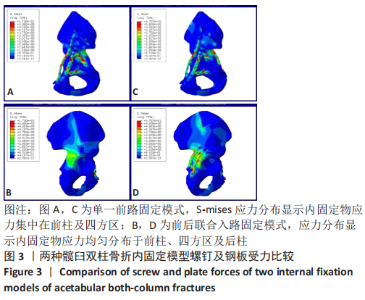
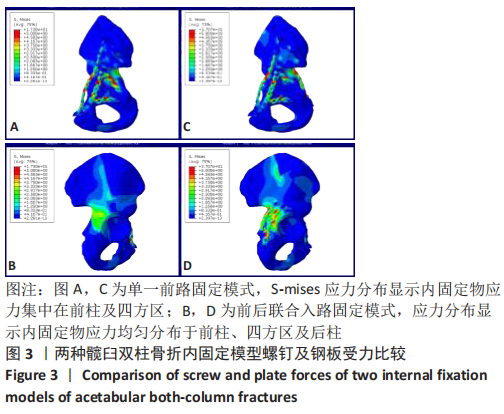
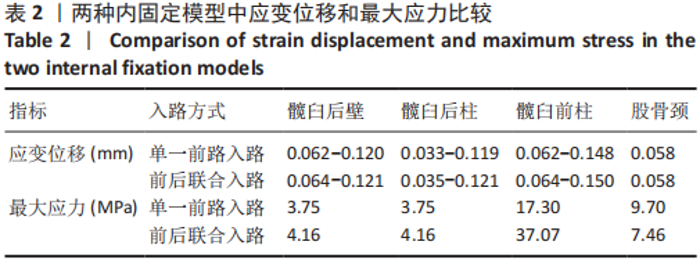
[1] BRIFFA N, PEARCE R, HILL AM, et al. Outcomes of acetabular fracture fixation with ten years’ follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Br Vol. 2011;93(2): 229-236.
[2] 张忠岩,祁同宁,穆怀昭,等.髋臼骨折固定3D打印技术辅助虚拟手术计划的疗效评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(15):2405-2409.
[3] 朱剑,孙俊英,叶峥,等.前后联合手术入路治疗累及双柱的髋臼骨折[J].苏州大学学报(医学版),2008,28(4):628-630.
[4] WANG P, ZHU X, XU P, et al. Modified ilioinguinal approach in combined surgical exposures for displaced acetabular fractures involving two columns. Springer Plus. 2016;5(1):1602.
[5] HARRIS AM, ALTHAUSEN P, KELLAM JF, et al. Simultaneous anterior and posterior approaches for complex acetabular fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22(7):494-497.
[6] SHARMA S, MATHUR H, ZINZUWADIA K, et al. Short-term follow-up of anterior and posterior both column fractures of acetabulum managed through both column plating. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2019;29(3):605-610.
[7] 樊仕才,刘涵,黄复铭.髋臼骨折手术入路选择的原则与复位固定技巧[J].中华骨科杂志,2021,41(1):58-66.
[8] 陈康,黄振飞,崔巍,等.高位髂腹股沟入路治疗累及四方区髋臼骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2014,34(7):723-729.
[9] KEEL MJB, ECKER TM, CULLMANN JL, et al. The Pararectus approach for anterior intrapelvic management of acetabular fractures: an anatomical study and clinical evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg British Vol. 2012;94(3):5.
[10] Rocca G , Spina M, Mazzi M. Anterior Combined Endopelvic (ACE) approach for the treatment of acetabular and pelvic ring fractures: a new proposal. Injury. 2014;45 Suppl 6:S9-S15.
[11] 吴海洋,邵启鹏,蔡贤华,等.新型动力化前路方形区钛板螺钉系统在不同置钉方法下固定髋臼骨折的有限元比较[J].创伤外科杂志,2021,23(1):10-14.
[12] 黄进成,刘曦明,蔡贤华,等.髋臼双柱骨折内固定生物力学稳定性的有限元分析[J].创伤外科杂志,2014,16(3):236-239.
[13] 吴海洋,蔡贤华,刘曦明,等.第二代动力化前路方形区钛板螺钉固定髋臼骨折有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(14):1297-1301.
[14] ANDERSON AE, PETERS CL, TUTTLE BD, et al. Subject-specific finite element model of the pelvis: development, validation and sensitivity studies. J Biomech Eng. 2005;127(3):364-373.
[15] SHIN JK, LIM BY, GOH TS, et al. Effect of the screw type (S2-alar-iliac and iliac), screw length, and screw head angle on the risk of screw and adjacent bone failures after a spinopelvic fixation technique: a finite element analysis. PLoS One. 2018;13(8):e0201801.
[16] 张馨元,丁晓红,段朋云.基于骨骼材料分布特征的髋关节有限元模型建立及其应力分析[J].北京生物医学工程,2020,39(5):462-469.
[17] 谢献进,王钢,童凯.骨盆内入路治疗髋臼后柱骨折的研究进展[J].临床与病理杂志,2020,40(4):1045-1050.
[18] 夏雄超,刘伟,林伟文,等.改良Stoppa入路切开复位内固定治疗Tile C型骨盆骨折合并髋臼双柱骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2019, 21(12):1069-1072.
[19] 张凤桐,冯学武,马建国,等.单一髂腹股沟入路弹性支撑固定后柱治疗复杂髋臼骨折的效果评估[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2018, 33(4):374-376.
[20] KELLY J, LADURNER A, RICKMAN M. Surgical management of acetabular fractures - a contemporary literature review. Injury. 2020;51(10):2267-2277.
[21] 陈开放,杨帆,郭晓东,等.髋臼四方区组合钢板治疗髋臼双柱骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(5):295-300.
[22] 苏达明,赵军华,胡伟,等.前路经腹直肌外侧小切口入路治疗髋臼骨折的临床疗效观察[J].骨科,2020,11(3):234-237.
[23] YANG Y, ZOU C, FANG Y. The Stoppa combined with iliac fossa approach for the treatment of both-column acetabular fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):588.PMID: 33287839.
[24] 杨晓东,夏广,樊仕才,等.单一腹直肌外侧切口治疗髋臼前后柱骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2015,35(4):335-340.
[25] PIERANNUNZII L, FISCHER F, TAGLIABUE L, et al. Acetabular both-column fractures:essentials of operative management. Injury. 2010; 41(11):1145-1149.
[26] 唐根林,陈琴,郭曙光,等.前后联合入路改良治疗髋臼双柱骨折42例分析[J].中外医疗,2011,14(14):104-106.
[27] ARCHDEACON MT. Comparison of the ilioinguinal approach and the anterior intrapelvic approaches for open reduction and internal fixation of the acetabulum. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29 Suppl 2:S6-S9.
[28] ANDRÉS-PEIRÓ JV, TEIXIDOR-SERRA J, TOMÁS-HERNÁNDEZ J, et al. Retrospective study of 16 acetabular fractures with involvement of the quadrilateral plate treated with an anterior intrapelvic modified Rives-Stoppa approach. Rev Esp Cir Ortop Traumatol. 2019;63(6):416-423.
[29] 杨晓东,刘涵,樊仕才,等.髂坐钢板经腹直肌外侧入路治疗涉及方形区的髋臼骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(20):1836-1840.
[30] 杨明辉.要对老年髋臼骨折进行更深入的探索[J].骨科临床与研究杂志,2020,5(6):321-323.
[31] 弓志国,吴新宝.老年髋臼骨折手术治疗的研究进展[J].中华创伤杂志,2020,36(11):983-989.
(责任编辑:WJ,ZN,ZH)
|