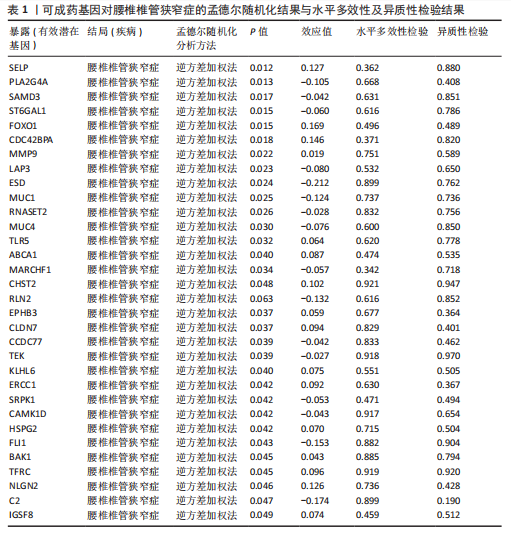
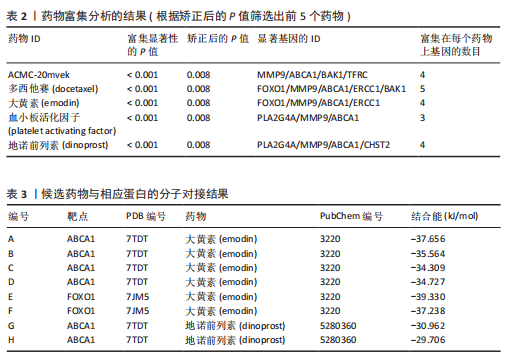
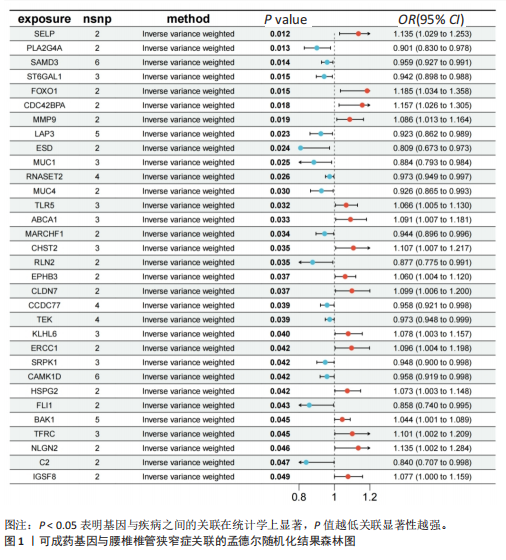
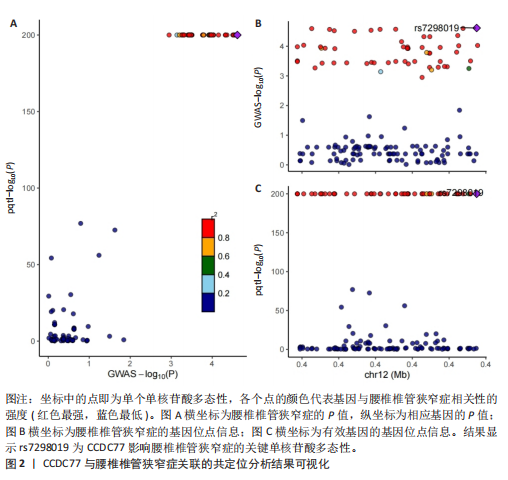
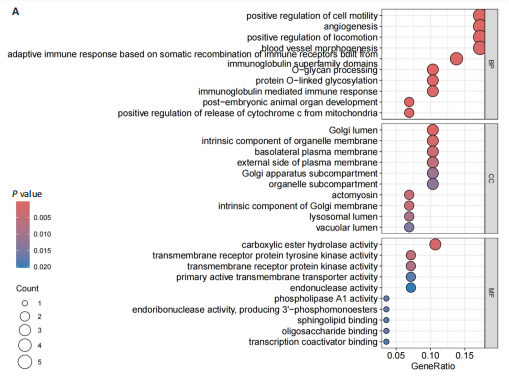
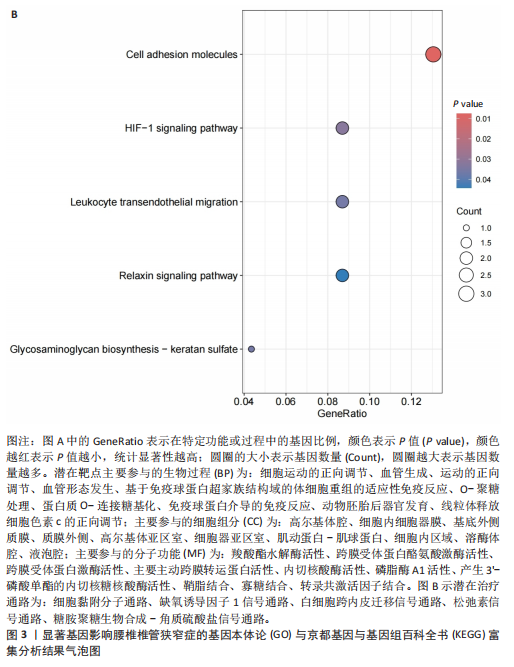
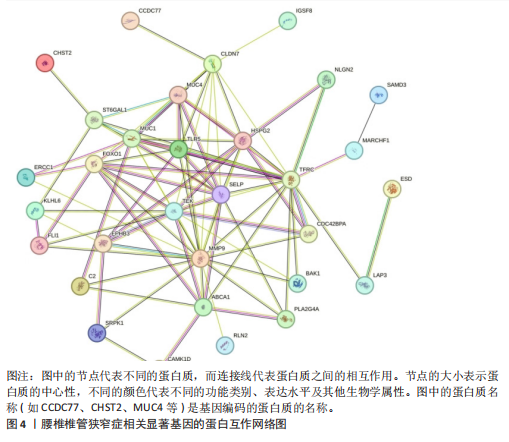
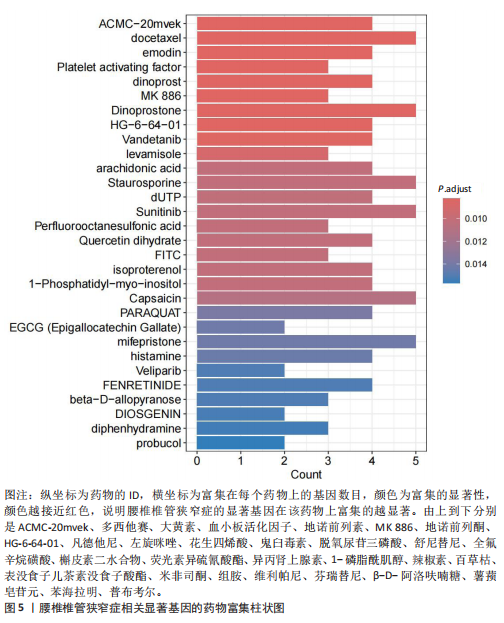
[1] KATZ JN, ZIMMERMAN ZE, MASS H, et al. Diagnosis and Management of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Review. JAMA. 2022;327(17):1688-1699.
[2] 库提鲁克·守克尔,艾克拜尔江·艾赛提,沙拉依丁·艾尔西丁,等.腰椎椎管狭窄症治疗现状的文献计量学研究[J].脊柱外科杂志,2024,22(3):189-194.
[3] ARABMOTLAGH M, SELLEI RM, VINAS-RIOS JM, et al. Klassifikation und Diagnostik der lumbalen Spinalkanalstenose [Classification and diagnosis of lumbar spinal stenosis]. Orthopade. 2019;48(10):816-823.
[4] KIM M, CHO S, NOH Y, et al. Changes in pain scores and walking distance after epidural steroid injection in patients with lumbar central spinal stenosis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(24):e29302.
[5] YANG F, WANG Y, MA Y, et al. Single-segment central lumbar spinal stenosis: Correlation with lumbar X-ray measurements. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2021;34(4):581-587.
[6] SCHROEDER GD, KURD MF, VACCARO AR. Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: How Is It Classified? J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2016;24(12):843-852.
[7] 张晗,孙超,刘新晖.腰椎黄韧带纤维化的研究进展[J].临床骨科杂志,2022, 25(3):450-453.
[8] LEE JY, CHOI HY, PARK CS, et al. Inhibition of COX-2 alleviates lumbar spinal stenosis-induced chronic mechanical allodynia in rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;75:105738.
[9] ZHANG G, ZHANG W, HOU Y, et al. Detection of miR 29a in plasma of patients with lumbar spinal stenosis and the clinical significance. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(1):223-229.
[10] WAWROSE RA, OYEKAN AA, TANG YM, et al. MicroRNA-29a: a novel target for non-operative management of symptomatic lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J. 2024; 33(3):892-899.
[11] MA Q. Pharmacological Inhibition of the NLRP3 Inflammasome: Structure, Molecular Activation, and Inhibitor-NLRP3 Interaction. Pharmacol Rev. 2023;75(3):487-520.
[12] NABA A. Mechanisms of assembly and remodelling of the extracellular matrix. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024;25(11):865-885.
[13] ZHANG J, ZHAO H. eQTL studies: from bulk tissues to single cells. J Genet Genomics. 2023;50(12):925-933.
[14] 1000 Genomes Project Consortium; AUTON A, BROOKS LD, DURBIN RM, et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature. 2015;526(7571):68-74.
[15] FINAN C, GAULTON A, KRUGER FA, et al. The druggable genome and support for target identification and validation in drug development. Sci Transl Med. 2017;9(383): eaag1166.
[16] TIN A, MARTEN J, HALPERIN KUHNS VL. Target genes, variants, tissues and transcriptional pathways influencing human serum urate levels. Nat Genet. 2019;51(10): 1459-1474.
[17] GIAMBARTOLOMEI C, VUKCEVIC D, SCHADT EE, et al. Bayesian test for colocalisation between pairs of genetic association studies using summary statistics. PLoS Genet. 2014; 10(5):e1004383.
[18] LIU Z, YAN W, LIU S, et al. Regulatory network and targeted interventions for CCDC family in tumor pathogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2023;565:216225.
[19] VIOREL VI, PASTORELLO Y, BAJWA N, et al. p38-MAPK and CDK5, signaling pathways in neuroinflammation: a potential therapeutic intervention in Alzheimer’s disease? Neural Regen Res. 2024;19(8):1649-1650.
[20] 郭云山,郝定均,王晓东,等.STIM1调控细胞运动促进骨肉瘤转移的研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2019,19(24):4601-4606.
[21] 戴祝,彭嘉斌,廖瑛,等.成年关节软骨碎块化后MT1-MMP表达与软骨细胞迁移的关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2018, 22(28):4457-4462.
[22] LA MENDOLA D, TRINCAVELLI ML, MARTINI C. Angiogenesis in Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(18):10962.
[23] 陈耀鑫,黎松波,方冠军,等.黄韧带中成纤维细胞生长因子1、血管内皮生长因子表达与腰椎管狭窄患者腰椎减压术后再狭窄的关系[J].实用医学杂志,2023, 39(18):2289-2293.
[24] LIN W, XU L, ZWINGENBERGER S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells homing to improve bone healing. J Orthop Translat. 2017; 9:19-27.
[25] HOSEINZADEH A, ESMAEILI SA, SAHEBI R, et al. Fate and long-lasting therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stromal/stem-like cells: mechanistic insights. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025;16(1):33.
[26] FABREGAT I, HERRERA B, SÁNCHEZ A. Editorial Special Issue TGF-beta/BMP Signaling Pathway. Cells. 2020;9(11):2363.
[27] WATTS E, WILLISON J, ARIENTI S, et al. Differential roles for the oxygen sensing enzymes PHD1 and PHD3 in the regulation of neutrophil metabolism and function. Wellcome Open Res. 2024;8:569.
[28] COSTA RO, MARTINS H, MARTINS LF, et al. Synaptogenesis Stimulates a Proteasome-Mediated Ribosome Reduction in Axons. Cell Rep. 2019;28(4):864-876.e6.
[29] ZHOU R, CHEN J, TANG Y, et al. Multi-omics uncovers immune-modulatory molecules in plasma contributing to resistance exercise-ameliorated locomotor disability after incomplete spinal cord injury. Genome Med. 2025;17(1):10.
[30] MALIK KN, GIBERSON C, BALLARD M, et al. Pain Management Interventions in Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Literature Review. Cureus. 2023;15(8):e44116.
[31] SHI Y, GILKES DM. HIF-1 and HIF-2 in cancer: structure, regulation, and therapeutic prospects. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025;82(1):44.
[32] 马瑗锾,石慧娟,温兰钰,等.组织化培养上调HIF-1α信号通路促进移植的间充质干细胞在脊髓损伤区存活的机制研究[C]//中国解剖学会.中国解剖学会2021年年会论文文摘汇编.中山大学中山医学院组织胚胎学教研室, 2021:1.
[33] FANG J, CHEN Z, LAI X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived HIF-1α-overexpressed extracellular vesicles ameliorate hypoxia-induced pancreatic β cell apoptosis and senescence through activating YTHDF1-mediated protective autophagy. Bioorg Chem. 2022;129:106194.
[34] SCHIMMEL L, HEEMSKERK N, VAN BUUL JD. Leukocyte transendothelial migration: A local affair. Small GTPases. 2017;8(1):1-15.
[35] DING H, LI A, SUN C, et al. Quantitative iTRAQ proteomics reveal the proteome profiles of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells after cocultures with Schwann cells in vitro. Ann Transl Med. 2022;10(18):962.
[36] 吴丛宇,周悦,上官璐茜,等.大黄素的药理作用机制研究进展[J].中国药科大学学报,2023,54(5):634-643.
[37] SAUNDERS IT, MIR H, KAPUR N, et al. Emodin inhibits colon cancer by altering BCL-2 family proteins and cell survival pathways. Cancer Cell Int. 2019;19:98.
[38] LI M, JIN S, CAO Y, et al. Emodin regulates cell cycle of non-small lung cancer (NSCLC) cells through hyaluronan synthase 2 (HA2)-HA-CD44/receptor for hyaluronic acid-mediated motility (RHAMM) interaction-dependent signaling pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21(1):19.
[39] 涂平华.芦荟大黄素介导的光动力诱导骨肉瘤MG63细胞自噬的研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2015.
[40] 刘琳.大黄素对结肠癌细胞凋亡相关分子Caspase-3的作用[J].中国医药导刊,2013, 15(9):1532-1533.
[41] 樊向文,张勇,席量,等.大黄素对人乳腺癌细胞MCF-7的促凋亡作用及其与JNK信号通路关系[J].中国肿瘤外科杂志, 2015,7(6):346-350+355.
[42] MCDONALD SJ, VANDERVEEN BN, VELAZQUEZ KT, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Emodin for Gastrointestinal Cancers. Integr Cancer Ther. 2022;21: 15347354211067469.
[43] ZHANG F, CUI D, WANG Z, et al. NOX4 Regulates NLRP3 by Inhibiting the Ubiquitination of LRRC8A to Promote Ferroptosis in Nucleus Pulposus Cells. Inflammation. 2025. doi: 10.1007/s10753-025-02253-0.
[44] 曾锦明,范成龙,邓姣,等.大黄素抑制背根神经节压迫小鼠模型STAT3、VEGFA、p-ERK蛋白表达及其镇痛作用研究[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2024, 44(9):1583-1591.
[45] 曾欢欢,黄英如,李子健,等.大黄素对大鼠急性脊髓损伤后继发脊髓水肿的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践,2018, 24(4):378-384.
[46] GAHBAUER S, DELEON C, BRAZ JM, et al. Docking for EP4R antagonists active against inflammatory pain. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):8067.
[47] HONG JY, KIM H, LEE J, et al. Epidural Injection Method for Long-Term Pain Management in Rats with Spinal Stenosis. Biomedicines. 2023;11(5):1390.
[48] COHEN SP, BICKET MC, JAMISON D, et al. Epidural steroids: a comprehensive, evidence-based review. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2013;38(3):175-200.
[49] 周若彤,庞倩倩,夏维波.前列腺素E2在骨形成中的作用机制[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2024,17(3):295-302.
[50] TAKASHIMA H, TAKEBAYASHI T, YOSHIMOTO M, et al. The Difference in Gender Affects the Pathogenesis of Ligamentum Flavum Hypertrophy. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2018; 2(4):263-269. |