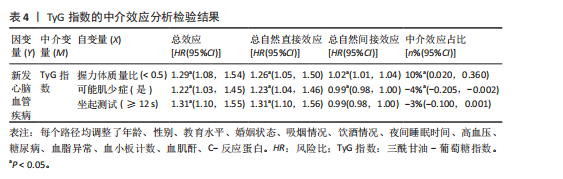
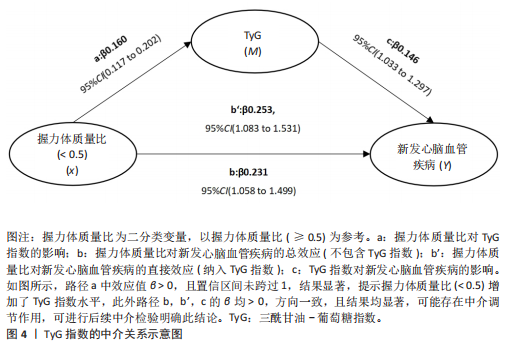
[1] ROTH GA, MENSAH GA, JOHNSON CO, et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990-2019: Update From the GBD 2019 Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76(25):2982-3021.
[2] VIRANI SS, ALONSO A, APARICIO HJ, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2021 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021;143(8): e254-e743.
[3] DISEASES NCFC, HEALTH TWCOTROC, CHINA DI. 中国心血管健康与疾病报告2023概要[J]. 中国循环杂志,2024,39(7):625-660.
[4] LI G, LU Y, SHAO L, et al. Handgrip strength is associated with risks of new-onset stroke and heart disease: results from 3 prospective cohorts. BMC Geriatr. 2023;23(1):268.
[5] GAO K, CAO LF, MA WZ, et al. Association between sarcopenia and cardiovascular disease among middle-aged and older adults: Findings from the China health and retirement longitudinal study. EClinicalMedicine. 2022;44:101264.
[6] DAMLUJI AA, ALFARAIDHY M, ALHAJRI N, et al. Sarcopenia and Cardiovascular Diseases. Circulation. 2023;147(20):1534-1553.
[7] 王茜婷, 刘梅林. 老年冠心病患者合并肌肉减少症的相关性研究 [J]. 临床心血管病杂志,2018,34(12):1182-1186.
[8] ZAMBONI M, MAZZALI G, FANTIN F, et al. Sarcopenic obesity: a new category of obesity in the elderly. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2008;18(5):388-395.
[9] HAIDAR S, MAHBOUB N, PAPANDREOU D, et al. Triglyceride and Glucose Index as an Optimal Predictor of Metabolic Syndrome in Lebanese Adults. Nutrients. 2024;16(21): 3718.
[10] 王馨, 周好奇, 胡真, 等. 职业人群中甘油三脂-葡萄糖指数与动脉粥样硬化的关系[J]. 中国心血管病研究,2024,22(11): 1007-1012.
[11] SAWAF B, SWED S, ALIBRAHIM H, et al. Triglyceride-Glucose Index as Predictor for Hypertension, CHD and STROKE Risk among Non-Diabetic Patients: A NHANES Cross-Sectional Study 2001-2020. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2024;14(3):1152-1166.
[12] SÁNCHEZ-ÍÑIGO L, NAVARRO-GONZÁLEZ D, FERNÁNDEZ-MONTERO A, et al. The TyG index may predict the development of cardiovascular events. Eur J Clin Invest. 2016;46(2):189-197.
[13] FAHED G, AOUN L, BOU ZERDAN M, et al. Metabolic Syndrome: Updates on Pathophysiology and Management in 2021. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(2):786.
[14] SOUSA AC, ZUNZUNEGUI MV, LI A, et al. Association between C-reactive protein and physical performance in older populations: results from the International Mobility in Aging Study (IMIAS). Age Ageing. 2016; 45(2):274-280.
[15] FERRUCCI L, PENNINX BW, VOLPATO S, et al. Change in muscle strength explains accelerated decline of physical function in older women with high interleukin-6 serum levels. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002;50(12):1947-1954.
[16] YOO JI, KIM MJ, NA JB, et al. Relationship between endothelial function and skeletal muscle strength in community dwelling elderly women. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2018;9(6):1034-1041.
[17] STUMP CS, HENRIKSEN EJ, WEI Y, et al. The metabolic syndrome: role of skeletal muscle metabolism. Ann Med. 2006;38(6): 389-402.
[18] KOSMAS CE, BOUSVAROU MD, KOSTARA CE, et al. Insulin resistance and cardiovascular disease. J Int Med Res. 2023;51(3): 3000605231164548.
[19] HILL MA, YANG Y, ZHANG L, et al. Insulin resistance, cardiovascular stiffening and cardiovascular disease. Metabolism. 2021; 119:154766.
[20] HOLTEN MK, ZACHO M, GASTER M, et al. Strength training increases insulin-mediated glucose uptake, GLUT4 content, and insulin signaling in skeletal muscle in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2004;53(2):294-305.
[21] ZHAO Y, HU Y, SMITH JP, et al. Cohort profile: the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS). Int J Epidemiol. 2014;43(1):61-68.
[22] MACKINNON DP, FAIRCHILD AJ, FRITZ MS. Mediation analysis. Annu Rev Psychol. 2007;58:593-614.
[23] SHI B, CHOIRAT C, COULL BA, et al. CMAverse: A Suite of Functions for Reproducible Causal Mediation Analyses. Epidemiology. 2021;32(5):e20-e22.
[24] LIU Z, SONG C, SUO C, et al. Alcohol consumption and hepatocellular carcinoma: novel insights from a prospective cohort study and nonlinear Mendelian randomization analysis. BMC Med. 2022; 20(1):413.
[25] CHEN LK, WOO J, ASSANTACHAI P, et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2020; 21(3):300-307.e302.
[26] LEE J, HONG YP, SHIN HJ, et al. Associations of Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity With Metabolic Syndrome Considering Both Muscle Mass and Muscle Strength. J Prev Med Public Health. 2016;49(1):35-44.
[27] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, SAYER AA. Sarcopenia. Lancet. 2019;393(10191): 2636-2646.
[28] HAMASAKI H, KAWASHIMA Y, ADACHI H, et al. Associations between lower extremity muscle mass and metabolic parameters related to obesity in Japanese obese patients with type 2 diabetes. PeerJ. 2015; 3:e942.
[29] KARLSEN T, NAUMAN J, DALEN H, et al. The Combined Association of Skeletal Muscle Strength and Physical Activity on Mortality in Older Women: The HUNT2 Study. Mayo Clin Proc. 2017;92(5):710-718.
[30] ZHANG K, LI X, GUO Q, et al. Lower extremity function and cardiovascular disease risk in hemodialysis patients: A multicenter cross-sectional study. Physiol Rep. 2024;12(16):e70014.
[31] FENG S, WANG J, YIN C, et al. The association between lower extremity function and cardiovascular diseases risk in older Chinese adults: Longitudinal evidence from a nationwide cohort. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2024;124:105463.
[32] CAMPO G, MAIETTI E, TONET E, et al. The Assessment of Scales of Frailty and Physical Performance Improves Prediction of Major Adverse Cardiac Events in Older Adults with Acute Coronary Syndrome. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2020;75(6):1113-1119.
[33] KUENZE C, PIETROSIMONE B, CURRIE KD, et al. Joint Injury, Osteoarthritis, and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors in Former National Football League Athletes: An NFL-LONG Study. J Athl Train. 2023;58(6): 528-535.
[34] 殷明越, 刘骞, 许雄壮, 等. 久坐间断对成年人血管功能的急性影响与调节因素:荟萃分析 [J]. 中国组织工程研究,2025, 29(17):3684-3696.
[35] ALCAZAR J, LOSA-REYNA J, RODRIGUEZ-LOPEZ C, et al. The sit-to-stand muscle power test: An easy, inexpensive and portable procedure to assess muscle power in older people. Exp Gerontol. 2018;112: 38-43.
[36] FACCIORUSSO S, GUANZIROLI E, BRAMBILLA C, et al. Muscle synergies in upper limb stroke rehabilitation: a scoping review. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2024;60(5):767-792.
[37] BARZEGAR N, TOHIDI M, HASHEMINIA M, et al. The impact of triglyceride-glucose index on incident cardiovascular events during 16 years of follow-up: Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020;19(1):155.
[38] ARAÚJO SP, JUVANHOL LL, BRESSAN J, et al. Triglyceride glucose index: A new biomarker in predicting cardiovascular risk. Prev Med Rep. 2022;29:101941.
[39] FRANKLIN BA, EIJSVOGELS TMH, PANDEY A, et al. Physical activity, cardiorespiratory fitness, and cardiovascular health: A clinical practice statement of the American Society for Preventive Cardiology Part II: Physical activity, cardiorespiratory fitness, minimum and goal intensities for exercise training, prescriptive methods, and special patient populations. Am J Prev Cardiol. 2022;12: 100425. |