[1] MIKULS TR. Gout. N Engl J Med. 2022; 387(20):1877-1887.
[2] REIS C, VIANA QUEIROZ M. Prevalence of self-reported rheumatic diseases in a Portuguese population. Acta Reumatol Port. 2014;39(1):54-59.
[3] WILSON L, SASEEN JJ. Gouty Arthritis: A Review of Acute Management and Prevention. Pharmacotherapy. 2016;36(8): 906-922.
[4] SCHUMACHER HR JR. The pathogenesis of gout. Cleve Clin J Med. 2008;75 Suppl 5:S2-4.
[5] KIM YS, KIM Y, PARK G, et al. Genetic analysis of ABCG2 and SLC2A9 gene polymorphisms in gouty arthritis in a Korean population. Korean J Intern Med. 2015;30(6):913-920.
[6] WAN GHAZALI WS, WAN ZAINUDIN WMKB, YAHYA NK, et al. Older age and diclofenac are associated with increased risk of upper gastrointestinal bleeding in gout patients. PeerJ. 2021;9:e11468.
[7] YARRARAPU SNS, GOYAL A, VENKATA VS, et al. Comprehensive review of statin-intolerance and the practical application of Bempedoic Acid. J Cardiol. 2024;84(1):22-29.
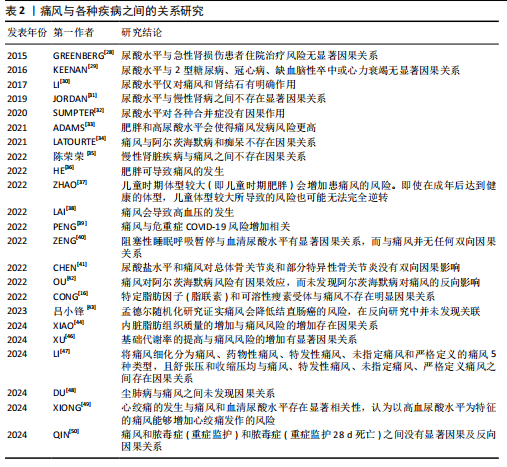
[8] 程文文,朱强,张红雨.矿物质营养与慢性病风险:孟德尔随机化研究[C]//2019中国化学会第十五届全国计算(机)化学学术会议论文集,2019:309.
[9] SYED AAS, HE L, SHI Y. The Potential Effect of Aberrant Testosterone Levels on Common Diseases: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Genes (Basel). 2020;11(7):721.
[10] YUAN S, LARSSON S. Causal associations of iron status with gout and rheumatoid arthritis, but not with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Nutr. 2020;39(10):3119-3124.
[11] YU X, WANG T, HUANG S, et al. Evaluation of the causal effects of blood lipid levels on gout with summary level GWAS data: two-sample Mendelian randomization and mediation analysis. J Hum Genet. 2021;66(5):465-473.
[12] ZHU J, SUN L, YANG J, et al. Genetic Predisposition to Type 2 Diabetes and Insulin Levels Is Positively Associated With Serum Urate Levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021;106(7):e2547-e2556.
[13] MCCORMICK N, O’CONNOR MJ, YOKOSE C, et al. Assessing the Causal Relationships Between Insulin Resistance and Hyperuricemia and Gout Using Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021;73(11):2096-2104.
[14] YANG Y, XIAN W, WU D, et al. The role of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic factors in gout: A Mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022; 13:917056.
[15] ZHAO SS, RAJASUNDARAM S, KARHUNEN V, et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 1 inhibition and gout: Mendelian randomisation study. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2022;56:152058.
[16] CONG R, ZHANG X, SONG Z, et al. Assessing the Causal Effects of Adipokines on Uric Acid and Gout: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients. 2022;14(5):1091.
[17] YUAN S, WANG L, SUN J, et al. Genetically predicted sex hormone levels and health outcomes: phenome-wide Mendelian randomization investigation. Int J Epidemiol. 2022;51(6):1931-1942.
[18] JOSHI AD, MCCORMICK N, YOKOSE C, et al. Prediagnostic Glycoprotein Acetyl Levels and Incident and Recurrent Flare Risk Accounting for Serum Urate Levels: A Population-Based, Prospective Study and Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023;75(9):1648-1657.
[19] UEDA M, FUKUI K, KAMATANI N, et al. GLUT9 as a potential drug target for chronic kidney disease: Drug target validation by a Mendelian randomization study. J Hum Genet. 2023;68(10):699-704.
[20] REN Y, JIANG Y, PENG H, et al. Causal association between several gender-driven factors and gout: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Int J Rheum Dis. 2024; 27(3):e15111.
[21] JIANG Y, LIU S, LIU G, et al. Association between sex hormones and gout: An analysis of the UK Biobank cohort. Steroids. 2024;207:109422.
[22] TAO HW, LIU ZY, JIANG W, et al. Lower plasma linoleic acids as a risk factor for gout: an integrated analysis of population-based cohort and genetic data. Food Funct. 2024;15(14):7567-7576.
[23] XIE Y, LI Y, ZHANG J, et al. Assessing the causal association between human blood metabolites and the risk of gout. Eur J Clin Invest. 2024;54(3):e14129.
[24] ZENG H, LAI J, LIU Z, et al. Specific blood metabolite associations with Gout: a Mendelian randomization study. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2025;79(1):24-32.
[25] ZHONG Y, YANG C, ZHANG B, et al. Causal impact of human blood metabolites and metabolic pathways on serum uric acid and gout: a mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024; 15:1378645.
[26] MCCORMICK N, JOSHI AD, YOKOSE C, et al. Prediagnostic Amino Acid Metabolites and Risk of Gout, Accounting for Serum Urate: Prospective Cohort Study and Mendelian Randomization. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2024;76(12):1666-1674.
[27] QIU Y, LI C, HUANG Y, et al. Exploring the causal associations of micronutrients on urate levels and the risk of gout: A Mendelian randomization study. Clin Nutr. 2024;43(4):1001-1012.
[28] GREENBERG KI, MCADAMS-DEMARCO MA, KÖTTGEN A, et al. Plasma Urate and Risk of a Hospital Stay with AKI: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;10(5):776-783.
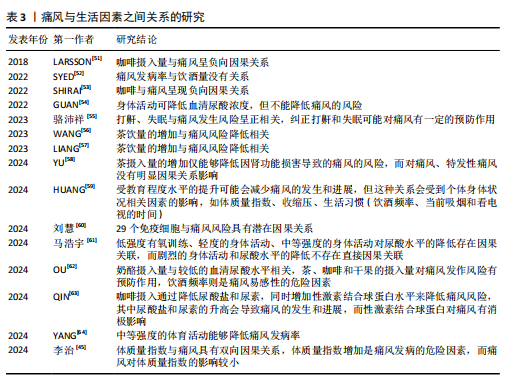
[29] KEENAN T, ZHAO W, RASHEED A, et al. Causal Assessment of Serum Urate Levels in Cardiometabolic Diseases Through a Mendelian Randomization Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;67(4):407-416.
[30] LI X, MENG X, TIMOFEEVA M, et al. Serum uric acid levels and multiple health outcomes: umbrella review of evidence from observational studies, randomised controlled trials, and Mendelian randomisation studies. BMJ. 2017;357:j2376.
[31] JORDAN DM, CHOI HK, VERBANCK M, et al. No causal effects of serum urate levels on the risk of chronic kidney disease: A Mendelian randomization study. PLoS Med. 2019;16(1):e1002725.
[32] SUMPTER NA, SAAG KG, REYNOLDS RJ, et al. Comorbidities in gout and hyperuricemia: causality or epiphenomena? Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2020;32(2):126-133.
[33] ADAMS CD, BOUTWELL BB. Using multiple Mendelian randomization approaches and genetic correlations to understand obesity, urate, and gout. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):17799.
[34] LATOURTE A, DUMURGIER J, PAQUET C, et al. Hyperuricemia, Gout, and the Brain-an Update. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2021;23(12):82.
[35] 陈荣荣,季世昌,宋飞超,等.基于孟德尔随机化方法分析尿酸与慢性肾脏病的因果关系[J].现代预防医学,2022, 49(22):4039-4044.
[36] HE C, ZHANG M, LI J, et al. Novel insights into the consequences of obesity: a phenotype-wide Mendelian randomization study. Eur J Hum Genet. 2022;30(5):540-546.
[37] ZHAO SS, BOWES J, BARTON A, et al. Separating the effects of childhood and adult body size on inflammatory arthritis: a Mendelian randomisation study. RMD Open. 2022;8(2):e002321.
[38] LAI B, YU HP, CHANG YJ, et al. Assessing the causal relationships between gout and hypertension: a bidirectional Mendelian randomisation study with coarsened exposures. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022;24(1):243.
[39] PENG H, WU X, XIONG S, et al. Gout and susceptibility and severity of COVID-19: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization analysis. J Infect. 2022;85(3):e59-e61.
[40] ZENG Z, JIN T, NI J, et al. Assessing the causal associations of obstructive sleep apnea with serum uric acid levels and gout: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2022;57:152095.
[41] CHEN D, XU H, SUN L, et al. Assessing causality between osteoarthritis with urate levels and gout: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(4):551-558.
[42] OU YN, ZHAO B, FU Y, et al. The Association of Serum Uric Acid Level, Gout, and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study. J Alzheimers Dis. 2022;89(3):1063-1073.
[43] 吕小锋,刘姗姗,陈雄,等.痛风与结直肠癌的因果关系:双向两样本孟德尔随机化研究[J].现代预防医学,2023,50(17): 3257-3264.
[44] XIAO W, WANG Q, LIU Y, et al. Association of visceral adipose tissue with gout: Observational and Mendelian randomization analyses. Chin Med J (Engl). 2024;137(19):2351-2357.
[45] 李治,陈锋,闫乾,等.基于两样本双向孟德尔随机化法分析体质指数与痛风的因果关系[J].广西医学,2024,46(8):1152-1159.
[46] XU C, LI K, WANG F. Basal metabolic rate is associated with increased risk of gout: a Mendelian randomization study. Clin Rheumatol. 2024;43(2):837-838.
[47] LI Y, XIE Y, LI J, et al. Diastolic and systolic blood pressure and gout: a Mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024;15:1367621.
[48] DU YJ, LU ZW, LI KD, et al. No causal association between pneumoconiosis and three inflammatory immune diseases: a Mendelian randomization study. Front Public Health. 2024;12:1373044.
[49] XIONG J, SUN Y, HUANG H, et al. The Causal Relationship between Angina Pectoris and Gout Based on Two Sample Mendelian Randomization. Pain Res Manag. 2024;2024:4564596.
[50] QIN Y, YANG X, NING Z. Causal roles of serum uric acid levels and gout in sepsis: a mendelian randomization study. Shock. 2024;62(1):44-50.
[51] LARSSON SC, CARLSTRÖM M. Coffee consumption and gout: a Mendelian randomisation study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018; 77(10):1544-1546.
[52] SYED AAS, FAHIRA A, YANG Q, et al. The Relationship between Alcohol Consumption and Gout: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Genes (Basel). 2022;13(4):557.
[53] SHIRAI Y, NAKAYAMA A, KAWAMURA Y, et al. Coffee Consumption Reduces Gout Risk Independently of Serum Uric Acid Levels: Mendelian Randomization Analyses Across Ancestry Populations. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2022;4(6):534-539.
[54] GUAN Y, WEI J, MENG L, et al. Genetically predicted physical activity is associated with lower serum urate concentrations. Genes Genomics. 2022;44(7):843-853.
[55] 骆沛洋,陈伟伟,刘彬,等.基于两样本孟德尔随机化方法探讨睡眠与痛风的关联[J].浙江中医药大学学报,2023, 47(8):932-937+943.
[56] WANG Q, LIU YN, ZHANG H, et al. Causal Association Between Tea Consumption and Gout: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Curr Med Sci. 2023;43(5):947-954.
[57] LIANG X, CAI J, FAN Y. Causal association between tea intake and risk for gout: a Mendelian randomization study. Front Genet. 2023;14:1220931.
[58] YU Y, YANG X, HU G, et al. Effect of tea intake on genetic predisposition to gout and uric acid: a Mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024; 14:1290731.
[59] HUANG X, CHEN X, LIU Q, et al. The relationship between education attainment and gout, and the mediating role of modifiable risk factors: a Mendelian randomization study. Front Public Health. 2024;11:1269426.
[60] 刘慧,朱瑜琪,赵英君,等.免疫细胞与炎性关节病风险的因果关系:一项孟德尔随机化研究[J].医学研究杂志,2024,53(8): 102-106+114.
[61] 马浩宇,史冬博.不同强度的身体活动与血清尿酸含量的关联研究:样本孟德尔随机化分析[J].湖北体育科技,2024, 43(4): 55-60+105.
[62] OU G, WU J, WANG S, et al. Dietary Factors and Risk of Gout: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Foods. 2024;13(8):1269.
[63] QIN T, CHU Y, YAO Y, et al. Coffee intake reduced gout risk by decreasing urate and urea while increasing SHBG levels in plasma: a mediation Mendelian randomization study. Clin Rheumatol. 2024;43(5):1735-1743.
[64] YANG T, BI S, ZHANG X, et al. The Impact of Different Intensities of Physical Activity on Serum Urate and Gout: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Metabolites. 2024; 14(1):66.
[65] 吴昱苇,朱江,郑兵,等.运动调控尿酸的作用机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2024, 28(34):5552-5557.
[66] EBSTEIN E, OTTAVIANI S. Managing Gout in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome. Drugs Aging. 2024;41(8):653-663.
[67] ZHANG L, ZHANG W, XIAO C, et al. Using human genetics to understand the epidemiological association between obesity, serum urate, and gout. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023;62(10):3280-3290.
[68] ZHU J, ZENG Y, ZHANG H, et al. The Association of Hyperuricemia and Gout With the Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Cohort and Mendelian Randomization Study in UK Biobank. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;8:817150.
[69] TOPLESS RK, PHIPPS-GREEN A, LEASK M, et al. Gout, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and the Risk of Death Related to Coronavirus Disease 2019: An Analysis of the UK Biobank. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2021;3(5):333-340.
[70] NISSEN CB, HENDRICKS O, SCHREIBER K. Women with gout and COVID-19-an unfortunate combination? Lancet Rheumatol. 2022;4(4):e233-e234.
[71] ELFISHAWI MM, ZLEIK N, KVRGIC Z, et al. The Rising Incidence of Gout and the Increasing Burden of Comorbidities: A Population-based Study over 20 Years. J Rheumatol. 2018;45(4):574-579.
[72] 林泽玉,徐林.痛风致骨破坏机制的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2024, 28(8):1295-1300.
[73] 邵子晨,李华南,顾兵,等.痛风过程中微小RNA、长链非编码RNA和环状RNA介导降尿酸、抗炎及调控骨代谢的协同调节作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2023, 27(5):765-771.
[74] PEREZ-RUIZ F, CASTILLO E, CHINCHILLA SP, et al. Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of gout. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2014; 40(2):193-206.
[75] REIJNIERSE M, SCHWABL C, KLAUSER A. Imaging of Crystal Disorders:: Calcium Pyrophosphate Dihydrate Crystal Deposition Disease, Calcium Hydroxyapatite Crystal Deposition Disease and Gout Pathophysiology, Imaging, and Diagnosis. Radiol Clin North Am. 2022;60(4):641-656.
[76] LIU Y, FENG J, JI P, et al. Association between gout and the risk of osteoporosis and fractures: a meta-analysis. Z Rheumatol. 2024;83(Suppl 1):191-199.
[77] KWON MJ, PARK JY, KIM SG, et al. Potential Association of Osteoporosis and Not Osteoporotic Fractures in Patients with Gout: A Longitudinal Follow-Up Study. Nutrients. 2022;15(1):134.
[78] KIM JH, KIM SR, KANG G, et al. Gout as a risk factor for osteoporosis: A Korean population-based study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(45):e31524.
[79] HOWREN A, SAYRE EC, CHOI HK, et al. Onset of depression and anxiety among patients with gout after diagnosis: a population-based incident cohort study. BMC Rheumatol. 2022;6(1):56.
[80] HOWREN A, BOWIE D, CHOI HK, et al. Epidemiology of Depression and Anxiety in Gout: A Systematic Review and Metaanalysis. J Rheumatol. 2021;48(1):129-137.
[81] WANG M, FAN J, HUANG Z, et al. Causal Relationship between Gut Microbiota and Gout: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(19):4260.
[82] LOU Y, LIU B, JIANG Z, et al. Assessing the causal relationships of gut microbial genera with hyperuricemia and gout using two-sample Mendelian randomization. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2024;34(4):1028-1035.
[83] TANG C, LI L, JIN X, et al. Investigating the Impact of Gut Microbiota on Gout Through Mendelian Randomization. Orthop Res Rev. 2024;16:125-136.
[84] QIN X, LI Y, HE M, et al. Folic acid therapy reduces serum uric acid in hypertensive patients: a substudy of the China Stroke Primary Prevention Trial (CSPPT). Am J Clin Nutr. 2017;105(4):882-889.
[85] SKALNY AV, KOROBEINIKOVA TV, SOTNIKOVA TI, et al. Estimation of Hair Toxic and Essential Trace Element and Mineral Profiles of Patients with Chronic Gout. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025;203(3):1351-1361.
[86] BELIZAIRE R, WONG WJ, ROBINETTE ML, et al. Clonal haematopoiesis and dysregulation of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2023;23(9):595-610.
[87] TSENG CC, WONG MC, LIAO WT, et al. Systemic Investigation of Promoter-wide Methylome and Genome Variations in Gout. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(13):4702.
[88] WANG Y, CHEN J, YAO H, et al. Mendelian randomization analysis identified potential genes pleiotropically associated with gout. Front Genet. 2024;15:1426860.
|