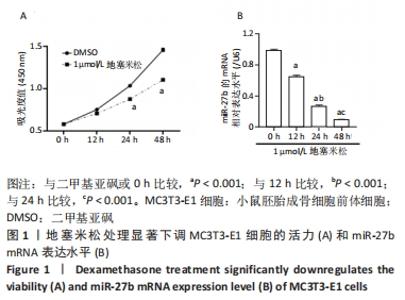
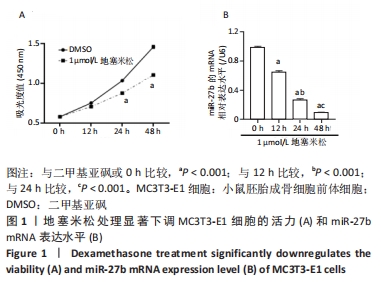
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (11): 1780-1786.doi: 10.12307/2023.129
Previous Articles Next Articles
Significance of miR-27b/peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor gamma 2 axis for proliferation and osteoblast differentiation of mouse embryonic osteogenic precursor cells
Wang Lei1, Bai Xuesong1, Du Yu1, He Aimin1, Zheng Jun1, Zhang Zhipeng1, Lyu Huicheng2
- 1Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010010, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 2Trauma Center, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010020, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2022-03-16Accepted:2022-05-13Online:2023-04-18Published:2022-09-24 -
Contact:Lyu Huicheng, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Trauma Center, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010020, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wang Lei, Master candidate, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010010, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China Bai Xuesong, Master candidate, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010010, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China Wang Lei and Bai Xuesong contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, No. 2017MS08118 (to LHC); Inner Mongolia Medical University Science and Technology Million Project, No. YKD2016kjbw010 (to LHC)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Lei, Bai Xuesong, Du Yu, He Aimin, Zheng Jun, Zhang Zhipeng, Lyu Huicheng. Significance of miR-27b/peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor gamma 2 axis for proliferation and osteoblast differentiation of mouse embryonic osteogenic precursor cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(11): 1780-1786.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
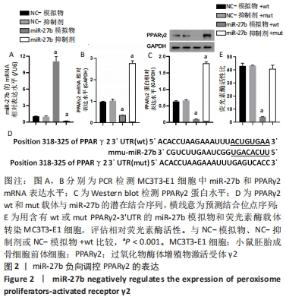
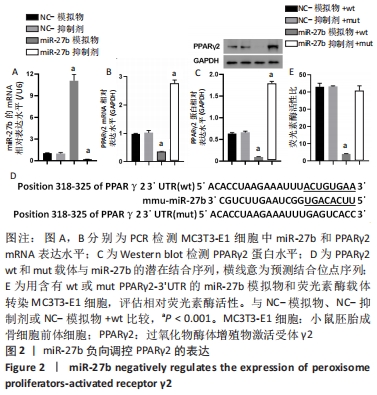
2.2 miR-27b可直接调控PPARγ2 通过之前的研究和生信分析的结果,预测PPARγ2与miR-27b相互作用。为了验证这种相互作用,将miR-27b模拟物和抑制剂转染到MC3T3-E1细胞中。结果表明,与相应的NC相比,miR-27b模拟物显著上调了miR-27b的表达水平,miR-27b的表达水平通过miR-27b抑制剂显著下调,见图2A。此外,与相应的NC相比,PPARγ2 mRNA和蛋白质表达被miR-27b模拟物抑制,并被miR-27b抑制剂显著增强,见图2B,C。为了进一步验证miR-27b靶向PPARγ2的分子机制,进行了荧光素酶检测,将miR-27b模拟物和含有wt或mut-PPARγ2-3’UTR的荧光素酶载体共转染MC3T3-E1细胞,见图2D。结果显示,与NC-模拟物相比,miR-27b通过结合PPARγ2-3’UTR wt序列显著降低了荧光素酶活性,然而,在与PPARγ2-3’UTR mut和miR-27b模拟物共转染后,荧光素酶活性没有观察到明显差异,见图2E。总之,这些结果表明miR-27b可直接调控并抑制PPARγ2的表达水平。"
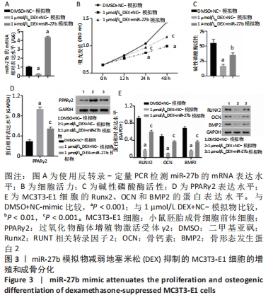
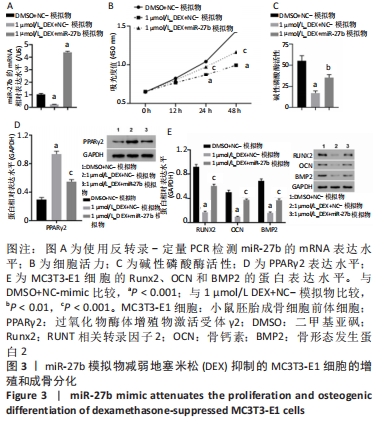
2.3 miR-27b过表达减弱了地塞米松抑制MC3T3-E1细胞的增殖和成骨分化 在地塞米松处理的MC3T3-E1细胞中转染miR-27b模拟物后观察miR-27b的潜在功能。结果表明,miR-27b过表达部分逆转了地塞米松对miR-7b表达和细胞增殖的抑制(图3A和B)。并且检测了M3T3-E1细胞的碱性磷酸酶活性(图3C),以及成骨细胞分化标志物的表达,包括骨形态发生蛋白2、Runx2及骨钙素。研究结果表明,与二甲基亚砜+NC-mimic组相比,地塞米松处理显著降低了碱性磷酸酶活性和骨形态发生蛋白2、Runx2和骨钙素蛋白表达水平,但增加了PPARγ2蛋白表达水平。但是,地塞米松介导的作用被miR-27b模拟物所减弱(图3D和E)。细胞碱性磷酸酶活性和骨形态发生蛋白2、Runx2和骨钙素蛋白表达水平部分恢复。这些结果表明miR-27b过表达减弱地塞米松介导的抑制成骨细胞分化作用。"
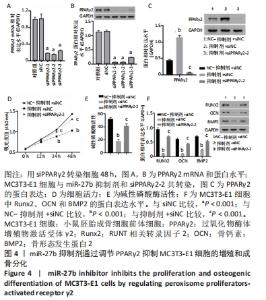
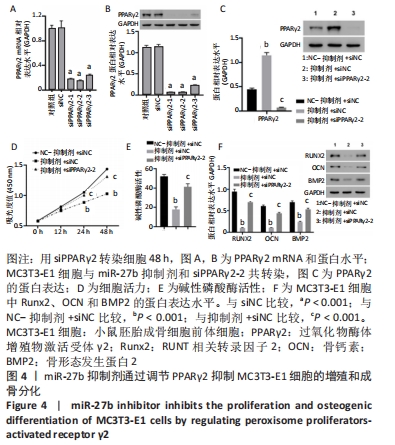
2.4 抑制miR-27b通过上调PPARγ2抑制MC3T3-E1细胞的增殖和成骨分化 通过RT-qPCR和Western blot分析证明了MC3T3-E1细胞中靶向PPARγ2的siRNA的转染效率,siPPARγ2-2转染的细胞中mRNA和蛋白表达量最低。因此,选择siPPARγ2-2进行后续分析(图4A和B)。为了研究miR-27b对PPARγ2的潜在调节作用,将MC3T3-E1细胞与miR-27b抑制剂和PPARγ2 siRNA共同转染。结果表明,通过对miR-27b的敲除,观察到了PPARγ2明显的表达增加,并降低了细胞活力、成骨细胞分化、碱性磷酸酶活性以及骨形态发生蛋白2、Runx2和骨钙素的表达水平。然而,这些影响被siPPARγ2-2转染所取代(图4C-F),miR-27b作用被重新激活。因此,miR-27b的敲除通过PPARγ2的上调抑制了MC3T3-E1细胞的增殖和成骨分化。"
| [1] FEEHAN J, AL SAEDI A, DUQUE G. Targeting fundamental aging mechanisms to treat osteoporosis. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2019;23: 1031-1039. [2] MENDOZA FA, LE ROUX M, AHMED I. Primary osteoporosis in men: an unmet medical need. Fertil Steril. 2019;112(5):791-798. [3] SALARI N, DARVISHI N, BARTINA Y, et al. Global prevalence of osteoporosis among the world older adults: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):669. [4] SALARI N, GHASEMI H, MOHAMMADI L, et al. The global prevalence of osteoporosis in the world: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):609. [5] CHEN P, LI Z, HU Y. Prevalence of osteoporosis in China: a meta-analysis and systematic review. BMC Public Health. 2016;16(1):1039. [6] CHENG X, ZHAO K, ZHA X, et al. Opportunistic Screening Using Low-Dose CT and the Prevalence of Osteoporosis in China: A Nationwide, Multicenter Study. J Bone Miner Res. 2021;36(3):427-435. [7] CUI Z, MENG X, FENG H, et al. Estimation and projection about the standardized prevalence of osteoporosis in mainland China. Arch Osteoporos. 2019;15(1):2. [8] WATANABE A, YONEYAMA S, NAKAJIMA M, et al. Osteosarcoma in Sprague-Dawley rats after long-term treatment with teriparatide (human parathyroid hormone (1-34)). J Toxicol Sci. 2012;37(3):617-629. [9] MALLUCHE HH, CHEN J, LIMA F, et al. Bone Quality and Fractures in Women With Osteoporosis Treated With Bisphosphonates for 1 to 14 Years. JBMR Plus. 2021;5(11):e10549. [10] LI J, CHEN X, LU L, et al. The relationship between bone marrow adipose tissue and bone metabolism in postmenopausal osteoporosis.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020;52:88-98. [11] MURUGANANDAN S, IONESCU AM, SINAL CJ. At the Crossroads of the Adipocyte and Osteoclast Differentiation Programs: Future Therapeutic Perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(7):2277. [12] MURUGANANDAN S, SINAL CJ. The impact of bone marrow adipocytes on osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation. IUBMB Life. 2014;66(3): 147-155. [13] MURUGANANDAN S, GOVINDARAJAN R, SINAL CJ. Bone Marrow Adipose Tissue and Skeletal Health. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2018;16(4): 434-442. [14] ZHAO X, PATIL S, XU F, et al. Role of Biomolecules in Osteoclasts and Their Therapeutic Potential for Osteoporosis.Biomolecules. 2021; 11(5):747. [15] YANG Y, YUJIAO W, FANG W, et al. The roles of miRNA, lncRNA and circRNA in the development of osteoporosis. Biol Res. 2020;53(1):40. [16] ZHAO H, LU A, HE X. Roles of MicroRNAs in Bone Destruction of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:600867. [17] 彭建强,黄年盛,黄胜,等.H_2O_2下调miR-21对MC3T3-E1细胞成骨分化影响的研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2018,32(3):276-284. [18] 郑峰,张富财,许喆.miR-98-5p促进成骨细胞增殖和分化的可能及机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(26):4112-4117. [19] 杨晓红,杨琨,廖立,等.微RNA-705对MC3T3-E1细胞成骨分化能力的影响[J].浙江大学学报(医学版),2016,45(6):575-580. [20] 赵长铭,黄萌,王振宁,等.miR-129-5p调控MC3T3-E1细胞成骨分化的体外研究[J].解放军医学院学报,2021,42(5):565-570. [21] HAN Z, ZHAN R, CHEN S, et al. miR-181b/Oncostatin m axis inhibits prostate cancer bone metastasis via modulating osteoclast differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 2020;121(2):1664-1674. [22] KARBIENER M, FISCHER C, NOWITSCH S, et al. microRNA miR-27b impairs human adipocyte differentiation and targets PPARgamma.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;390(2):247-251. [23] JACKSON SM, DEMER LL. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor activators modulate the osteoblastic maturation of MC3T3-E1 preosteoblasts. FEBS Lett. 2000;471(1):119-124. [24] FAJAS L, AUBOEUF D, RASPÉ E, et al. The organization, promoter analysis, and expression of the human PPARgamma gene. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(30):18779-18789. [25] 朱磊,路瑛丽,冯连世,等.低氧训练诱导miR-27/PPARγ调控肥胖大鼠腓肠肌脂肪酸代谢的研究[J].体育科学,2019,39(6):55-61. [26] 郭鑫,宗欢欢,李杜达,等.PPARγ在肿瘤中的双重作用[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2021,43(2):460-468. [27] WEI W, ZEVE D, WANG X, et al. Osteoclast progenitors reside in the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ-expressing bone marrow cell population. Mol Cell Biol. 2011;31(23):4692-4705. [28] MITTAL S, INAMDAR S, ACHARYA J, et al. miR-3666 inhibits development of hepatic steatosis by negatively regulating PPARγ.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2020;1865(10):158777. [29] WANG X, XU Y, ZHU YC, et al. LncRNA NEAT1 promotes extracellular matrix accumulation and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by targeting miR-27b-3p and ZEB1 in diabetic nephropathy. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(8):12926-12933. [30] WANG X, LU Y, ZHU L, et al. Inhibition of miR-27b Regulates Lipid Metabolism in Skeletal Muscle of Obese Rats During Hypoxic Exercise by Increasing PPARγ Expression. Front Physiol. 2020;11:1090. [31] Xu J, Lv S, Hou Y, et al. miR-27b promotes type II collagen expression by targetting peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ2 during rat articular chondrocyte differentiation.Biosci Rep. 2018;38(1): BSR20171109. [32] 董莹莹,王猛,郭艳,等.低钙饲料联合地塞米松致大鼠骨质疏松模型的建立[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(10):1393-1397+1404. [33] YANG L, LIU S, MU S, et al. Paeoniflorin Attenuates Dexamethasone-Induced Apoptosis of Osteoblast Cells and Promotes Bone Formation via Regulating AKT/mTOR/Autophagy Signaling Pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021:6623464. [34] PIGNOLO RJ, LAW SF, CHANDRA A. Bone Aging, Cellular Senescence, and Osteoporosis. JBMR Plus. 2021;5(4):e10488. [35] PAIK J, SCOTT LJ. Romosozumab: A Review in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Drugs Aging. 2020;37(11):845-855. [36] TASNIM N, DUTTA P, NAYEEM J, et al. Osteoporosis, an Inevitable Circumstance of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review. Cureus. 2021;13(10):e18488. [37] BABAN YN, EDICHERIA CM, JOSEPH J, et al. Osteoporosis Complications in Crohn’s Disease Patients: Factors, Pathogenesis, and Treatment Outlines. Cureus. 2021;13(12):e20564. [38] DRAKE MT, MURAD MH, MAUCK KF, et al. Clinical review. Risk factors for low bone mass-related fractures in men: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97(6):1861-1870. [39] BUCKLEY L, HUMPHREY MB. Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis.N Engl J Med. 2018;379(26):2547-2556. [40] ZHANG L, LI G, WANG K, et al. MiR-30 family members inhibit osteoblast differentiation by suppressing Runx2 under unloading conditions in MC3T3-E1 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020; 522(1):164-170. [41] 段克友,官建中.外泌体在骨质疏松症治疗中的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(12):1642-1649. [42] KONG Y, NIE ZK, LI F, et al. MiR-320a was highly expressed in postmenopausal osteoporosis and acts as a negative regulator in MC3T3E1 cells by reducing MAP9 and inhibiting PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Exp Mol Pathol. 2019;110:104282. [43] FAN Q, LI Y, SUN Q, et al. miR-532-3p inhibits osteogenic differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells by downregulating ETS1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;525(2):498-504. [44] 孙芬,刘名燕,刘铭,等.miR-132-3p过表达对MC3T3-E1细胞增殖分化的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(1):59-64. [45] 王丽娜,刘春梅,胡叶青,等.血清miR-27、PPAR-γ表达与妊娠期糖尿病胰岛素抵抗[J].中国计划生育学杂志,2021,29(5):1021-1024. [46] LEE JJ, DRAKAKI A, ILIOPOULOS D, et al. MiR-27b targets PPARγ to inhibit growth, tumor progression and the inflammatory response in neuroblastoma cells. Oncogene. 2012;31(33):3818-3825. [47] SEENPRACHAWONG K, TAWORNSAWUTRUK T, NANTASENAMAT C, et al. miR-130a and miR-27b Enhance Osteogenesis in Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells via Specific Down-Regulation of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ. Front Genet. 2018;9:543. [48] WAN Y, CHONG LW, EVANS RM. PPAR-γ regulates osteoclastogenesis in mice.Nat Med. 2007;13(12):1496-1503. [49] GU C, XU Y, ZHANG S, et al. miR-27a attenuates adipogenesis and promotes osteogenesis in steroid-induced rat BMSCs by targeting PPARγ and GREM1. Sci Rep. 2016;6:38491. |
| [1] | He Xi, Wan Yu, Tang Yuting, Yang Anning, Wu Kai, Jiao Yun, Bai Zhigang, Jiang Yideng, Shen Jiangyong. Erastin inhibits proliferation of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Zhu Guangyu, Wang Rongtian, Wang Jian, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Changes of lower limb force line and knee function after high tibial osteotomy in osteoporotic medial ventricular knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [3] | Jiang Xiaocheng, Shi Lu, Wang Yinbin, Li Qiujiang, Xi Chuangzhen, Ma Zefeng, Cai Lijun. Systematical evaluation of bone fusion rate after interbody fusion in patients with osteoporosis and lumbar degenerative disease treated with teriparatide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1427-1433. |
| [4] | Yang Zhishan, Tang Zhenglong. YAP/TAZ, a core factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, is involved in bone formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| [5] | Sun Jiajia, Zhu Haidi, Lu Yun, Zhang Kai. Comparison of bone metabolism markers between type 2 diabetes mellitus and non-type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with hip fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1156-1160. |
| [6] | Liu Xiaolin, Mu Xinyue, Ma Ziyu, Liu Shutai, Wang Wenlong, Han Xiaoqian, Dong Zhiheng. Effect of hydrogel-loaded simvastatin microspheres on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 998-1003. |
| [7] | Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 840-845. |
| [8] | Long Yanming, Xie Mengsheng, Huang Jiajie, Xue Wenli, Rong Hui, Li Xiaojie. Casein kinase 2-interaction protein-1 regulates the osteogenic ability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in osteoporosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 878-882. |
| [9] | Li Xinyue, Li Xiheng, Mao Tianjiao, Tang Liang, Li Jiang. Three-dimensional culture affects morphology, activity and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 846-852. |
| [10] | Yuan Wei, Liu Jingdong, Xu Guanghui, Kang Jian, Li Fuping, Wang Yingjie, Zhi Zhongzheng, Li Guanwu. Osteogenic differentiation of human perivascular stem cells and its regulation based on Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 866-871. |
| [11] | Qiao Luhui, Ma Ziyu, Guo Haoyu, Hou Yudong. Comparison of puerarin and icariin on the biological properties of mouse preosteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 872-877. |
| [12] | Hao Liufang, Duan Hongmei, Wang Zijue, Hao Fei, Hao Peng, Zhao Wen, Gao Yudan, Yang Zhaoyang, Li Xiaoguang. Spatiotemporal dynamic changes of ependymal cells after spinal cord injury in transgenic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 883-889. |
| [13] | Li Long, Li Guangdi, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 751-757. |
| [14] | Zhang Min, Zhang Xiaoming, Liu Tongbin. Application potential of naringin in bone tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 787-792. |
| [15] | Wang Jinling, Huang Xiarong, Qu Mengjian, Huang Fujin, Yin Lingwei, Zhong Peirui, Liu Jin, Sun Guanghua, Liao Yang, Zhou Jun. Effects of exercise training on bone mass and bone microstructure in aged osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 676-682. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||