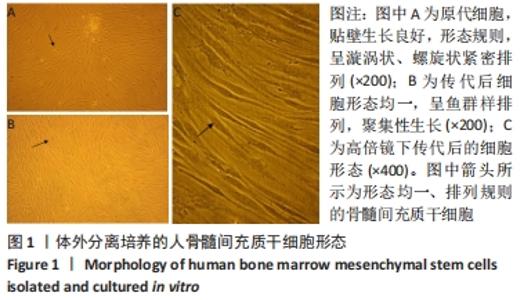
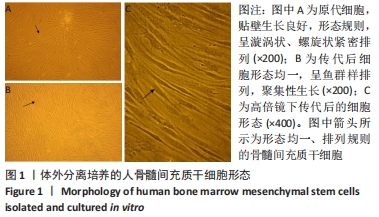
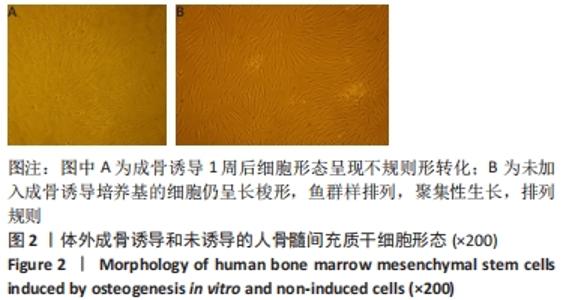
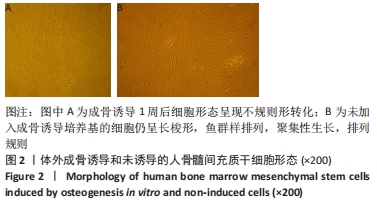
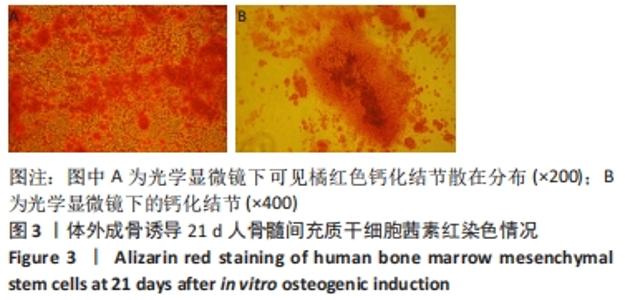
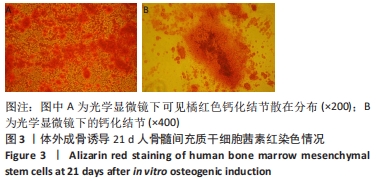
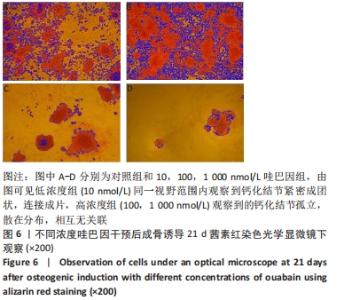
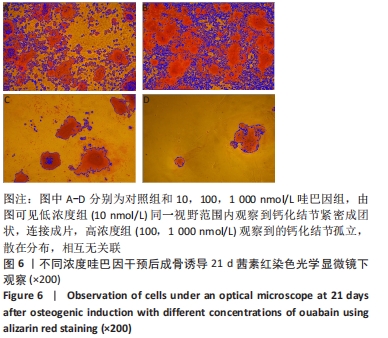
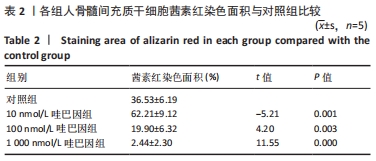
[1] MEPPELINK AM, WANG XH, BRADICA G, et al. Rapid isolation of bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells using integrated centrifuge-based technology. Cytotherapy. 2016;18(6):729-739.
[2] JOHNSTONE BH, MILLER HM, BECK MR, et al. Identification and characterization of a large source of primary mesenchymal stem cells tightly adhered to bone surfaces of human vertebral body marrow cavities. Cytotherapy. 2020;22(11):617-628.
[3] MAHBOUDI H, KAZEMI B, SOLEIMANI M, et al. Enhanced chondrogenesis of human bone marrow mesenchymal Stem Cell (BMSC) on nanofiber-based polyethersulfone (PES) scaffold. Gene. 2018;643:98-106.
[4] RATH SN, NOOEAID P, ARKUDAS A, et al. Adipose- and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells display different osteogenic differentiation patterns in 3D bioactive glass-based scaffolds. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016;10(10):E497-E509.
[5] HUANG GT, GRONTHOS S, SHI S. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from dental tissues vs. those from other sources: their biology and role in regenerative medicine. J Dent Res. 2009;88(9):792-806.
[6] CENTENO CJ, BUSSE D, KISIDAY J, et al. Increased knee cartilage volume in degenerative joint disease using percutaneously implanted, autologous mesenchymal stem cells. Pain Physician. 2008;11(3):343-353.
[7] SHAO X, GOH JC, HUTMACHER DW, et al. Repair of large articular osteochondral defects using hybrid scaffolds and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in a rabbit model. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(6):1539-1551.
[8] MORENO C, YANO S, BEZANILLA F, et al. Transient Electrical Currents Mediated by the Na+/K+-ATPase: A Tour from Basic Biophysics to Human Diseases. Biophys J. 2020;119(2):236-242.
[9] LI Z, CAI T, TIAN J, et al. NaKtide, a Na/K-ATPase-derived peptide Src inhibitor, antagonizes ouabain-activated signal transduction in cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(31):21066-21076.
[10] GABLE ME, ABDALLAH SL, NAJJAR SM, et al. Digitalis-induced cell signaling by the sodium pump: on the relation of Src to Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;446(4):1151-1154.
[11] HAMLYN JM, BLAUSTEIN MP, BOVA S, et al. Identification and characterization of a ouabain-like compound from human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991;88(14):6259-6263.
[12] OTSU K, KURUMA A, YANAGIDA E, et al. Na+/K+ ATPase and its functional coupling with Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in mouse embryonic stem cells during differentiation into cardiomyocytes. Cell Calcium. 2005;37(2):137-151.
[13] LEE YK, NG KM, LAI WH, et al. Ouabain facilitates cardiac differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells through ERK1/2 pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2011;32(1):52-61.
[14] SAYED M, DRUMMOND CA, EVANS KL, et al. Effects of Na/K-ATPase and its ligands on bone marrow stromal cell differentiation. Stem Cell Res. 2014;13(1):12-23.
[15] TIAN J, LI X, LIANG M, et al. Changes in sodium pump expression dictate the effects of ouabain on cell growth. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(22): 14921-14929.
[16] MAKIHIRA S, NIKAWA H, KAJIYA M, et al. Blocking of sodium and potassium ion-dependent adenosine triphosphatase-α1 with ouabain and vanadate suppresses cell-cell fusion during RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011;670(2-3):409-418.
[17] 潘欣宇,崔颖,马林祥,等.骨髓间充质干细胞的研究进展及临床应用前景[J].中国医学工程,2011,19(5):173-174.
[18] ZHOU Y, WU C, CHANG J. Bioceramics to regulate stem cells and their microenvironment for tissue regeneration. Materials Today. 2019;24: 41-56.
[19] LAM ATL, REUVENY S, OH SK. Human mesenchymal stem cell therapy for cartilage repair: Review on isolation, expansion, and constructs. Stem Cell Res. 2020;44:101738.
[20] 王承云,石磊,夏春,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞分离培养方法的改进[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(32):5896-5900.
[21] DOMINICI M, LE BLANC K, MUELLER I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.
[22] 石志红,袁祖贻,张慧峰,等.不同浓度哇巴因对A549细胞增殖及死亡的影响[J].现代肿瘤医学,2011,19(8):1515-1518.
[23] OLIVEIRA TN, POSSIDONIO AC, SOARES CP, et al. The role of Na+/K+-ATPase during chick skeletal myogenesis. PLoS One. 2015;10(3): e0120940.
[24] HUANG T, YU Z, YU Q, et al. Inhibition of osteogenic and adipogenic potential in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells under osteoporosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;525(4):902-908.
[25] LIU L, IVANOV AV, GABLE ME, et al. Comparative properties of caveolar and noncaveolar preparations of kidney Na+/K+-ATPase. Biochemistry. 2011;50(40):8664-8673.
[26] KUANG Z, BAI J, NI L, et al. Withanolide B promotes osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via ERK1/2 and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;88:106960.
|