Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (27): 4414-4420.doi: 10.12307/2023.603
Previous Articles Next Articles
Significance of Piezo1 protein in the pathogenesis of osteonecrosis of femoral head
Chen Bohao1, He Qi1, Yang Junzheng1, Pan Zhaofeng1, Xiao Jiacong1, Li Miao1, Li Shaocong1, Zeng Jiaxu1, Wang Haibin2, Zheng Jia3, Zhang Meng3
- 1First Clinical Medicine School, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, Henan Provincial People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou 450003, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2022-06-08Accepted:2022-07-21Online:2023-09-28Published:2022-11-08 -
Contact:Zhang Meng, MD, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, Henan Provincial People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou 450003, Henan Province, China -
About author:Chen Bohao, Master candidate, First Clinical Medicine School, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Medical Science and Technology Public Relations Program Joint Co-Construction Project of Henan Province, No. LHGJ20210035 (to ZM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Bohao, He Qi, Yang Junzheng, Pan Zhaofeng, Xiao Jiacong, Li Miao, Li Shaocong, Zeng Jiaxu, Wang Haibin, Zheng Jia, Zhang Meng. Significance of Piezo1 protein in the pathogenesis of osteonecrosis of femoral head[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4414-4420.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
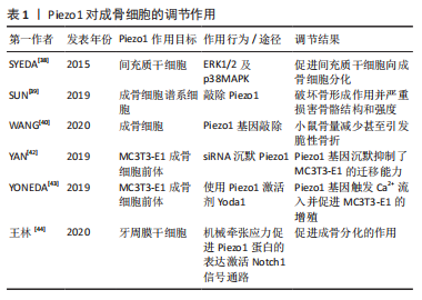
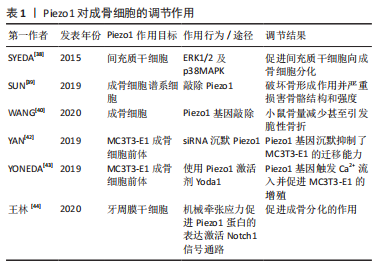
2.1 Piezo1在创伤性股骨头坏死中的作用 2.1.1 创伤性股骨头坏死的研究进展 创伤性股骨头坏死是由股骨颈骨折、髋关节脱位以及其他髋部创伤引起的股骨头坏死的一种重要类型。股骨颈骨折是导致创伤性股骨头坏死的主要原因,一旦发生骨折后其坏死发生率高达30%-40%[33-34]。现代医学研究表明,创伤性股骨头坏死的发病原因主要有以下几个:①骨折处机械应力分布不均、局部炎症等因素抑制了股骨头区域成骨细胞的增殖活性,并促进破骨细胞的增殖;②骨折断端产生的应激反应会引起股骨近端血流动力学改变,导致股骨头血供永久性或暂时性中断,股骨头区域发生低血低氧造成不同程度的骨细胞凋亡;③创伤导致股骨头区域主要血管不同程度的损伤,阻断了股骨头的正常血运,同时血管新生速度较慢或侧支循环不能充分满足股骨头血供需要[35-36]。 2.1.2 Piezo1在骨骼和血管中的作用 (1) Piezo1和成骨细胞:间充质干细胞具有成骨分化或脂肪分化的特点,Piezo1则可以通过ERK1/2及p38MAPK信号通路起到促进间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化、抑制向脂肪细胞分化的作用[37-38]。在成骨细胞谱系细胞中敲除 Piezo1 会破坏成骨细胞的骨形成作用并严重损害骨骼结构和强度[39]。WANG等[40-41]研究发现小鼠成骨细胞中的 Piezo1基因敲除会导致小鼠骨量减少甚至引发脆性骨折。YAN等[42] 在MC3T3-E1成骨细胞前体中用siRNA沉默Piezo1,结合Transwell细胞迁移实验和细胞划痕实验表明,Piezo1-siRNA组每孔迁移的细胞数和划痕愈合率均显著降低,说明Piezo1基因沉默显著抑制了MC3T3-E1的迁移能力。反之用Piezo1激活剂Yoda1将触发Ca2+流入并促进MC3T3-E1的增殖[43]。王林等[44]证明机械牵张应力可以促进Piezo1蛋白的表达,并以Ca2+为第二信使,激活Notch1信号通路,从而激活碱性磷酸酶、Runt相关转录因子2、骨钙素和骨唾液酸蛋白的表达,达到促进牙周膜干细胞(H-PDLSC)成骨分化的作用。在具体机制方面,有研究表明成骨细胞中Piezo1的失活还可以通过AKT/GSK-3β/β-catenin通路抑制成骨细胞分化[45]。见表1。"
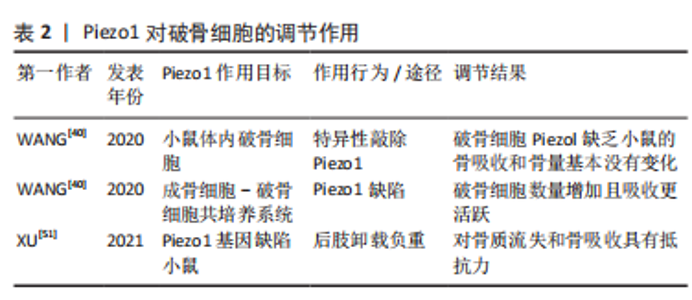
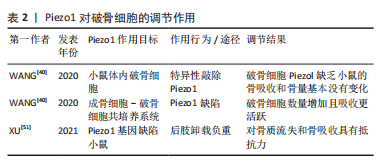
(2) Piezo1和破骨细胞:破骨细胞主要负责启动正常的骨重塑,并通过增加其吸收活性介导病理条件下的骨丢失[46]。破骨细胞附着在旧骨区,感知周围的机械环境,分泌酸和蛋白酶消化骨基质,形成骨吸收腔[47-48]。在骨重建过程中,破骨细胞受到成骨细胞和骨细胞的调节,以维持骨稳态[49-50]。为了测试 Piezo1 是否影响破骨细胞的骨吸收,WANG等[40]特异性敲除小鼠体内破骨细胞的Piezo1,与对照组小鼠相比,破骨细胞中Piezol缺乏小鼠的骨吸收和骨量基本没有变化。这些发现表明,Piezol在破骨细胞中没有作用。然而在成骨细胞-破骨细胞共培养系统中,与对照组相比,骨吸收陷窝测定数据表明Piezo1缺陷的共培养系统中的破骨细胞数量增加且吸收更活跃。在力学刺激条件下,成骨细胞中的 Piezo1 通过YAP核定位控制Ⅱ型和Ⅸ型胶原蛋白的表达从而影响破骨细胞的生成。此外,还有研究发现Piezo1 缺陷小鼠对后肢卸载负重引起的进一步骨质流失和骨吸收具有抵抗力,骨吸收减少是由于破骨细胞数量和活性降低所致,这些研究都表明了机械敏感蛋白 Piezo1 可以通过成骨细胞-破骨细胞串扰调节骨稳态[51]。见表2。"
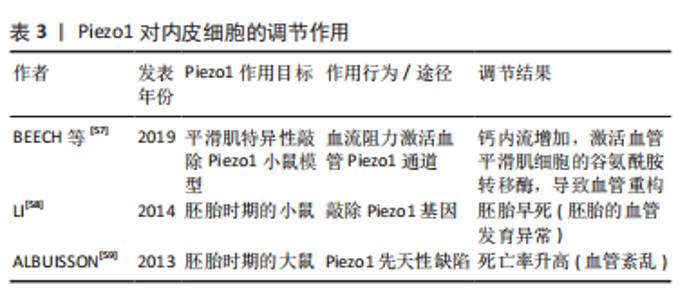
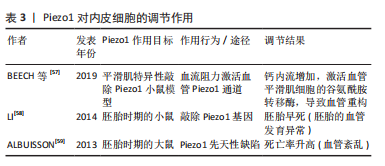
(3) Piezo1和内皮细胞:Piezo1与心血管系统关系密切,在分泌心脏相关因子、改变红细胞体积、控制动脉血压等生理过程中发挥着积极的作用。Piezo1可以将机械应力转化为生物电信号,而在哺乳动物心血管系统中,动脉血管、毛细微血管、心脏和红细胞等都可感受来自细胞外环境机械应力刺激,Piezo1通过介导血管内皮细胞的重塑而改善血管形态,还可以促进血管新生[52-54]。Piezo1能根据血液流动时对内皮细胞的不同作用力,从而对血管展现不同的作用[55]。高血压状态下,血流阻力激活血管Piezo1通道,使钙内流增加,激活血管平滑肌细胞的谷氨酰胺转移酶,导致血管重构,表明 Piezo1参与高血压引起的小血管重构[19,56-57]。此外,LI等[58]研究表明敲除Piezo1基因导致胚胎早死,此时胚胎的血管发育异常,刚好相对应心血管系统发育的时期,说明Piezo1基因在胚胎血管形成中起着关键的作用。同时,Piezo1先天性缺陷也会增加大鼠胚胎时期的死亡率,血管内皮细胞中Piezo1缺失则会导致血管紊乱[59]。进一步使用siRNA方法干扰人脐静脉内皮细胞实验,证实Piezo1基因介导内皮细胞的细胞骨架排列,而Piezo1 的缺失则会影响内皮细胞在受到剪切应力时改变其排列的能力[60]。见表3。"
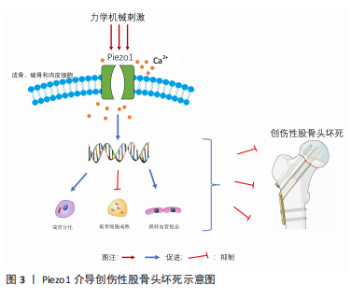
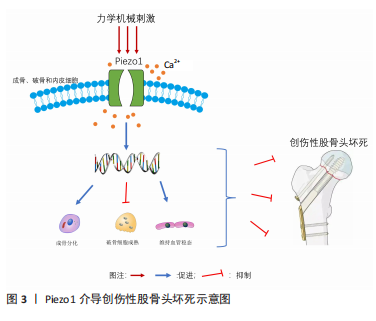
骨代谢稳态是骨组织修复的关键,而成骨细胞主导的骨形成和破骨细胞主导的骨吸收共同维持骨代谢的动态平衡,因此促进成骨分化、抑制破骨细胞增殖分化成为促进骨修复、延缓及阻止股骨头坏死进展的重要策略[61]。骨代谢需要血液的正常供应,骨创伤区域的骨修复则更加需要新生血管的构建,以确保受伤骨骼的血液供应。充足的血供是防止股骨头区域骨细胞坏死的必要条件,这对于防止骨坏死和开展后续的治疗都至关重要[62]。根据近年来的大量研究表明,Piezo1蛋白可通过接受细胞外环境的力学机械刺激,影响成骨细胞、破骨细胞和内皮细胞的分化与增殖,从而达到促进骨再生、改善股骨头血液流变学和促进血管新生的效果。综上,Piezo1作为机械敏感性离子蛋白可能成为创伤性股骨头坏死治疗策略中重要的靶点。见图3。"
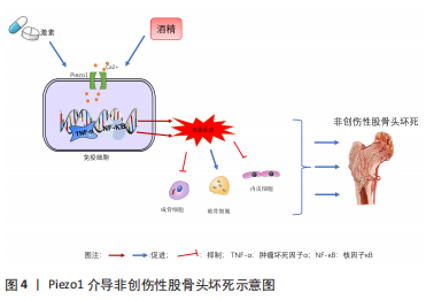
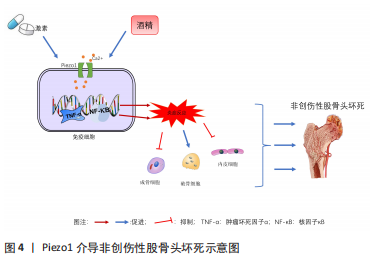
2.2 Piezo1在非创伤性股骨头坏死中的作用 2.2.1 非创伤性股骨头坏死与炎症反应的研究进展 (1)激素性股骨头坏死与炎症反应的研究进展:激素性股骨头坏死的发病率目前已超过了创伤所致的股骨头坏死。虽然种族、地区之间存在差异,但总体上中青年男性患者人数偏多[11,63]。目前,大多数研究者认为激素性股骨头坏死是由多种机制共同作用的结果,如:凝血功能障碍、细胞凋亡异常和脂质代谢功能障碍等[14,64]。随着研究深入发现炎症也是激素性股骨头坏死发生发展的重要促进因素之一,糖皮质激素可以激活炎症信号转导通路,促使核因子κB入核,释放大量炎症因子,如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6等,并抑制间充质干细胞成骨分化及钙盐沉积,促进破骨细胞成熟,破坏血管稳态,最终导致股骨头坏死[65-68]。此外,也有研究表明炎性小体结合细胞因子引发炎症级联反应导致细胞焦亡在激素性股骨头坏死的各个阶段均发挥着关键的作用,如NLRP3炎性小体的激活可以导致炎症小体蛋白复合物组装、半胱天冬酶激活及其下游底物白细胞介素前体1β/18和Gasdermin D蛋白活化成熟,从而释放白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18,参与机体的免疫炎性反应,诱导骨髓间充质干细胞焦亡发生[69-70] 。体内实验中,徐西林等[71]通过ELISA等实验发现激素性股骨头坏死造模小鼠的白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6及白细胞介素8水平与正常小鼠相比有明显增加,而且证实白细胞介素1β,白细胞介素6及白细胞介素8等炎症因子与激素性股骨头坏死密切相关[72]。综上,炎症反应作为激素性股骨头坏死促进因素之一,在激素性股骨头坏死的发生发展中起着至关重要的作用。 (2)酒精性股骨头坏死与炎症反应的研究进展:相关研究表明,酒精性股骨头坏死也与炎症反应失衡密切相关。长期饮用酒精会诱导肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6等炎症因子分泌,从而发生股骨头缺血与坏死。肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6已被证实是酒精性股骨头坏死等疾病的关键因子,而白细胞介素1β是炎症级联反应的始动因子,可促进骨基质降解酶释放及软骨细胞终末化,加重股骨头坏死[73-75]。另有研究发现酒精性股骨头坏死患者外周血中的CD86和CD19B细胞均升高,而外周血中的白细胞介素33水平在FicatⅢ-Ⅳ期股骨头坏死患者中显著高于FicatⅠ-Ⅱ期患者,进一步提示炎症反应与股骨头坏死进程呈正相关[76]。在机制方面,有相关研究发现酒精性股骨头坏死患者坏死的骨细胞刺激巨噬细胞产生炎症反应主要通过Toll样受体4激活,并经NF-κB通路调控炎症反应[77]。OLIVA等[78]通过体内实验也证实了此观点,酒精喂饲的实验组大鼠Toll样受体2和Toll样受体4基因表达较对照组上调,表明酒精可导致Toll样受体炎症通路的激活。经典的炎症通路Toll样受体/髓样分化因子88/核转录因子κB(TLR/MyD88/NF-κB)及相关炎性因子在酒精性股骨头坏死发生过程中扮演了重要角色[79]。 2.2.2 Piezo1与炎症反应的研究进展 Piezo1作为一种机械敏感性离子通道蛋白,除了可以感受细胞膜机械力变化,并将细胞膜感受到的机械信号转化为化学信号或电信号外,还在机械刺激参与的炎症反应中充当着重要的角色[22-28,80]。近来研究发现,Piezo1在巨噬细胞和其他免疫细胞中高度表达,使它们能够感知全方位压力[81]。循环静水压力可以通过Piezo1激活巨噬细胞和单核细胞的炎症反应。从机制上发现,循环压力会激活单核细胞中的Piezo1-Ca2+流入,从而增加内皮素1的表达和分泌。然后内皮素1以自分泌方式发回信号,稳定缺氧诱导因子1α,最终增加单核细胞中趋化因子 CXCL2 的表达和分泌。最后,中性粒细胞沿着CXCL2 梯度从血液迁移到肺中并启动促炎反应[25]。总之,机械刺激在先天免疫细胞的激活中起作用,并且可以通过 Piezo1触发炎症反应[82]。此外,SUN等[26]观察到Piezo1激活后可上调髓核细胞中白细胞介素1β水平,认为 Piezo1 可能通过激活 NLRP3炎症小体以加速白细胞介素1β 的产生和成熟来介导炎症,随后该团队通过实验证实了这一假想。机械拉伸后Piezo1和炎性小体NLRP3的表达呈时间依赖性增加,下游基因半胱天冬酶1激活和白细胞介素1β上调都可以证实激活Piezo1可以促进NLRP3炎性小体合成,反之使用siRNA沉默Piezo1则可逆转这一过程。而且Ca2+/NF-κB通路的抑制降低了Piezo1依赖性NLRP3炎症小体的激活,因此他们认为Piezo1通过Ca2+/NF-κB途径介导髓核细胞NLRP3炎性小体激活是椎间盘退变进展的一种新的发病机制。随后,SUN等[27]研究也发现,没有终板结构破坏的单次冲击损伤也可以引发椎间盘变性,这可能是由激活 Piezo1 诱导的炎症和椎间盘细胞的异常能量代谢介导的,两个冲击组的椎间盘均在14 d后出现退行性变化,显示 Piezo1、NLRP3炎症小体、分解代谢物(基质金属蛋白酶9、基质金属蛋白酶13)和白细胞介素1β表达均显著高于对照组(P < 0.05),沉默 Piezo1降低了冲击损伤诱导的髓核中 NLRP3 炎性体的激活和白细胞介素1β 的表达。另一方面,ZHAO等[83]结合前人经验总结得Piezo1在脂肪组织中表达丰富,可增强脂肪细胞可塑性,抑制炎症反应,脂解减弱导致脂肪沉积。通过实验证明脂肪特异性敲除Piezo1基因后,脂肪细胞的可塑性降低,炎症反应增加,脂解增强,此特征在高脂饮食小鼠中表现的更加明显。因此Piezo1作为脂肪细胞可塑性的调控机制通道,可以起到抑制肥胖促炎反应的作用,为新的抑炎靶标。 综上所述,Piezo1蛋白在不同组织细胞的炎症反应中均充当着重要的角色,尤其是在机械应力参与的炎症反应中。通过体外和体内实验,糖皮质激素和酒精的长期使用都被证实了可以促进炎症反应进展,见图4。炎症信号转导通路的激活促进炎性因子的大量释放并作用于股骨头区域,破坏局部的骨重塑和血管稳态,促进股骨头坏死的发生发展进程。而Piezo1作为介导炎症反应的关键因素,具备通过炎症反应途径调控股骨头坏死发生发展过程的巨大潜力,值得被广泛研究人员关注。"
| [1] MONT MA, CHERIAN JJ, SIERRA RJ, et al. Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Where Do We Stand Today? A Ten-Year Update. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(19):1604-1627. [2] 朱道宇,杨前昊,高悠水,等.TLR4通路与激素性股骨头坏死关系的研究进展[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2019,8(1):75-79. [3] 刘铁钢,陈卫衡.非创伤性股骨头坏死的流行病学研究进展[J].医学综述,2009,15(17):2637-2639. [4] MONT MA, ZYWIEL MG, MARKER DR, et al. The natural history of untreated asymptomatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a systematic literature review. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(12):2165-2170. [5] LIEBERMAN JR, ENGSTROM SM, MENEGHINI RM, et al. Which factors influence preservation of the osteonecrotic femoral head. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(2):525-534. [6] LIEBERMAN JR, BERRY DJ, MONT MA, et al. Osteonecrosis of the hip: management in the 21st century. Instr Course Lect. 2003;52:337-355. [7] IKEUCHI K, HASEGAWA Y, SEKI T, et al. Epidemiology of nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head in Japan. Mod Rheumatol. 2015; 25(2):278-281. [8] HINES JT, JO WL, CUI Q, et al. Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: an Updated Review of ARCO on Pathogenesis, Staging and Treatment. J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(24):e177. [9] ZHAO DW, YU M, HU K, et al. Prevalence of Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head and its Associated Risk Factors in the Chinese Population: Results from a Nationally Representative Survey. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015;128(21):2843-2850. [10] SEAMON J, KELLER T, SALEH J, et al. The pathogenesis of nontraumatic osteonecrosis. Arthritis. 2012;2012:601763. [11] CUI L, ZHUANG Q, LIN J, et al. Multicentric epidemiologic study on six thousand three hundred and ninety five cases of femoral head osteonecrosis in China. Int Orthop. 2016;40(2):267-276. [12] MIYANISHI K, YAMAMOTO T, IRISA T, et al. Bone marrow fat cell enlargement and a rise in intraosseous pressure in steroid-treated rabbits with osteonecrosis. Bone. 2002;30(1):185-190. [13] ZHAO D, CUI D, WANG B, et al. Treatment of early stage osteonecrosis of the femoral head with autologous implantation of bone marrow-derived and cultured mesenchymal stem cells. Bone. 2012;50(1):325-330. [14] CHANG C, GREENSPAN A, GERSHWIN ME. The pathogenesis, diagnosis and clinical manifestations of steroid-induced osteonecrosis. J Autoimmun. 2020;110:102460. [15] GE J, LI W, ZHAO Q, et al. Architecture of the mammalian mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel. Nature. 2015;527(7576):64-69. [16] COSTE B, MATHUR J, SCHMIDT M, et al. Piezo1 and Piezo2 are essential components of distinct mechanically activated cation channels. Science. 2010;330(6000):55-60. [17] HASELWANDTER CA, MACKINNON R. Piezo’s membrane footprint and its contribution to mechanosensitivity. Elife. 2018;7:e41968. [18] 何琪,张罡瑜,王海彬,等.大型跨膜蛋白Piezo1在骨科相关疾病中的参与及意义[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(30):4882-4888. [19] DOUGUET D, PATEL A, XU A, et al. Piezo Ion Channels in Cardiovascular Mechanobiology. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2019;40(12):956-970. [20] LIN YC, GUO YR, MIYAGI A, et al. Force-induced conformational changes in PIEZO1. Nature. 2019;573(7773):230-234. [21] SAOTOME K, MURTHY SE, KEFAUVER JM, et al. Structure of the mechanically activated ion channel Piezo1. Nature. 2018;554(7693): 481-486. [22] ALBARRÁN-JUáREZ J, IRING A, WANG S, et al. Piezo1 and G(q)/G(11) promote endothelial inflammation depending on flow pattern and integrin activation. J Exp Med. 2018;215(10):2655-2672. [23] ATCHA H, JAIRAMAN A, HOLT JR, et al. Mechanically activated ion channel Piezo1 modulates macrophage polarization and stiffness sensing. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):3256. [24] BARATCHI S, ZALDIVIA MTK, WALLERT M, et al. Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Represents an Anti-Inflammatory Therapy Via Reduction of Shear Stress-Induced, Piezo-1-Mediated Monocyte Activation. Circulation. 2020;142(11):1092-1105. [25] SOLIS AG, BIELECKI P, STEACH HR, et al. Mechanosensation of cyclical force by PIEZO1 is essential for innate immunity. Nature. 2019; 573(7772):69-74. [26] SUN Y, LENG P, SONG M, et al. Piezo1 activates the NLRP3 inflammasome in nucleus pulposus cell-mediated by Ca(2+)/NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;85:106681. [27] SUN Z, ZHENG X, LI S, et al. Single Impact Injury of Vertebral Endplates Without Structural Disruption, Initiates Disc Degeneration Through Piezo1 Mediated Inflammation and Metabolism Dysfunction. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2022;47(5):E203-E213. [28] YANG Y, WANG D, ZHANG C, et al. Piezo1 mediates endothelial atherogenic inflammatory responses via regulation of YAP/TAZ activation. Hum Cell. 2022;35(1):51-62. [29] KIM H, IWASAKI K, MIYAKE T, et al. Changes in bone turnover markers during 14-day 6 degrees head-down bed rest. J Bone Miner Metab. 2003;21(5):311-315. [30] RICE JC, COWIN SC, BOWMAN JA. On the dependence of the elasticity and strength of cancellous bone on apparent density. J Biomech. 1988; 21(2):155-168. [31] KOIKE M, NOJIRI H, OZAWA Y, et al. Mechanical overloading causes mitochondrial superoxide and SOD2 imbalance in chondrocytes resulting in cartilage degeneration. Sci Rep. 2015;5:11722. [32] LEE W, LEDDY HA, CHEN Y, et al. Synergy between Piezo1 and Piezo2 channels confers high-strain mechanosensitivity to articular cartilage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(47):E5114-E5122. [33] 沈晓峰,姜宏.全髋关节置换术后神经损伤的原因及预防措施[J].中医正骨,2013,25(1):46-48. [34] 郑超,郑秋坚,林帧,等. 缺血性股骨头坏死的治疗进展[J].实用骨科杂志,2014,20(1):43-47. [35] 石淇允,李无阴,张颖,等.补肾活血法防治创伤性股骨头坏死机制研究进展[J].河北中医,2019,41(8):1277-1280. [36] 中国医师协会骨科医师分会骨循环与骨坏死专业委员会,中华医学会骨科分会骨显微修复学组,国际骨循环学会中国区.中国成人股骨头坏死临床诊疗指南(2020)[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2020,40(20): 1365-1376. [37] SUGIMOTO A, MIYAZAKI A, KAWARABAYASHI K, et al. Piezo type mechanosensitive ion channel component 1 functions as a regulator of the cell fate determination of mesenchymal stem cells. Sci Rep. 2017; 7(1):17696. [38] SYEDA R, XU J, DUBIN AE, et al. Chemical activation of the mechanotransduction channel Piezo1. Elife. 2015;4:e07369. [39] SUN W, CHI S, LI Y, et al. The mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel is required for bone formation. Elife. 2019;8:e47454. [40] WANG L, YOU X, LOTINUN S, et al. Mechanical sensing protein PIEZO1 regulates bone homeostasis via osteoblast-osteoclast crosstalk. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):282. [41] ZHOU T, GAO B, FAN Y, et al. Piezo1/2 mediate mechanotransduction essential for bone formation through concerted activation of NFAT-YAP1-ß-catenin. Elife. 2020;9:e52779. [42] YAN L, JIANG J, MA C, et al. Effect of knocking down Piezo1 mechanically sensitive protein on migration of MC3T3-E1 osteoblast cells. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019; 33(1):28-34. [43] YONEDA M, SUZUKI H, HATANO N, et al. PIEZO1 and TRPV4, which Are Distinct Mechano-Sensors in the Osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 Cells, Modify Cell-Proliferation. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(19):4960. [44] 王林,王熙,季楠,等.机械激活性离子通道压电蛋白Piezo1通过Notch信号通路介导牙周膜干细胞成骨分化作用机制研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2020,38(6):628-636. [45] SONG J, LIU L, LV L, et al. Fluid shear stress induces Runx-2 expression via upregulation of PIEZO1 in MC3T3-E1 cells. Cell Biol Int. 2020;44(7): 1491-1502. [46] BACK SH, ADAPALA NS, BARBE MF, et al. TULA-2, a novel histidine phosphatase, regulates bone remodeling by modulating osteoclast function. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013;70(7):1269-1284. [47] BOYCE BF, YAO Z, XING L. Osteoclasts have multiple roles in bone in addition to bone resorption. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2009;19(3): 171-180. [48] KURATA K, UEMURA T, NEMOTO A, et al. Mechanical strain effect on bone-resorbing activity and messenger RNA expressions of marker enzymes in isolated osteoclast culture. J Bone Miner Res. 2001;16(4): 722-730. [49] BONEWALD LF. The amazing osteocyte. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(2): 229-238. [50] SIMS NA, MARTIN TJ. Coupling the activities of bone formation and resorption: a multitude of signals within the basic multicellular unit. Bonekey Rep. 2014;3:481. [51] XU X, LIU S, LIU H, et al. Piezo Channels: Awesome Mechanosensitive Structures in Cellular Mechanotransduction and Their Role in Bone. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(12):6429. [52] 黄鹏,尚画雨,李顺昌,等.机械敏感离子通道Piezo1在心血管系统中的作用[J].生命的化学,2020,40(3):369-377. [53] CAHALAN SM, LUKACS V, RANADE SS, et al. Piezo1 links mechanical forces to red blood cell volume. Elife. 2015;4:e07370. [54] ZENG WZ, MARSHALL KL, MIN S, et al. PIEZOs mediate neuronal sensing of blood pressure and the baroreceptor reflex. Science. 2018; 362(6413):464-467. [55] 吴霁,李萍. Piezo1离子通道在心血管病中的作用[J].中华高血压杂志,2021,29(3):228-232. [56] RETAILLEAU K, DUPRAT F, ARHATTE M, et al. Piezo1 in Smooth Muscle Cells Is Involved in Hypertension-Dependent Arterial Remodeling. Cell Rep. 2015;13(6):1161-1171. [57] BEECH DJ, KALLI AC. Force Sensing by Piezo Channels in Cardiovascular Health and Disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019;39(11):2228-2239. [58] LI J, HOU B, TUMOVA S, et al. Piezo1 integration of vascular architecture with physiological force. Nature. 2014;515(7526):279-282. [59] ALBUISSON J, MURTHY SE, BANDELL M, et al. Dehydrated hereditary stomatocytosis linked to gain-of-function mutations in mechanically activated PIEZO1 ion channels. Nat Commun. 2013;4:1884. [60] RANADE SS, QIU Z, WOO SH, et al. Piezo1, a mechanically activated ion channel, is required for vascular development in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(28):10347-10352. [61] ZHANG Y, WEI QS, DING WB, et al. Increased microRNA-93-5p inhibits osteogenic differentiation by targeting bone morphogenetic protein-2. PLoS One. 2017;12(8):e0182678. [62] SCHELL H, DUDA GN, PETERS A, et al. The haematoma and its role in bone healing. J Exp Orthop. 2017;4(1):5. [63] LUO P, GAO F, HAN J, et al. The role of autophagy in steroid necrosis of the femoral head: a comprehensive research review. Int Orthop. 2018; 42(7):1747-1753. [64] 赵海燕,夏亚一,康鹏德. 股骨头坏死病因与发病机制研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(8):604-607. [65] TIAN L, WEN Q, DANG X, et al. Immune response associated with Toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway leads to steroid-induced femoral head osteonecrosis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15:18. [66] 田雷,周东生,孙水,等.Toll样受体4信号通路过度激活在大鼠激素性股骨头坏死中的作用[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2014, 35(5):622-629. [67] LIU H, LI D, ZHANG Y, et al. Inflammation, mesenchymal stem cells and bone regeneration. Histochem Cell Biol. 2018;149(4):393-404. [68] GÜLER-YüKSEL M, HOES JN, BULTINK IEM, et al. Glucocorticoids, Inflammation and Bone. Calcif Tissue Int. 2018;102(5):592-606. [69] CHEN B, LIU Y, CHENG L. IL-21 Enhances the Degradation of Cartilage Through the JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway During Osteonecrosis of Femoral Head Cartilage. Inflammation. 2018;41(2):595-605. [70] 王多贤,曹林忠,蒋玮,等.激素性股骨头坏死中的炎症小体激活与细胞焦亡[J].生命的化学,2021,41(8):1733-1739. [71] 徐西林,赵军,杨福彪,等.活骨灌注液不同给药途径对激素性股骨头坏死相关炎性因子表达的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2019,27(10):10-13. [72] LI JK, CHENG L, ZHAO YP, et al. ADAMTS-7 exhibits elevated expression in cartilage of osteonecrosis of femoral head and has a positive correlation with TNF- α and NF- κ B P65. Mediators Inflamm. 2015; 2015:196702. [73] 丁文波,杨璐,宫兆奇,等.辅酶Q10辅助辛伐他汀治疗激素相关性兔股骨头坏死的疗效和可能机制[J].中国老年学杂志,2018, 38(5):1215-1217. [74] 王涛,张育民,王军伟,等.辛伐他汀联合抗凝药物治疗老年激素性股骨头坏死临床效果及安全性分析[J].解放军医药杂志,2017, 29(7):54-57,61. [75] 陆咨儒,谢林,相萍萍,等.辛伐他汀治疗酒精性股骨头坏死的效果及机制初步探讨[J].实用临床医药杂志,2021,25(8):96-100. [76] ZHENG L, WANG W, NI J, et al. Plasma interleukin 33 level in patients with osteonecrosis of femoral head: an alarmin for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Investig Med. 2014;62(3):635-637. [77] 赵红星,黄媛霞,徐海斌,等.他汀类药物治疗激素性股骨头坏死的效果及机制研究[J].西北药学杂志,2017,32(3):359-363. [78] OLIVA J, BARDAG-GORCE F, LI J, et al. S-adenosylmethionine prevents the up regulation of Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling caused by chronic ethanol feeding in rats. Exp Mol Pathol. 2011;90(3):239-243. [79] 陈亦轩,朱道宇,殷俊辉,等. 酒精性股骨头坏死研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2018,39(1):28-32. [80] 赵钟涵,杜玉香,张玲莉.机械敏感性离子通道蛋白Piezo1响应力学刺激的研究进展[J].生命的化学,2021,41(4):804-811. [81] TOLAR P, WACK A. Monocytes work harder under pressure. Nat Immunol. 2019;20(11):1422-1424. [82] WILLIAMS ER. PIEZO1 promotes inflammation. Science Signaling. 2019; 12(598). doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaz4154 [83] ZHAO C, SUN Q, TANG L, et al. Mechanosensitive Ion Channel Piezo1 Regulates Diet-Induced Adipose Inflammation and Systemic Insulin Resistance. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019;10:373. [84] QIN L, HE T, CHEN S, et al. Roles of mechanosensitive channel Piezo1/2 proteins in skeleton and other tissues. Bone Res. 2021;9(1):44. [85] 潘兆丰,杨均政,何琪,等.内皮细胞Piezo1敲除对激素性股骨头坏死模型小鼠的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(32):5107-5111. [86] 魏腾飞,何晓铭,韦雨柔,等. Piezo1在激素性和酒精性股骨头坏死骨组织中的差异表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(2):270-275. [87] ZHAO D, ZHANG F, WANG B, et al. Guidelines for clinical diagnosis and treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in adults (2019 version). J Orthop Translat. 2020;21:100-110. [88] CARINA V, DELLA BELLA E, COSTA V, et al. Bone’s Response to Mechanical Loading in Aging and Osteoporosis: Molecular Mechanisms. Calcif Tissue Int. 2020;107(4):301-318. [89] SECOMB TW. Hemodynamics. Compr Physiol. 2016; 6(2):975-1003. [90] WEN P, ZHANG Y, HAO L, et al. The effect of the necrotic area on the biomechanics of the femoral head - a finite element study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):211. [91] FENG C, WANG L, XU P, et al. Microstructural and mechanical evaluations of region segmentation methods in classifications of osteonecrosis. J Biomech. 2021;119:110208. [92] KERACHIAN MA, HARVEY EJ, COURNOYER D, et al. Avascular necrosis of the femoral head: vascular hypotheses. Endothelium. 2006;13(4): 237-244. |
| [1] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | Fang Xingyan, Tian Zhenli, Zhao Zheyi, Wen Ping, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and sphingosine kinases 1/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling axis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [3] | Liang Jiaqi, Liu Hengxu, Yang Jinxin, Yang Yi, Deng Xuhui, Tan Mingjian, Luo Jiong. Health benefit relationship between exercise and intestinal bacteria [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1292-1299. |
| [4] | Gao Yu, Han Jiahui, Ge Xin. Immunoinflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [5] | Tang Liang, Li Xiheng, Niu Ruijuan, Li Xinyue, Zou Xinying, Mao Tianjiao, Li Jiang. Naringin regulates the function of RAW264.7 macrophages to affect the osteogenic differentiation of MC-3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1205-1210. |
| [6] | Xu Yan, Li Ping, Lai Chunhua, Zhu Peijun, Yang Shuo, Xu Shulan. Piezoelectric materials for vascularized bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1126-1132. |
| [7] | Wang Min, Yin Xiushan, Wang Yingxi, Zhang Yan, Zhao Long, Xia Shuyue. Inhalation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviates inflammatory injury in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 827-834. |
| [8] | Wang Jinling, Huang Xiarong, Qu Mengjian, Huang Fujin, Yin Lingwei, Zhong Peirui, Liu Jin, Sun Guanghua, Liao Yang, Zhou Jun. Effects of exercise training on bone mass and bone microstructure in aged osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 676-682. |
| [9] | Li Zhichao, Tan Guoqing, Su Hui, Xu Zhanwang, Xue Haipeng. Regulatory role of non-coding RNAs as potential therapeutic targets in spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 758-764. |
| [10] | Zhang Lichen, Chen Liang, Gu Yong. Inorganic ion bionic periosteum regulates immune microenvironment to promote bone repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 346-353. |
| [11] | Liu Gang, Deng Bowen, Jiang Shengyuan, Xu Lin, Fan Xiao, Tao Jingwei, Zhang Houjun, He Feng, Zhao Yi, Mu Xiaohong. Tetramethylpyrazine improves hemorheological indexes in rats with complete spinal cord transection: a dynamic observation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 282-286. |
| [12] | Liu Yinghong, Yi Yating. Mechanism and implication of angiogenesis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 307-313. |
| [13] | Wei Tengfei, He Xiaoming, Wei Yurou, Zhan Zhiwei, He Mincong, He Wei, Wei Qiushi. Differential expression of Piezo1 in osseous tissue of steroid- and alcohol-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 270-275. |
| [14] | Xie Pingjin, Luo Zhen, Lu Qigui, Guo Yanxing, Chen Qunqun, Li Feilong. Effect of ligustrazine and overexpression of miR-20b-5p on synovial, cartilage and subchondral bone angiogenesis in rats with early-stage knee osteoarthritis: a histological observation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 237-245. |
| [15] | Li Zhe, Yuan Changshen, Guan Yanbing, Xu Wenfei, Liao Shuning, Rong Weiming, Mei Qijie, Duan Kan. Bioinformatic analysis and experimental validation of ferroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(17): 2637-2643. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||