| [1] 刘继平,程玥.中药促进成骨细胞功能和ALP活性影响研究的意义[J].陕西中医学院学报,2010,33(1):7-8.
[2] 邓敦,曹成福,纪斌,等.复方中药治疗原发性骨质疏松的实验研究进展[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2007,15(8):68-69.
[3] 秧荣昆,郭磊磊.骨碎补提取液对成骨细胞增殖的影响[J].贵阳中医学院学报,2006,28(4):61-62.
[4] 柴天川,刘丽芬.汤剂与单味中药提取物颗粒混合液之比较[J].河北中医,2006,28(3):199-200.
[5] 洪曼杰,卢丽,王晓东,等.中药复方护骨胶囊治疗原发性骨质疏松症的临床研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2008,14(12):891-895.
[6] 郭杨,马勇.中医药治疗骨质疏松症的常用处方分析[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2010,16(7):188-191.
[7] 孙兰英,李秀萍,杨永胜,等.中药复方治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的临床研究[J].中国中医药咨讯,2012,4(2):28-30.
[8] 宋鹏,姚娟,马慧萍,等.脱水淫羊藿素与山柰素对体外培养成骨细胞成熟矿化影响的比较研究[J].药学学报,2012,47(7): 890-896.
[9] 唐泉,孙元明.经典Wnt信号通路对成骨细胞增殖和分化的影响[J].天津医药,2012,40(2):187-189.
[10] 张宁,李铁男,任燕冬,等.基于方/证/病本质联系的方剂药效物质基础及作用机理研究构想[J].时珍国医国药,2010,21(5): 1284-1285.
[11] Scutt A,Bertram P,Bräutigam M.The role of glucocorticoids and prostaglandin E2 in the recruitment of bone marrow mesenchymal cells to the osteoblastic lineage: positive and negative effects.Calcif Tissue Int. 1996;59(3):154-162.
[12] Petersen DN,Tkalcevic GT,Mansolf AL,et al.Identification of osteoblast/osteocyte factor 45 (OF45), a bone-specific cDNA encoding an RGD-containing protein that is highly expressed in osteoblasts and osteocytes. J Biol Chem.2000;275(46): 172-180.
[13] 张声鹏,施旭光,桂蜀华,等.关于中药血清药理学中血清供体动物是否造模的思考[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2001,21(5):388-389.
[14] 胡冰,傅炳国,沈霖,等.复方中药含药血清对大鼠成骨细胞增殖及矿化功能的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2003,11(4):8-10.
[15] Mosmann T.Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays.J Immunol Methods.1983;65(1-2):55-63.
[16] 中国知网.中国学术期刊总库[DB/OL].2013-5-15. https://www.cnki.net
[17] 张荣华,舒晓春.中药复方补肾活血液对成骨细胞影响的实验研究[J].中国病理生理杂志,2003,19(6):769-772.
[18] 姚新苗,陈于东,方芳.益骨汤含药血清对成骨细胞增殖和ALP影响的实验研究[J].浙江中医药大学学报,2007,31(2):158-159.
[19] 黄洁,程云英.大鼠成骨细胞的体外培养和生物学特性的研究[J].南京铁道医学院学报,2000,19(2):88-90.
[20] 龚泰芳,夏仁云,段永芳,等.鼠骨组织成骨细胞的离体培养和生长特性[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2002,9(5):470-472.
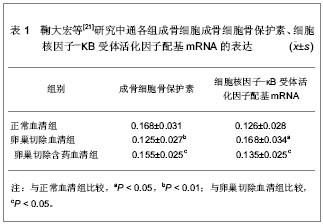
[21] 鞠大宏,刘梅洁,赵宏艳,等.左归丸含药血清对成骨细胞OPG、RANKL mRNA表达的影响[J].北京中医药大学学报,2008, 31(5):312-315.
[22] 孙晖,张宁,李力静,等.六味地黄丸主要血中移行成分对培养大鼠成骨细胞促增殖作用的研究[J].中国中药杂志,2008,33(17): 2161-2164.
[23] 李根林,尹君,杜志谦.研究补肾方药对去势大鼠骨质疏松模型骨生物力学性能的影响应注意的几个问题[J].中医正骨,2009, 21(7): 27-29.
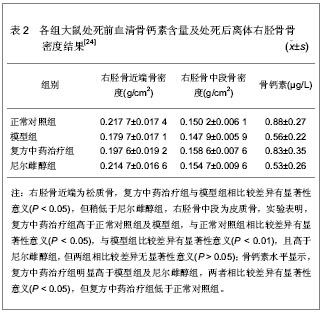
[24] 熊学华,刘庆思,余克强.中药骨康对去势大鼠血清骨钙素及离体骨密度的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2002,10(2):14-16.
[25] 贾经汉,邱新建,陈志坚.骨质疏松动物模型的研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2007,22(8):765-768.
[26] Kalu DN.The ovariectomized rat model of postmenopausal bone loss.Bone Miner.1991;15(3):175-191.
[27] Gilles JA,Carnes DL,Dallas MR,et al.Oral bone loss is increased in ovariectomized rats.J Endod.1997;23(7): 419-422.
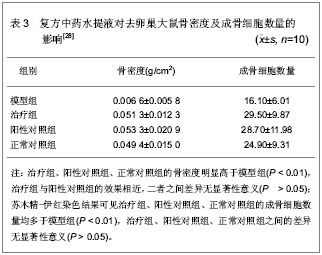
[28] 杨林,姚新苗,黄竞,等.益骨汤对去卵巢大鼠骨密度骨钙素及成骨细胞增殖的影响[J].辽宁中医杂志,2006,33(10):1356-1358.
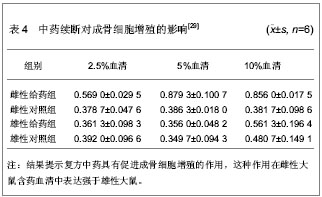
[29] 王威,何永志,史红,等.不同性别大鼠中药含药血清对成骨细胞增殖的影响[J].天津中医药,2009,26(1):9-11.
[30] 周丽珍,王淑丽,秦腊梅,等.复方仙贞汤对去卵巢大鼠模型骨密度和骨形态的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2006,12(5):492-495.
[31] 胡光亮,杜靖远,王洪,等.补肾密骨液对骨代谢影响的体外实验研究[J].中国骨伤,2000,13(2):83-85.
[32] 张丹,马砚涛,邢玉瑞.近十年来中医药治疗骨质疏松症临床研究进展[J].陕西中医学院学报,2009,32(6):89-91. |