Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (25): 4076-4083.doi: 10.12307/2022.417
Previous Articles Next Articles
Future of exosomes and mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in the diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson’s disease
Wei Yufan1, Fan Feiyan1, Li Shuangli1, Zhang Yunke1, 2
- 1Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; 2First Affiliated Hospital, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2021-06-04Accepted:2021-07-09Online:2022-09-08Published:2022-01-26 -
Contact:Zhang Yunke, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Post-doctoral cooperative supervisor, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; First Affiliated Hospital, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Wei Yufan, Master candidate, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81974564 (to ZYK); Henan Science and Technology Innovation Outstanding Talents Project, No. 2018JR0006 (to ZYK)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wei Yufan, Fan Feiyan, Li Shuangli, Zhang Yunke. Future of exosomes and mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in the diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson’s disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 4076-4083.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

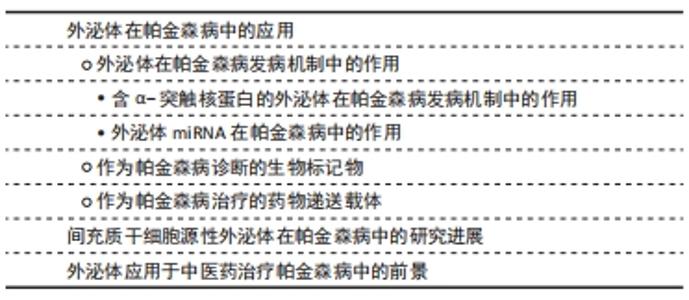
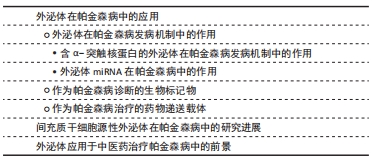
2.1 外泌体在帕金森病中的应用 外泌体是一种纳米级的、脂质双分子层的膜性囊泡,是细胞外囊泡的一种[17]。外泌体起源于内吞途径,其形成的早期内体逐步形成晚期内体或多泡体,其中成熟早期内体通过出芽运动形成内囊泡,而一部分多泡体与细胞膜融合,内囊泡被释放到细胞外[18-19],释放到细胞外的外泌体被微环境中的靶细胞摄取或者通过体液运送到身体其他部位[20]。通过电子显微镜观察,在腔内/细胞外间隙中发现,并被所有类型的细胞分泌,已知外泌体存在于血浆、血清、尿液、脑脊液、唾液、母乳和其他分泌物中[21]。 并且外泌体含有一些重要的生物活性分子,如蛋白质、脂质、功能性mRNA以及大量非编码核酸(miRNA、lncRNA和circRNA),这些内容物在外泌体形成、被靶细胞摄取过程以及细胞间物质信息传递中发挥重要作用[13]。研究发现,外泌体的产生和释放依赖于原始细胞和靶细胞的生理状态和条件,因此不同的外泌体具有不同的蛋白质、脂质和核酸分布[22]。 20世纪80年代之前,研究者们未予足够重视,误认为外泌体是装载和运送细胞成熟过程中所产生的废弃物[23-24],例如1967年,WOLF教授[25]在血浆中第一次发现细胞外囊泡,并将其描述为血小板衍生的直径和密度不同的微粒结构,但在当时被认为是血小板废弃物。直到1983年,JOHNSTONE教授[24]首次发现在绵羊网织红细胞体外培养上清液中存在外泌体,并被定义为转铁蛋白受体的排泄通道;随着研究深入,于1987年JOHNSTONE教授[26]首次正式提出外泌体的概念,将其命名为“exosome”。1996年RAPOSO教授[27]发现,B淋巴细胞分泌的外泌体携带主要组织相容性复合物-Ⅱ类分子、共刺激因子和黏附因子,可以改变细胞外微环境、提呈抗原、刺激T细胞增殖、诱导机体免疫反应以及影响机体健康。随着二代测序、蛋白质组学和脂质组学等技术的进步,人们发现外泌体是由活细胞分泌的一种亚细胞结构,而不是简单的细胞碎片,2007年,VALADI教授[28]发现人的肥大细胞可以捕获来源于鼠的肥大细胞分泌的外泌体,其携带的mRNA可以被转移到细胞质中,并翻译成蛋白质,这一结果首次证实了细胞分泌的外泌体中含有的mRNA及miRNA均具有良好的生物活性,这表明外泌体在细胞间通讯起着重要作用。2013年hoJames E. Rothman、Randy W. Schekman和Thomas C. Südhof也因发现囊泡运输调控机制而获得诺贝尔生理学或医学奖,进而推动了外泌体的基础研究。随后,于2015年ZOMER等[29]发现肿瘤细胞分泌的细胞外囊泡可以被靶细胞摄取并改变靶细胞状态,证明了外泌体的体内传递;同年,MELO等[30]发现胰腺癌患者血清中磷脂酰肌醇1阳性的外泌体占比显著高于正常人群,这为胰腺癌的前期诊断提供依据;同时,HOSHINO等[31]也发现肿瘤细胞释放的外泌体会先行到达预期转移器官,而外泌体表面的整合素种类决定着靶器官的特异性,那么以整合素靶点降低靶器官的摄取可以降低肿瘤转移,这为抑制肿瘤转移提供了治疗新思路。此后大量研究表明,外泌体具有免疫调节、增殖分化、细胞迁移以及介导细胞间的物质传递等不同的生物学特性,并在疾病早期诊断、临床治疗中发挥着不可或缺的作用。外泌体发现过程记时线图,见图3。"

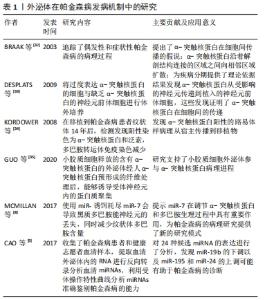
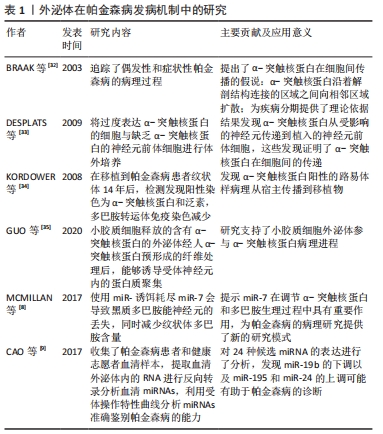
(1)含α-突触核蛋白的外泌体在帕金森病发病机制中的作用:既往尸检结果表明,帕金森病的两个病理特征是中脑黑质和纹状体区域多巴胺能神经元的进行性缺失,以及路易小体的形成。已知α-突触核蛋白是一个由140个氨基酸组成的蛋白质,主要存在于突触前神经元,其功能可能与神经元的可塑性、细胞分化、囊泡运输及多巴胺摄取调节有关[36-37]。 正常情况下α-突触核蛋白以非折叠的结构形式存在于细胞浆,此时并不具有毒性,只有当其氨基末端结构域结合到细胞膜形成α-螺旋结构[38],并在细胞膜上发生错误折叠和聚集[39],以及非淀粉样成分结构域由随机卷曲结构形成片层结构,导致纤维形成[40],此时错误折叠和纤维聚集的α-突触核蛋白具有细胞毒性,不仅破坏突触传递,还具有病毒样性质,可从受病理影响的神经元传播到健康未受影响的神经元[5-6,41]。早在2003年,BRAAK等[32]就提出了α-突触核蛋白在细胞间传播的假说:α-突触核蛋白沿着解剖结构连接的区域之间向相邻区域扩散,具体而言,首先出现在嗅球和舌咽迷走神经背核,当有临床症状时已扩散到黑质、中脑和基底神经节,到临床晚期弥散到整个大脑皮质。并且越来越多的体内外研究支持α-突触核蛋白可引起病理学扩散,进而导致多巴胺神经元变性和帕金森病进展。将过度表达α-突触核蛋白的细胞与缺乏α-突触核蛋白的神经元前体细胞进行体外培养,证明了这种蛋白在细胞间的传递[33]。此外,将从帕金森病患者大脑中提取的血浆注入实验动物大脑,能够触发α-突触核蛋白的聚集及其在注射动物的中枢神经系统中的传播[42];在移植了中脑细胞的帕金森病患者中,发现α-突触核蛋白阳性的路易体样病理从宿主传播到移植物[34]。然而,尚不清楚α-突触核蛋白在细胞间传播的确切分子机制。 但是,现已发现外泌体更像分子货物囊泡,可以作为mRNA、miRNA和特定蛋白质的天然载体[43-44]。因此,它们可能在细胞间通讯和疾病传播中起作用,这可能通过错误折叠的α-突触核蛋白和炎性细胞因子转移至邻近细胞而促进神经退行性疾病(包括帕金森病)的进展[45]。在人脑脊髓液和血浆中分离出的外泌体中发现了α-突触核蛋白,这表明外泌体与供体神经元释放的α-突触核蛋白有关[46]。另外,DANZER等[47]发现当自噬机制不足时,细胞会清除有毒的α-突触核蛋白寡聚体,通过诱导自噬来预防外泌体释放和摄取可能是阻止疾病在帕金森病中传播的一种新方法。 GHIDONI等[48]也提出了神经退行性疾病中外泌体“特洛伊木马”的假说,即外泌体通过在细胞间运输毒性剂导致细胞死亡,这是继神经元细胞死亡之后的关键机制。近来,神经炎症与帕金森病发病机制的联系也越来越受人们关注。 小胶质细胞代表中枢神经系统的常驻巨噬细胞,约占神经胶质细胞的10%[49],与帕金森病的发病机制密切相关[50]。研究表明,α-突触核蛋白可以激活帕金森病中的小胶质细胞,引起以核因子κB信号通路为中心的炎症级联反应,并上调白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18和肿瘤坏死因子α等炎性细胞因子,从而诱导神经炎和多巴胺神经元变性[7]。活化的小胶质细胞可以分泌富含主要组织相容性复合物分子Ⅱ和肿瘤坏死因子α的外泌体[51],并且小胶质细胞分泌的外泌体已被证明有助于α-突触核蛋白在神经元之间的传递活性[35,52]。而NLRP3炎性小体是小胶质细胞中表达最高的炎性小体,不仅与人体对病原体入侵的抵抗力有关,而且还与帕金森病、阿尔茨海默病和动脉粥样硬化等各种疾病的进展有关[53]。研究表明,在帕金森病中,α-突触核蛋白可通过刺激小胶质细胞中的NLRP3炎症小体活化,促进小胶质细胞中外泌体的形成,并导致外泌体分泌到细胞外空间,而分泌的外泌体含有内吞的成熟促炎因子,从而诱导神经炎症[54]。 (2)外泌体miRNA在帕金森病中的作用:miRNA是单链非编码RNA分子,可调节编码蛋白质的基因表达,并参与多个基本生物学过程。越来越多的证据表明,miRNA表达失调会导致多种神经退行性疾病(包括帕金森病)的病理过程[55-56]。迄今为止,已经发现帕金森病患者的脑组织、脑脊液和血液样本以及帕金森病动物模型中有数种miRNA失调[57]。一些失调的miRNA,例如miR-7/153/34,已直接参与帕金森病的发病机制,因为它们调节SNCA基因抑制α-突触核蛋白的聚集[8,58]。其他miRNA也参与了帕金森病发病机制的关键途径调控,包括自噬[59]、氧化应激和炎症[60-61]。另外,帕金森病致病基因LRRK2基因的表达也受miRNA调控,例如miRNA-205[62]。 此外,miRNA可以通过外泌体在细胞间传播,诱导靶细胞遗传程序发生变化,从而促进帕金森病进程。 miRNA代表外泌体转运物的重要组成部分,外泌体转移miRNA是细胞遗传交换的重要机制[27]。最近的研究表明,外泌体miRNA参与了中枢神经系统疾病的发病机制。但是,关于外泌体miRNA在帕金森病中的意义,文献仍然很少。一项细胞培养研究表明,星形胶质细胞释放的外泌体携带一种特定的miRNA,这在帕金森病的发病机制中起着至关重要的作用[63]。2014年,WINKLER等[64]证明了let-7(一种在帕金森病模型中过表达的miRNA)可以在外泌体中运输,并且它可以激活神经元中的Toll样受体,从而导致神经变性。还有几项研究发现,帕金森病患者的脑脊液和血清中的外泌体miRNA含量发生了变化,GUI等[65]对帕金森病患者脑脊液中的外泌体miRNA进行了唯一的差异表达分析,发现一些差异表达的外泌体miRNA。相反,CAO等[9]对帕金森病和健康患者的血清外泌体中24种候选miRNA的表达进行了分析,发现miR-19b的下调以及miR-195和miR-24的上调;这些miRNA先前被报道为帕金森病的临床生物标志物[66]。JIANG等[67]报告说,帕金森病小鼠中血清来源的外泌体miRNA137被上调,并在诱导帕金森病中神经元氧化应激中发挥着至关重要的作用。 2.1.2 作为帕金森病诊断的生物标记物 在帕金森病典型运动症状出现之前存在一个症状前阶段,直到纹状体多巴胺的水平减少70%-80%以上以及黑质多巴胺能神经元丢失50%以上才会出现临床症状[68],并且早期临床症状并非特异性,缺乏有效的生物标记物,故诊断仍然主要根据英国脑库标准的运动症状以及患者对多巴胺能药物的反应。由于外泌体的含量因其起源细胞和受体细胞而异[69],例如,血液中脑源性外泌体可能反映了脑部疾病中其祖先脑细胞发育的致病性过程[70],因此,在帕金森病中寻找脑脊液和血浆生物标志物在早期疾病病理诊断中有最重要意义[71]。对从帕金森病患者血浆中提取的星形胶质细胞和少突胶质细胞的研究表明了血浆脑源性外泌体的浓度与疾病的严重程度的相关性,尤其在疾病早期,故可作为监测帕金森病疾病进展的潜在替代生物标志物[10,70]。 在脑脊液和血浆中均含有丰富的miRNA,而在帕金森病中,miRNA的表达水平有很大差异:目前发现在帕金森病脑脊液外泌体中miR-153、miR-409-3p、miR-10a-5p、let-7g-3p会升高,miR-1、miR-19b-3p则相反;而在血清外泌体中发现miR-153、miR-195、miR-24的上调和miR-19b的下调;同样在血浆中也出现了miR-331-5p上调和miR-505的下调,因而这些miRNA也有可能成为帕金森病检测的生物学标志[72]。 2.1.3 作为帕金森病治疗的药物递送载体 见表2。"
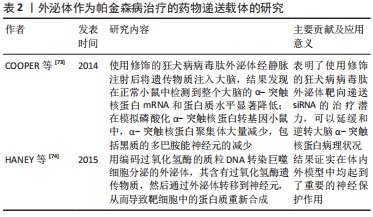
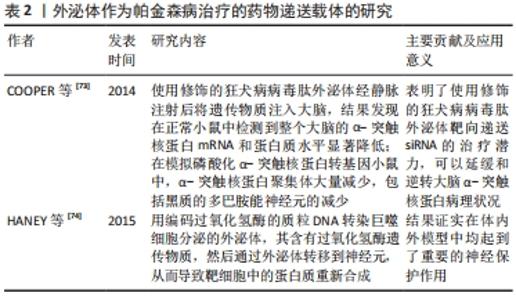
目前,帕金森病药物治疗以基于多巴胺替代策略为主,虽取得一定疗效,但由于血脑屏障的存在,约98%的可能治疗中枢神经系统疾病的有效药物无法得到使用,只有分子质量< 400 Da的脂溶性小分子才容易通过血脑屏障进入脑部组织[75]。并且多巴胺药物由于其分子本身具有亲水性和高氢键性,使其难以通过血脑屏障;而多巴胺结构类似物通过连续刺激多巴胺受体,此类激动剂生物利用度很低,作用时间也短,必须每日多次给药[2]。因此,开发能将药物稳定递送至大脑的载体显得尤为重要[76]。而外泌体是天然存在的纳米级囊泡,可以穿过血脑屏障[77],同时还具有在细胞间运输生物分子的天然能力以及免疫惰性、膜融合入胞等优势,可以逃避宿主免疫系统的快速药物清除,故被应用于脑部疾病的药物递送[78]。 尽管使用外泌体作为治疗药物的递送载体进行了广泛的研究,但是将外泌体作为帕金森病治疗的药物载体的研究仍非常有限。目前已有不同类型的载体用于递送外源遗传物质,包括病毒、阳离子聚合物载体如聚阳离子聚乙烯亚胺纳米颗粒和脂质体,但是这些方法受到立体定向手术、免疫原性、细胞毒性和非特异性靶向的限制,而外泌体有潜力克服几乎所有这些问题,而且是核酸到靶向细胞的天然载体[79]。COOPER等[73]前期已证明,使用α-突触核蛋白siRNA可降低小鼠大脑中总α-突触核蛋白和聚集的α-突触核蛋白水平;为了实现将siRNA广泛递送至大脑,他们使用修饰的狂犬病病毒肽外泌体经静脉注射后将遗传物质注入大脑,结果发现在正常小鼠中检测到整个大脑的α-突触核蛋白mRNA和蛋白水平显著降低;在模拟磷酸化α-突触核蛋白转基因小鼠中,α-突触核蛋白聚集体大量减少,包括黑质的多巴胺能神经元的减少。这项研究表明了使用修饰的狂犬病病毒肽外泌体靶向递送siRNA的治疗潜力,可以延缓和逆转大脑α-突触核蛋白病理状况。此外,HANEY等[74]用编码过氧化氢酶的质粒DNA转染巨噬细胞分泌的外泌体,其含有过氧化氢酶遗传物质,然后通过外泌体转移到神经元,从而导致靶细胞中的蛋白质重新合成,结果证实在帕金森病的体外及体内模型中均起到了重要的神经保护作用。并且将治疗剂掺入外泌体中可以保持药物治疗活性,延长循环时间,并改善治疗剂向大脑的输送[80]。 2.2 间充质干细胞源性外泌体在帕金森病中的研究进展 间充质干细胞是于1992年由CAPLAN教授首次确定命名的[81],作为一种具有多向分化潜能、高度自我更新能力的来源于中胚层的多能干细胞,广泛存在于人体多种组织中,并在不同诱导条件下有分化为间充质组织谱系,包括骨、软骨、脂肪、肌腱、肌肉和骨髓的能力[82]。间充质干细胞具有免疫调节[83]、组织损伤修复[84]、神经保护等多种功能[85-86],而且不同类型的间充质干细胞在神经系统疾病的治疗与研究中扮演着重要角色[87-88]。近年来,随着研究的不断深入,发现间充质干细胞可通过短暂旁分泌生长因子、趋化因子和细胞因子等,减少细胞凋亡和纤维化,促进血管生成和组织修复等治疗作用[89-90]。此外,大量的研究表明间充质干细胞源性外泌体在神经退行性疾病中参与炎症信号通路的调节、血管重构、促内皮细胞增殖、抗细胞凋亡及免疫调节等,后续的临床试验也证明间充质干细胞旁分泌机制在刺激组织再生方面拥有更好的安全性与可行性,这预示着运用间充质干细胞源性外泌体可能成为治疗神经退行性疾病的重要手段之一[91-92]。 作用机制:外泌体因具有低免疫原性、在循环中长半衰期以及可携带小分子物质如miRNA和蛋白质等跨越血脑屏障等特点,所以在中枢神经系统再生医学中有望成为新治疗策略的基础[93-95]。而间充质干细胞源性外泌体如今被广泛认为是间充质干细胞发挥生理功能的重要方式,在临床上不仅能介导间充质干细胞的治疗效力,而且在取代干细胞治疗疾病方面也具备巨大的潜力[96]。有研究表明,间充质干细胞源性外泌体可通过调节神经干细胞、神经元和胶质细胞以及轴突在体外内环境中的生长,成为神经保护、神经分化的重要启动子[97-98]。 目前间充质干细胞源外泌体在神经系统疾病的病理研究中已取得成效。例如,在脑卒中,静脉注射骨髓间充质干细胞源外泌体可促进神经生成、神经突起重塑和血管生成增加,并促进动物模型的功能恢复[99];在创伤性脑损伤大鼠模型中,间充质干细胞产生的外泌体通过促进内源性血管生成和神经发生以及通过减少颅脑损伤后大鼠的炎症而有效改善了功能恢复[96];注射骨髓间充质干细胞源外泌体也被证明是治疗脊髓损伤、减轻炎症和促进损伤后神经再生的一种可能方法[100]。在阿尔茨海默症等神经退行性疾病中,研究表明骨髓间充质干细胞源外泌体高水平表达淀粉样β降解酶,可使脑β-淀粉样蛋白水平降低,从而影响疾病进展。并且不断有研究证实间充质干细胞源外泌体有助于改善受损的神经系统功能和增强血管神经发生,因而有可能成为治疗神经退行性疾病的有效方法[101]。近期大量的临床前研究也发现基于间充质干细胞的神经再生方法可促进受损神经元的突触连接和内源性神经元生长[102-103]。 关于间充质干细胞源性外泌体在帕金森病中的作用主要表现在抑制多巴胺神经元凋亡、发挥神经保护,见表3。"
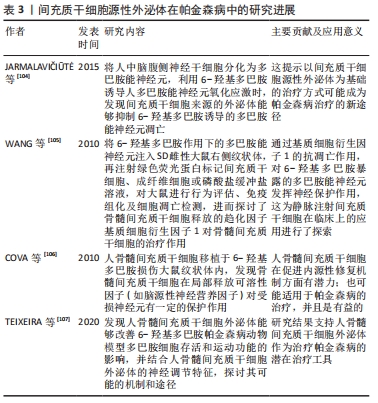

研究表明将人中脑腹侧神经干细胞分化为多巴胺能神经元,利用6-羟基多巴胺诱导人多巴胺能神经元氧化应激时,发现间充质干细胞来源的外泌体能抑制6-羟基多巴胺诱导的多巴胺能神经元凋亡,这提示以间充质干细胞源性外泌体为基础的治疗方式可能成为帕金森病治疗的新途径[104]。骨髓间充质干细胞移植对6-羟基多巴胺作用下的多巴胺能神经元通过骨髓间充质干细胞释放的趋化因子基质细胞衍生因子1的抗凋亡作用发挥神经保护作用,从而增加了多巴胺的释放[105]。并且相关研究发现,间充质干细胞源性外泌体中存在重要的神经调节分子,包括脑源性神经营养因子、胰岛素样生长因子、血管内皮生长因子、色素上皮衍生因子、DJ-1基因和血清胱抑素C,以及基质金属蛋白酶,它们被描述为潜在的治疗介质,并能够降解α-突触核蛋白聚集体,进而改善在体内外模型中观察到的症状[108-109]。此外,COVA团队[106]也报道了人骨髓间充质干细胞移植于6-羟基多巴胺损伤大鼠纹状体内,对多巴胺能神经元有保护作用,并可诱导神经发生,提示骨髓间充质干细胞在局部释放可溶性因子(如脑源性神经营养因子)对受损神经元有一定的保护作用。TEIXEIRA等[107]则通过与左旋多巴的比较,探讨了人骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体对6-羟基多巴胺模型动物运动性能的影响,以及酪氨酸羟化酶的表达对黑质和纹状体组织学参数的影响,研究发现人骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体能够改善动物模型多巴胺细胞存活和运动功能的影响,同时结合人骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体的神经调节特征,候选可能的生物活性分子,探讨其可能的机制和途径。这些报道为间充质干细胞释放的生物活性分子发挥神经保护和抗凋亡作用提供了思路。 另外,外泌体最常见的组成物之一是遗传物质的存在,如miRNA,负责通过mRNA降解或抑制其翻译来调控特定基因,而很多疾病,包括帕金森病都表现出基因表达失调,特别是在miRNA水平。一些miRNAs被认为是α-突触核蛋白调节剂,例如,干扰miR-433与成纤维细胞生长因子20 mRNA结合导致成纤维细胞生长因子20水平的增加,这反过来也增加了α-突触核蛋白在细胞中的水平[110]。此外,还发现其他miRNAs可以调节神经炎症相关基因的表达,例如miR-155在上调α-突触核蛋白纤维的炎症反应中起着关键作用,这是因为miR-155是诸如白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α和一氧化氮合酶等促炎分子的调节因子,可导致其上调[111]。而由miR-17、miR-18a、miR-19a/b、miR-20a和miR-90a形成的miRNA簇存在于间充质干细胞来源外泌体中,被描述为神经突起重塑和神经发生的重要调节剂,以及轴突生长和中枢神经系统恢复的刺激剂[112]。同样,mimic-miR-124能促进脑室下区神经发生,并且能观察到6-羟基多巴胺处理下帕金森病模型小鼠行为的改善[113];miR-155在帕金森病小胶质细胞的激活中起着关键作用,从而导致神经炎症[114];miR-126的过度表达导致胰岛素样生长因子信号传导损伤,增加了多巴胺能神经元对帕金森病神经毒素6-羟基多巴胺的易感性,当使用沉默miR-126(antago-miR-126),会发生相反的情况,从而产生胰岛素样生长因子所引起的神经保护作用[115]。 2.3 外泌体应用于中医药治疗帕金森病中的前景 近年来,中医药在整体观及辨证论治的独特理论体系指导下,凭借可靠的临床疗效越来越被人们所接受,外泌体相关研究也逐渐应用于中医药领域,但有关外泌体联合中医药治疗帕金森病的研究尚缺乏。然而目前中医药对于帕金森病的治疗具有改善帕金森病症状,减轻西药不良反应,发挥增效减毒的作 用[116],并且课题组前期已经证明,经补阳还五汤有效成分处理的大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞产生的外泌体,能够激活血管内皮生长因子、上调microRNA-126表达、降低miR-221与miR-222表达,从而促进脑缺血组织血管新生,进而减少缺血性损伤[117]。这一研究为间充质干细胞源性外泌体作为中药载体应用于帕金森病提供了依据。"

| [1] KALIA LV, LANG AE. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet. 2015;386(9996):896-912. [2] ARMSTRONG MJ, OKUN MS. Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson Disease: A Review. JAMA. 2020;323(6):548-560. [3] CHEN HX, LIANG FC, GU P, et al. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells repair a Parkinson’s disease model by inducing autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(4):288. [4] BEATRIZ M, VILAÇA R, LOPES C. Exosomes: Innocent Bystanders or Critical Culprits in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:635104. [5] DEHAY B, BOURDENX M, GORRY P, et al. Targeting α-synuclein for treatment of Parkinson’s disease: mechanistic and therapeutic considerations. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14(8):855-866. [6] LI JY, ENGLUND E, HOLTON JL, et al. Lewy bodies in grafted neurons in subjects with Parkinson’s disease suggest host-to-graft disease propagation. Nat Med. 2008;14(5):501-503. [7] HICKMAN S, IZZY S, SEN P, et al. Microglia in neurodegeneration. Nat Neurosci. 2018;21(10):1359-1369. [8] MCMILLAN KJ, MURRAY TK, BENGOA-VERGNIORY N, et al. Loss of MicroRNA-7 Regulation Leads to α-Synuclein Accumulation and Dopaminergic Neuronal Loss In Vivo. Mol Ther. 2017;25(10):2404-2414. [9] CAO XY, LU JM, ZHAO ZQ, et al. MicroRNA biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease in serum exosome-like microvesicles. Neurosci Lett. 2017;644:94-99. [10] OHMICHI T, MITSUHASHI M, TATEBE H, et al. Quantification of brain-derived extracellular vesicles in plasma as a biomarker to diagnose Parkinson’s and related diseases. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2019;61:82-87. [11] IZCO M, CARLOS E, ALVAREZ-ERVITI L. The Two Faces of Exosomes in Parkinson’s Disease: From Pathology to Therapy. Neuroscientist. 2021:1073858421990001. [12] YEO RW, LAI RC, ZHANG B, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell: an efficient mass producer of exosomes for drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(3):336-341. [13] DENG H, SUN C, SUN Y, et al. Lipid, Protein, and MicroRNA Composition Within Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes. Cell Reprogram. 2018;20(3):178-186. [14] HAN Y, LI X, ZHANG Y, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Regenerative Medicine. Cells. 2019;8(8):886. [15] FAN XL, ZHANG Y, LI X, et al. Mechanisms underlying the protective effects of mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020;77(14):2771-2794. [16] D’ANGELO M, CIMINI A, CASTELLI V. Insights into the Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Secretome in Parkinson’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(15):5241. [17] CODISPOTI B, MARRELLI M, PADUANO F, et al. NANOmetric BIO-Banked MSC-Derived Exosome (NANOBIOME) as a Novel Approach to Regenerative Medicine. J Clin Med. 2018;7(10):357. [18] BÁTIZ LF, CASTRO MA, BURGOS PV, et al. Exosomes as Novel Regulators of Adult Neurogenic Niches. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016;9:501. [19] LIEW LC, KATSUDA T, GAILHOUSTE L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: a glimmer of hope in treating Alzheimer’s disease. Int Immunol. 2017;29(1):11-19. [20] LOU G, CHEN Z, ZHENG M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a new therapeutic strategy for liver diseases. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49(6):e346. [21] DOYLE LM, WANG MZ. Overview of Extracellular Vesicles, Their Origin, Composition, Purpose, and Methods for Exosome Isolation and Analysis. Cells. 2019;8(7):727. [22] PEGTEL DM, GOULD SJ. Exosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2019;88:487-514. [23] SUGAYA K, VAIDYA M. Stem Cell Therapies for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1056:61-84. [24] PAN BT, JOHNSTONE RM. Fate of the transferrin receptor during maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro: selective externalization of the receptor. Cell. 1983;33(3):967-978. [25] WOLF P. The nature and significance of platelet products in human plasma. Br J Haematol. 1967;13(3):269-88. [26] JOHNSTONE RM, ADAM M, HAMMOND JR, et al. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem. 1987;262(19): 9412-9420. [27] RAPOSO G, NIJMAN HW, STOORVOGEL W, et al. B lymphocytes secrete antigen-presenting vesicles. J Exp Med. 1996;183(3):1161-1172. [28] VALADI H, EKSTRÖM K, BOSSIOS A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654-959. [29] ZOMER A, MAYNARD C, VERWEIJ FJ, et al. In Vivo imaging reveals extracellular vesicle-mediated phenocopying of metastatic behavior. Cell. 2015;161(5):1046-1057. [30] MELO SA, LUECKE LB, KAHLERT C, et al. Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2015;523(7559):177-182. [31] HOSHINO A, COSTA-SILVA B, SHEN TL, et al. Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis. Nature. 2015;527(7578):329-335. [32] BRAAK H, DEL TREDICI K, RÜB U, et al. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2003;24(2):197-211. [33] DESPLATS P, LEE HJ, BAE EJ, et al. Inclusion formation and neuronal cell death through neuron-to-neuron transmission of alpha-synuclein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(31):13010-13015. [34] KORDOWER JH, CHU Y, HAUSER RA, et al. Lewy body-like pathology in long-term embryonic nigral transplants in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Med. 2008;14(5):504-506. [35] GUO M, WANG J, ZHAO Y, et al. Microglial exosomes facilitate α-synuclein transmission in Parkinson’s disease. Brain. 2020;143(5):1476-1497. [36] NEMANI VM, LU W, BERGE V, et al. Increased expression of alpha-synuclein reduces neurotransmitter release by inhibiting synaptic vesicle reclustering after endocytosis. Neuron. 2010;65(1):66-79. [37] COOPER AA, GITLER AD, CASHIKAR A, et al. Alpha-synuclein blocks ER-Golgi traffic and Rab1 rescues neuron loss in Parkinson’s models. Science. 2006;313(5785): 324-328. [38] JO E, MCLAURIN J, YIP CM, et al. alpha-Synuclein membrane interactions and lipid specificity. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(44):34328-34334. [39] DIKIY I, ELIEZER D. Folding and misfolding of alpha-synuclein on membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1818(4):1013-1018. [40] SERPELL LC, BERRIMAN J, JAKES R, et al. Fiber diffraction of synthetic alpha-synuclein filaments shows amyloid-like cross-beta conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(9):4897-4902. [41] 张美美,冯涛. α-突触核蛋白致病机制研究进展[J].中华神经科杂志,2020, 53(3):227-231. [42] RECASENS A, DEHAY B, BOVÉ J, et al. Lewy body extracts from Parkinson disease brains trigger α-synuclein pathology and neurodegeneration in mice and monkeys. Ann Neurol. 2014;75(3):351-362. [43] DUAN L , XU L , XU X , et al. Exosome-mediated delivery of gene vectors for gene therapy. Nanoscale. 2021;13(3):1387-1397. [44] SCHOREY JS, BHATNAGAR S. Exosome function: from tumor immunology to pathogen biology. Traffic. 2008;9(6):871-881. [45] LUK KC, KEHM V, CARROLL J, et al. Pathological α-synuclein transmission initiates Parkinson-like neurodegeneration in nontransgenic mice. Science. 2012;338(6109):949-953. [46] EMMANOUILIDOU E, MELACHROINOU K, ROUMELIOTIS T, et al. Cell-produced alpha-synuclein is secreted in a calcium-dependent manner by exosomes and impacts neuronal survival. J Neurosci. 2010; 30(20):6838-6851. [47] DANZER KM, KRANICH LR, RUF WP, et al. Exosomal cell-to-cell transmission of alpha synuclein oligomers. Mol Neurodegener. 2012;7:42. [48] GHIDONI R, BENUSSI L, BINETTI G. Exosomes: the Trojan horses of neurodegeneration. Med Hypotheses. 2008;70(6):1226-1227. [49] BENVENISTE EN. Role of macrophages/microglia in multiple sclerosis and experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Mol Med (Berl). 1997; 75(3):165-173. [50] 邵方泽,梁世倩,秦鸿雁.小胶质细胞在帕金森病中的作用及其研究进展[J].神经解剖学杂志,2020,36(5):565-569. [51] CHANG C, LANG H, GENG N, et al. Exosomes of BV-2 cells induced by alpha-synuclein: important mediator of neurodegeneration in PD. Neurosci Lett. 2013;548:190-195. [52] MAROGIANNI C, SOKRATOUS M, DARDIOTIS E, et al. Neurodegeneration and Inflammation-An Interesting Interplay in Parkinson’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(22):8421. [53] HAQUE ME, AKTHER M, JAKARIA M, et al. Targeting the microglial NLRP3 inflammasome and its role in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2020;35(1):20-33. [54] CYPRYK W, NYMAN TA, MATIKAINEN S. From Inflammasome to Exosome-Does Extracellular Vesicle Secretion Constitute an Inflammasome-Dependent Immune Response? Front Immunol. 2018;9:2188. [55] SCHULZ J, TAKOUSIS P, WOHLERS I, et al. Meta-analyses identify differentially expressed micrornas in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol. 2019;85(6):835-851. [56] HOSS AG, LABADORF A, BEACH TG, et al. microRNA Profiles in Parkinson’s Disease Prefrontal Cortex. Front Aging Neurosci. 2016;8:36. [57] SINGH A, SEN D. MicroRNAs in Parkinson’s disease. Exp Brain Res. 2017; 235(8): 2359-2374. [58] ADUSUMILLI L, FACCHINELLO N, TEH C, et al. miR-7 Controls the Dopaminergic/Oligodendroglial Fate through Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Regulation. Cells. 2020; 9(3):711. [59] ALVAREZ-ERVITI L, SEOW Y, SCHAPIRA AH, et al. Influence of microRNA deregulation on chaperone-mediated autophagy and α-synuclein pathology in Parkinson’s disease. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4(3):e545. [60] CHEN Y, GAO C, SUN Q, et al. MicroRNA-4639 Is a Regulator of DJ-1 Expression and a Potential Early Diagnostic Marker for Parkinson’s Disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2017;9:232. [61] NIES YH, MOHAMAD NAJIB NH, LIM WL, et al. MicroRNA Dysregulation in Parkinson’s Disease: A Narrative Review. Front Neurosci. 2021;15: 660379. [62] CHO HJ, LIU G, JIN SM, et al. MicroRNA-205 regulates the expression of Parkinson’s disease-related leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 protein. Hum Mol Genet. 2013;22(3):608-620. [63] MAO S, SUN Q, XIAO H, et al. Secreted miR-34a in astrocytic shedding vesicles enhanced the vulnerability of dopaminergic neurons to neurotoxins by targeting Bcl-2. Protein Cell. 2015;6(7):529-540. [64] WINKLER CW, TAYLOR KG, PETERSON KE. Location is everything: let-7b microRNA and TLR7 signaling results in a painful TRP. Sci Signal. 2014;7(327):pe14. [65] GUI Y, LIU H, ZHANG L, et al. Altered microRNA profiles in cerebrospinal fluid exosome in Parkinson disease and Alzheimer disease. Oncotarget. 2015;6(35): 37043-37053. [66] MATHEW B, MANSURI MS, WILLIAMS KR, et al. Exosomes as Emerging Biomarker Tools in Neurodegenerative and Neuropsychiatric Disorders-A Proteomics Perspective. Brain Sci. 2021;11(2):258. [67] JIANG Y, LIU J, CHEN L, et al. Serum secreted miR-137-containing exosomes affects oxidative stress of neurons by regulating OXR1 in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res. 2019;1722:146331. [68] FEARNLEY JM, LEES AJ. Ageing and Parkinson’s disease: substantia nigra regional selectivity. Brain. 1991;114(5):2283-2301. [69] RASTOGI S, SHARMA V, BHARTI PS, et al. The Evolving Landscape of Exosomes in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Exosomes Characteristics and a Promising Role in Early Diagnosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(1):440. [70] YU H, SUN T, AN J, et al. Potential Roles of Exosomes in Parkinson’s Disease: From Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment to Prognosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:86. [71] CHANG CW, YANG SY, YANG CC, et al. Plasma and Serum Alpha-Synuclein as a Biomarker of Diagnosis in Patients With Parkinson’s Disease. Front Neurol. 2020;10:1388. [72] ZHAO Y, YANG G. Potential of extracellular vesicles in the Parkinson’s disease - Pathological mediators and biomarkers. Neurochem Int. 2021;144:104974. [73] COOPER JM, WIKLANDER PB, NORDIN JZ, et al. Systemic exosomal siRNA delivery reduced alpha-synuclein aggregates in brains of transgenic mice. Mov Disord. 2014;29(12):1476-1485. [74] HANEY MJ, KLYACHKO NL, ZHAO Y, et al. Exosomes as drug delivery vehicles for Parkinson’s disease therapy. J Control Release. 2015;207:18-30. [75] PARDRIDGE WM. Drug transport across the blood-brain barrier. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2012;32(11):1959-1972. [76] LI W, QIU J, LI XL, et al. BBB pathophysiology-independent delivery of siRNA in traumatic brain injury. Sci Adv. 2021;7(1):eabd6889. [77] HA D, YANG N, NADITHE V. Exosomes as therapeutic drug carriers and delivery vehicles across biological membranes: current perspectives and future challenges. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2016;6(4):287-296. [78] TIAN Y, LI S, SONG J, et al. A doxorubicin delivery platform using engineered natural membrane vesicle exosomes for targeted tumor therapy. Biomaterials. 2014;35(7):2383-2390. [79] CHISTIAKOV DA, CHISTIAKOV AA. α-Synuclein-carrying extracellular vesicles in Parkinson’s disease: deadly transmitters. Acta Neurol Belg. 2017;117(1):43-51. [80] WU X, ZHENG T, ZHANG B. Exosomes in Parkinson’s Disease. Neurosci Bull. 2017;33(3):331-338. [81] HAYNESWORTH SE, BABER MA, CAPLAN AI. Cell surface antigens on human marrow-derived mesenchymal cells are detected by monoclonal antibodies. Bone. 1992;13(1):69-80. [82] PITTENGER MF, MACKAY AM, BECK SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147. [83] 余思,刘尧,陈旭.间充质干细胞外泌体免疫调节作用及其机制的研究进展[J].中国医科大学学报,2018,47(10):939-941+947. [84] 李超然,黄桂林,王帅.间充质干细胞来源外泌体促进损伤组织修复与再生的应用与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(1):133-139. [85] 王康,智晓东,王伟.干细胞来源外泌体修复周围神经损伤的效应[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(19):3083-3089. [86] 高振橙,刘欣.间充质干细胞外泌体在神经系统疾病修复过程中的作用与应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(19):3048-3054. [87] TSAI YA, LIU RS, LIRNG JF, et al. Treatment of Spinocerebellar Ataxia With Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Phase I/IIa Clinical Study. Cell Transplant. 2017;26(3): 503-512. [88] LO FURNO D, MANNINO G, GIUFFRIDA R. Functional role of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of chronic neurodegenerative diseases. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(5):3982-3999. [89] JANOCKOVA J, SLOVINSKA L, HARVANOVA D, et al. New therapeutic approaches of mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes. J Biomed Sci. 2021;28(1):39. [90] ISO Y, SPEES JL, SERRANO C, et al. Multipotent human stromal cells improve cardiac function after myocardial infarction in mice without long-term engraftment. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;354(3):700-706. [91] DE WINDT TS, VONK LA, SLAPER-CORTENBACH IC, et al. Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Stimulate Cartilage Regeneration and Are Safe for Single-Stage Cartilage Repair in Humans upon Mixture with Recycled Autologous Chondrons. Stem Cells. 2017;35(1):256-264. [92] 陈晨,黄辉,胡文佳,等.间充质干细胞源性外泌体治疗神经退行性疾病:应用中的问题及未来前景[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(9):1441-1447. [93] MANEK R, MOGHIEB A, YANG Z, et al. Protein Biomarkers and Neuroproteomics Characterization of Microvesicles/Exosomes from Human Cerebrospinal Fluid Following Traumatic Brain Injury. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55(7):6112-6128. [94] LI JJ, WANG B, KODALI MC, et al. In vivo evidence for the contribution of peripheral circulating inflammatory exosomes to neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15(1):8. [95] KALANI A, TYAGI A, TYAGI N. Exosomes: mediators of neurodegeneration, neuroprotection and therapeutics. Mol Neurobiol. 2014;49(1):590-600. [96] ZHANG Y, CHOPP M, MENG Y, et al. Effect of exosomes derived from multipluripotent mesenchymal stromal cells on functional recovery and neurovascular plasticity in rats after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg. 2015;122(4):856-867. [97] TEIXEIRA FG, CARVALHO MM, NEVES-CARVALHO A, et al. Secretome of mesenchymal progenitors from the umbilical cord acts as modulator of neural/glial proliferation and differentiation. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2015; 11(2):288-297. [98] ASSUNÇÃO-SILVA RC, MENDES-PINHEIRO B, PATRÍCIO P, et al. Exploiting the impact of the secretome of MSCs isolated from different tissue sources on neuronal differentiation and axonal growth. Biochimie. 2018;155:83-91. [99] XIN H, LI Y, CUI Y, et al. Systemic administration of exosomes released from mesenchymal stromal cells promote functional recovery and neurovascular plasticity after stroke in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013;33(11):1711-1715. [100] HAN D, WU C, XIONG Q, et al. Anti-inflammatory Mechanism of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation in Rat Model of Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015;71(3):1341-1347. [101] PHINNEY DG, PITTENGER MF. Concise Review: MSC-Derived Exosomes for Cell-Free Therapy. Stem Cells. 2017;35(4):851-858. [102] LASSO JM, PÉREZ CANO R, CASTRO Y, et al. Xenotransplantation of human adipose-derived stem cells in the regeneration of a rabbit peripheral nerve. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2015;68(12):e189-197. [103] ZHANG Y, CHOPP M, LIU XS, et al. Exosomes Derived from Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Promote Axonal Growth of Cortical Neurons. Mol Neurobiol. 2017;54(4):2659-2673. [104] JARMALAVIČIŪTĖ A, TUNAITIS V, PIVORAITĖ U, et al. Exosomes from dental pulp stem cells rescue human dopaminergic neurons from 6-hydroxy-dopamine-induced apoptosis. Cytotherapy. 2015;17(7):932-939. [105] WANG F, YASUHARA T, SHINGO T, et al. Intravenous administration of mesenchymal stem cells exerts therapeutic effects on parkinsonian model of rats: focusing on neuroprotective effects of stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha. BMC Neurosci. 2010;11:52. [106] COVA L, ARMENTERO MT, ZENNARO E, et al. Multiple neurogenic and neurorescue effects of human mesenchymal stem cell after transplantation in an experimental model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res. 2010;1311:12-27. [107] TEIXEIRA FG, VILAÇA-FARIA H, DOMINGUES AV, et al. Preclinical Comparison of Stem Cells Secretome and Levodopa Application in a 6-Hydroxydopamine Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Cells. 2020;9(2):315. [108] PIRES AO, MENDES-PINHEIRO B, TEIXEIRA FG, et al. Unveiling the Differences of Secretome of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells, and Human Umbilical Cord Perivascular Cells: A Proteomic Analysis. Stem Cells Dev. 2016;25(14):1073-1083. [109] OH SH, KIM HN, PARK HJ, et al. The Cleavage Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cell and Its Derived Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 on Extracellular α-Synuclein Aggregates in Parkinsonian Models. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(3):949-961. [110] WANG G, VAN DER WALT JM, MAYHEW G, et al. Variation in the miRNA-433 binding site of FGF20 confers risk for Parkinson disease by overexpression of alpha-synuclein. Am J Hum Genet. 2008;82(2):283-289. [111] THOME AD, HARMS AS, VOLPICELLI-DALEY LA, et al. microRNA-155 Regulates Alpha-Synuclein-Induced Inflammatory Responses in Models of Parkinson Disease. J Neurosci. 2016;36(8):2383-2390. [112] XIN H, KATAKOWSKI M, WANG F, et al. MicroRNA cluster miR-17-92 Cluster in Exosomes Enhance Neuroplasticity and Functional Recovery After Stroke in Rats. Stroke. 2017;48(3):747-753. [113] SARAIVA C, PAIVA J, SANTOS T, et al. MicroRNA-124 loaded nanoparticles enhance brain repair in Parkinson’s disease. J Control Release. 2016;235:291-305. [114] VILAÇA-FARIA H, SALGADO AJ, TEIXEIRA FG. Mesenchymal Stem Cells-derived Exosomes: A New Possible Therapeutic Strategy for Parkinson’s Disease? Cells. 2019;8(2):118. [115] KIM W, LEE Y, MCKENNA ND, et al. miR-126 contributes to Parkinson’s disease by dysregulating the insulin-like growth factor/phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling. Neurobiol Aging. 2014;35(7):1712-1721. [116] 张蕾,何建成.何建成教授从肝肾论治帕金森病[J].中华中医药学刊,2021, 39(2):23-25. [117] YANG J, GAO F, ZHANG Y, et al. Buyang Huanwu Decoction (BYHWD) Enhances Angiogenic Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cell by Upregulating VEGF Expression After Focal Cerebral Ischemia. J Mol Neurosci. 2015;56(4):898-906. |
| [1] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhou Qian, Zhang Qiang, Chen Qiu. Human salivary components and osteoporosis/osteopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [2] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [3] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [4] | Chen Shijian, Li Ge, Zhang Yu, Guan Yalun, Li Xuejiao, Liu Shuhua, Li Yongchao, Li Yunfeng, Gao Jinfeng, Wei Xiaoyue, Zhao Yuhong. Comparison and evaluation of MPTP-induced subacute and chronic models of Parkinson’s disease in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1247-1252. |
| [5] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [6] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [7] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [8] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [9] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [10] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [11] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [12] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [13] | Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| [14] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [15] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||