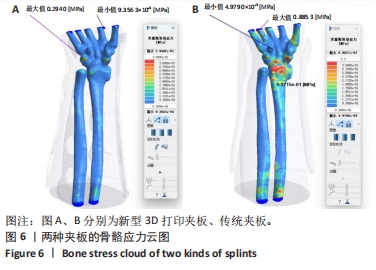
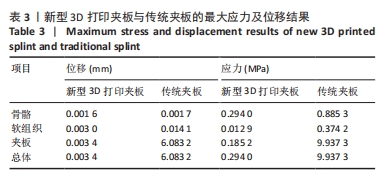
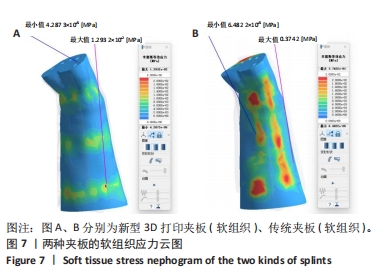
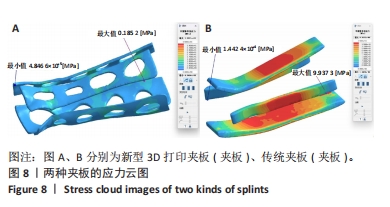
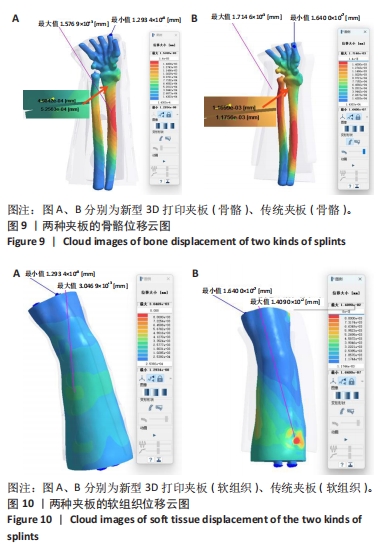
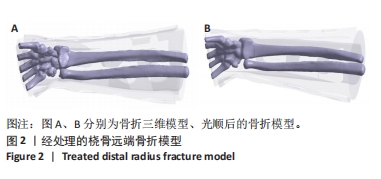
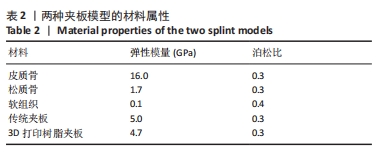
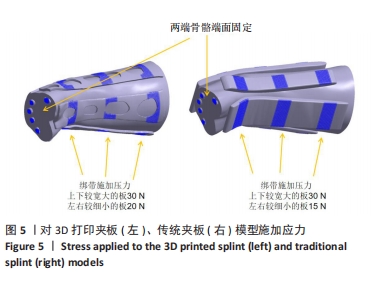
[1] 中华医学会骨科学分会创伤骨科学组, 中华医学会骨科学分会外固定与肢体重建学组. 中国成人桡骨远端骨折诊疗指南(2023)[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2023,25(1):6-13.
[2] 陈天鑫, 张智龙, 杨胜平, 等. 手法复位小夹板固定治疗桡骨远端骨折的可视化分析[J]. 中国医药导报,2022,19(36):86-91.
[3] YAN W, DING M, KONG B, et al. Lightweight Splint Design for Individualized Treatment of Distal Radius Fracture. J Med Syst. 2019; 43(8):284.
[4] 李国梁, 赵建勇, 李晓明, 等. 数字化中医手法复位结合3D打印小夹板外固定治疗A型桡骨远端骨折的近期疗效观察[J].中国骨伤, 2023,36(9):809-814.
[5] VERSCHOOR H, TOXOPEUS M, ALTNJI S, et al. LCA comparing 3D printed splints to conventional splints for traumatic injuries. Procedia CIRP. 2024;122:1000-1005.
[6] 陈轶强, 孙斐予, 黄志俭. 改良手法复位夹板固定治疗桡骨骨折的临床疗效[J]. 实用临床医药杂志,2014,18(21):116-118.
[7] 莫冰峰, 尹东, 黄宇, 等. 手法整复小夹板固定与外固定架固定治疗老年桡骨远端骨折效果对比观察[J]. 山东医药,2016,56(44):89-91.
[8] 曹学伟,路嵘,刘金文,等. 手法复位配合中药治疗老年桡骨远端骨折326例[J]. 河南中医,2003,23(7):46-47.
[9] 曾祥永. 骨远端稳定性骨折手法复位石膏夹板与小夹板固定的疗效研究[J]. 医学信息(上旬刊),2010,23(8):2852-2854.
[10] 陈昌博. 小夹板固定与外固定架固定治疗老年桡骨远端骨折的近期疗效比较[J]. 临床合理用药杂志,2017,10(6):148-150.
[11] 方玉树, 何伟清. 旋转石膏夹板固定与传统小夹板固定治疗桡骨远端C3型伸直型骨折疗效观察[J]. 新中医,2011,43(6):56-57.
[12] 刘敏强, 毛吉刚, 何大川, 等. 不同外固定方法治疗老年粉碎性Colles骨折的疗效对比[J]. 黑龙江医学,2015,39(7):812-814.
[13] 刘勇. 基层医院杉树皮小夹板固定治疗桡骨远端骨折[J]. 中国临床研究,2010,23(6):462.
[14] 马丽杰, 谢冬梅. 手法复位小夹板合树脂石膏固定治疗桡骨远端骨折[J]. 中医正骨,2009,21(9):43-44.
[15] 彭斌, 王健, 毛峰. 手术与石膏外固定治疗桡骨远端不稳定骨折疗效比较[J]. 中国骨伤,2013,26(1):41-46.
[16] 汤昌平, 张喜飞, 王平. 小夹板外固定治疗桡骨远端伸直型骨折[J]. 齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2008,29(14):1693-1694.
[17] 杨洪佳, 周长友, 魏钢, 等. 小夹板结合石膏外固定治疗桡骨远端骨折的疗效分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(9):878-879.
[18] 余黎明, 张仁明, 朱健, 等. 手法牵引复位石膏夹板固定治疗桡骨远端骨折140例的疗效分析[J]. 医学临床研究,2008,25(7):1180-1183.
[19] 郑建桥. 手法复位石膏托及石膏夹板外固定序贯小夹板固定治疗桡骨远端骨折的疗效观察[J]. 中医外治杂志,2023,32(5):63-65.
[20] HUANG F, TAN R, WANG MW, et al. Three‑dimensional finite element analysis: Anatomical splint fixation for Colles fractures. Exp Ther Med. 2024;27(3):98.
[21] 李永耀, 程灏, 赵勇, 等. 夹板固定治疗尺骨茎突骨折的三维有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(11):1737-1742.
[22] 姜自伟, 黄枫, 成思源, 等. 数字化夹板设计及有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2017,21(7):1052-1056.
[23] KONRADS C, GONSER C, BAHRS C. Fractures of the Distal Radius. Z Orthop Unfall. 2021;159(2):217-231.
[24] RUNDGREN J, BOJAN A, MELLSTRAND NAVARRO C, et al. Epidemiology, classification, treatment and mortality of distal radius fractures in adults: an observational study of 23,394 fractures from the national Swedish fracture register. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):88.
[25] NELLANS KW, KOWALSKI E, CHUNG KC. The epidemiology of distal radius fractures. Hand Clin. 2012;28(2):113-125.
[26] BARTOLOTTA RJ, DANIELS SP, VERRET CI, et al. Current Fixation Options for Elbow, Forearm, Wrist, and Hand Fractures. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2019;23(2):109-125.
[27] 许明熙, 汪礼军, 黄珍谷, 等. 谈《外科学》Colles骨折的表述存疑[J]. 医学与哲学,2021,42(17):68-70.
[28] WANG G, HUO L, XU Y, et al. Clinical observation on the treatment of displaced distal radial and ulnar fractures in children by closed manipulation combined with splinting. Front Surg. 2023;10:1199437.
[29] 李静, 徐一杰, 江丽. 早期功能锻炼治疗桡骨远端骨折手法复位后动态小夹板固定患者的临床疗效[J]. 中国中西医结合外科杂志, 2024,30(3):338-342.
[30] LOOSE O, FERNANDEZ F, MORRISON S, et al. Treatment of nonunion after forearm fractures in children: a conservative approach. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2021;47(2):293-301.
[31] 刘凯, 叶永亮, 胡建炜, 等. 手法复位桡骨远端骨折后再移位92例原因分析[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2020,28(10):61-64.
[32] 何云涛, 孔博, 奚小冰, 等. 一种用于桡骨远端骨折的新型医用小夹板设计与评价[J]. 上海交通大学学报,2018,52(2):194-199.
[33] 孟宪宇, 李凤久, 张旭, 等. 一体化扎带压垫夹板簾治疗桡骨远端伸直型骨折的临床应用[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2022,30(10):38-42.
[34] 邱雪, 吴荷玉. 3D 打印结合数字化技术在数字骨科医学发展中的应用配合[J]. 护理研究,2015,29(10):3839-3840.
[35] 王雨辰, 马勇, 俞伟忠, 等. 计算机虚拟复位结合3D打印技术在髋臼骨折中的临床应用[J]. 中国骨伤,2017,30(7):627-632.
[36] 邹其声, 孙欣, 魏波, 等. 拓扑优化技术在骨科植入物创新设计的应用进展[J]. 生物骨科材料与临床研究,2022,19(4):82-85,90.
[37] AIMAR A, PALERMO A, INNOCENTI B. The Role of 3D Printing in Medical Applications: A State of the Art. J Healthc Eng. 2019;2019: 5340616.
[38] 刘奎, 唐雪梅, 唐波, 等. 数字化设计及3D打印技术在肋骨骨折外固定中的临床应用研究[J]. 中国现代手术学杂志,2023,27(6):454-459.
[39] 李明洋, 王俐慧, 李朋亚, 等. 3D打印个体化髋臼翻修假体设计及应用[J]. 中国医疗设备,2024,39(6):30-36.
[40] 龙旭东, 方家栋, 杨黎. 数字化技术在骨科手术中的应用进展[J]. 海南医学,2022,33(13):1737-1740.
[41] 周涵薇, 陈涛, 杜伟斌, 等. 3D打印技术在骨科领域的应用进展[J]. 中医正骨,2022,34(12):52-55,59.
[42] JANZING HMJ, BESSEMS SAM, LIGTHART MAP, et al. Treatment of dorsally dislocated distal radius fractures with individualized 3D printed bracing: an exploratory study. 3D Print Med. 2020;6(1):22.
[43] 孙巍, 韦祎, 郑雪君, 等. 三维有限元分析技术、3D打印生物模型技术在退行性腰椎侧凸精准手术中的应用价值[J]. 中国医师杂志, 2023,25(11):1692-1696.
[44] 曾焘, 高大伟, 吴宇峰, 等. 小夹板结合3D打印支具外固定治疗Colles骨折[J]. 中国骨伤,2019,32(6):513-518.
[45] 刘康, 蒋国璋, 盛然, 等. 3D打印腕手矫形器辅助腕关节骨折术后康复的疗效观察[J]. 中国康复,2021,36(10):633-636.
[46] 丁玲, 李远艺. 3D打印小夹板应用于Colles骨折临床研究[J]. 山东中医杂志,2018,37(2):123-125.
[47] 白宇, 王坤. 基于参数化的3D打印个性化外固定支具设计研究[J]. 图学学报,2023,44(5):1050-1056.
[48] 毛昭冲, 李福伟, 杨凤云, 等. 有限元分析在桡骨远端骨折研究中的应用进展[J]. 中医正骨,2023,35(2):30-32,45.
[49] 王聪轩, 萨日娜, 包呼和. 桡骨远端骨折夹板外固定的骨折缝应力预测[J]. 医用生物力学,2023,38(6):1179-1185.
[50] 彭志鑫, 闫文刚, 王坤, 等. 3D打印前臂外固定支具的有限元分析与结构优化设计[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(9):1340-1345.
[51] 王爱国, 陆贲琪, 李沿鑫, 等. 桡骨远端骨折夹板外固定有限元模型的建立及其愈合过程的应力分析[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2024, 32(3):7-11.
|