. 2012;137(4):513‐525. [84] PAULA‐SILVA FW, GHOSH A, ARZATE H, et al. Calcium hydroxide promotes cementogenesis and induces cementoblastic differentiation of mesenchymal periodontal ligament cells in a CEMP1‐ and ERK‐dependent manner. Calcif Tissue Int. 2010;87(2):144‐157. [85] TSANG EJ, WU B, ZUK P. MAPK signaling has stage‐dependent osteogenic effects on human adipose‐derived stem cells in vitro. Connect Tissue Res. 2018;59(2):129‐146. [86] JIAN CX, FAN QS, HU YH, et al. IL‐7 suppresses osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells through inactivation of mitogen‐activated protein kinase pathway. Organogenesis. 2016;12(4):183‐193. [87] TANG Y, LIU L, WANG P, et al. Periostin promotes migration and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament mesenchymal stem cells via the Jun amino‐terminal kinases (JNK) pathway under inflammatory conditions. Cell Prolif. 2017;50(6):e12369. [88] ZHUANG H, ZHANG X, ZHU C, et al. Molecular mechanisms of PPAR‐γ governing MSC osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;11(3):255‐264. [89] DENG C, SUN Y, LIU H, et al. Selective adipogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells stimulated with high doses of glucose. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(7):e0199603. [90] YAN W, LI L, GE L, et al. The cannabinoid receptor I (CB1) enhanced the osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by rescue impaired mitochondrial metabolism function under inflammatory condition. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):22. [91] MONTECUCCO F, BURGER F, MACH F, et al. Cb2 cannabinoid receptor agonist jwh-015 modulates human monocyte migration through defined intracellular signaling pathways. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008; 294(3):H1145-H1155. [91] WANG J, XU J, PENG Y, et al. Phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase as a biomarker for cannabinoid receptor 2 activation. Heliyon. 2018;4(11):e00909. [93] HYTTI M, ANDJELIC S, JOSIFOVSKA N, et al. Cb2 receptor activation causes an erk1/2-dependent inflammatory response in human rpe cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):16169. [94] QI X, LIU C, LI G, et al. Investigation of in vitro odonto/osteogenic capacity of cannabidiol on human dental pulp cell. J Dent. 2021;109:103673. [95] ZHU M, YU B, BAI J, et al. Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Agonist Prevents Local and Systemic Inflammatory Bone Destruction in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34(4):739-751. [96] LIU H, ZHOU C, QI D, et al. Inhibiting Monoacylglycerol Lipase Suppresses RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis and Alleviates Ovariectomy-Induced Bone Loss. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:640867. [97] JÜTTLER E, POTROVITA I, TARABIN V, et al. The cannabinoid dexanabinol is an inhibitor of the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappa B). Neuropharmacology. 2004;47(4):580-592. [98] MAENG YS, MIN JK, KIM JH, et al. Erk is an anti-inflammatory signal that suppresses expression of nf-κb-dependent inflammatory genes by inhibiting ikk activity in endothelial cells. Cell Signal. 2006;18(7):994-1005. [99] MAEDA K, TAKAHASHI N, KOBAYASHI Y. Roles of Wnt signals in bone resorption during physiological and pathological states. Mol Med ( Berl). 2013;91(1):15-23. [100] JIANG T, ZHOU B, HUANG L, et al. Andrographolide Exerts Pro-Osteogenic Effect by Activation of Wnt /β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Vitro. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36(6):2327-2339. [101] LIU N, SHI S, DENG M, et al. High levels of β-catenin signaling reduce osteogenic differentiation of stem cells in inflammatory microenvironments through inhibition of the noncanonical Wnt pathway. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(9):2082-2095. [102] ERN C, BERGER T, FRASHERI I, et al. Differentiation of hMSCs and hPDLSCs induced by PGE2 or BMP-7 in 3D models. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2017;122:30-37. [103] MAO CY, WANG YG, ZHANG X, et al. Double-edged-sword effect of IL-1β on the osteogenesis of periodontal ligament stem cells via crosstalk between the NF-κB, MAPK and BMP /Smad signaling pathways. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7:e2296. [104] 骆姝含,张岚,黄定明.炎症微环境影响牙周膜干细胞成骨分化的信号通路[J].口腔生物医学,2021,12(2):136-140. [105] DUAN Y, AN W, WU H, et al. Salvianolic Acid C Attenuates LPS-Induced Inflammation and Apoptosis in Human Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells via Toll-Like Receptors 4 ( TLR4) /Nuclear Factor κB ( NF-κB) Pathway. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:9499-9508. [106] LIU H, ZHENG J, ZHENG T, et al. Exendin-4 regulates Wnt and NFκB signaling in lipopolysaccharide-induced human periodontal ligament stem cells to promote osteogenic differentiation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;75:105801. [107] TANG XL, WANG Y, LI DL, et al. Orphan G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs): biological functions and potential drug targets. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012; 33(3):363-371. |
| [1] | Fang Xingyan, Tian Zhenli, Zhao Zheyi, Wen Ping, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and sphingosine kinases 1/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling axis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-8. |
| [3] | Tang Liang, Li Xiheng, Niu Ruijuan, Li Xinyue, Zou Xinying, Mao Tianjiao, Li Jiang. Naringin regulates the function of RAW264.7 macrophages to affect the osteogenic differentiation of MC-3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1205-1210. |
| [4] | Li Mengfei, Zhang Hong, Zhao Shaojian, Yin Guanghao, Wang Qibao. Expression of forkhead box protein 3 in refractory periapical periodontitis in rats with Enterococcus faecalis infection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1187-1192. |
| [5] | Liang Jiaqi, Liu Hengxu, Yang Jinxin, Yang Yi, Deng Xuhui, Tan Mingjian, Luo Jiong. Health benefit relationship between exercise and intestinal bacteria [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1292-1299. |
| [6] | Gao Yu, Han Jiahui, Ge Xin. Immunoinflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [7] | Wang Min, Yin Xiushan, Wang Yingxi, Zhang Yan, Zhao Long, Xia Shuyue. Inhalation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviates inflammatory injury in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 827-834. |
| [8] | Li Zhichao, Tan Guoqing, Su Hui, Xu Zhanwang, Xue Haipeng. Regulatory role of non-coding RNAs as potential therapeutic targets in spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 758-764. |
| [9] | Zhang Lichen, Chen Liang, Gu Yong. Inorganic ion bionic periosteum regulates immune microenvironment to promote bone repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 346-353. |
| [10] | Chen Bohao, He Qi, Yang Junzheng, Pan Zhaofeng, Xiao Jiacong, Li Miao, Li Shaocong, Zeng Jiaxu, Wang Haibin, Zheng Jia, Zhang Meng. Significance of Piezo1 protein in the pathogenesis of osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4414-4420. |
| [11] | Fang Xingyan, Tian Zhenli, Zhao Zheyi, Wen Ping, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and sphingosine kinases 1/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling axis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(26): 4161-4167. |
| [12] | Zhao Zirui, Hu Qiaoyu, Qi Xia, Liu Qing. Metabolomics evaluation of periodontitis: biomarkers, pathological mechanism and systemic relationship [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(26): 4239-4245. |
| [13] | Deng Moyuan, Peng Kun. Role and regulation of macrophages in biomaterial-mediated fibrosis formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(25): 4085-4092. |
| [14] | Wang Dongxu, Ren Jing, Li Jiping, Wang Yusu, Hu Pengfei, Zhang Guokun, Li Chunyi. Deer antler stem cell-derived exosomes prevent alcoholic liver injury via modulating nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(24): 3824-3830. |
| [15] | Wang Yiying, Li Ruiqing, Li Jingwen, Mei Jinjin, Zhang Jianyun, Zhang Lihong, Fan Yongfu, Guo Jian. Exosome-mediated cellular communication: a potential biomarker for Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(24): 3883-3891. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||