Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (22): 3587-3593.doi: 10.12307/2023.389
Previous Articles Next Articles
Influencing factors and current situation of parametric design of knee prosthesis
Liu Chang1, Liu Lei1, Ma Chaoqun1, Cao Chuanxu1, Xu Changzhi2
- 1School of Mechanical and Material Engineering, 2School of Applied Technology, Huaiyin Institute of Technology, Huai’an 223001, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2022-05-18Accepted:2022-07-19Online:2023-08-08Published:2022-11-02 -
Contact:Liu Lei, PhD, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, School of Mechanical and Material Engineering, Huaiyin Institute of Technology, Huai’an 223001, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Liu Chang, Master candidate, School of Mechanical and Material Engineering, Huaiyin Institute of Technology, Huai’an 223001, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:The 2022 College Students Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program of Huaiyin Institute of Technology, No. 202211049020Z (to XCZ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Chang, Liu Lei, Ma Chaoqun, Cao Chuanxu, Xu Changzhi. Influencing factors and current situation of parametric design of knee prosthesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(22): 3587-3593.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
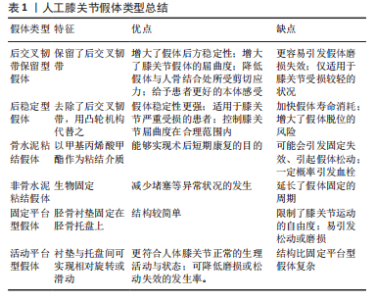
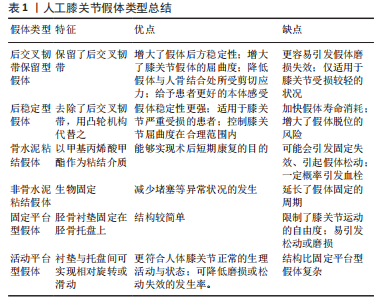
2.1 膝关节假体的类型 2.1.1 后交叉韧带保留型假体与后稳定型假体 后交叉韧带是位于人体膝关节股骨与胫骨之间的维持膝关节正常运行的结构,其通过限制股骨位移过度以及防止膝关节过度伸展,从而起到保护膝关节的作用[6]。后交叉韧带保留型假体保留了这一结构,从而增大了假体的后稳定性[7],防止假体脱位;假体屈曲时,股骨能够如正常人体膝关节股骨一般向后转动,增大了膝关节假体的屈曲度;同时,后交叉韧带能够吸收一部分应力,降低假体与人骨结合处所受剪切应力;并且后交叉韧带的保留能够使假体有更接近正常膝关节的步态与运动特性,从而给予患者更好的本体感受。但后交叉韧带保留型膝关节假体在理论上增大了关节面之间的接触应力,更容易引起假体磨损失效的发生,仅适用于膝关节受损较轻的状况[8]。 后稳定型假体则移除了人体后交叉韧带。在设计上,假体股骨两髁与胫骨衬垫之间增加了一种凸轮设计[9],在某些层面上,这一设计不仅能够代替后交叉韧带,并且能起到更好地稳定假体作用。这种假体更适合应用于膝关节严重受损的患者,减轻患者痛感,并控制膝关节屈曲度在一个合理的范围之内。但由于完全切除了后交叉韧带,膝部所受应力更多的将通过假体进行传导[10],这将加快假体寿命消耗,增大了假体脱位的风险。 2.1.2 骨水泥粘结假体与非骨水泥粘结假体 骨水泥粘结假体所用到的骨水泥即甲基丙烯酸甲酯,其能够被人骨兼容且具有较高的黏贴性,能够实现术后短期康复的目的。但骨水泥粘结可能会引发固定失效,从而引起假体松动,并且在进行骨水泥填充时,有一定概率导致血管堵塞从而引发血栓。 非骨水泥粘结假体装配了一种“加压结构”,其能够促进人体骨组织生长进入假体,从而达到生物固定的效果。这种固定方式能够减少堵塞等异常状况的发生,但同时延长了假体固定的周期。 2.1.3 固定平台型假体与活动平台型假体 固定平台型假体将胫骨衬垫固定在胫骨托盘上,限制了其自由度。活动平台型假体则模拟了人体膝关节正常的生理活动与状态,在设计上表现为衬垫与托盘间的非固定性,可实现相对旋转或滑动。各种类型膝关节假体总结见表1。 "
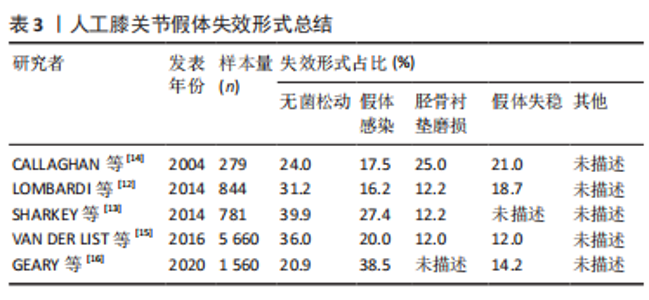
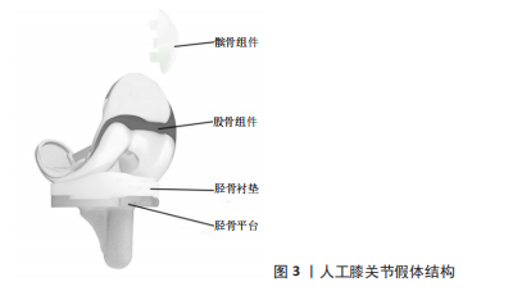
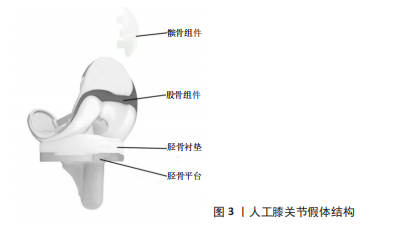
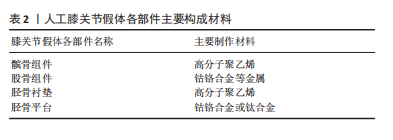
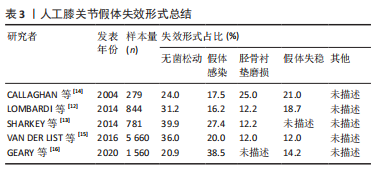
正如表2中所示,膝关节假体各组件的材料属性不同,彼此之间可能存在不兼容现象。并且引言中也指出,膝关节是人体承重最大的关节,假体植入人体后,必将处于高频重载之环境,从而导致假体出现失效。膝关节假体的失效形式多种多样。LOMBARDI团队[12]历时数年,对844例接受全膝关节置换并进行过翻修手术的患者进行跟踪调查与研究,从这些样本中得出人工膝关节假体失效的主要形式有:假体的无菌松动(31.2%)、假体失稳(18.7%)、假体感染(16.2%)及胫骨衬垫磨损(12.2%)等。Sharkey团队[13]也进行了类似的调查,他们从781例患者样本中得到的数据结果为:无菌松动(39.9%)、假体感染(27.4%)、胫骨衬垫磨损(12.2%)以及假体失稳、假体周围骨折等其他失效形式。此外,其他一些研究者通过调查研究也得出了各自的结论[12-16],具体归纳见表3。"
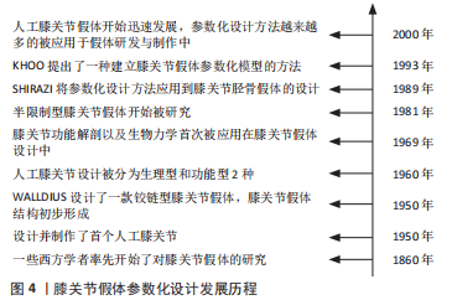
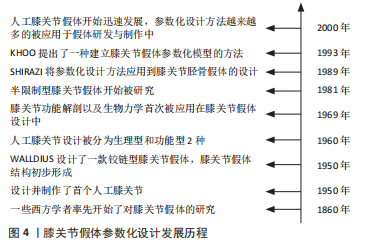
因此,人工膝关节假体的主要失效形式可总结为无菌松动、假体感染、胫骨衬垫磨损以及假体失稳4种,其中最主要的是无菌松动、假体感染和胫骨衬垫磨损。 2.2.1 无菌松动 无菌松动是膝关节假体的主要失效形式之一,在股骨组件与胫骨组件中都能检测到这种现象。如CALLAGHAN等[14]在观察患者假体医学影像时,便发现了与假体相接触的胫骨部分存在骨质流失现象。而J?RVENP??团队[17]在对接受全膝关节置换治疗患者进行的7年随访研究结果则表明,无菌松动现象从手术完成后便开始发生,术后3个月内骨质流失速度较快,随后渐趋平缓但一直存在。 假体发生无菌松动时,会降低关节稳定性、使假体活动范围减少,同时加剧患者痛感。无菌松动现象被发现的案例已经屡见不鲜,但关于其病发机制,学术界目前没有给出明确解释,甚至对于其概念、如何进行有效治疗与预防都处于争议之中[18]。 对于无菌松动的产生原因,目前主要观点认为是属性差异引发的。假体材料与人体骨骼属性不同,当假体受到外界作用力时,会将载荷传导至其周围的人体组织,这种属性上的差异不可避免的会对附近人体组织的重建产生影响。FUIKO等[19]使用荧光镜辅助技术,对101例接受假体置换的患者进行了2年的膝关节功能调查分析,发现大多数患者胫骨假体与胫骨面之间出现了从胫骨中心向四周增加的楔形间隙,这表明患者在接受全膝关节置换手术后,假体产生的力破坏了原有膝关节的平衡。PATEL等[20]在对比骨水泥粘结与非骨水泥粘结假体稳定性时,发现两种类型假体都会产生较小幅度微动,并且随着时间的推移,这种微动所带来的胫骨组件位移愈发明显。膝关节假体植入人体后需保留数年,骨质流失与原有膝关节平衡的破坏都会对病情恢复与人体健康产生不利影响,此现象应当引起重视。 除此之外,一些学者也努力探究导致无菌松动发生的其他原因,如BERLET等[21]尝试研究胫骨柄长度与无菌松动之间的关系,但结果表示两者相关性较低。而LEVENT等[22]的最新一项研究表明,股骨近端20 cm处骨干直径是预测无菌松动产生的可靠指标。 2.2.2 胫骨衬垫的磨损 大多数胫骨衬垫由高分子聚乙烯制作,高分子聚乙烯化学性质稳定,耐磨性好,且生物相容性较高,是制作膝关节假体的优选材料[23]。早在20世纪90年代,就已经有学者对胫骨衬垫的表面或材料属性进行了处理与调整[24]。CURRIER等[25]比较分析了若干不同抗氧化聚乙烯材料的回收率,指出不同类型的聚乙烯材料在最大氧化值上存在显著差异,并提出一种可作为临床医师较好选择的抗氧化聚乙烯材料。首先,近代一些学者在胫骨衬垫特定运动方面进行了改进[25-26],但无论怎样处理,胫骨衬垫与钴铬合金或钛合金的属性还是有较大差异的,这种材料属性的不同,不可避免的会给胫骨衬垫带来磨损等失效。其次,磨损导致磨屑产生,磨屑进入人体组织后引发免疫系统作用,破坏骨组织,从而引发骨溶解[27]。最后,人工膝关节胫骨衬垫与真实膝关节的形态不一致,完整膝关节胫骨平台略微凸出,而现代大多数胫骨插入物则是被设计成对称凹形,这也可能会给膝关节假体带来运动异常状况[28]。 高分子聚乙烯的主要失效形式有点蚀、层间分层和黏附磨损[25,29]。长期在高频重载环境中的高分子聚乙烯胫骨衬垫易产生点蚀与层间分层现象[30]。点蚀现象是由胫骨衬垫表面某处产生的裂纹向内部或四周扩展,或因重载情况导致内部首先产生裂纹而向表面扩展。层间分层现象是高分子聚乙烯胫骨衬垫内部首先产生裂纹,并且裂纹沿表面切向方向进行扩展,从而引起对膝关节假体的破坏。最大切应力与von Mises应力被用作高分子聚乙烯强度评估的一般指标,理论上,随着胫骨衬垫假体受到接触应力的增加,其最大切应力与von Mises应力也会随之增加[31]。黏着磨损是一种相对比较缓和的失效形式,其受两物体之间的接触载荷、物体本身的曲面形态与运动学特征等因素的影响[32-33]。在进行假体设计时,假体关节之间的磨损约束成负相关[32],即关节之间的约束越多,其相对滑动与磨损就越少。因此学者们在进行假体设计时一般会增大上下2部分之间的接触面积,以减少假体组件之间的磨损。 高分子聚乙烯胫骨衬垫的磨损受接触应力、与其他组件接触面积的影响,同时关节假体各组件之间的配合状况、手术技术等也与其息息相关[23,25,34]。高分子聚乙烯胫骨衬垫的磨损一旦发生,便会带来关节失稳等一些严重后果,给膝关节假体带来极大损害,这是研究者们应当注意的。 2.2.3 膝关节假体感染 膝关节假体感染是全膝关节置换早期较为常见的失效形式,在晚期的失效修复治疗中出现的频次也是仅次于无菌松动[13]。导致假体发生感染的因素较多,大致可分为3类,分别是术前假体感染、围术期假体感染以及术后假体感染[35]。患者术前存在的破损、感染等皮肤疾病,或其身体素质差、年龄较大、患有糖尿病、风湿病及各种慢性疾病等因素,都将增大假体感染的病发率。在围术期中,置换假体的类型、手术环境以及抗生素的使用等也会影响假体感染的发生率。滥用静脉注射药物、不良的生活习惯以及患者术后长时间卧床所导致压疮、坠积性肺炎等也是潜在的危险因素[36]。 相较于假体磨损或松动的状况,感染所带来的后果则是极其严重的,甚至不排除会使患者膝关节功能永久丧失。尽管现代医学在进行全膝关节置换时会用到预防性抗生素或其他一些预防感染的办法,但膝关节假体感染失效仍屡见不鲜。吴宇黎等[37]从动物模型中提取出多黏物质,并通过药敏实验法测定了这种提取物对抗生素的影响,实验结果表明,多黏物质能够破坏抗生素的杀菌作用,加剧膝关节假体受感染的风险。JANZ 等[38]通过对284例接受假体翻修患者的单个假体组件进行提取液的培养,探究受感染假体的病菌分布状况,结果表明,聚乙烯组分的假体细菌分离率明显高于其他材质假体,即聚乙烯假体某一处发生的病菌感染很可能会扩撒到整个假体,因此在对聚乙烯假体进行修复时,应当注意辅以抗菌性药物,防止发生假体感染。方恺[35]总结了若干份关于膝关节假体感染的报告,指出仅仅依靠抗生素很难清除病菌。因此,接受全膝关节置换手术的患者应当意识到假体感染的潜在性与可能性,一旦发生假体感染,应尽快根据病情进行诊治。 2.3 膝关节假体参数化设计发展历程 早在19世纪60年代,西方一些学者便开始了对膝关节假体的研究,然而受当时技术的限制,一直到20世纪50年代,有研究设计并制作了第一个人工膝关节,膝关节假体才初现雏形[39]。不久后,WALLDIUS团队设计了一种铰链型膝关节假体,其用骨水泥将假体固定,使之只能做屈曲运动[40]。这种最原始的膝关节假体虽然存在诸多弊病,但却开启了膝关节假体设计的先河。20世纪60年代,人工膝关节假体的设计被分为生理型和功能型2种。在20世纪60年代末,GUNSTON在进行膝关节假体设计时,首次应用了膝关节功能性解剖方法与生物力学方法。20世纪70年代,全膝关节置换手术开始被应用膝关节疾病的治疗[41]。然而因为假体设计的不合理以及技术不成熟等原因,导致全膝关节置换假体存活率较低。20世纪80年代以后,学者们渐渐开始了半限制性膝关节假体的研究[42],这种假体在上一代的基础上,增加了假体运动的自由度,对病患的治疗起到了一定的帮助。1989年,SHIRAZI将参数化设计方法应用到膝关节胫骨假体的设计,这是参数化设计方法首次被应用到胫骨假体的设计。不久后,KHOO等[43]提出了一种建立膝关节假体参数化模型的方法,这是一项膝关节假体参数化建模的早期研究,对学者们进行假体参数化设计起到了重要的参考作用。而后膝关节假体功能不断完善,逐渐出现了假体功能性解剖、髌骨假体设计、生物力学对假体的辅助设计等技术[44-45]。膝关节假体参数化设计发展历程见图4。"

2.4 完善膝关节假体参数化设计 由于中国对人工膝关节假体的研究起步较晚,在早些时期,中国用于全膝关节置换的手术器材与假体部件大部分依赖进口。但中国人与欧美地区人种在体态上有较大差别,以外国人体态特征为依据制作的膝关节假体用到国人身上时,经常会出现不匹配状况[46]。为解决这一问题,诸多中国学者用不同方法测量了国人膝关节的形态学尺寸与解剖学结构[47-49],李兴[50]对膝关节假体的三维模型构建过程作了详细介绍。这些研究都为人工膝关节假体的设计与开发做出巨大贡献。 2.4.1 膝关节假体参数化设计的概念与意义 膝关节假体的设计特征在很大程度上影响患者的膝关节性能[51-52],不合理的假体设计将导致患者很难拥有患病之前的状态与灵活性,甚至会给患者带来无法弥补的严重后果。假体的性能指标包括可靠性、耐用性以及生物相容性等[53],在工程学上表现为假体与假体之间、假体与骨之间的接触力学与摩擦学特征[54]。相关研究表明,膝关节假体的几何特征不仅对假体与假体、假体与骨之间的接触力学特性有较大影响、在摩擦学性能上起到至关重要的作用,其对假体的性能也起到决定性作用[54-56]。因而良好的假体设计应使其具备较优的生物相容性、良好的接触性能、稳定的运动学特征与较低的摩擦力,从而使患者获得更佳的康复效果。 假体参数化设计指使用参数与约束完全定义一个初始的几何模型,改变模型中某一个或若干个参数,将自动生成一个全新并且保持原有约束的几何模型。参数化设计完成后,研究者在修改模型时便无需考虑约束问题,只需通过修改模型参数便可适配不同的需求与状况。在膝关节假体参数化设计过程中,需对假体模型几何特征进行充分分析、科学取样,选取合适的参数值与约束,以达到高度数字化的目的。一套完整的人工膝关节假体参数化设计完成后,将为假体后期型号变更、批量生产起到极大的便利作用。 2.4.2 运动学性能与接触力学性能对膝关节假体参数化设计的影响 运动学特性与接触力学特性都是膝关节假体的重要性能指标,然而两者之间存在一种“竞争关系”,当对假体运动学性能进行优化时,会降低其接触力学性能,反之,优化接触力学性能时,运动学性能也会受到影响[57-58]。为验证这种“矛盾关系”,WILLING等[59]根据假体耐久性与运动学性能Pareto曲线,使用自适应加权法与多目标设计优化法对植入膝关节假体进行测试实验。在验证过程中,WILLING运用参数化的方法,量化了假体的运动性能与耐久性能,并指出,在一定范围内,运动性能指标与耐久性能指标的权重值越接近,越能够获得更优的平衡,然而一旦某个指标的权重值突破了极限,继续对其进行优化时则会破坏另一指标的性能[59]。KOH等[60]自主开发了一种自适应型计算模拟方法,对3种不同形态后稳定型全膝关节置换假体股骨与胫骨之间的一致性对磨损性能的影响进行模拟评估,结果表明,内侧枢轴一致型膝关节假体在单位时间内的磨损量最小;而解剖一致型全膝关节假体比起一般假体,则具有更具高的胫骨内侧相对旋转功能。不同形态的后稳定型膝关节假体表现出不同的磨损性能,充分证明了假体胫股骨间一致性对其寿命有很大影响。王猛等[61]以美国强生公司所研发的膝关节假体为标准建立了数个三维有限元模型,每个模型中设置不同的曲率半径等参数,模拟假体植入人体后的步态周期状况,实验结果表明,假体接触力学性能与运动学性能分别受冠状面曲率半径和矢状面曲率半径一致性影响[61]。 综上所述,膝关节假体运动学性能与接触力学性能分别受不同参数影响,而参数的变化必然引起性能的变化,所以膝关节假体运动学性能与接触力学性能之间的竞争关系是不可避免的。参数化假体的优化目标是使两者控制在一个合理的范围内。目前的研究虽无法做到让两者都达到最优值,但可使运动性能指标与接触性能指标的权重值尽量接近,以获得更优、更平衡的参数化设计假体。 2.4.3 形合度对膝关节假体参数化设计的影响 在假体参数化设计中,形合度是其完善程度的重要指标之一。形合度指假体股骨与胫骨在矢状面与冠状面上几何参数的一致性[61]。一般情况下,当股骨假体与胫骨假体在矢状面或冠状面上曲率相差较大时,认为其形合度较低,反之则表示形合度较高。KOH等[62]通过对现有三维膝关节模型进行模拟,比较接受全膝关节置换手术治疗的患者中使用传统假体与使用特定假体在步态载荷条件下的磨损性能,结果表明,不同形合度的膝关节假体所产生的内外运动学变化是不同的,这种区别甚至可以使磨损率相差达到29%甚至更多。BROCKETT等[63]使用Leeds ProSim气动六工位膝关节模拟器模拟实验了2种不同条件下矢状面形合度对膝关节假体磨损性能的影响,实验结果显示,唇形嵌件磨损面积相较于扁平嵌件更大,且磨损率也显著高于扁平嵌件,这表明假体形合度对磨损性能有显著的影响。通过对材料与设计方法的改进,能够在一定程度上缓解假体磨损状况。而WILLING等[64]自行研发了一个用以生成全膝关节置换假体设计的股骨组件和高分子聚乙烯嵌件模型,并通过改进Archard磨损模型用以模拟ISO标准条件下的全膝关节置换假体磨损试验。实验计算了不同条件下的接触压力、磨损系数与滑动距离,通过修改冠状面与矢状面上两个部件的曲率半径,降低植入组件之间的一致性,使得高分子聚乙烯假体年磨损量从55.248 mm3降低到45.013 mm3。此项研究在产生了一种新的膝关节假体设计的同时,使假体年磨损量降低了18.5%,是假体设计上的一个新突破。 目前,虽然关于膝关节假体形合度研究逐渐增多,但至今仍没有一套标准的取值范围来确定形合度的高低水平。研究者常以股骨假体与胫骨假体在矢状面和冠状面上的差异来表达一个假体模型形合度的大小,但这个差异值是未被量化的,其数值的大小与假体模型其他参数间是否存在一定的函数关系不得而知,其对假体性能的影响也无规律可循,研究者只能根据待研究假体的具体状况来确定研究方法,而这也是膝关节假体参数化设计过程中要克服的一个重要问题。 2.4.4 影响膝关节假体参数化设计的其他因素 几何参数随机取样法、主成分分析法以及概率方法等也被广泛运用到假体模型计算与仿真中,以预测假体的性能分布和不可确定条件或可变参数对假体设计所带来的影响。FITZPATRICK等[55]在对关节假体进行研究时,结合概率方法与主成分分析法,深入探究了假体设计与力学之间的重要关系。此外,在膝关节假体参数化设计中,应优先考虑与目标性能相关度较高的参数,相关度低的参数可以次要考虑但不容忽视。同时,参数间应彼此兼容,以避免功能限制与不利约束的产生。这些方法的发展与完善,对测定假体几何参数、预测给定变量对假体功能的影响以及完善假体设计起到了辅助作用。参数化设计能够为假体的理论设计、生产开发与临床应用提供指导与保证,对假体的检测与仿真起到积极促进作用,同时也能够在一定程度上防止膝关节假体发生失效,延长假体的使用寿命,并有助于推进膝关节假体的发展。 "

| [1] WU VJ, ILOANYA MC, SANCHEZ FL, et al. Is Patient-reported penicillin allergy independently associated with increased risk of prosthetic joint infection after total joint arthroplasty of the hip, knee, and shoulder? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020;478(12):2699-2709. [2] IMAN K, ELLIOT F, JAN F. Dedicated CT and MRI Techniques for the evaluation of the postoperative knee. Semin Musculoskel Radiol. 2018;22(4):444-456. [3] 裴福兴.中国髋、膝关节置换的现状及展望[J].中国骨与关节杂志, 2012,1(1):4-8. [4] KATZ JN, ARANT KR, LOESER RF. Diagnosis and treatment of hip and knee osteoarthritis: a review. JAMA. 2021;325(6):568-578. [5] ALRAWASHDEH W, ESCHWEILER J, MIGLIORINI F, et al. Effectiveness of total knee arthroplasty rehabilitation programmes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Rehabil Med. 2021;53(6):jrm00200. [6] SCHREIER FJ, BANOVETZ MT, RODRIGUEZ AN, et al. Cutting-edge posterior cruciate ligament reconstruction principles. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2021;9(6): 607-617. [7] CHEN L, XU J, LIN Y, et al. The effect of sacrificing the posterior cruciate ligament on total knee arthroplasty with cruciate retaining highly congruent rotating platform prosthesis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):299. [8] MOST E, LI G, SULTAN PG, et al. Kinematic analysis of conventional and high-flexion cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasties: an in vitro investigation. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(4):529-535. [9] BAEK JH, LEE SC, CHOI K, et al. Long-term survivorship of total knee arthroplasty with a single-radius, high-flexion posterior stabilized prosthesis. Knee. 2021;30:275-282. [10] WANG XH, BI Z, DONG X, et al. Increasing the height of the anterior lip on a tibial insert in a posterior stabilized knee prosthesis has little effect on the wear rate. Med Eng Phys. 2021;91:48-53. [11] SOBAJIMA A, OKIHARA T, MORIYAMA S, et al. Multiwall carbon nanotube composites as artificial joint materials. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(12): 7032-7040. [12] LOMBARDI AV JR, BEREND KR, ADAMS JB. Why knee replacements fail in 2013: patient, surgeon, or implant? Bone Joint J. 2014;96-b(11 Supple A): 101-104. [13] SHARKEY PF, LICHSTEIN PM, SHEN C, et al. Why are total knee arthroplasties failing today—has anything changed after 10 years? J Arthroplasty. 2014; 29(9):1774-1778. [14] CALLAGHAN JJ, O’ROURKE MR, SALEH KJ. Why knees fail: lessons learned. J Arthroplasty. 2004;19(4 Suppl 1):31-34. [15] VAN DER LIST JP, ZUIDERBAAN HA, PEARLE AD. Why do medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasties fail today? J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(5):1016-1021. [16] GEARY MB, MACKNET DM, RANSONE MP, et al. Why do revision total knee arthroplasties fail? a single-center review of 1632 revision total knees comparing historic and modern cohorts. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(10): 2938-2943. [17] JÄRVENPÄÄ J, SOININVAARA T, KETTUNEN J, et al. Changes in bone mineral density of the distal femur after total knee arthroplasty: a 7-year DEXA follow-up comparing results between obese and nonobese patients. Knee. 2014;21(1):232-235. [18] MENKEN LG, FLEURISCAR J, WEINER T, et al. Aseptic tibial Implant loosening after total knee arthroplasty: preventable? J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2021; 29(8):326-330. [19] FUIKO R, ZEMBSCH A, LOYODDIN M, et al. Osteointegration and implant position after cementless total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;408:201-208. [20] PATEL AH, WILDER JH, WELDY JM, et al. Patella strength characteristics in cemented vs press-fit implants: a biomechanical analysis of initial stability. Arthroplast Today. 2022;14:140-147. [21] BERLET GC, LANGAN TM, JAMIESON MD, et al. Analysis of the effect of tibial stem length on coronal plane deformity of the tibial component in total ankle arthroplasty. Foot Ankle Int. 2019;40(10):1166-1174. [22] LEVENT A, SUERO EM, GEHRKE T, et al. Risk factors for aseptic loosening after total knee arthroplasty with a rotating-hinge implant: a case-control study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2021;103(6):517-523. [23] POURZAL R, CIP J, RAD E, et al. Joint line elevation and tibial slope are associated with increased polyethylene wear in cruciate-retaining total knee replacement. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(7):1596-1606. [24] MURATOGLU OK, BRAGDON CR, O’CONNOR DO, et al. Unified wear model for highly crosslinked ultra-high molecular weight polyethylenes (UHMWPE). Biomaterials. 1999;20(16):1463. [25] CURRIER BH, CURRIER JH, HOLDCROFT LA, et al. Effectiveness of anti-oxidant polyethylene: What early retrievals can tell us. J Biomed Mater Res Part B Applied Biomaterials. 2018;106(1):353-359. [26] MATHIS DT, LOHRER L, AMSLER F, et al. Reasons for failure in primary total knee arthroplasty - An analysis of prospectively collected registry data. J Orthop. 2020;23:60-66. [27] ZHANG M, WANG JY, SU J, et al. Wear assessment of tibial inserts made of highly cross-linked polyethylene supplemented with dodecyl gallate in the total knee arthroplasty. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(11):1847. [28] KEOGH CJ, KEOHANE D, HARTY JA, et al. Nontraumatic tibial polyethylene insert cone fracture in rotating-platform total knee arthroplasty. Arthroplast Today. 2021;8:283-288.e1. [29] MURATOGLU OK, RUBERTI J, MELOTTI S, et al. Optical analysis of surface changes on early retrievals of highly cross-linked and conventional polyethylene tibial inserts. J Arthroplasty. 2003;18(7 Suppl 1):42-47. [30] 杜明明,张宽,闫松华.全膝关节置换胫骨平台截骨后倾角对关节接触力的影响[J].北京生物医学工程,2021,40(3):227-232. [31] KUNKEL ST, MOSCHETTI WE, WERTH P, et al. Tobacco exposure is associated with extremely low polyethylene oxidation in total knee arthroplasty components. Arthroplast Today. 2021;8:243-246. [32] PÉCORA JR, ROMERO V. Evaluation of polyethylene wear in a brazilian ultracongruent knee prosthesis with a rotating platform. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2021;56(1):42-46. [33] SHU L, HASHIMOTO S, SUGITA N. Enhanced in-silico polyethylene wear simulation of total knee replacements during daily activities. Ann Biomed Eng. 2021;49(1):322-333. [34] ARGENSON JN, O’CONNOR JJ. Polyethylene wear in meniscal knee replacement. A one to nine-year retrieval analysis of the Oxford knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br Vol. 1992;74(2):228. [35] 方恺.人工膝关节置换后的假体周围感染[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(30):5650-5653. [36] CHEN MJ, HUNG JF, CHANG CH, et al. Periprosthetic knee infection reconstruction with a hinged prosthesis: implant survival and risk factors for treatment failure. Knee. 2020;27(3):1035-1042. [37] 吴宇黎,李晓华,钱齐荣,等.感染性人工关节生物膜中细胞外多粘质物质对抗生素的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2002,9(10):980-981. [38] JANZ V, WASSILEW GI, PERKA CF, et al. Increased rate of bacterial colonization on PE-components in total joint arthroplasty: an evaluation through sonication. Tech Health Care. 2017;25(1):137-142. [39] DRIBAN JB, HARKEY MS, BARBE MF, et al. Risk factors and the natural history of accelerated knee osteoarthritis: a narrative review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):332. [40] MOLL JM, CHESTERMAN PJ, MEANOCK RI, et al. Walldius arthroplasty of the knee. Follow-up study of 51 operations. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973;32(5):397-405. [41] NIINIMÄKI T, ESKELINEN A, MÄKELÄ K, et al. Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty survivorship is lower than TKA survivorship: a 27-year Finnish registry study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(5):1496-1501. [42] HASEBE Y, AKASAKA K, YAMAMOTO M. Factors affecting early knee-flexion range of motion after total knee arthroplasty. J Phys Ther Sci. 2021;33(9): 672-675. [43] KHOO LP, GOH J C, CHOW SL. Parametric modelling of a knee joint prosthesis. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 1993;207(2):115-120. [44] BROWN ML, WENDT CS, SEYLER TM, et al. Gait and functional outcomes between cruciate-retaining and cruciate-substituting implants in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized study. J Surg Orthop Adv. 2019;28(3):215-223. [45] ATHWAL KK, HUNT NC, DAVIES AJ, et al. Clinical biomechanics of instability related to total knee arthroplasty. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2014;29(2): 119-128. [46] 张博,林源,任世祥,等.后交叉韧带保留型膝关节假体置换中部分保留与完整保留后交叉韧带的疗效比较[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2021, 35(1):51-57. [47] 邹磊,孙栋,詹朝双,等.国人正常膝关节几何学参数测量及临床意义[J].解剖与临床,2010,15(4):4. [48] 张卓越,王慧枝,石沁祎,等.前交叉韧带尺寸与骨尺寸的相关性研究[J].医用生物力学,2021,36(S1):218. [49] 宋艳.膝关节后外侧复合体的数字解剖学及有限元生物力学研究[D].重庆:中国人民解放军陆军军医大学,2020. [50] 李兴.人工膝关节假体承载面几何设计及接触力学研究[D].太原:中北大学,2018. [51] SMITH AJ, LLOYD DG, WOOD DJ. Pre-surgery knee joint loading patterns during walking predict the presence and severity of anterior knee pain after total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Res. 2004;22(2):260-266. [52] SCHNEIDER BL, LING DI, KLEEBAD LJ, et al. Comparing return to sports after patellofemoral and knee arthroplasty in an age-and sex-matched cohort. Orthop J Sports Med. 2020. doi: 10.1177/2325967120957425. [53] RYAN J, MORA JP, SCUDERI GR, et al. Total knee arthroplasty design and kinematics: past, present, and future. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2021; 31(3):1-14. [54] 宋春燕,刘峰,李宏伟.基于接触力学的膝关节假体几何参数研究[J].机械设计与制造工程,2021,50(4):5. [55] FITZPATRICK CK, BALDWIN MA, RULLKOETTER PJ, et al. Combined probabilistic and principal component analysis approach for multivariate sensitivity evaluation and application to implanted patellofemoral mechanics. J Biomech. 2011;44(1):13-21. [56] SONG SJ, KIM KI, SUH DU, et al. Comparison of patellofemoral-specific clinical and radiographic results after total knee arthroplasty using a patellofemoral design-modified prosthesis and its predecessor. Clin Orthop Surg. 2021;13(2):175-184. [57] LEE JA, KOH YG, KANG KT. Effect of post-cam design on the kinematics and contact stress of posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Biomed Mater Eng. 2021;32(6):323-332. [58] ABHARI S, HSING TM, MALKANI MM, et al. Patient satisfaction following total knee arthroplasty using restricted kinematic alignment. Bone Joint J. 2021;103-b(6 Supple A):59-66. [59] WILLING R, KIM I Y. Quantifying the competing relationship between durability and kinematics of total knee replacements using multiobjective design optimization and validated computational models. J Biomech. 2012; 45(1):141-147. [60] KOH YG, SON J, KWON OR, et al. Tibiofemoral conformity variation offers changed kinematics and wear performance of customized posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(4):1213-1223. [61] 王猛,李兴,成博,等.膝关节假体胫骨衬垫几何设计对其接触力学和运动的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(18):2794-2799. [62] KOH YG, PARK KM, LEE HY, et al. Prediction of wear performance in femoral and tibial conformity in patient-specific cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):24. [63] BROCKETT CL, CARBONE S, FISHER J, et al. Influence of conformity on the wear of total knee replacement: an experimental study. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2018;232(4):127-134. [64] WILLING R, KIM IY. A holistic numerical model to predict strain hardening and damage of UHMWPE under multiple total knee replacement kinematics and experimental validation. J Biomech. 2009;42(15):2520-2527. |
| [1] | Nong Fuxiang, Jiang Zhixiong, Li Yinghao, Xu Wencong, Shi Zhilan, Luo Hui, Zhang Qinglang, Zhong Shuang, Tang Meiwen. Bone cement augmented proximal femoral nail antirotation for type A3.3 intertrochanteric femoral fracturalysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10. |
| [2] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [3] | Cai Zhihao, Xie Zhaoyong. Femoral neck anteversion measurement assessment: how to establish a unified method and standard [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1448-1454. |
| [4] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [5] | Bi Gengchao, Zhang Yanlong, Li Qiuyue, Hu Longwei, Zhang Yu. Knee joint mechanics and activation characteristics of surrounding muscles during deep jumps at different heights and distances [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1211-1218. |
| [6] | Wang Ji, Zhang Min, Yang Zhongya, Zhang Long. A review of physical activity intervention in type 2 diabetes mellitus with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1272-1277. |
| [7] | Nie Chenchen, Su Kaiqi, Gao Jing, Fan Yongfu, Ruan Xiaodi, Yuan Jie, Duan Zhaoyuan, Feng Xiaodong. The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| [8] | Gao Yu, Han Jiahui, Ge Xin. Immunoinflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [9] | Xu Xingxing, Wen Chaoju, Meng Maohua, Wang Qinying, Chen Jingqiao, Dong Qiang. Carbon nanomaterials in oral implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1062-1070. |
| [10] | Li Cheng, Zheng Guoshuang, Kuai Xiandong, Yu Weiting. Alginate scaffold in articular cartilage repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1080-1088. |
| [11] | Chen Shisong, Liu Xiaohong, Xu Zhiyun. Current status and prospects of bioprosthetic heart valves [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1096-1102. |
| [12] | Lu Di, Zhang Cheng, Duan Rongquan, Liu Zongxiang. Osteoinductive properties of calcium phosphate ceramic bone repair materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1103-1109. |
| [13] | Shi Yehong, Wang Cheng, Chen Shijiu. Early thrombosis and prevention of small-diameter blood vessel prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1110-1116. |
| [14] | Tang Haotian, Liao Rongdong, Tian Jing. Application and design of piezoelectric materials for bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1117-1125. |
| [15] | Bai Siqi, Xiao Zhen, Liu Jing. Application potential of adipose-derived stem cells in female pelvic floor dysfunction diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 921-927. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||