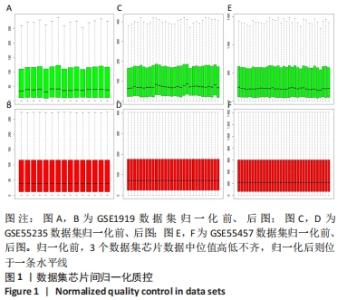
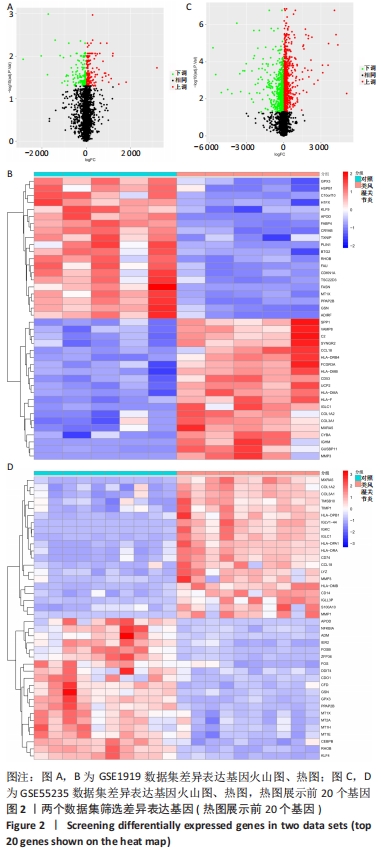
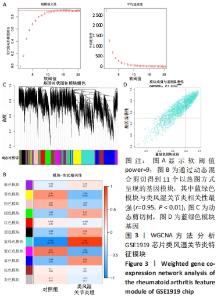
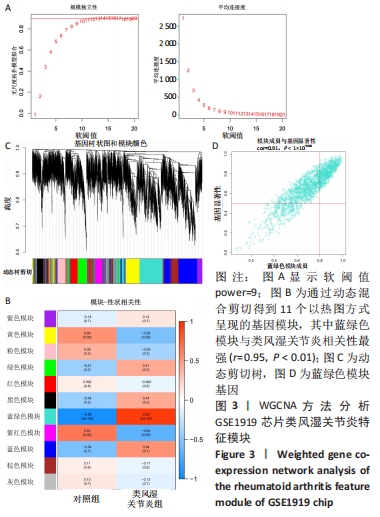
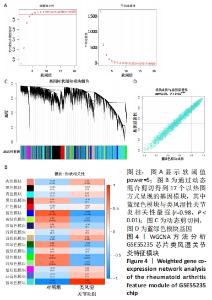
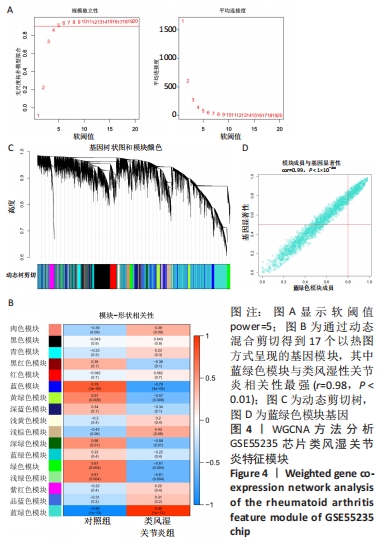
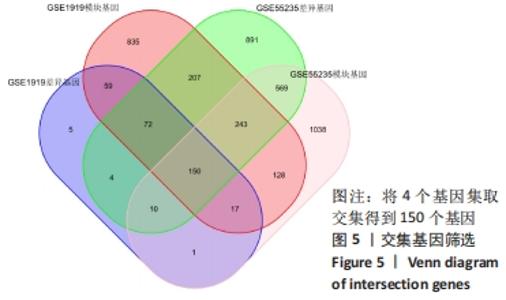
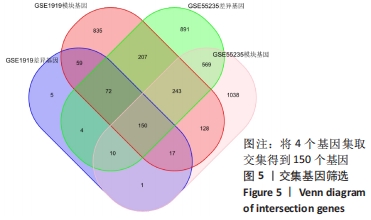
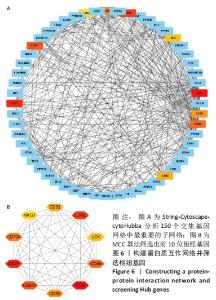
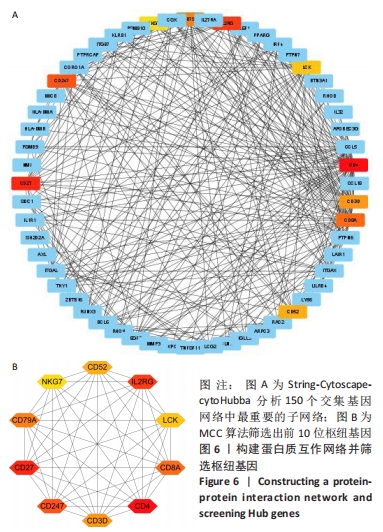
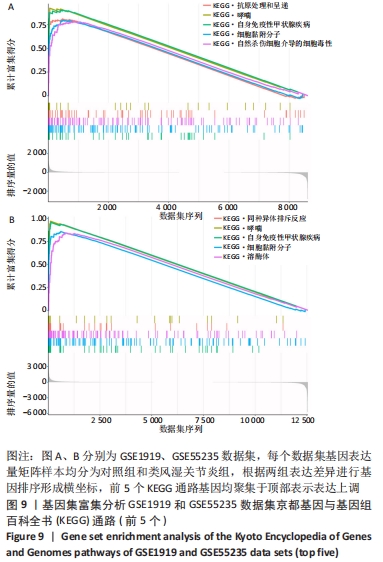
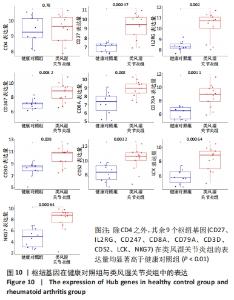
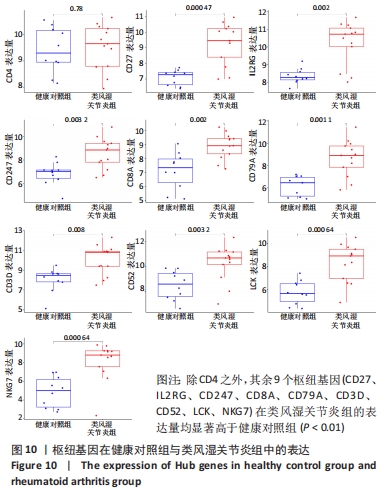
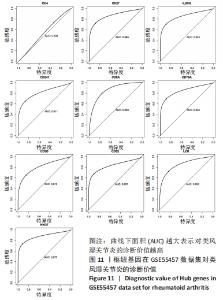
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (11): 1787-1795.doi: 10.12307/2023.147
Previous Articles Next Articles
Rheumatoid arthritis Hub genes and their significance with gene set enrichment analysis and weighted gene co-expression network analysis methods
Sun Yumin1, Song Jiexin2, Yang Yanmei3, Yang Dongliang4
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, 3Physiology Teaching and Research Section, 4Mathematics Teaching and Research Section, Cangzhou Medical College, Cangzhou 061001, Hebei Province, China; 2China Medical University - The Queen’s University of Belfast Joint College, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2022-03-21Accepted:2022-05-19Online:2023-04-18Published:2022-09-27 -
Contact:Yang Dongliang, Master, Associate professor, Mathematics Teaching and Research Section, Cangzhou Medical College, Cangzhou 061001, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Sun Yumin, Master, Associate professor, Attending physician, Department of Internal Medicine, Cangzhou Medical College, Cangzhou 061001, Hebei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sun Yumin, Song Jiexin, Yang Yanmei, Yang Dongliang. Rheumatoid arthritis Hub genes and their significance with gene set enrichment analysis and weighted gene co-expression network analysis methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(11): 1787-1795.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
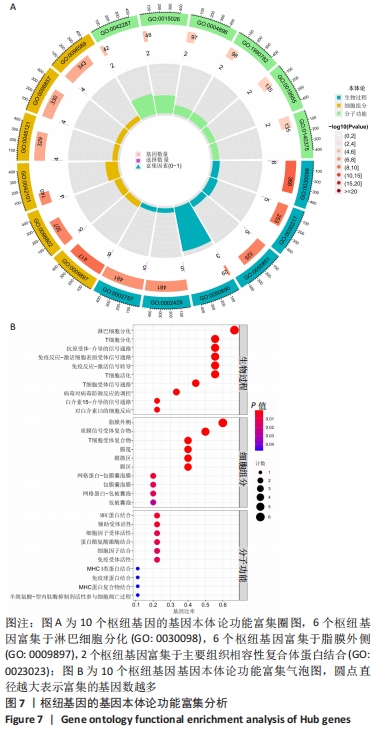
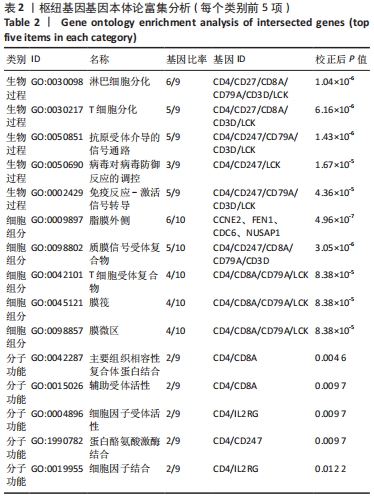
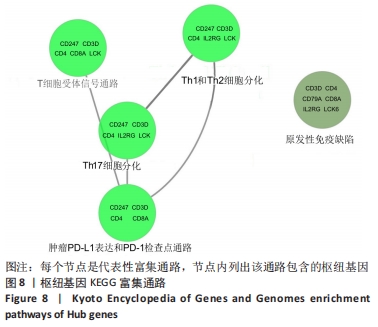
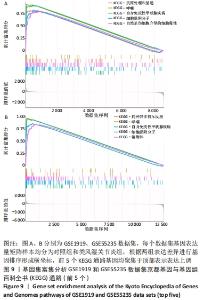
| [1] 周新朋,金晔华,张润润,等.类风湿关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA网络构建及关键基因预测[J]. 中国医药导报, 2021,18(9):12-16. [2] ANAPARTI V, AGARWAL P, SMOLIK I, et al. Whole Blood Targeted Bisulfite Sequencing and Differential Methylation in the C6ORF10 Gene of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2020;47(11):1614-1623. [3] ZHOU S, LU H, XIONG M. Identifying Immune Cell Infiltration and Effective Diagnostic Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Bioinformatics Analysis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:1-12. [4] LONG NP, PARK S, ANH NH, et al. Efficacy of Integrating a Novel 16-Gene Biomarker Panel and Intelligence Classifiers for Differential Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis. J Clin Med. 2019;8(1):1-16. [5] KMIOLEK T, PARADOWSKA-GORYCKA A. miRNAs as Biomarkers and Possible Therapeutic Strategies in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cells. 2022; 11(3):1-22. [6] GOMES DA SILVA IIF, BARBOSA AD, SOUTO FO, et al. MYD88, IRAK3 and Rheumatoid Arthritis pathogenesis: Analysis of differential gene expression in CD14 + monocytes and the inflammatory cytokine levels. Immunobiology. 2021;226(6):1-16. [7] HUA L, ZHOU P, LIU H, et al. Mining susceptibility gene modules and disease risk genes from SNP data by combining network topological properties with support vector regression. J Theor Biol. 2011;289:225-236. [8] 史晋宇,乔军,胡方媛. 基于基因芯片公共数据库及生物信息学方法筛选类风湿关节炎滑膜组织关键基因及通路[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志,2020,24(11):743-746. [9] WU R, LONG L, ZHOU Q, et al. Identification of hub genes in rheumatoid arthritis through an integrated bioinformatics approach. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):458-466. [10] HU H, ZHANG F, LI L, et al. Identification and Validation of ATF3 Serving as a Potential Biomarker and Correlating With Pharmacotherapy Response and Immune Infiltration Characteristics in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:1-18. [11] MA C, LV Q, TENG S, et al. Identifying key genes in rheumatoid arthritis by weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2017;20(8):971-979. [12] REN C, LI M, ZHENG Y, et al. Identification of diagnostic genes and vital microRNAs involved in rheumatoid arthritis: based on data mining and experimental verification. Peer J. 2021;9:1-24. [13] HOU J, YE X, LI C, et al. K-Module Algorithm: An Additional Step to Improve the Clustering Results of WGCNA Co-Expression Networks. Genes (Basel). 2021;12(1):1-15. [14] HE P, MO XB, LEI SF, et al. Epigenetically regulated co-expression network of genes significant for rheumatoid arthritis. Epigenomics. 2019;11(14):1-12. [15] REN C, LI M, DU W, et al. Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis Reveals Hub Genes and Inflammation State of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:1-13. [16] CHEN Y, LIAO R, YAO Y, et al. Machine learning to identify immune-related biomarkers of rheumatoid arthritis based on WGCNA network. Clin Rheumatol. 2021;41(4):1057-1068. [17] CAI P, JIANG T, LI B, et al. Comparison of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis (OA) based on microarray profiles of human joint fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Cell Biochem Funct. 2019;37(1):31-41. [18] WOODWARD AA, TAYLOR DM, GOLDMUNTZ E, et al. Gene-Interaction-Sensitive enrichment analysis in congenital heart disease. BioData Min. 2022;15(1):1-16. [19] LU J, BI Y, ZHU Y, et al. CD3D, GZMK, and KLRB1 Are Potential Markers for Early Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis, Especially in Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibody-Negative Patients. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:1-12. [20] WENJING Z, YANG C, QIN L, et al. Emerging nanotherapeutics alleviating rheumatoid arthritis by readjusting the seeds and soils. J Control Release. 2022;345:851-879. [21] FERNANDA LF, BRUNO N, EDSON M, et al. Rheumatoid Meningitis as an Extra-articular Manifestation of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Neurol India. 2021;69(6):1903-1904. [22] ZECHEN M, HANYAN Z, MARY-CLAIR Y, et al. Prevalence and trajectory of erosions, synovitis, and bone marrow edema in feet of patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2021;40(9):3575-3579. [23] CHAOJUN W, YONG Q, JINGHUA X, et al. Correlation of Ultrasound Synovitis Joint Count with Disease Activity and Its Longitudinal Variation with Treatment Response to Etanercept in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2021;47(9):2543-2549. [24] OMA I, OLSTAD OK, ANDERSEN JK, et al. Differential expression of vitamin D associated genes in the aorta of coronary artery disease patients with and without rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS One. 2018;13(8): 1-13. [25] JABADO O, MALDONADO MA, SCHIFF M, et al. Differential Changes in ACPA Fine Specificity and Gene Expression in a Randomized Trial of Abatacept and Adalimumab in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatol Ther. 2022;9(2):391-409. [26] QIAN K, ZHENG XX, WANG C, et al. β-Sitosterol Inhibits Rheumatoid Synovial Angiogenesis Through Suppressing VEGF Signaling Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;12:1-13. [27] ELLIOTT SE, KONGPACHITH S, LINGAMPALLI N, et al. Affinity Maturation Drives Epitope Spreading and Generation of Proinflammatory Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibodies in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(12):1946-1958. [28] NAGAI K, ISHII T, OHNO T, et al. Overload of the Temporomandibular Joints Accumulates gammadelta T Cells in a Mouse Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Morphological and Histological Evaluation. Front Immunol. 2021;12(753754):1-10. [29] XIAO J, WANG R, CAI X, et al. Coupling of Co-expression Network Analysis and Machine Learning Validation Unearthed Potential Key Genes Involved in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Genet. 2021;12:1-19. [30] NOVALIA P, THIBAULT H, LIYAN YS, et al. Induction of antigen-specific tolerance by nanobody-antigen adducts that target class-II major histocompatibility complexes. Nat Biomed Eng. 2021;5(11):1389-1401. [31] ANIRUDDHA B, PARASAR G, ALAKENDU G, et al. Role of oxidative stress in induction of trans-differentiation of neutrophils in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Free Radic Res. 2022;22:1-13. [32] LI WC, BAI L, XU Y, et al. Identification of differentially expressed genes in synovial tissue of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis in patients. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(3):4533-4544. [33] HUSSIEN Y, DAMIATI L, ALHARBI A, et al. Correlations of TGF-β1 (869C/T), CD4- (11743 A/C) and CD4- (10845 A/G) Polymorphism with Biochemical Risk Factor Predict in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Progression. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2015;74(Suppl 2): 987.981-987. [34] ZHANG R, YANG X, WANG J, et al. Identification of potential biomarkers for differential diagnosis between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis via integrative genomewide gene expression profiling analysis. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(1):30-40. [35] HU F, ZHANG W, SHI L, et al. Impaired CD27(+)IgD(+) B Cells With Altered Gene Signature in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2018; 9:626-635. [36] YE Y, LIU M, TANG L, et al. Iguratimod represses B cell terminal differentiation linked with the inhibition of PKC/EGR1 axis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):1-14. [37] ABREU M, CARVALHEIRO H, DUARTE C, et al. Expression of CD62L, CD27 and CD11b define a marked cytotoxic effector role for NK cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(Suppl 2):1-94. [38] BURSKA AN, THU A, PARMAR R, et al. Quantifying circulating Th17 cells by qPCR: potential as diagnostic biomarker for rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019;58(11):2015-2024. |
| [1] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Zhu Guangyu, Wang Rongtian, Wang Jian, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Changes of lower limb force line and knee function after high tibial osteotomy in osteoporotic medial ventricular knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [2] | Huang Linke, Wei Linhua, Jiang Jie, Liu Qian, Chen Weiwei. Effects of estrogen combined with treadmill exercise on bone mass and articular cartilage in ovariectomized mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [3] | Li Long, Li Guangdi, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 751-757. |
| [4] | Yuan Changshen, Guan Yanbing, Li Zhe, Rong Weiming, Liao Shuning, Chen Lewei, Mei Qijie, Duan Kan. Screening and verification of key genes of necroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 695-700. |
| [5] | Wan Guoli, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan, Li Ang, Shi Xunda, Cai Yi. Retrospective analysis of the influencing factors of chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 558-564. |
| [6] | Gu Mingxi, Wang Bo, Tian Fengde, An Ning, Hao Ruihu, Wang Changcheng, Guo Lin. Comparison of early efficacy and safety of simultaneous and staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 565-571. |
| [7] | Yu He, Zheng Jiafa, Song Xiufeng, Guan Shengyi. Tibiotalocalcaneal arthrodesis with blood supplied fibular flap combined with hollow screw in the treatment of end-stage ankle osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 588-593. |
| [8] | Guo Yingqi, Gong Xianxu, Zhang Yan, Xiao Han, Wang Ye, Gu Wenguang. Meniscus extrusion and patellofemoral joint cartilage injury and bone marrow lesions: MRI semi-quantitative score [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 600-605. |
| [9] | Yu Jiaan, Liu Xinwei, Lian Hongyu, Liu Kexin, Li Zitao. Medial open-wedge tibial osteotomy versus lateral closed-wedge tibial osteotomy for unicompartmental knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 632-639. |
| [10] | Li Mingxiu, Wang Xuan, Yang Jie, Li Yi. An osteoarthritis model in vitro: characteristics and new design idea [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 300-306. |
| [11] | Liu Yinghong, Yi Yating. Mechanism and implication of angiogenesis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 307-313. |
| [12] | Xie Pingjin, Luo Zhen, Lu Qigui, Guo Yanxing, Chen Qunqun, Li Feilong. Effect of ligustrazine and overexpression of miR-20b-5p on synovial, cartilage and subchondral bone angiogenesis in rats with early-stage knee osteoarthritis: a histological observation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 237-245. |
| [13] | Wang Huanhuan, Wang Qing, Tang Peng, Zhang Rui, Min Hongwei. Effects of extracorporeal shock wave on the proliferation and autophagy of chondrocytes from osteoarthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 252-257. |
| [14] | Li Shichao, Xie Guangyue, Sun Zhen, Han Peng, Hou Xiaohua, Sun Xiaowei, Zhang Qidong. Correlation of knee joint alignment correction between valgus stress and postoperative radiography after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(18): 2910-2914. |
| [15] | Shi Sifeng, Lin Qiang, Zhou Bing, Chen Xiangyang, Lu Wenhai. Comparison of cementless and cemented femoral prosthesis for unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in the treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(18): 2848-2853. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||