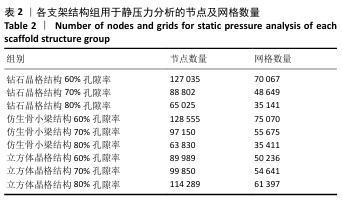
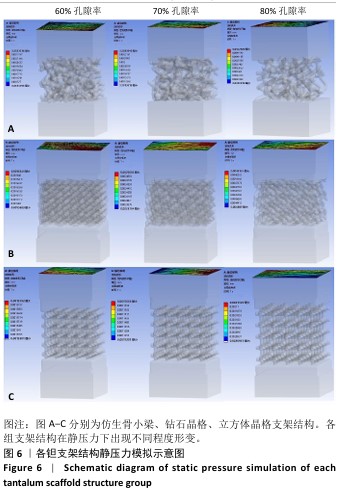
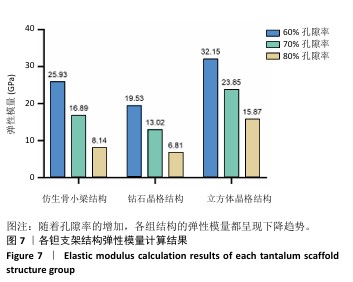
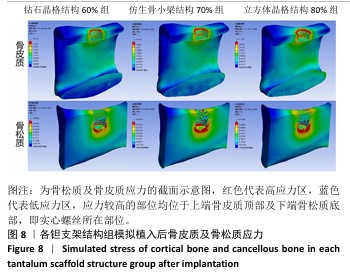
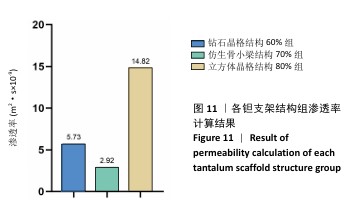
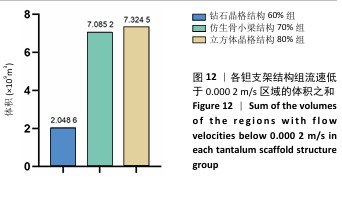
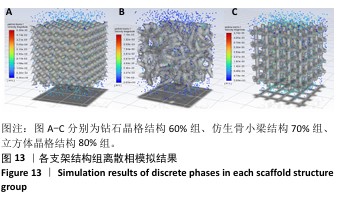
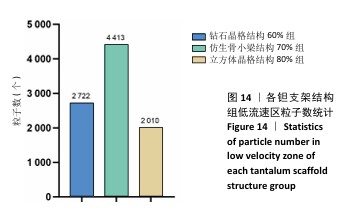
[1] 田敏.牙列缺损种植固定修复体种植体周围病的影响因素研究[D].西安:第四军医大学,2016.
[2] MEISCHEL M, HORMANN D, DRAXLER J, et al. Bone-implant degradation and mechanical response of bone surrounding Mg-alloy implants. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017;71:307-313.
[3] AHN TK, LEE DH, KIM TS, et al. Modification of Titanium Implant and Titanium Dioxide for Bone Tissue Engineering. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1077:355-368.
[4] 单验博,乔波,杨烁,等.口腔种植体新材料的研究进展[J].解放军医学院学报,2023,44(1):74-78,85.
[5] 宋凯乐.面向即刻种植的根形种植体功能性重建研究[D].济南:山东大学,2021.
[6] WANG X, XU S, ZHOU S, et al. Topological design and additive manufacturing of porous metals for bone scaffolds and orthopaedic implants: A review. Biomaterials. 2016;83:127-141.
[7] 黄伟.面向性能调控的多孔空间结构骨组织工程支架设计[D].大连:大连交通大学,2021.
[8] LIANG D, ZHONG C, JIANG F, et al. Fabrication of Porous Tantalum with Low Elastic Modulus and Tunable Pore Size for Bone Repair. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(3):1720-1728.
[9] KOVÁCS ÁÉ, CSERNÁTONY Z, CSÁMER L, et al. Comparative Analysis of Bone Ingrowth in 3D-Printed Titanium Lattice Structures with Different Patterns. Materials (Basel). 2023;16(10):3861.
[10] DENG F, LIU L, LI Z, et al. 3D printed Ti6Al4V bone scaffolds with different pore structure effects on bone ingrowth. J Biol Eng. 2021; 15(1):4.
[11] CHEN H, LIU Y, WANG C, et al. Design and properties of biomimetic irregular scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Comput Biol Med. 2021;130:104241.
[12] 廖波.胫骨填充多孔钛合金支架仿生设计及服役和骨再生行为研究[D].成都:西南交通大学,2022.
[13] BENCHARIT S, BYRD WC, ALTARAWNEH S, et al. Development and Applications of Porous Tantalum Trabecular Metal‐Enhanced Titanium Dental Implants. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2013;16(6):817-826.
[14] MA R, LIU Q, ZHOU L, et al. High porosity 3D printed titanium mesh allows better bone regeneration. BMC Oral Health. 2023;23(1):6.
[15] 徐伟.基于SLM梯度多孔钛口腔种植体结构设计及应用基础研究[D].北京:北京科技大学,2021.
[16] WANG X, NING B, PEI X. Tantalum and its derivatives in orthopedic and dental implants: Osteogenesis and antibacterial properties. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021;208:112055.
[17] LU MM, WU PS, GUO XJ, et al. Osteoinductive effects of tantalum and titanium on bone mesenchymal stromal cells and bone formation in ovariectomized rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(21): 7087-7104.
[18] DOMMETI VK, ROY S, PRAMANIK S, et al. Design and Development of Tantalum and Strontium Ion Doped Hydroxyapatite Composite Coating on Titanium Substrate: Structural and Human Osteoblast-like Cell Viability Studies. Materials (Basel). 2023;16(4):1499.
[19] ZHU Y, GU Y, QIAO S, et al. Bacterial and mammalian cells adhesion to tantalum-decorated micro-/nano-structured titanium. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(3):871-878.
[20] GUO Y, XIE K, JIANG W, et al. In Vitro and in Vivo Study of 3D-Printed Porous Tantalum Scaffolds for Repairing Bone Defects. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019;5(2):1123-1133.
[21] 王铭.电子束增材制造钛合金组织与力学性能研究[D].淄博:山东理工大学,2019.
[22] JAFARI MS, BENDER B, COYLE C, et al. Do Tantalum and Titanium Cups Show Similar Results in Revision Hip Arthroplasty? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(2):459-465.
[23] ISOBE D, YANG Q. An integrated finite element analysis and virtual reality system for structural and indoor nonstructural components of buildings under seismic excitations. J Building Eng. 2024;98. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2024.111320.
[24] GIA NINH D, TRONG LONG N, VAN VANG T, et al. A new study for aeroplane wing shapes made of boron nitride nanotubes-reinforced aluminium, Part I: review, dynamical analyses and simulation. Compos Struct. 2023;303. doi:10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.116239.
[25] MESLIER QA,SHEFELBINE SJ. Using Finite Element Modeling in Bone Mechanoadaptation. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2023;21(2):105-116.
[26] 彭琳晶,干耀恺,姚怡飞.多孔钽植入物在骨缺损中的应用进展[J].材料工程,2022,50(11):1-13.
[27] 吴先哲.骨科植入用多孔钽激光3D打印成形工艺及生物力学性能研究[D].北京:机械科学研究总院,2021.
[28] 王靖.基于SLM的Ti6Al4V梯度多孔牙种植体结构设计及力学特性研究[D].福州:福建工程学院, 2023.
[29] ZHANG J, ZHANG X, CHEN Y, et al. Novel Design and Finite Element Analysis of Diamond-like Porous Implants with Low Stiffness. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(22):6918.
[30] CHAKRABORTY A, DATTA P, MAJUMDER S, et al. Finite element and experimental analysis to select patient’s bone condition specific porous dental implant, fabricated using additive manufacturing. Comput Biol Med. 2020;124:103839.
[31] LIU Z, TAMADDON M, CHEN SM, et al. Determination of an Initial Stage of the Bone Tissue Ingrowth Into Titanium Matrix by Cell Adhesion Model. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:736063.
[32] 吴桐.TPMS多孔材料渗透率的评估模型研究[D].广州:华南理工大学,2021.
[33] 吴其右,崔博宇,夏炜,等.基于细胞黏附的不同微结构3D打印多孔生物支架流体力学有限元分析 [J].组织工程与重建外科,2024, 20(3):293-299.
[34] TIAN Y, TONG Z, LU F, et al. Tantalum composite gold coupled on 3D printed Ti6Al4V with a bone-like porous surface structures. Appl Surface Sci. 2025;689. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2025.162532.
[35] YU H, XU M, DUAN Q, et al. 3D-printed porous tantalum artificial bone scaffolds: fabrication, properties, and applications. Biomed Mater. 2024;19(4). doi:10.1088/1748-605X/ad46d2.
[36] 郭芳,黄硕,胡敏,等.3D打印表面多孔钛根形种植体的生物力学研究[J].医用生物力学,2021,36(1):85-91.
[37] CHASTAND V, QUAEGEBEUR P, MAIA W, et al. Comparative study of fatigue properties of Ti-6Al-4V specimens built by electron beam melting (EBM) and selective laser melting (SLM). Mater Charact. 2018;143:76-81.
[38] WANG X, ZHANG S, WANG Z Y, et al. 3D printing externally reinforced layers for high-speed railway brake discs: Adaptability of SLM processes for manufacturing gradient materials. Mater Today Commun. 2022;31. doi:org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.103778.
[39] PALMQUIST A, JOLIC M, HRYHA E, et al. Complex geometry and integrated macro-porosity: Clinical applications of electron beam melting to fabricate bespoke bone-anchored implants. Acta Biomater. 2023;156:125-145.
[40] HERRERA P, HERNANDEZ-NAVA E, THORNTON R, et al. Abrasive wear resistance of Ti-6AL-4V obtained by the conventional manufacturing process and by electron beam melting (EBM). Wear. 2023;524-525.
[41] CALIGNANO F, GALATI M, IULIANO L, et al. Design of Additively Manufactured Structures for Biomedical Applications: A Review of the Additive Manufacturing Processes Applied to the Biomedical Sector. J Healthc Eng. 2019;2019:9748212.
[42] RUPPERT DS, HARRYSSON OLA, MARCELLIN-LITTLE DJ, et al. Osseointegration of Coarse and Fine Textured Implants Manufactured by Electron Beam Melting and Direct Metal Laser Sintering. 3D Print Addit Manuf. 2017;4(2):91-97.
[43] MAO S, LIU Y, WANG F, et al. Design and biomechanical analysis of patient-specific porous tantalum prostheses for knee joint revision surgery. Int J Bioprint. 2024;9(4):735.
[44] 邓富元.3D打印不同几何形状孔隙的钛合金支架对骨长入影响研究[D].泸州:西南医科大学, 2021.
[45] 高媛.舌侧活动翼矫治器内收上前牙的三维有限元研究[D].西安:中国人民解放军空军军医大学,2024.
[46] RICHERT R, FARGES JC, TAMIMI F, et al. Validated Finite Element Models of Premolars: A Scoping Review. Materials (Basel). 2020;13(15):3280.
[47] ZHAI M, ZHU Y, YANG M, et al. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosomes Enhance Cell-Free Bone Regeneration by Altering Their miRNAs Profiles. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;7(19):2001334.
[48] 徐震超.多孔钽载双抗生素微球支架的构建及成骨和抗菌性能评估[D].长沙:中南大学,2023.
[49] BABEY ME, KRAUSE WC, CHEN K, et al. A maternal brain hormone that builds bone. Nature. 2024;632(8024):357-365.
[50] WANG R, NI S, MA L, et al. Porous construction and surface modification of titanium-based materials for osteogenesis: A review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:973297.
[51] HUANG G, PAN ST, QIU JX. The Clinical Application of Porous Tantalum and Its New Development for Bone Tissue Engineering. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(10):2647. |