Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (35): 5716-5723.doi: 10.12307/2022.927
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect and mechanism of non-coding RNA regulating autophagy in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury
Fan Jilin1, Zhu Tingting2, Tian Xiaoling2, Liu Sijia3, Su Jing3, Zhang Shiliang3
- 1Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China; 2Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical College, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China; 3Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2021-12-02Accepted:2022-01-30Online:2022-12-18Published:2022-05-18 -
Contact:Zhang Shiliang, Doctoral supervisor, Chief physician, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Fan Jilin, MD candidate, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Major Science and Technology Project for New Drug Creation, No. 2017ZX09301003 (to ZSL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fan Jilin, Zhu Tingting, Tian Xiaoling, Liu Sijia, Su Jing, Zhang Shiliang. Effect and mechanism of non-coding RNA regulating autophagy in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(35): 5716-5723.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

2.1 自噬与心肌缺血再灌注损伤 自噬的分子机制是由Yoshinori Ohsumi教授及其团队在1990年代初期通过鉴定酵母中的自噬相关基因发现的[12]。自此以后自噬领域得到重大发展。自噬包括巨自噬、微自噬和分子伴侣介导的自噬3种类型,3种自噬类型的不同之处在于将不同的成分输送到溶酶体中最终能够降解,其中在哺乳动物中表现最多的巨自噬是最具典型特征的形式[13]。自噬是一个重要的代谢过程,老化或受损的蛋白质和细胞器被分解成氨基酸和脂肪酸以产生能量和循环利用[14]。以上代谢过程在营养缺乏或代谢应激期间被激活,以维持组织功能和动态平衡[15]。 心肌缺血再灌注损伤的主要发病因素包括自噬、氧化应激、线粒体功能障碍、炎症、内皮细胞损伤和细胞凋亡等机制[16]。在心肌缺血再灌注初期主要是心肌细胞的供血受限,ATP生成低,导致供血和能量需求失衡,AMPK作为心肌缺血中重要的自噬启动因子,被较低的ATP水平所激活,激活的AMPK可以直接磷酸化并激活ULK1[17],从而在心肌缺血过程中启动自噬,保护心肌细胞免受缺血导致的损伤。此外,低氧诱导因子1α作为缺氧过程中的重要调控因子,其过表达参与多种细胞的自噬过程,在心肌细胞缺血缺氧条件下,低氧诱导因子1α被激活,其可能通过调控自噬在心肌缺血的条件下对心肌细胞发挥有益作用[18]。以上表明,在心肌缺血阶段,由于心肌细胞的能量危机和氧化应激,自噬被激活,这有助于维持心肌细胞的结构和功能,保护心脏的生理功能。自噬在心肌再灌注过程中也起着重要作用,可以作为内源性机制修复心肌损伤。在再灌注阶段,自噬被过度激活,导致心肌细胞自噬死亡和组织损伤[19]。适度的自噬水平参与心肌再灌注损伤和心肌细胞缺氧复氧过程,是维持心肌细胞稳态和保护细胞所必需的[13]。因此,研究自噬的动态平衡机制已成为保护心肌细胞免受心肌再灌注损伤的重要领域。 2.2 非编码RNA功能及对自噬的调控 "

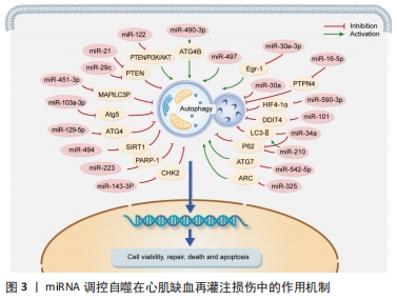
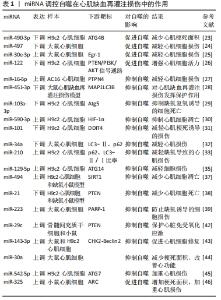
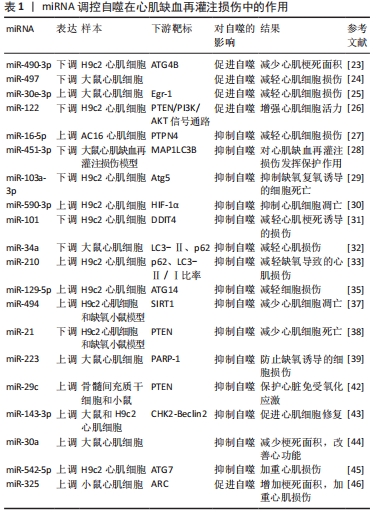
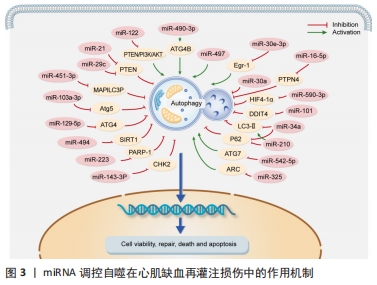
2.2.1 miRNAs功能及对自噬的调控 MicroRNAs (miRNAs/miRs)是由18-22个核苷酸组成的RNA调节剂,可以与mRNA结合并减少蛋白质翻译[20]。成熟的miRNAs有效地结合到目标mRNA的3'-非翻译区,导致它们的降解或翻译抑制(即基因表达的调节)[21]。单个miRNA可以调控多个靶基因的mRNA,每个靶基因mRNA也可以被多个miRNA调控。与靶标结合的miRNA主要通过转录后抑制mRNA翻译或通过裂解或降解mRNA发挥调节作用[22],包括自噬。越来越多的研究表明miRNA可以通过调节自噬参与心肌再灌注损伤的过程。 (1)miRNA促进自噬减轻心肌缺血再灌注损伤:相关研究表明部分miRNA通过促进自噬参与心肌再灌注损伤的过程,从而抑制心肌细胞死亡,保护缺血缺氧损伤的心肌细胞。在心肌再灌注损伤过程中,抑制miR-490-3p或过表达ATG4B可促进LC3Ⅱ的表达,增加自噬溶酶体,抑制p62的表达,减少梗死面积[23],因此,通过沉默miR-490-3p表达从而上调ATG4B来促进自噬以保护心肌细胞免受再灌注损伤。此外,在心肌梗死心脏和培养的新生大鼠心肌细胞中,miR-497的表达明显降低。体内和体外研究表明miR-497的低表达增加了自噬通量,这些结果表明,抑制miR-497通过增强自噬来减轻心肌缺血再灌注损伤[24]。另有相关报道miR-30家族成员miR-30e-3p在缺血缺氧大鼠的心肌细胞模型中显著下调,过表达miR-30e-3p后LC3Ⅱ水平显著增加,p62和Egr-1表达显著降低,从而减少了缺血缺氧诱导的心肌损伤,以上研究表明miR-30e-3p的过表达抑制了Egr-1的表达,增强了自噬,从而减轻了心肌细胞损伤[25]。MiR-122在缺氧的H9c2心肌细胞中显著表达,其过表达会抑制自噬相关通路PI3K/AKT的失活从而导致缺氧诱导的H9c2心肌细胞凋亡[26],推测通过抑制miR-122表达调节 PTEN/PI3K/AKT信号通路和促进自噬增强心肌细胞活力,从而保护H9c2心肌细胞免受缺氧诱导的损伤。 (2)miRNA抑制自噬减轻心肌缺血再灌注损伤:缺氧/复氧是心肌缺血再灌注损伤的主要原因之一,缺氧/复氧后心肌细胞易发生过度自噬,可引起部分心脏组织损伤,部分miRNA可以通过抑制自噬的过度激活进而保护受损的心肌细胞。据报道,miR-16-5p在缺氧复氧处理的AC16心肌细胞中高表达,乳酸脱氢酶、肌酸激酶同工酶等心肌损伤标志物和自噬水平也明显升高,敲除miR-16-5p能够显著抑制经缺氧/复氧处理的AC16细胞自噬通量,而沉默PTPN4会逆转这种作用,因此,miR-16-5p可以通过负调节PTPN4的表达抑制自噬来减轻缺氧/复氧诱导的心肌损伤程度[27]。此外,miR-451-3p在心肌缺血再灌注损伤大鼠模型中显著下调,其可以通过抑制MAP1LC3B介导的自噬在心肌缺血再灌注损伤中发挥保护作用,从而可能为心肌缺血再灌注损伤的治疗提供新的分子靶点[28]。ZHANG等[29]通过研究发现miR-103a-3p在心肌再灌注损伤中可以通过靶向Atg5的表达发挥抗自噬的作用,这些结果为心肌再灌注损伤的靶向治疗提供了新的见解。另外,缺氧诱导因子1α在缺氧/复氧诱导的心肌细胞中高表达,其过度表达可以在多种类型的细胞中诱导自噬,miR-590-3p表达增加可以通过靶向缺氧诱导因子1α抑制心肌细胞的过度自噬,从而减轻心肌缺血再灌注损伤[30]。此外,miR-101在体内外心肌缺血再灌注损伤小鼠模型中均低表达,miR-101可以通过靶向DDIT4调节自噬来减轻缺血再灌注诱导的心肌损伤[31]。另有报道称miR-34a在再灌注后大鼠心肌细胞和心脏组织中表达降低,其能够降低缺氧/复氧心肌细胞中LC3-Ⅱ、p62的表达,这表明miR-34a可以抑制再灌注损伤后的自噬水平,从而减轻心肌损伤[32]。同样的,miR-210通过上调p62水平和降低缺氧心肌细胞中的LC3-Ⅱ/Ⅰ比率来抑制自噬[33],从而减轻缺氧引起的心肌损伤。 众多证据表明miRNA可以通过调控AMPK/mTOR和Akt/mTOR通路诱导心肌细胞自噬来减轻心肌缺血再灌注损伤[34]。在H2O2诱导的H9C2细胞中,细胞活力降低,细胞自噬增加,miR-129-5p过表达会抑制自噬减轻H2O2引起的细胞损伤,此外,miR-129-5p能够通过靶向ATG14的表达或激活 PI3K/AKT/mTOR通路的磷酸化抑制H2O2诱导的心肌细胞自噬,从而减轻细胞损伤[35]。另外,SIRT1是与细胞凋亡和自噬相关的关键调节因子[36],miR-494过表达可以抑制SIRT1的表达,同时调控PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路[37],可以减轻心肌细胞的凋亡和自噬,从而保护心肌细胞免受缺血再灌注损伤。同样的,miR-21在缺血缺氧损伤H9C2细胞中表达降低,PTEN是miR-21下游的靶基因,miR-21的上调会抑制PTEN的表达并激活PI3K/Akt/mTOR通路,从而抑制自噬活性和减少心肌细胞死亡[38]。此外,miR-223在人类梗死心肌组织和心肌梗死大鼠模型中均高表达,其可以通过靶向PARP-1介导的Akt/mTOR通路保护心肌细胞免受缺氧诱导的过度自噬[39],因此,miR-223可能是治疗心肌再灌注损伤的潜在靶点。 外泌体是源自细胞的纳米囊泡,其中含有各种mRNA、miRNA、蛋白质和脂质,以调节靶细胞的生物过程[40]。大量的研究表明,外泌体分泌的miRNA在心肌保护机制中发挥重要作用[41]。据报道,骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体中miR-29c表达水平较高,miR-29c的过表达保护心脏免受心脏再灌注损伤。另外,miR-29c的过表达通过在心肌再灌注期间抑制PTEN的表达和激活AKT/mTOR信号通路来减少过度自噬[42],从而保护心脏免受再灌注损伤。此外,间充质干细胞分泌的外泌体miR-143-3p直接靶向并负调节CHK2表达,经体内外研究证实,外泌体miR-143-3p能够通过CHK2-Beclin2通路调节自噬有效减少细胞死亡,从而减轻心肌细胞损伤和促进心肌细胞修复[43],总之,间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体miR-143-3p可能是治疗再灌注损伤的一种有前景的选择。另有相关报道由于缺血再灌注会导致自噬的过度激活,而外泌体携带的miR-30a抑制剂可通过降低自噬过度激活抑制再灌注损伤大鼠心肌细胞死亡[44],从而减少梗死面积,改善心功能。 (3)miRNA促进/抑制自噬加重心肌缺血再灌注损伤:部分miRNA还可以通过促进或抑制自噬加重心肌再灌注损伤,对心脏产生不利影响。缺氧/复氧损伤后H9c2细胞中miR-542-5p表达和自噬激活显著增加,而miR-542-5p的强制表达进一步加重了H9c2细胞中的缺氧/复氧损伤,其可能通过靶向自噬相关基因ATG7抑制自噬,加重心肌损伤[45]。另有相关研究表明miR-325在缺血再灌注损伤小鼠心肌细胞中表达上调,其特异性过表达增强了自噬和心肌梗死面积,此外,E2F1促进miR-325的表达以抑制ARC,miR-325对ARC的抑制导致其无法抑制自噬程序,从而导致自噬增强,加重心肌缺血再灌注损伤[46]。 了解miRNA在心肌再灌注损伤中调控自噬的分子机制有助于为心肌再灌注损伤提供新的治疗靶点,见图3和表1。 "
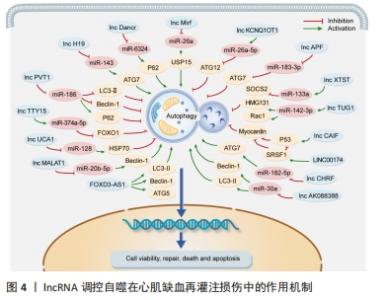
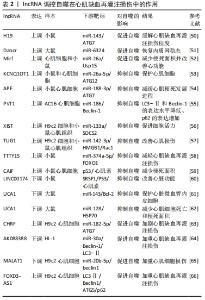
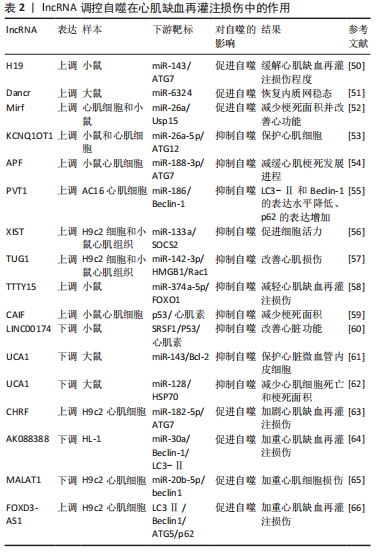
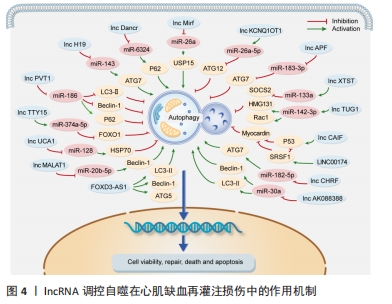
2.2.2 lncRNAs功能及对自噬的调控 LncRNA是一个新的长非编码转录物家族,长度从200到数千个核苷酸不等[47]。LncRNAs可以形成分子支架影响染色质修饰,参与表观遗传调控和海绵miRNAs,进一步调控相应靶基因的表达[48]。大量证据表明,lncRNA是心肌再灌注损伤的关键因素,并可以通过调控自噬参与心肌再灌注损伤的发生和发展[49]。 (1)lncRNA促进自噬减轻心肌缺血再灌注损伤:LncRNA参与许多生物过程的调节,包括心脏和非心脏细胞的自噬。越来越多的研究证明lncRNA能够在心肌缺血再灌注损伤期间促进自噬从而发挥对心肌细胞的保护作用。Lv等[50]通过研究表明LncRNA H19能够直接与miR-143相互作用并通过充当分子海绵来降低其表达,ATG7被证实为miR-143的靶向基因,lncRNA H19与miR-143竞争性结合导致ATG7表达增加,进而促进自噬过程,因此lncRNA H19可能通过H19/miR-143/ATG7轴增强自噬缓解心肌缺血再灌注损伤程度。内质网应激在心肌缺血再灌注损伤中具有关键作用,lncRNA Dancr对心肌细胞的内质网应激具有调节作用,Tm诱导自噬并导致Beclin 1水平和LC3Ⅱ/Ⅰ比值的增加以及p62表达的降低,同时lncRNA Dancr过表达会导致自噬增加和miR-6324的低表达, miR-6324的表达会消除lncRNA Dancr过表达对自噬的影响,以上发现表明上调lncRNA Dancr并与miR-6324竞争性结合增强自噬,从而恢复内质网稳态,减轻心肌缺血再灌注损伤[51]。此外,LncRNA 2810403D21Rik/Mirf在H2O2处理的心肌细胞中和心肌梗死小鼠模型的心脏组织中显著上调,miR-26a作为其竞争性内源性RNA在心肌细胞和缺血性心肌组织中显著下调,沉默lncRNA2810403D21Rik/Mirf和过表达miR-26a都降低了自噬水平,从而减少了梗死面积并改善了心脏功能,另外,miR-26a过表达通过靶向Usp15激活心肌细胞的自噬[52],这些发现表明通过lncRNA2810403D21Rik/Mirf能够与miR-26a竞争性结合并调控Usp15的表达,从而增强心肌细胞自噬,保护心肌细胞免受缺血再灌注损伤。 (2)lncRNA抑制自噬减轻心肌缺血再灌注损伤:在再灌注损伤期间容易导致心肌细胞自噬的过度激活,因此部分lncRNA可以通过调控自噬相关基因(包括Beclin-1、Atg5、Atg7和Atg12)抑制自噬的过度激活,从而维持其细胞的稳态。LI等[53]研究发现LncRNA KCNQ1OT1在心肌梗死患者、再灌注损伤小鼠和缺氧复氧诱导的细胞模型中均过表达,荧光素酶报告基因检测表明LncRNA KCNQ1OT1抑制miR-26a-5p水平,而miR-26a-5p抑制ATG12的表达,KCNQ1OT1可以通过上调miR-26a-5p抑制细胞自噬并保护心肌细胞免于缺血再灌注损伤。此外,ATG7是关键的自噬促进基因,其参与再灌注诱导的心肌损伤,miR-188-3p可以通过靶向ATG7抑制自噬程序和心肌梗死,lncRNA自噬促进因子APF能够与miR-188-3p结合并降低其活性[54],结果表明 lncRNA APF通过调控APF/miR-188-3p/ATG7轴抑制自噬和心肌梗死。另外,在经缺氧/复氧处理的人类AC16心肌细胞中LncRNA PVT1被上调,而PVT1经敲低后可以阻断缺氧/复氧损伤,此外,PVT1的敲低减轻了缺氧/复氧心肌细胞过度自噬,这是由LC3-Ⅱ和Beclin-1的表达水平降低、p62的表达增加和自噬泡的积累减少决定的。总之,PVT1作为miR-186的竞争内源性RNA能够通过调控miR-186/Beclin-1轴保护AC16心肌细胞免受缺氧/复氧诱导的损伤[55]。 另有相关报道LncRNA XIST、TUG1、TTTY15在体内外再灌注损伤模型中均被验证且高表达,这对于临床成果的转化显得尤为重要。LI等[56]通过动物实验发现lncRNAXIST在缺氧/复氧心肌细胞中表达上调,XIST的沉默可以抑制自噬从而提高细胞活力,而抑制miR-133a可以逆转这种情况,然而过表达miR-133a可以通过调节SOCS2减少缺氧/复氧诱导的细胞损伤和自噬,因此XIST的低表达通过抑制自噬和调节miR-133a/SOCS2轴在心肌缺血再灌注期间发挥心肌保护作用。与lnRNA XIST类似,lncRNA TUG1在体内外心肌再灌注损伤模型中上调而miR-142-3p下调,抑制TUG1和过表达miR-142-3p可抑制心肌细胞的凋亡和自噬,HMGB1和Racl基本上都介导了TUG1诱导的细胞凋亡和自噬[57],因此TUG1通过靶向miR-142-3p并上调HMGB1和Rac1可改善心肌损伤并预防急性心肌梗死。与前两者相同,LncRNA TTTY15在体内外心肌再灌注损伤模型中均高表达,lncRNA TTTY15调节miR-374a-5p表达,从而影响再灌注损伤期间心肌细胞中FOXO1的表达和自噬[58]。 心肌素是一种在心肌中特异性表达的核蛋白,心肌素的敲低能够抑制自噬并减轻缺血引起的心肌损伤,p53作为一种肿瘤抑制蛋白,能够增加参与自噬过程激活的心肌素的表达,而p53-心肌素信号轴的过度激活自噬会导致心肌细胞的死亡和缺血性加速,LncRNA CAIF可直接与p53结合降低心肌素的表达[59],从而抑制心肌缺血再灌注损伤中自噬细胞死亡,进而减少梗死面积,以上表明lncRNACAIF通过CAIF-p53-心肌素信号轴抑制心脏自噬并保护心脏免受再灌注损伤。外泌体中LINC00174在再灌注损伤小鼠中表达降低,并通过抑制心肌细胞的自噬、凋亡和空泡形成改善再灌注损伤诱导的心肌损伤,其机制与LINC00174直接靶向调控SRSF1表达,然后降低心肌细胞中p53和心肌素的表达相关[60],这些数据表明LINC00174-SRSF1-P53-心肌素通路可能作为治疗靶点来减轻缺血再灌注损伤后的过度自噬,从而改善心脏功能。LncRNA UCA1在缺氧复氧心肌细胞和心肌组织中表达降低,其可以通过吸附miR-143并调控Bcl-2的表达抑制心肌细胞的过度自噬,从而保护心脏微血管内皮细胞免受缺氧/复氧引起的损伤[61]。此外,缺血再灌注诱导心肌细胞过度自噬,lncRNA UCA1在缺血再灌注的心脏组织中低表达,UCA1能够直接靶向调控miR-128的表达,而miR-128靶向HSP70来调节其表达,而吗啡治疗通过调控UCA1/miR-128/HSP70轴显著抑制心肌细胞的过度自噬,从而减少心肌细胞死亡和梗死面积[62]。 (3)lncRNA促进/抑制自噬加重心肌缺血再灌注损伤:部分lncRNA在心肌缺血再灌注损伤后上调,并通过抑制miRNA表达和增强自噬相关靶基因的表达对心脏产生不利影响。CHRF在心肌缺血再灌注损伤模型中表达上调,并负调控miR-182-5p的表达,另外ATG7过表达可以抑制沉默CHRF对自噬的影响,因此CHRF可以通过miR-182-5p/ATG7通路增强自噬,从而加剧心肌缺血再灌注损伤[63]。WANG等[64]通过软件分析和双荧光素酶报告基因检测表明miR-30a与lncRNA AK088388和Beclin-1都具有结合位点,miR-30a在缺氧/复氧心肌细胞中表达上调,而lncRNA AK088388、Beclin-1和LC3-Ⅱ表达下调,lncRNA AK088388可以与miR-30a竞争性结合,促进Beclin-1和LC3-Ⅱ 的表达、自噬,并最终导致心肌细胞损伤。 氧糖剥夺/复氧常用于构建心肌缺血再灌注损伤体外模型,WANG等[65]通过研究证实MALAT1能够直接与miR-20b-5p结合,并作为miR-20b-5p的ceRNA发挥调节beclin1的作用,MALAT1敲低增强了miR-20b-5p对氧糖剥夺/复氧损伤中beclin1相关心肌细胞自噬的抑制作用,因此,LncRNA MALAT1通过海绵miR-20b-5p增强beclin1介导的自噬,从而促进氧糖剥夺/复氧诱导的心肌细胞损伤。FOXD3-AS1在氧糖剥夺/复氧处理的H9C2细胞中表达增加,FOXD3-AS1过表达上调LC3Ⅱ、Beclin1、ATG5的表达,同时下调p62的表达,另外,FOXD3-AS1的过表达激活氧糖剥夺/复氧诱导的H9C2细胞中的NF-κB/COX2/iNOS信号通路,加速自噬[66],进而加重心肌缺血再灌注的损伤。 通过综述lncRNA调控自噬干预再灌注损伤的作用机制为心肌再灌注损伤的靶向治疗提供了一种的新的策略与方法,见图4和表2。 "
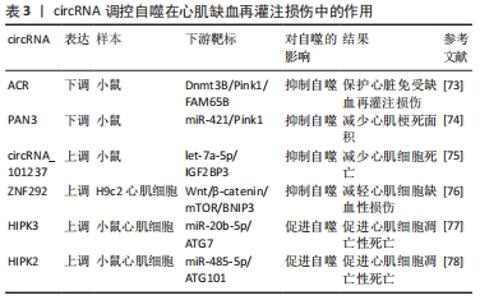
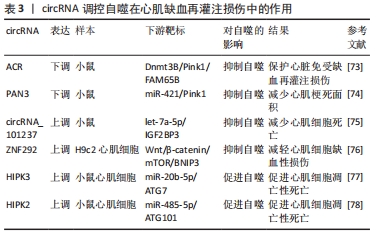
2.2.3 circRNAs功能及对自噬的调控 circRNA是一大类非编码RNA,这些分子的特点是通过将RNA 的3'端连接到5'端形成共价闭环结构[67]。由于circRNA是闭合的连续环,不受外切核酸酶介导的降解,比大多数线性RNA更稳定[68]。研究发现,circRNA作为miRNA海绵,富含与miRNA结合位点,通过减轻miRNA对其靶基因的抑制来增加靶基因的表达[69]。越来越多的研究表明circRNA与许多疾病有关,例如心血管疾病、神经退行性疾病、免疫调节和癌症[70]。circRNAs在心肌再灌注损伤中的功能和潜在机制仍然鲜为人知。 (1)cicRNA抑制自噬减轻心肌缺血再灌注损伤:circRNA可能被自噬降解切割并相应地调节自噬[71],从而抑制心肌缺血再灌注损伤的发展进程。Pink1在心脏、肌肉和睾丸中表达,并与自噬密切相关[72]。circRNA(ACR)和circPAN3均可以通过调控Pink1表达介导心肌再灌注损伤中的自噬。circRNA(ACR)在缺氧复氧诱导的心肌细胞中低表达,其作为调节心肌细胞的自噬环状RNA,能够直接靶向Dnmt3B并激活Pink1表达,这种相互作用阻断了Dnmt3B介导的Pink1启动子的DNA甲基化,同时证明Pink1在丝氨酸46处磷酸化来激活FAM65B抑制心肌细胞的自噬[73]。另有研究发现circPAN3在心肌缺血再灌注损伤模型中显著下调,其过表达能够显著抑制心肌细胞自噬并减轻了心肌细胞损伤,miR-421作为circPAN3的下游靶标并负向调控Pink1,Pink1的下调消除了心肌缺血再灌注损伤中由circPAN3过表达诱导的抗自噬[74],由此证明circPAN3通过调节circPAN3-miR-421-Pink1轴对心肌缺血再灌注损伤中自噬发挥新的作用。 另有研究表明circRNA_101237作为 let-7a-5p 的海绵来调节IGF2BP3依赖的自噬,let-7a-5p能够通过靶向IGF2BP3和灭活自噬来抑制心肌细胞死亡,因此,circRNA_101237下调会降低IGF2BP3的表达,进而抑制缺氧/复氧诱导的原代心肌细胞自噬[75]。circZNF292在氧糖剥夺的心肌细胞中显著上调,BNIP3是参与调节细胞自噬和细胞凋亡的关键因素,并与Wnt/β-catenin和mTOR信号通路密切相关[76],因此circRNA ZNF 292可以通过激活Wnt/β-catenin和mTOR信号通路靶向调节BNIP3抑制自噬来减轻氧糖剥夺诱导的H9c2细胞缺血性损伤。 (2)cicRNA抑制自噬加重心肌缺血再灌注损伤:再灌注损伤后自噬活性的增强与自噬相关基因(ATG7和ATG101)的表达密切相关。心肌缺血再灌注损伤和心肌细胞缺氧/ 复氧损伤后自噬活性增强伴随circHIPK3表达增加,circHIPK3可以通过海绵化miR-20b-5p增强缺氧/复氧心肌细胞自噬,miR-20b-5p能够直接靶向ATG7,因此,circHIPK3通过充当miR-20b-5p海绵来增加ATG7的表达促进心肌细胞的自噬和死亡[77]。此外,ATG101敲低通过减弱H2O2损伤的小鼠新生心肌细胞的自噬来促进增殖和限制细胞死亡,circ-HIPK2通过海绵miR-485-5p正向调节ATG101表达[78],总之,circ-HIPK2通过miR-485-5p/ATG101通路加速H2O2引起的心肌氧化损伤中的细胞自噬和细胞死亡。 通过总结circRNAs在心肌再灌注损伤中的作用机制有助于更好地促进相关结果的临床转化,为心肌再灌注损伤的药物开发提供新的靶点,见表3。 "
| [1] FERRARO R, LATINA JM, ALFADDAGH A, et al. Evaluation and Management of Patients With Stable Angina: Beyond the Ischemia Paradigm: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020; 76(19):2252-2266. [2] WANG JC, LU L, CHEN SS, et al. PERK Overexpression-Mediated Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway Alleviates Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-Induced Injury in Neonatal Murine Cardiomyocytes via Improving Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:6458060. [3] HUANG XW, PAN MD, DU PH, et al. Arginase-2 protects myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via NF-κB/TNF-α pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(19):6529-6537. [4] LI T, TAN Y, OUYANG S, et al. Resveratrol protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via attenuating ferroptosis. Gene. 2022; 808:145968. [5] XIA M, ZU XY, CHEN ZY, et al. Noncoding RNAs in triple negative breast cancer: Mechanisms for chemoresistance. Cancer Lett. 2021;523:100-110. [6] ARYAL B, SUÁREZ Y. Non-coding RNA regulation of endothelial and macrophage functions during atherosclerosis. Vascul Pharmacol. 2019; 114:64-75. [7] ZHANG L, XU X, SU X. Noncoding RNAs in cancer immunity: functions, regulatory mechanisms, and clinical application. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):48. [8] WADLEY GD, LAMON S, ALEXANDER SE, et al. Noncoding RNAs regulating cardiac muscle mass. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019;127(2):633-644. [9] CHEN HY, XIAO ZZ, LING X, et al. ELAVL1 is transcriptionally activated by FOXC1 and promotes ferroptosis in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating autophagy. Mol Med. 2021;27(1):14. [10] WANG JP, CHI RF, WANG K, et al. Oxidative stress impairs myocyte autophagy, resulting in myocyte hypertrophy. Exp Physiol. 2018;103(4): 461-472. [11] SUN T, LI MY, LI PF, et al. MicroRNAs in Cardiac Autophagy: Small Molecules and Big Role. Cells. 2018;7(8):104. [12] OHSUMI Y. Historical landmarks of autophagy research. Cell Res. 2014; 24(1):9-23. [13] MA S, WANG Y, CHEN Y, et al. The role of the autophagy in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1852(2):271-276. [14] CĂTANĂ CS, ATANASOV AG, BERINDAN-NEAGOE I. Natural products with anti-aging potential: Affected targets and molecular mechanisms. Biotechnol Adv. 2018;36(6):1649-1656. [15] WU X, IROEGBU CD, PENG J, et al. Cell Death and Exosomes Regulation After Myocardial Infarction and Ischemia-Reperfusion. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:673677. [16] HUANG J, QING W, PAN Y. NPAS2 ameliorates myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury in rats via CX3CL1 pathways and regulating autophagy. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(16):20569-20584. [17] KHAN SH, KUMAR R. Role of an intrinsically disordered conformation in AMPK-mediated phosphorylation of ULK1 and regulation of autophagy. Mol Biosyst. 2012;8(1):91-96. [18] YANG L, XIE P, WU J, et al. Deferoxamine Treatment Combined With Sevoflurane Postconditioning Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Restoring HIF-1/BNIP3-Mediated Mitochondrial Autophagy in GK Rats. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:6. [19] KALUDERCIC N, MAIURI MC, KAUSHIK S, et al. Comprehensive autophagy evaluation in cardiac disease models. Cardiovasc Res. 2020;116(3):483-504. [20] HALUSHKA PV, GOODWIN AJ, HALUSHKA MK. Opportunities for microRNAs in the Crowded Field of Cardiovascular Biomarkers. Annu Rev Pathol. 2019;14:211-238. [21] LU TX, ROTHENBERG ME. MicroRNA. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018; 141(4):1202-1207. [22] WU P. Inhibition of RNA-binding proteins with small molecules. Nat Rev Chem. 2020;4(9):441-458. [23] WU Y, MAO Q, LIANG X. Targeting the MicroRNA-490-3p-ATG4B-Autophagy Axis Relieves Myocardial Injury in Ischemia Reperfusion. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2021;14(1):173-183. [24] LI X, ZENG Z, LI Q, et al. Inhibition of microRNA-497 ameliorates anoxia/reoxygenation injury in cardiomyocytes by suppressing cell apoptosis and enhancing autophagy. Oncotarget. 2015;6(22):18829-18844. [25] SU B, WANG X, SUN Y, et al. miR-30e-3p Promotes Cardiomyocyte Autophagy and Inhibits Apoptosis via Regulating Egr-1 during Ischemia/Hypoxia. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:7231243. [26] ZHANG Z, LI H, CHEN S, et al. Knockdown of MicroRNA-122 Protects H9c2 Cardiomyocytes from Hypoxia-Induced Apoptosis and Promotes Autophagy. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:4284-4290. [27] CAO Z, LIU J, ZHAO Z, et al. miR-16-5p Regulates PTPN4 and Affects Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis and Autophagy Induced by Hypoxia/Reoxygenation. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021: 5599031. [28] LV XW, HE ZF, ZHU PP, et al. miR-451-3p alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting MAP1LC3B-mediated autophagy. Inflamm Res. 2021;70(10-12):1089-1100. [29] ZHANG C, LU J, WANG H, et al. Effects of miR-103a-3p on the autophagy and apoptosis of cardiomyocytes by regulating Atg5. Int J Mol Med. 2019;43(5):1951-1960. [30] GONG N, YANG X, LI X, et al. MicroRNA-590-3p relieves hypoxia/reoxygenation induced cardiomyocytes apoptosis and autophagy by targeting HIF-1α. Exp Ther Med. 2021;22(4):1077. [31] LI Q, GAO Y, ZHU J, et al. MiR-101 Attenuates Myocardial Infarction-induced Injury by Targeting DDIT4 to Regulate Autophagy. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2020;17(2):123-130. [32] SHAO H, YANG L, WANG L, et al. MicroRNA-34a protects myocardial cells against ischemia-reperfusion injury through inhibiting autophagy via regulating TNF alpha expression. Biochem Cell Biol. 2018;96(3):349-354. [33] WU TY, LENG Q, TIAN LQ. The microRNA-210/Casp8ap2 Axis Alleviates Hypoxia-Induced Myocardial Injury by Regulating Apoptosis and Autophagy. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2021;161(3-4):132-142. [34] LIU L, JIN X, HU CF, et al. Exosomes Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Rescue Myocardial Ischaemia/Reperfusion Injury by Inducing Cardiomyocyte Autophagy Via AMPK and Akt Pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(1):52-68. [35] ZHANG H, ZHANG X, ZHANG J. MiR-129-5p inhibits autophagy and apoptosis of H9c2 cells induced by hydrogen peroxide via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway by targeting ATG14. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;506(1):272-277. [36] LUO G, JIAN Z, ZHU Y, et al. Sirt1 promotes autophagy and inhibits apoptosis to protect cardiomyocytes from hypoxic stress. Int J Mol Med. 2019;43(5):2033-2043. [37] NING S, LI Z, JI Z, et al. MicroRNA-494 suppresses hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and autophagy via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway by targeting SIRT1. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(6):5231-5242. [38] HUANG Z, WU S, KONG F, et al. MicroRNA-21 protects against cardiac hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by inhibiting excessive autophagy in H9c2 cells via the Akt/mTOR pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(3):467-474. [39] LIU X, DENG Y, XU Y, et al. MicroRNA-223 protects neonatal rat cardiomyocytes and H9c2 cells from hypoxia-induced apoptosis and excessive autophagy via the Akt/mTOR pathway by targeting PARP-1. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2018;118:133-146. [40] MA W, ZHOU Y, LIU M, et al. Long non-coding RNA LINC00470 in serum derived exosome: a critical regulator for proliferation and autophagy in glioma cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21(1):149. [41] NASSER MI, MASOOD M, ADLAT S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome microRNA as therapy for cardiac ischemic injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;143:112118. [42] LI T, GU J, YANG O, et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal miRNA-29c Decreases Cardiac Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Through Inhibition of Excessive Autophagy via the PTEN/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Circ J. 2020;84(8):1304-1311. [43] CHEN G, WANG M, RUAN Z, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-143-3p suppresses myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating autophagy. Life Sci. 2021;280:119742. [44] XU YQ, XU Y, WANG SH. Effect of exosome-carried miR-30a on myocardial apoptosis in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury rats through regulating autophagy. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019; 23(16):7066-7072. [45] WANG F, MIN X, HU SY, et al. Hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced upregulation of miRNA-542-5p aggravated cardiomyocyte injury by repressing autophagy. Hum Cell. 2021;34(2):349-359. [46] BO L, SU-LING D, FANG L, et al. Autophagic program is regulated by miR-325. Cell Death Differ. 2014;21(6):967-977. [47] CHEN G, YUE A, WANG M, et al. The Exosomal lncRNA KLF3-AS1 From Ischemic Cardiomyocytes Mediates IGF-1 Secretion by MSCs to Rescue Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:671610. [48] TONG X, CHEN J, LIU W, et al. LncRNA LSINCT5/miR-222 regulates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through PI3K/AKT pathway. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2021;52(3):720-729. [49] ZHAO G, HAILATI J, MA X, et al. LncRNA Gm4419 Regulates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Through Targeting the miR-682/TRAF3 Axis. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2020;76(3):305-312. [50] LV XW, WANG MJ, QIN QY, et al. 6-Gingerol relieves myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury by regulating lncRNA H19/miR-143/ATG7 signaling axis-mediated autophagy. Lab Invest. 2021;101(7):865-877. [51] LI J, XIE J, WANG YZ, et al. Overexpression of lncRNA Dancr inhibits apoptosis and enhances autophagy to protect cardiomyocytes from endoplasmic reticulum stress injury via sponging microRNA-6324. Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(2):116. [52] LIANG H, SU X, WU Q, et al. LncRNA 2810403D21Rik/Mirf promotes ischemic myocardial injury by regulating autophagy through targeting Mir26a. Autophagy. 2020;16(6):1077-1091. [53] LI J, TONG Y, ZHOU Y, et al. LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 as a miR-26a-5p sponge regulates ATG12-mediated cardiomyocyte autophagy and aggravates myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 2021;338:14-23. [54] WANG K, LIU CY, ZHOU LY, et al. APF lncRNA regulates autophagy and myocardial infarction by targeting miR-188-3p. Nat Commun. 2015;6:6779. [55] OUYANG M, LU J, DING Q, et al. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA PVT1 protects human AC16 cardiomyocytes from hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis and autophagy by regulating miR-186/Beclin-1 axis. Gene. 2020;754:144775. [56] LI Z, ZHANG Y, DING N, et al. Inhibition of lncRNA XIST Improves Myocardial I/R Injury by Targeting miR-133a through Inhibition of Autophagy and Regulation of SOCS2. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;18:764-773. [57] SU Q, LIU Y, LV XW, et al. Inhibition of lncRNA TUG1 upregulates miR-142-3p to ameliorate myocardial injury during ischemia and reperfusion via targeting HMGB1-and Rac1-induced autophagy. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019;133:12-25. [58] CHEN YQ, YANG X, XU W, et al. Knockdown of lncRNA TTTY15 alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through the miR-374a-5p/FOXO1 axis. IUBMB Life. 2021;73(1):273-285. [59] LIU CY, ZHANG YH, LI RB, et al. LncRNA CAIF inhibits autophagy and attenuates myocardial infarction by blocking p53-mediated myocardin transcription. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):29. [60] SU Q, LV XW, XU YL, et al. Exosomal LINC00174 derived from vascular endothelial cells attenuates myocardial I/R injury via p53-mediated autophagy and apoptosis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021;23:1304-1322. [61] DIAO L, ZHANG Q. Transfer of lncRNA UCA1 by hUCMSCs-derived exosomes protects against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury through impairing miR-143-targeted degradation of Bcl-2. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(4):5967-5985. [62] CHEN Z, LIU R, NIU Q, et al. Morphine Postconditioning alleviates autophage in ischemia-reperfusion induced cardiac injury through up-regulating lncRNA UCA1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;108:1357-1364. [63] MO Y, WU H, ZHENG X, et al. LncRNA CHRF aggravates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by enhancing autophagy via modulation of the miR-182-5p/ATG7 pathway. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2021;35(4): e22709. [64] WANG JJ, BIE ZD, SUN CF. Long noncoding RNA AK088388 regulates autophagy through miR-30a to affect cardiomyocyte injury. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(6):10155-10163. [65] WANG S, YAO T, DENG F, et al. LncRNA MALAT1 Promotes Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation and Reoxygenation Induced Cardiomyocytes Injury Through Sponging miR-20b to Enhance beclin1-Mediated Autophagy. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2019;33(6):675-686. [66] TONG G, WANG Y, XU C, et al. Long non-coding RNA FOXD3-AS1 aggravates ischemia/reperfusion injury of cardiomyocytes through promoting autophagy. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(9):5634-5644. [67] SUN Z, YU T, JIAO Y, et al. Expression Profiles and Ontology Analysis of Circular RNAs in a Mouse Model of Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury (vol 2020, 2346369, 2020). Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:2346369. [68] YU J, KANG X, XIONG Y, et al. Gene Expression Profiles of Circular RNAs and MicroRNAs in Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyps. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:643504. [69] BEERMANN J, PICCOLI MT, VIERECK J, et al. Non-coding RNAs in Development and Disease: Background, Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Approaches. Physiol Rev. 2016;96(4):1297-1325. [70] BAI XF, NIU RZ, LIU J, et al. Roles of noncoding RNAs in the initiation and progression of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Epigenomics. 2021;13(9):715-743. [71] YAO H, HAN B, ZHANG Y, et al.Non-coding RNAs and Autophagy. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1206:199-220. [72] FAN G, CHEN MJ, WEI J. Involvement of phosphatase and tensin homolog-induced putative kinase 1/Parkin-mediated autophagy in angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy in C57BL/6 mice. J Int Med Res. 2020;48(5):300060519896143. [73] ZHOU LY, ZHAI M, HUANG Y, et al. The circular RNA ACR attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing autophagy via modulation of the Pink1/FAM65B pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2019; 26(7):1299-1315. [74] ZHANG CL, LONG TY, BI SS, et al. CircPAN3 ameliorates myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury by targeting miR-421/Pink1 axis-mediated autophagy suppression (vol 63, pg 717, 2021). Lab Invest. 2021;101(1): 89-103. [75] GAN J, YUAN J, LIU Y, et al. Circular RNA_101237 mediates anoxia/reoxygenation injury by targeting let-7a-5p/IGF2BP3 in cardiomyocytes. Int J Mol Med. 2020;45(2):451-460. [76] REN Q, LI H, WANG X. The circular RNA ZNF292 alleviates OGD-induced injury in H9c2 cells via targeting BNIP3. Cell Cycle. 2019;18(23):3365-3377. [77] QIU Z, WANG Y, LIU W, et al. CircHIPK3 regulates the autophagy and apoptosis of hypoxia/reoxygenation-stimulated cardiomyocytes via the miR-20b-5p/ATG7 axis. Cell Death Discov. 2021;7(1):64. [78] ZHOU J, LI L, HU H, et al. Circ-HIPK2 Accelerates Cell Apoptosis and Autophagy in Myocardial Oxidative Injury by Sponging miR-485-5p and Targeting ATG101. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2020;76(4):427-436. |
| [1] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhou Qian, Zhang Qiang, Chen Qiu. Human salivary components and osteoporosis/osteopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [2] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [3] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [4] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [5] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [6] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [7] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [8] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [9] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [10] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [11] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [12] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [13] | Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| [14] | Cui Xing, Sun Xiaoqi, Zheng Wei, Ma Dexin. Huangqin Decoction regulates autophagy to intervene with intestinal acute graft-versus-host disease in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1057-1062. |
| [15] | Xu Jing, Yan Yongmin, Cai Mengjie . miR-373 inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation by downregulating transforming growth factor beta type II receptor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 756-761. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||