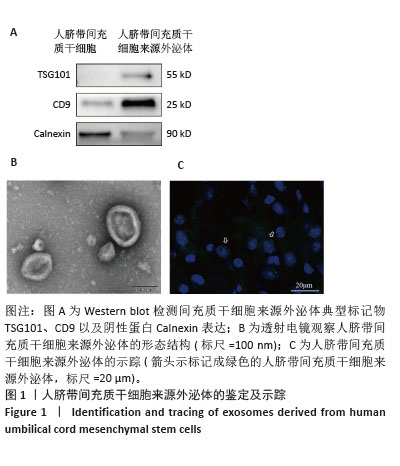
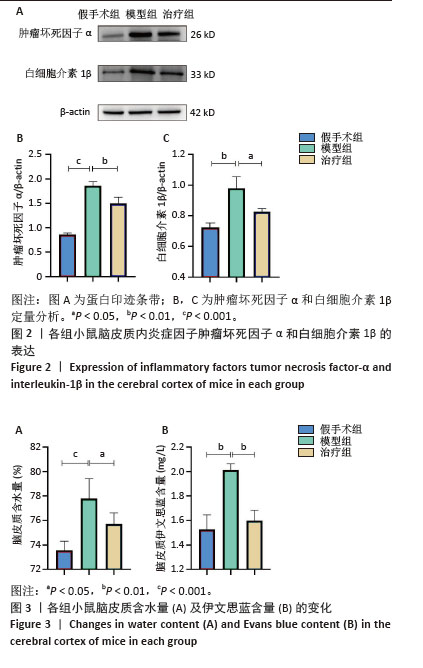
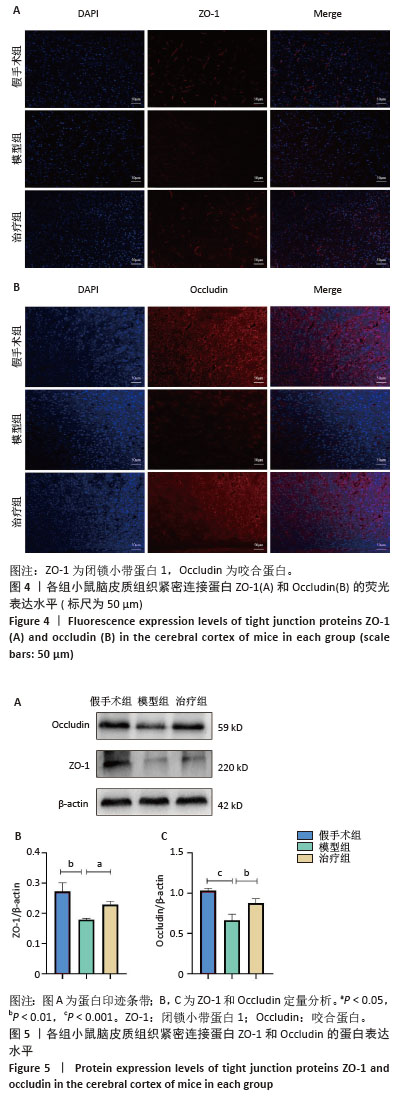
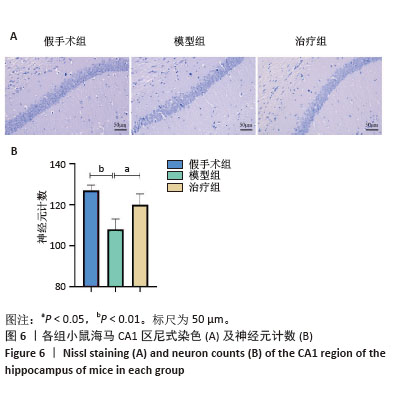
[1] FLEISCHMANN C, SCHERAG A, ADHIKARI NK, et al. Assessment of Global Incidence and Mortality of Hospital-treated Sepsis. Current Estimates and Limitations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;193(3): 259-272.
[2] HUANG Y, CHEN R, JIANG L, et al. Basic research and clinical progress of sepsis-associated encephalopathy. J Intensive Med. 2021;1(2):90-95.
[3] IWASHYNA TJ, ELY EW, SMITH DM, et al. Long-term cognitive impairment and functional disability among survivors of severe sepsis. JAMA. 2010;304(16):1787-1794.
[4] 唐梅,马艳,张西京,等.脓毒症脑病的诊疗进展[J].空军军医大学学报,2023,44(4):375-379+384.
[5] GAO Q, HERNANDES MS. Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy and Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction. Inflammation. 2021;44(6):2143-2150.
[6] 王雪,刘阳,徐剑峰,等.脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体对脑出血模型小鼠海马神经元的保护作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2022, 26(31):4928-4934.
[7] YIN S, JI C, WU P, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells and exosomes: bioactive ways of tissue injury repair. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(3):1230-1240.
[8] PATEL G, AGNIHOTRI TG, GITTE M, et al. Exosomes: a potential diagnostic and treatment modality in the quest for counteracting cancer. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2023;46(5):1159-1179.
[9] ROSZKOWSKI S. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for regenerative medicine applications. Clin Exp Med. 2024;24(1):46.
[10] LIU SF, LI LY, ZHUANG JL, et al. Update on the application of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review. Front Neurol. 2022;13: 950715.
[11] LI J, HUANG Y, SUN H, et al. Mechanism of mesenchymal stem cells and exosomes in the treatment of age-related diseases. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1181308.
[12] TAN F, LI X, WANG Z, et al. Clinical applications of stem cell-derived exosomes. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024;9(1):17.
[13] BANKS WA, SHARMA P, BULLOCK KM, et al. Transport of Extracellular Vesicles across the Blood-Brain Barrier: Brain Pharmacokinetics and Effects of Inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(12):4407.
[14] YAGHOUBI Y, MOVASSAGHPOUR A, ZAMANI M, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells derived-exosomes in diseases treatment. Life Sci. 2019;233:116733.
[15] 李潇,颜海鹏,肖政辉.脓毒症动物模型的制备方法及影响因素[J].实验动物与比较医学,2022,42(3):207-212.
[16] MA Y, SHE X, LIU Y, et al. MSC-derived exosomal miR-140-3p improves cognitive dysfunction in sepsis-associated encephalopathy by HMGB1 and S-lactoylglutathione metabolism. Commun Biol. 2024;7(1):562.
[17] YIN XY, TANG XH, WANG SX, et al. HMGB1 mediates synaptic loss and cognitive impairment in an animal model of sepsis-associated encephalopathy. J Neuroinflammation. 2023;20(1):69.
[18] YANG YL, CHENG X, LI WH, et al. Kaempferol Attenuates LPS-Induced Striatum Injury in Mice Involving Anti-Neuroinflammation, Maintaining BBB Integrity, and Down-Regulating the HMGB1/TLR4 Pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(3):491.
[19] WANG TH, XIONG LL, YANG SF, et al. LPS Pretreatment Provides Neuroprotective Roles in Rats with Subarachnoid Hemorrhage by Downregulating MMP9 and Caspase3 Associated with TLR4 Signaling Activation. Mol Neurobiol. 2017;54(10):7746-7760.
[20] GU Z, YIN Z, SONG P, et al. Safety and biodistribution of exosomes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:949724.
[21] ZHAO R, WANG L, WANG T, et al. Inhalation of MSC-EVs is a noninvasive strategy for ameliorating acute lung injury. J Control Release. 2022; 345:214-230.
[22] CUI F, CHEN Y, WU X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes carrying miR-486-5p inhibit glycolysis and cell stemness in colorectal cancer by targeting NEK2. BMC Cancer. 2024;24(1):1356.
[23] ZHANG C, LIAO W, LI W, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells derived extracellular vesicles alleviate salpingitis by promoting M1-to-M2 transformation. Front Physiol. 2023;14:1131701.
[24] ZHONG X, CHEN Z, WANG Y, et al. JQ1 attenuates neuroinflammation by inhibiting the inflammasome-dependent canonical pyroptosis pathway in SAE. Brain Res Bull. 2022;189:174-183.
[25] LUO Q, XIAN P, WANG T, et al. Antioxidant activity of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles restores hippocampal neurons following seizure damage. Theranostics. 2021;11(12):5986-6005.
[26] ZHOU Y, BAI L, TANG W, et al. Research progress in the pathogenesis of sepsis-associated encephalopathy. Heliyon. 2024;10(12):e33458.
[27] LU X, QIN M, WALLINE JH, et al. Clinical phenotypes of sepsis-associated encephalopathy: a retrospective cohort study. Shock. 2023;59(4):
583-590.
[28] GE X, MENG Q, LIU X, et al. Extracellular vesicles from normal tissues orchestrate the homeostasis of macrophages and attenuate inflammatory injury of sepsis. Bioeng Transl Med. 2023;9(1):e10609.
[29] LIU X, MENG P, LIU Z, et al. New insights on targeting extracellular vesicle release by GW4869 to modulate lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation in mice model. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2024;19(30):2619-2632.
[30] JU Y, HU Y, YANG P, et al. Extracellular vesicle-loaded hydrogels for tissue repair and regeneration. Mater Today Bio. 2022;18:100522.
[31] SAVI FF, DE OLIVEIRA A, DE MEDEIROS GF, et al. What animal models can tell us about long-term cognitive dysfunction following sepsis: A systematic review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021;124:386-404.
[32] KUO WT, ODENWALD MA, TURNER JR, et al. Tight junction proteins occludin and ZO-1 as regulators of epithelial proliferation and survival. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2022;1514(1):21-33.
[33] DITHMER S, BLASIG IE, FRASER PA, et al. The Basic Requirement of Tight Junction Proteins in Blood-Brain Barrier Function and Their Role in Pathologies. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(11):5601.
[34] SUNNY A, JAMES RR, MENON SR, et al. Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 inhibitors as therapeutic drugs for traumatic brain injury. Neurochem Int. 2024;172:105642.
[35] ZAGREAN AM, HERMANN DM, OPRIS I, et al. Multicellular Crosstalk Between Exosomes and the Neurovascular Unit After Cerebral Ischemia. Therapeutic Implications. Front Neurosci. 2018;12:811.
[36] WANG Y, LIU J, WANG H, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Ameliorate Diabetic Kidney Disease Through the NLRP3 Signaling Pathway. Stem Cells. 2023;41(4):368-383.
[37] ZHANG N, LUO Y, ZHANG H, et al. Exosomes Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorate the Progression of Atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- Mice via FENDRR. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2022;22(6):528-544.
[38] FANG S, LIU Z, WU S, et al. Pro-angiognetic and pro-osteogenic effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-21-5p in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8(1):226.
[39] KARIMI A, POURREZA S, VAJDI M, et al. Evaluating the effects of curcumin nanomicelles on clinical outcome and cellular immune responses in critically ill sepsis patients: A randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled trial. Front Nutr. 2022;9:1037861.
[40] YANG Y, GAO L, XI J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles mitigate neuronal damage from intracerebral hemorrhage by modulating ferroptosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024;15(1):255.
[41] ABBASI R, ALAMDARI-MAHD G, MALEKI-KAKELAR H, et al. Recent advances in the application of engineered exosomes from mesenchymal stem cells for regenerative medicine. Eur J Pharmacol. 2025;989:177236.
|