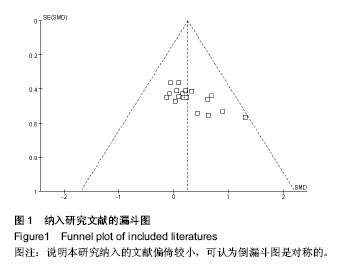
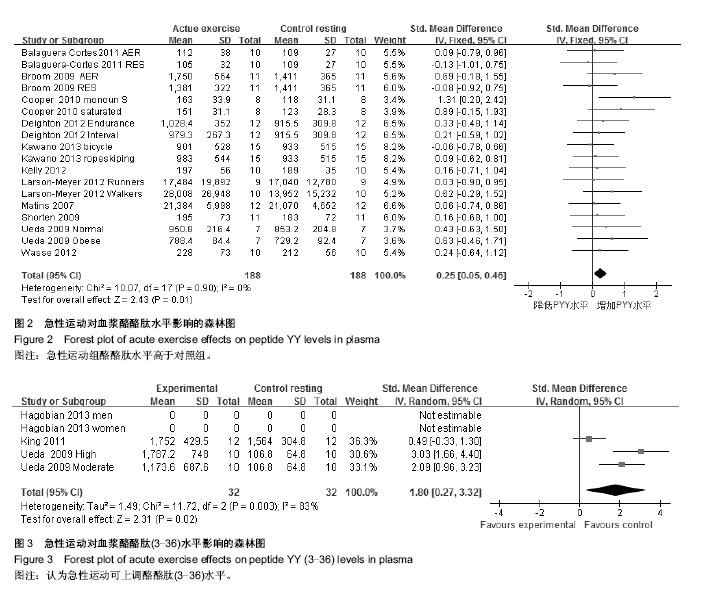
| [1] Ballantyne GH. Peptide YY(1-36) and peptide YY(3-36): Part I. Distribution, release and actions. Obes Surg.2006;16(5):651-658.
[2] King NA, Blundell JE. High-fat foods overcome the energy expenditure induced by high-intensity cycling or running. Eur J Clin Nutr.1995;49(2):114-123.
[3] Schubert MM, Sabapathy S, Leveritt M, et al. Acute exercise and hormones related to appetite regulation: a meta-analysis. Sports Med.2014;44(3):387-403.
[4] Balaguera-Cortes L, Wallman KE, Fairchild TJ, et al.Energy intake and appetite-related hormones following acute aerobic and resistance exercise. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab.2011;36(6): 958-966.
[5] Broom DR, Batterham RL, King JA, et al. Influence of resistance and aerobic exercise on hunger, circulating levels of acylated ghrelin, and peptide YY in healthy males. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.2009;296(1):R29-R35.
[6] Cooper JA, Watras AC, Paton CM, et al.Impact of exercise and dietary fatty acid composition from a high-fat diet on markers of hunger and satiety. Appetite.2011;56(1):171-178.
[7] Deighton K, Barry R, Connon CE, et al. Appetite, gut hormone and energy intake responses to low volume sprint interval and traditional endurance exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol.2013; 113(5):1147-1156.
[8] Kawano H, Mineta M, Asaka M, et al. Effects of different modes of exercise on appetite and appetite-regulating hormones. Appetite.2013;66:26-33.
[9] Kelly PJ, Guelfi KJ, Wallman KE, et al. Mild dehydration does not reduce postexercise appetite or energy intake. Med Sci Sports Exerc.2012;44(3):516-524.
[10] Larson-Meyer DE, Palm S, Bansal A, et al.Influence of running and walking on hormonal regulators of appetite in women. J Obes.2012;2012:730409.
[11] Martins C, Morgan LM, Bloom SR, et al. Effects of exercise on gut peptides, energy intake and appetite. J Endocrinol.2007; 193(2):251-258.
[12] Shorten AL, Wallman KE, Guelfi KJ. Acute effect of environmental temperature during exercise on subsequent energy intake in active men.Am J Clin Nutr.2009;90(5): 1215-1221.
[13] Ueda SY, Yoshikawa T, Katsura Y, et al.Changes in gut hormone levels and negative energy balance during aerobic exercise in obese young males.J Endocrinol.2009;201(1): 151-159.
[14] Wasse LK, Sunderland C, King JA, et al. Influence of rest and exercise at a simulated altitude of 4,000 m on appetite, energy intake, and plasma concentrations of acylated ghrelin and peptide YY. J Appl Physiol (1985).2012;112(4):552-559.
[15] Hagobian TA, Yamashiro M, Hinkel-Lipsker J, et al. Effects of acute exercise on appetite hormones and ad libitum energy intake in men and women. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab.2013; 38(1): 66-72.
[16] King JA, Wasse LK, Ewens J, et al. Differential acylated ghrelin, peptide YY3-36, appetite, and food intake responses to equivalent energy deficits created by exercise and food restriction. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2011;96(4):1114-1121.
[17] Ueda SY, Yoshikawa T, Katsura Y, et al. Comparable effects of moderate intensity exercise on changes in anorectic gut hormone levels and energy intake to high intensity exercise. J Endocrinol.2009;203(3):357-364.
[18] le Roux CW, Batterham RL, Aylwin SJ, et al. Attenuated peptide YY release in obese subjects is associated with reduced satiety. Endocrinology.2006;147(1):3-8.
[19] Korner J, Bessler M, Cirilo LJ, et al. Effects of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery on fasting and postprandial concentrations of plasma ghrelin, peptide YY, and insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2005;90(1):359-365.
[20] Batterham RL, Cohen MA, Ellis SM, et al. Inhibition of food intake in obese subjects by peptide YY3-36. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(10): 941-948.
[21] Roth CL, Enriori PJ, Harz K, et al.Peptide YY is a regulator of energy homeostasis in obese children before and after weight loss. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90(12): 6386-6391.
[22] le Roux CW, Batterham RL, Aylwin SJ, et al. Attenuated peptide YY release in obese subjects is associated with reduced satiety. Endocrinology.2006;147(1): 3-8.
[23] Karra E, Batterham RL. The role of gut hormones in the regulation of body weight and energy homeostasis. Mol Cell Endocrinol.2010;316(2): 120-128.
[24] Gibbons C, Caudwell P, Finlayson G, et al. Comparison of postprandial profiles of ghrelin, active GLP-1, and total PYY to meals varying in fat and carbohydrate and their association with hunger and the phases of satiety. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98(5): E847-E855. |