Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (29): 4716-4722.doi: 10.12307/2022.842
Previous Articles Next Articles
Aerobic exercise improves the cognitive function of elderly patients with mild cognitive impairment
Yang Yi1, Wang Kun1, Liu Hengxu1, Zhang Tingran1, Lu Wenyun2, Chen Peijie3, Luo Jiong1
- 1Research Centre for Exercise Detoxification, College of Physical Education, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China; 2School of Leisure, 3School of Kinesiology, Shanghai University of Sport, Shanghai 200438, China
-
Received:2021-09-26Accepted:2021-11-15Online:2022-10-18Published:2022-03-28 -
Contact:Luo Jiong, PhD, Professor, Research Centre for Exercise Detoxification, College of Physical Education, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China -
About author:Yang Yi, Master candidate, Research Centre for Exercise Detoxification, College of Physical Education, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China -
Supported by:the Special Fund for Major National Social Science Project, No. 19ZDA352 (to CPJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Yi, Wang Kun, Liu Hengxu, Zhang Tingran, Lu Wenyun, Chen Peijie, Luo Jiong. Aerobic exercise improves the cognitive function of elderly patients with mild cognitive impairment[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(29): 4716-4722.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
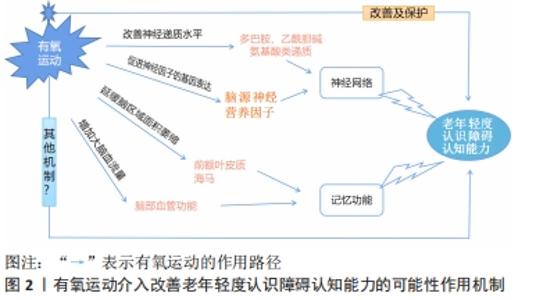
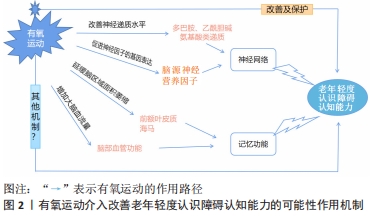
2.1.1 延缓脑区域面积萎缩 年龄的增加导致老年人记忆相关的脑区域的萎缩,海马与前额叶皮质是人体记忆的主要作用部分,该部分的损伤会造成轻度认知障碍疾病的高发[27],有氧运动可增强老年轻度认知障碍患者右半球颞顶交界处、腹外侧前额叶皮质和背外侧前额叶皮质网络的活动,从而增强记忆功能和反应速度[28]。有研究结果表明,参与有氧运动对轻度认知障碍患者的大脑结构功能会发生不同程度的改变,主要表现为延缓大脑皮质的萎缩,以减少海马体积损失为主,从而维持认知功能的稳定性。有氧运动可能通过增加前海马体积[29]、前额叶皮质,改善神经活动和血管生成,以此延缓轻度认知障碍向痴呆症的发展。在多项随机对照试验的研究调查中指出,有氧运动训练同样延缓了左右海马体积的损失[30],调节海马和前扣带皮质的区域波动和灰质体积[29,31],加强了海马与其他脑功能的连接性。此外,研究发现海马与角回的静息状态功能连接增加,从而保护老年人年龄增长导致的海马体积损失,增强海马的内在功能,从而改善了空间记忆[32]。另外,有学者推测有氧运动可能导致大脑神经元和突触发生形态学变化,表现为相关脑区面积、皮质厚度和体积的增加,对脑萎缩的抑制、相关树突形态的改变、脑网络功能连接、皮质激活的增加和神经递质的改变等也会起作用[33]。因此,有氧运动能够有效保护大脑皮质完整性和缓解脑区体积萎缩,减缓老年轻度认知障碍疾病向其他认知疾病的发展进程。 2.1.2 促进脑源性神经营养因子的表达 认知功能与大脑调节神经连接和功能的能力有关,神经营养因子是促进大脑神经网络的重要链接[12],支持神经生长、存活和突触可塑性[34],并高度集中于海马和皮质。实验表明,运动通过各种生物力学促进神经可塑性[34],诱导脑源性神经营养因子 [31],增强脑源性神经营养因子的基因表达[35-36],为海马回提供养分,强化认知表现。在一项动物实验中,发现有氧运动有效改善了抑郁小鼠海马脑源性神经营养因子表达水平[37]。急性有氧运动可以显著提高轻度认知障碍患者的脑源性神经营养因子水平[28],中等强度的短时间有氧运动可增加血清脑源性神经营养因子水平[24,34],对运动的诱导和认知功能的积极作用有关。有氧运动还通过降低促炎细胞因子水平,改善神经营养因子外周浓度[38-39],从而强化认知表现,可见有氧运动的干预加强了神经营养因子的表达,达到延缓轻度认知障碍患者的认知衰退的目的。 2.1.3 增加大脑血流量 大脑血流量是脑功能作用的供能机制,为大脑提供营养物质。相关研究证实,大脑血流量在一定程度上影响着老年人的认知能力[40],有氧运动改善脑血管功能,提高大脑记忆功能和抑制控制[12],从而稳定认知功能。另外大脑血流量对老年轻度认知障碍患者的语言流畅的提高也有较大影响。通过有氧运动的干预后,患者的大脑血管功能得到改善,心肺功能也呈现正面效益,供氧能力的加强有利于脑部血流量的运输[41]。有氧运动介入后,大脑中与运动激活相关的大脑血流量增加,促进老年轻度认知障碍患者的记忆功能的改善,改善的程度可能与前扣带皮质和相邻前额叶皮质的大脑血流量增加相关,学者推断其可能的原因是通过患者敏感区域的血流量的再分配和神经活动二者造成的[9]。在正常认知过渡到轻度认知障碍的过程中,伴随着局部大脑血流量的增加和减少,当皮质下的脑血流呈现下降时,同时也就可能意味着认知能力的下降,甚至进一步发展为老年性痴呆。有氧运动介入,增加大脑循环血量,对于身体健康素质和认知能力均有益处。 2.1.4 提高神经递质水平 神经递质是神经元和效应器之间传递信息的物质,主要包括多巴胺、乙酰胆碱和5-羟色胺等,适度的有氧运动可提高多巴胺系统、氨基酸类神经递质等的水平[27]。叶柄照等[42]认为有氧运动可能通过调控神经系统,保护老年轻度认知障碍患者的认知能力。 综上所述,轻度认知障碍改善机制存在一定的复杂性,具体机制图见图2。"
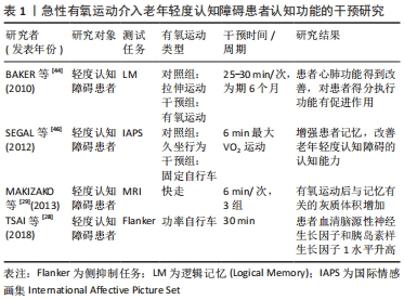
2.2.1 急性有氧运动介入对轻度认知障碍患者认知功能的影响 急性有氧运动是指短时间的一次性运动,持续时间在10- 60 min[43]。许多研究证实急性有氧运动对轻度认知障碍老年人的认知功能具有正面效益,对不同的认知领域起作用,主要作用于大脑功能即刻表现。在33例健忘性轻度认知障碍患者的随机试验中,将患者分为拉伸运动组(心率维持在不大于心率储备的50%)和高强度有氧运动组(以心率储备的75%-85%进行锻炼),研究结果认为有氧运动不仅增进心肺健康的影响,而且还与改善注意力和执行功能有关,特别是改善了老年女性的认知衰退的抑制控制过程[44]。参与急性有氧运动干预之后,22例久坐性老年人的脑源性神经营养因子水平显著变化,循环脑源性神经营养因子的调节会受到老年人体能水平的影响,对改善老年人的认知功能起积极作用[45]。尽管学者认为一次性激烈运动会造成执行功能上的后遗症,但是不足以造成严重的危害,急性有氧运动对认知性能是有益处的[44,46]。 有学者采用急性有氧运动处方对66例遗忘型老年轻度认知障碍患者的分组干预研究中发现,患者的行为表现得到有效改善,神经保护生长因子水平也发生显著变化,急性期的有氧运动显著增加了轻度认知障碍患者脑源性神经营养因子和胰岛素样生长因子(Insulin-like growth factor,IGF-1)水平,并有增加血清血管内皮生长因子(serum vascular endothelial growth factor,SVEGF)水平的趋势,急性有氧运动处方可能成为干预和延缓神经性衰退的有效模式[28-29]。急性有氧运动的研究资料较少,这可能与老年患者的特殊生理有关,另外,笔者推断可能急性有氧运动的干预操作难度较大,特别是在运动变量方面,面对不同病患的介入方法和剂量上存在不统一的标准,存在安全操作隐患,见表1。"
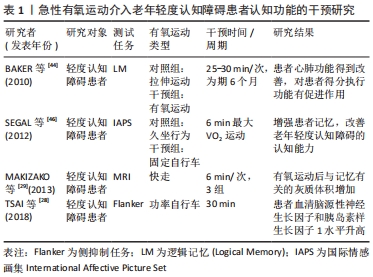
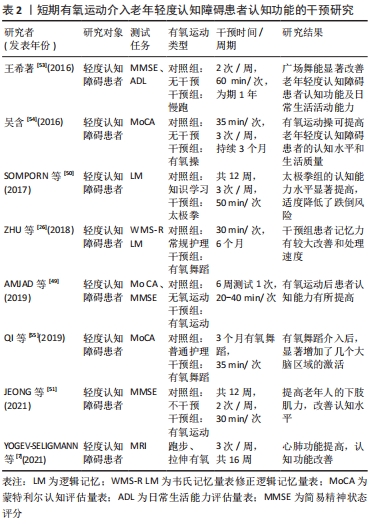
2.2.2 短期有氧运动介入对轻度认知障碍患者认知功能的影响 短期有氧运动的干预时间大多数研究中为3个月。通过大量试验,采取不同有氧运动方式进行对照研究结果显示,有氧运动对老年轻度认知障碍患者的记忆部分起着重要的正面影响。 6 min步行测试的结果显示,逻辑记忆、视觉记忆与6 min有氧步行呈正相关,推测记忆功能的改善可能与灰质体积的大小变化有关[29]。在随机分组调查中,采用健身操和广场舞等加以干预,有氧运动干预组的认知能力水平高于对照组,主要表现于注意力、延迟回忆和语言表达等[47],对不爱运动的老年人的空间记忆产生强烈刺激[48]。经过特别设计有氧运动舞蹈带来的效益主要为改善情景记忆和处理速度。调查研究还发现,如果降低运动强度或停止练习,老年轻度认知障碍患者的认知水平将受到影响[26]。 有学者认为轻度到中度的有氧运动对老年轻度认知障碍患者的认知功能改善具有短期和长期的作用,干预方式为跑步机或自行车[49]。当语言记忆、情景记忆、视觉空间能力等认知领域受损时,患者的生理性跌倒风险增加,有研究者认为15周的有氧运动可提高相关领域的认知能力,适度降低患者的跌倒风险[50],日常生活所需要的活动能力可以通过有氧运动获得,并且通过有氧锻炼之后,认知功能和身体活动能力双向提高,有利于老年人的日常行为活动开展,提高生活质量[51]。16周的有氧运动训练可以提高高阶认知区域的可塑性,并且心肺功能的改善可能帮助神经认知功能的改善[7],有氧运动的锻炼效益就可以通过提高老年人的身体机能素质,而间接性介导神经认知功能,有氧运动潜在益处得到发现。一项Meta 分析指出,有氧运动持续 3 个月以上有助于提高老年人的执行能力、记忆力、协调性和平衡能力等,促进和改善患者的认知功能[52-53]。为期3个月的有氧运动操干预,然后进行随访调查研究发现,有氧运动操提高了轻度认知障碍患者的认知功能水平,对患者的生活质量和身体健康均有改善[54]。在静休状态功能磁共振成像(RS-fMRI)技术观察下,表明有氧舞蹈显著增加了大脑多个区域的功能激活,并有助于有效改善老年轻度认知障碍患者的认知功能[55]。在18周的有氧运动情况下,一组进行有氧方形舞蹈,对照组则进行正常的生活方式,在第9,18周的测试比较发现,有氧运动组量表得分比对照组评分高,得出结论:中等强度有氧运动一定程度上提高轻度认知障碍患者的整体认知功能,对记忆能力也有积极影响[22,56],但作用不明显,可能是研究测试的差异性。短期有氧运动在多种运动模式干预研究中优势明显,通过阻力运动、多模式运动等多种运动处方对轻度认知障碍患者的干预对比研究中发现,有氧运动在老年轻度认知障碍患者的身心健康上总体上呈现正面效应,达到强身健体、愉悦身心的目的,着重强调中等强度的有氧运动对认知领域的效用更好[57-58],另外的研究也认为中等强度有氧运动在提高记忆力和执行功能方面具有积极意义[59]。因此对老年轻度认知障碍患者采取有氧运动中等强度的运动干预效果更好,这也是设计运动处方时应该考虑的运动剂量之一,见表2。"
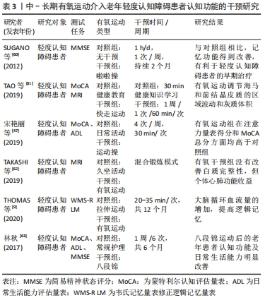
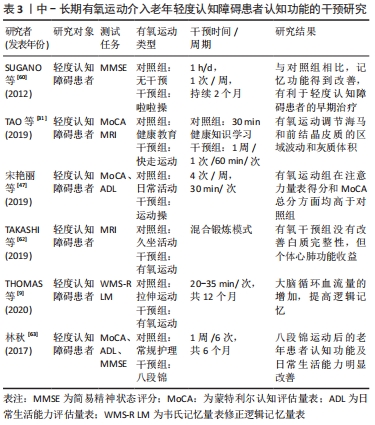
2.2.3 中长期有氧运动介入对轻度认知障碍患者认知功能的影响 中长期的有氧运动对维持老年人的健康生活的是有益的,长期进行有氧运动的锻炼,有利于延长生命线,提高晚年生命质量。研究资料指出,在非药物干预的前提下,以认知功能、日常生活能力、人际关系和身体机能4个评估标准进行干预评估,轻度认知障碍组与未干预组相比,记忆功能得到改善,认为有氧运动可改善老年轻度认知障碍患者的记忆[60]。还有研究着重强调的是对工作记忆的影响[19],为期1年的有氧运动提高了心肺适能,通过大脑循环血量的增加也改善了记忆功能[9]。长期性认知障碍性疾病的住院患者,在药物治疗不能取得良好的效果时,非药物干预是较好的治疗手段,通过有氧运动与久坐娱乐性活动的干预对比研究,最后调查结果证实,久坐行为组的患者认知能力水平呈下降趋势,在锻炼组中,神经精神病症状、记忆功能和功能移动性显著改善,并且分析指出有氧运动似乎对患有严重认知障碍的人有更大的影响,对改善痴呆症住院人员的认知功能、行为和日常生活能力有积极影响,在社区和医院的护理工作中具有重要的参考实践意义[61]。 脑白质是神经元的基板,阿尔茨海默病会损伤白质,研究认为,长期的有氧运动虽然不能完全保证白质的完整性,但是可以改变前额叶皮质的性能,因为前额叶皮质与白质通道完整性的改善相关[62]。身体功能的增强,特别是心肺功能水平的提高,均与长期坚持锻炼是分不开的。太极拳、八段锦、广场舞等作为中国传统体育项目代表,是老年人喜爱的有氧运动项目,身心协调发展,能够有效的提高身体机能的能力,这方面的效益已得到科学的证实。轻度认知障碍患者参与此类有氧运动,由于该类的运动项目特性,对身体造成的负面压力较小,便于开展和学习。多项研究认为长期坚持太极拳、八段锦、舞蹈等有氧锻炼,患者的整体认知功能、延迟回忆和主观认知抱怨方面均有改善作用[31],适度缓和抑郁情绪[22,47,63-64],提高老年轻度认知障碍的日常生活能力,对改善生活质量有积极意义,在临床上也推荐作为疗法。一综述也支持了该观点,另外随着着年龄的增加,语言功能和逻辑能力下降,通过有氧运动可改善语义记忆、语言学习与记忆、自我认知记忆和视觉空间技能等运用[63],见表3。"
| [1] PETERSEN RC, SMITH GE, WARING SC, et al. Mild cognitive impairment: clinical characterization and outcome. Arch Neurol. 1999;56(3):303-308. [2] LITVAN I, AARSLAND D, ADLER CH, et al. MDS Task Force on mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease: critical review of PD-MCI. Mov Disord. 2011;26(10):1814-1824. [3] PEDERSEN KF, LARSEN JP, TYSNES OB, et al. Prognosis of mild cognitive impairment in early parkinson disease: the norwegian park west study. JAMA Neurol. 2013;70(5):1-7. [4] OTTOY J, NIEMANTSVERDRIET E, VERHAEGHE J, et al. Association of short-term cognitive decline and MCI-to-AD dementia conversion with CSF, MRI, amyloid- and 18F-FDG-PET imaging. NeuroImage Clin. 2019;22:101771. [5] 王广州.新中国70年:人口年龄结构变化与老龄化发展趋势[J].中国人口科学,2019(3):2-15, 126. [6] 刘煜敏.中国老年痴呆的现状、面临的问题及对策[J].中国社会工作,2018(14):28-29. [7] YOGEV-SELIGMANN G, EISENSTEIN T, ASH E, et al. Neurocognitive plasticity is associated with cardiorespiratory fitness following physical exercise in older adults with amnestic mild cognitive impairment. J Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021;81(1):91-112. [8] BLUMENTHAL JA, SMITH PJ, MABE S, et al. Longer term effects of diet and exercise on neurocognition: 1‐year follow‐up of the ENLIGHTEN trial. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2020;68(3):559-568. [9] THOMAS BP, TARUMI T, SHENG M, et al. Brain perfusion change in patients with mild cognitive impairment after 12 months of aerobic exercise training. J Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020;75(2):617-631. [10] BLISS ES, WONG RHX, HOWE PRC, et al. Benefits of exercise training on cerebrovascular and cognitive function in ageing. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2021;41(3):447-470 [11] 果召全.有氧运动训练治疗老年轻度认知功能障碍的疗效观察[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2016,38(1):45-46. [12] 郑妍,陈桂秋,马思慧,等.有氧运动联合认知训练干预老年人轻度认知功能障碍的作用[J].中国老年学杂志,2020,40(18):4016-4019. [13] 江文静,单培彦,马俊,等.老年人轻度认知功能障碍与睡眠障碍的相关性研究[J].中华老年医学杂志,2020,39(8):896-900. [14] BANGEN KJ, NATION DA, CLARK LR, et al. Interactive effects of vascular risk burden and advanced age on cerebral blood flow. Front Aging Neurosci. 2014;6:159. [15] 刘涵慧,李会杰.老化认知神经科学:研究现状与未来展望[J].中国科学:生命科学,2021,51(6):743-763. [16] OSUKA Y, KOJIMA N, SASAI H, et al. Exercise types and the risk of developing cognitive decline in older women: a prospective study. J Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020;77(4):1733-1742. [17] MADDEN DJ, BENNETT IJ, SONG AW. Bennett and allen w. song. cerebral white matter integrity and cognitive aging: contributions from diffusion tensor imaging. Neuropsychol Rev. 2009;19(4):415-435. [18] 杨帆,王超,毛宗福.武汉市社区老年人轻度认知功能障碍患病现状及其影响因素分析[J].中国公共卫生,2016,32(12):1705-1707. [19] LAW CK, LAM FMH, CHUNG RCK, et al. Physical exercise attenuates cognitive decline and reduces behavioural problems in people with mild cognitive impairment and dementia: a systematic review. J Physiother. 2020;66(1):9-18. [20] 王石艳.有氧运动对AD及MCI患者认知和运动功能干预作用的研究[D].南京:南京医科大学,2015. [21] 袁雪丽,张雪姣,白雅敏,等.慢性病高危人群体力活动现况及影响因素分析[J].中国慢性病预防与制,2016,24(2):107-110. [22] CHANG J, CHEN Y, LIU C, et al. Effect of square dance exercise on older women with mild mental disorders. Front Psychiatry. 2021;12:699778. [23] DA SILVEIRA LANGONI C, DE LIMA RESENDE T, BARCELLOS AB, et al. Effect of exercise on cognition, conditioning, muscle endurance, and balance in older adults with mild cognitive impairment: a randomized controlled trial. J Geriatric Phys Ther. 2019;42(2):E15-E22. [24] DEVENNEY KE, GUINAN EM, KELLY ÁM, et al. Acute high-intensity aerobic exercise affects brain-derived neurotrophic factor in mild cognitive impairment: a randomised controlled study. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2019. doi: 10.1136/bmjsem-2018-000499. [25] SONG D, DORIS SF. Effects of a moderate-intensity aerobic exercise programme on the cognitive function and quality of life of community-dwelling elderly people with mild cognitive impairment: a randomised controlled trial. Int J Nursing Studies. 2019;93:97-105. [26] ZHU Y, WU H, QI M, et al. Effects of a specially designed aerobic dance routine on mild cognitive impairment. Clin Interven Aging. 2018;2018 (default):1691-1700. [27] 周香莲,周媛媛,王丽娜,等.老年性轻度认知功能障碍患者运动干预策略的研究进展[J].中国全科医学,2018,21(12):1408-1412. [28] TSAI CL, UKROPEC J, UKROPCOVÁ B, et al. An acute bout of aerobic or strength exercise specifically modifies circulating exerkine levels and neurocognitive functions in elderly individuals with mild cognitive impairment. NeuroImage. 2018;17:272-284. [29] MAKIZAKO H, SHIMADA H, DOI T, et al. Six-minute walking distance correlated with memory and brain volume in older adults with mild cognitive impairment: a voxel-based morphometry study. Dementia Geriatric Cogn Disorders Extra. 2013;3(1):223-232. [30] TEN BRINKE LF, BOLANDZADEH N, NAGAMATSU LS, et al. Aerobic exercise increases hippocampal volume in older women with probable mild cognitive impairment: a 6-month randomised controlled trial. Br J Sports Med. 2015;49(4):248-254. [31] TAO J, LIU J, CHEN X, et al. Mind-body exercise improves cognitive function and modulates the function and structure of the hippocampus and anterior cingulate cortex in patients with mild cognitive impairment. NeuroImage. 2019;23:101834 [32] ERICKSON KI, VOSS MW, PRAKASH RS, et al. Exercise training increases size of hippocampus and improves memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(7):3017-3022. [33] 李懿婷,王君,戴向唯,等.有氧运动干预对轻度认知障碍患者脑功能影响的神经生物学机制[J].生命的化学,2020,40(6):903-910. [34] LECKIE RL, OBERLIN LE, VOSS MW. et al. BDNF mediates improvements in executive function following a 1-year exercise intervention. Front Human Neurosci. 2014;8:985. [35] AHLSKOG JE, GEDA YE, GRAFF-RADFORD NR, et al. Physical exercise as a preventive or disease-modifying treatment of dementia and brain aging. Mayo Clin Proc. 2011;86(9):876-884. [36] UYSAL N, KIRAY M, SISMAN AR, et al. Effects of voluntary and involuntary exercise on cognitive functions, and VEGF and BDNF levels in adolescent rats. Biotech Histochem. 2015;90(1):55-68. [37] 屈红林,谢军,陈嘉勤,等.有氧运动激活BDNF/miR-195/Bcl-2信号通路抑制CUMS抑郁小鼠海马神经细胞凋亡[J].天津体育学院学报,2018,33(2):148-155, 176. [38] MANUELA CRISPIM NASCIMENTO C, RODRIGUES PEREIRA J, PIRES DE ANDRADE L, et al. Physical exercise in MCI elderly promotes reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines and improvements on cognition and BDNF peripheral levels. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2014;11(8):799-805. [39] SHIMADA H, MAKIZAKO H, YOSHIDA D, et al. A large, cross-sectional observational study of serum bdnf, cognitive function, and mild cognitive impairment in the elderly. Front Aging Neuroscie. 2014. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2014.00069. [40] ALFINI AJ, WEISS LR, NIELSON KA, et al. Resting cerebral blood flow after exercise training in mild cognitive impairment. J Alzheimer’s Dis. 2019;67(2):671-684. [41] TOMOTO T, TARUMI T, CHEN JN, et al. One-year aerobic exercise altered cerebral vasomotor reactivity in mild cognitive impairment. J App Pphysiol. 2021;131:119-130. [42] 叶柄照,夏锐,邱娉婷,等.有氧运动对轻度认知障碍患者脑结构重塑的研究进展[J].神经损伤与功能重建,2019,14(1):36-39. [43] THEMANSON JR, HILLMAN CH. Cardiorespiratory fitness and acute aerobic exercise effects on neuroelectric and behavioral measures of action monitoring. Neuroscience. 2006;141(2):757-767. [44] BAKER LD, FRANK LL, FOSTER-SCHUBERT K, et al. Effects of aerobic exercise on mild cognitive impairment: a controlled trial of aerobic exercise for mild cognitive impairment. Arch Neurol. 2010;67(1):71-79. [45] MÁDEROVÁ D, KRUMPOLEC P, SLOBODOVÁ L, et al. Acute and regular exercise distinctly modulate serum, plasma and skeletal muscle BDNF in the elderly. Neuropeptides. 2019;78:101961. [46] SEGAL SK, COTMAN CW, CAHILL LF. Exercise-induced noradrenergic activation enhances memory consolidation in both normal aging and patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;32(4):1011-1018. [47] 宋艳丽,刘伟.有氧运动操对养老机构轻度认知障碍老人的干预[J].中国老年学杂志,2019,39(13):3176-3178. [48] MEROM D, GRUNSEIT A, ERAMUDUGOLLA R, et al. Cognitive benefits of social dancing and walking in old age: the dancing mind randomized controlled trial. Fronti Aging Neurosci. 2016;8:26. [49] AMJAD I, TOOR H, NIAZI IK, et al. Therapeutic effects of aerobic exercise on EEG parameters and higher cognitive functions in mild cognitive impairment patients. Int J Neurosci. 2019;129(6):551-562. [50] SUNGKARAT S, BORIPUNTAKUL S, CHATTIPAKORN N, et al. Effects of tai chi on cognition and fall risk in older adults with mild cognitive impairment: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Geriatrics Soc. 2017; 65(4):721-727. [51] JEONG MK, PARK KW, RYU JK, et al. Multi-Component intervention program on habitual physical activity parameters and cognitive function in patients with mild cognitive impairment: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(12):6240. [52] 刘东祺,李荣梅,张美琪,等.有氧运动干预老年轻度认知功能障碍的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(35):5727-5731. [53] 王希著.有氧运动对老年轻度认知功能障碍的影响[J].实用医药杂志,2016,33(11):991-992. [54] 吴含. 有氧运动为主综合训练方式对轻度认知障碍的干预作用研究[D].南京:南京医科大学,2016. [55] QI M, ZHU Y, ZHANG L, et al. The effect of aerobic dance intervention on brain spontaneous activity in older adults with mild cognitive impairment: a resting-state functional MRI study. Exp Ther Med. 2019; 17(1):715-722. [56] ZHENG G, XIA R, ZHOU W, et al. Aerobic exercise ameliorates cognitive function in older adults with mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br J Sports Med. 2016;50(23):1443-1450. [57] SONG D, DORIS SF, LI PWC, et al. The effectiveness of physical exercise on cognitive and psychological outcomes in individuals with mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Nursing Studies. 2018;79:155-164. [58] LEE J. Effects of aerobic and resistance exercise interventions on cognitive and physiologic adaptations for older adults with mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized control trials. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(24): 9216-9216. [59] CAI Y, ABRAHAMSON K. How exercise influences cognitive performance when mild cognitive impairment exists: a literature review. J Psychosoc Nursing Mental Health Services. 2016;54(1):25-35. [60] SUGANO K, YOKOGAWA M, YUKI S, et al. Effect of cognitive and aerobic training intervention on older adults with mild or no cognitive impairment: a derivative study of the nakajima project. Dement Geriatric Cogn Disorders Extra. 2012;2(1):69-80. [61] CANCELA JM, AYÁN C, VARELA S, et al. Effects of a long-term aerobic exercise intervention on institutionalized patients with dementia. J Sci Med Sport. 2016;19(4):293-298. [62] TARUMI T, THOMAS BP, TSENG BY, et al. Cerebral white matter integrity in amnestic mild cognitive impairment: a 1-year randomized controlled trial of aerobic exercise training. J Alzheimer’s Dis. 2019;73(2):489-501. [63] 林秋.八段锦健身运动在老年轻度认知功能障碍患者中的应用效果及认知功能改善情况[J].中国老年学杂志,2017,37(14):3558-3560. [64] LIM KHL, PYSKLYWEC A, PLANTE M, et al. The effectiveness of Tai Chi for short-term cognitive function improvement in the early stages of dementia in the elderly: a systematic literature review. Clin Interv Aging. 2019;14:827-839. |
| [1] | Wu Liang, Wang Qiang, Wang Wenbo, Xin Tianwen, Xi Kun, Tang Jincheng, Xu Jingzhi, Chen Liang, Gu Yong. Risk factors for traumatic central cord syndrome underlying with cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1388-1394. |
| [2] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhou Qian, Zhang Qiang, Chen Qiu. Human salivary components and osteoporosis/osteopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [3] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [4] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [5] | Kong Yamin, Yan Juntao, Ma Bingxiang, Li Huawei. Massage vibration intervenes with MyoD expression and proliferation and differentiation of muscle satellite cells in rats with sciatic nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1160-1166. |
| [6] | Wu Cong, Jia Quanzhong, Liu Lun. Relationship between transforming growth factor beta1 expression and chondrocyte migration in adult articular cartilage after fragmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1167-1172. |
| [7] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [8] | Wang Qin, Shen Cheng, Liao Jing, Yang Ye. Dapagliflozin improves renal injury in diabetic nephropathy rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1216-1222. |
| [9] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [10] | Tang Wenjing, Wu Siyuan, Yang Chen, Tao Xi. Inflammatory responses in post-stroke depression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1278-1285. |
| [11] | Xiao Yang, Gong Liqiong, Fei Jing, Li Leiji. Effect of electroacupuncture on nerve growth factor and its receptor expression in facial nerve nucleus after facial nerve injury in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1253-1259. |
| [12] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [13] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [14] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [15] | Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||