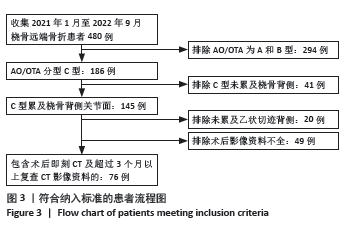
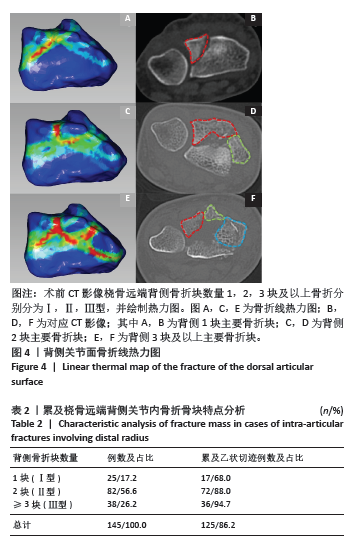
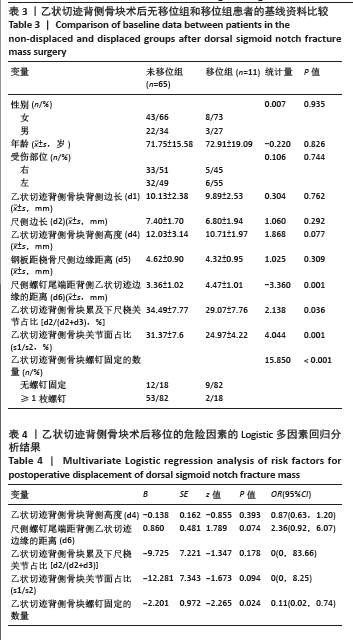
[1] LUO Z, ZHU W, JIANG C, et al. Characteristics of distal radius fractures in east China-an observational cohort study of 1954 individual fractures. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):627.
[2] MACINTYRE NJ, DEWAN N. Epidemiology of distal radius fractures and factors predicting risk and prognosis. J Hand Ther. 2016;29(2):136-145.
[3] PORRINO JJ, MALONEY E, SCHERER K, et al. Fracture of the distal radius: epidemiology and premanagement radiographic characterization. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014;203(3):551-559.
[4] MAUCK BM, SWIGLER CW. Evidence-Based Review of Distal Radius Fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 2018;49(2):211-222.
[5] LUCAS B, LIPPISCH R, PLISKE G, et al. [Conservative management of distal radius fractures]. Unfallchirurgie (Heidelb). 2023;126(3): 227-237.
[6] 欧梁, 卢敏, 张永辉, 等. 手法复位小夹板固定治疗老年桡骨远端骨折临床疗效Meta分析[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志,2019,39(1):57-62.
[7] HASSELLUND SS, WILLIKSEN JH, LAANE MM, et al. Cast immobilization is non-inferior to volar locking plates in relation to QuickDASH after one year in patients aged 65 years and older: a randomized controlled trial of displaced distal radius fractures. Bone Joint J, 2021;103-B(2): 247-255.
[8] ALLURI RK, HILL JR, GHIASSI A. Distal Radius Fractures: Approaches, Indications, and Techniques. J Hand Surg Am. 2016;41(8):845-854.
[9] ALI R, ILYAS A, RIAZ H, et al. Outcome Of The Distal Radius Fractures Managed With Across Wrist External Fixator Vs Buttress Plates. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2023;35(1):32-36.
[10] GHAFOOR H, HAEFELI M, STEIGER R, et al. Dorsal Plate Osteosynthesis in Simple and Complex Fractures of the Distal Radius: A Radiological Analysis of 166 Cases. J Wrist Surg. 2022;11(2):134-144.
[11] PATINO JM, RULLAN CA, MICHELINI A, et al. Distal radius fractures- Treatment with volar locking plates - Functional results according to fracture type. Rev Fac Cien Med Univ Nac Cordoba. 2020;77(4): 272-275.
[12] PIESKE O, STURMER KM, BONNAIRE F, et al. [Guideline Report Distal radius fracture]. Chirurgie (Heidelb). 2023;94(11):965-966.
[13] 季佳庆, 樊健, 王健, 等. 掌侧锁定钢板治疗伴背侧骨块的桡骨远端骨折[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2021,27(8):678-683.
[14] 吴世桐, 宁仁德, 方闰, 等. 桡骨远端骨折尺背侧骨折块不同固定方法的疗效比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(21):3343-3348.
[15] 吴世桐, 宁仁德, 方闰, 等. 掌侧入路内固定治疗桡骨远端粉碎性骨折合并尺背侧骨折块的临床研究[J]. 创伤外科杂志,2021,23(5): 338-341.
[16] BRINK PR, RIKLI DA. Four-Corner Concept: CT-Based Assessment of Fracture Patterns in Distal Radius. J Wrist Surg. 2016;5(2):147-151.
[17] 蒋代翔, 鲁辉, 马玲, 等. 基于三维骨折地图技术的跟骨骨折线分布研究[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(18):2842-2847.
[18] 王永钦, 徐子环, 李鹏飞, 等. 基于骨折地图技术的青壮年股骨颈骨折特征分析[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2022,36(9):1078-1083.
[19] ARMITAGE BM, WIJDICKS CA, TARKIN IS, et al. Mapping of scapular fractures with three-dimensional computed tomography. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(9):2222-2228.
[20] 居家宝, 陈建海, 张一翀, 等. 骨折地图在创伤骨科中的应用[J]. 中华肩肘外科电子杂志,2020,8(3):283-286.
[21] ZHANG X, ZHANG Y, FAN J, et al. Analyses of fracture line distribution in intra-articular distal radius fractures. Radiol Med. 2019;124(7): 613-619.
[22] LI S, ZHANG YQ, WANG GH, et al. Melone’s concept revisited in comminuted distal radius fractures: the three-dimensional CT mapping. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):222.
[23] MISIR A, OZTURK K, KIZKAPAN TB, et al. Fracture lines and comminution zones in OTA/AO type 23C3 distal radius fractures: The distal radius map. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2018;26(1):613414395.
[24] NYPAVER C, BOZENTKA DJ. Distal Radius Fracture and the Distal Radioulnar Joint. Hand Clin. 2021;37(2):293-307.
[25] TANABE K, NAKAJIMA T, SOGO E, et al. Intra-articular fractures of the distal radius evaluated by computed tomography. J Hand Surg Am, 2011;36(11):1798-1803.
[26] HEO YM, ROH JY, KIM SB, et al. Evaluation of the sigmoid notch involvement in the intra-articular distal radius fractures: the efficacy of computed tomography compared with plain X-ray. Clin Orthop Surg. 2012;4(1):83-90.
[27] VITALE MA, BROGAN DM, SHIN AY, et al. Intra-articular Fractures of the Sigmoid Notch of the Distal Radius: Analysis of Progression to Distal Radial Ulnar Joint Arthritis and Impact on Upper Extremity Function in Surgically Treated Fractures. J Wrist Surg. 2016;5(1):52-58.
[28] BOMBACI H, POLAT A, DENIZ G, et al. The value of plain X-rays in predicting TFCC injury after distal radial fractures. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2008;33(3):322-326.
[29] MIYASHIMA Y, KANESHIRO Y, YANO K, et al. Size and stabilization of the dorsoulnar fragment in AO C3-type distal radius fractures. Injury. 2019;50(11):2004-2008.
[30] TAVAKOLIAN JD, JUPITER JB. Dorsal plating for distal radius fractures. Hand Clin. 2005;21(3):341-346.
[31] AYALON O, PAKSIMA N. Dorsal Plating of Distal Radius Fractures Historical Context and Appropriate Use. Bull Hosp Jt Dis (2013). 2017; 75(1):4-8.
[32] DISSELDORP DJ, HANNEMANN PF, POEZE M, et al. Dorsal or Volar Plate Fixation of the Distal Radius: Does the Complication Rate Help Us to Choose? J Wrist Surg. 2016;5(3):202-210.
[33] IKEDA K, OSAMURA N, TADA K. Fixation of an ulnodorsal fragment when treating an intra-articular fracture in the distal radius. Hand Surg. 2014;19(1):139-144.
[34] LEE JI, CHO JH, LEE SJ. The effects of the Frag-Loc((R)) compression screw on distal radius fracture with a displaced dorsoulnar fragment. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015;135(9):1315-1321.
[35] KANAZAWA T, TOMITA K, KAWASAKI K, et al. Comparison of Locking and Frag-Loc Screws for Fixation of Die-Punch Fragments. J Wrist Surg. 2018;7(3):205-210.
[36] SAKAMOTO S, DOI K, HATTORI Y, et al. Comminuted Dorsal Ulnar Fragment in Distal Radius Fractures Treated Using the Integrated Compression Screw With a Mini-Plate. J Hand Surg Am. 2022;47(4): 391-394.
|