中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (36): 7872-7879.doi: 10.12307/2025.555
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
间充质干细胞衍生外泌体在结直肠癌治疗中的作用
郭 昭1,庄浩岩1,史学文2
- 1山东中医药大学第一临床医学院,山东省济南市 250000;2山东中医药大学附属医院肛肠科,山东省济南市 250000
-
收稿日期:2024-04-22接受日期:2024-09-21出版日期:2025-12-28发布日期:2025-03-24 -
通讯作者:史学文,博士,主任医师,山东中医药大学附属医院肛肠科,山东省济南市 250000 -
作者简介:郭昭,女,1999年生,山东省招远市人,汉族,山东中医药大学在读硕士,主要从事肛肠疾病临床与基础研究。 -
基金资助:山东省中医药科技发展项目(2019-0187),项目负责人:史学文;齐鲁中医药优势专科集群建设项目(YWC2022ZKJQ0003),项目负责人:史学文
Role of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of colorectal cancer
Guo Zhao1, Zhuang Haoyan1, Shi Xuewen2
- 1First Clinical Medical College, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250000, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Anorectal Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250000, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2024-04-22Accepted:2024-09-21Online:2025-12-28Published:2025-03-24 -
Contact:Shi Xuewen, MD, Chief physician, Department of Anorectal Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250000, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Guo Zhao, Master candidate, First Clinical Medical College, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250000, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:Shandong Province Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Development Project, No. 2019-0187 (to SXW); Qilu Traditional Chinese Medicine Advantage Specialty Cluster Construction Project, No. YWC2022ZKJQ0003 (to SXW)
摘要:
文题释义:
结直肠癌:结直肠癌的发病较为隐匿,通常被诊出时已经是晚期。目前治疗结直肠癌的方法包括早期手术治疗和晚期化学治疗。但是手术治疗的风险较高且术后并发症多,化学治疗需要长期进行,耐药性及患者依从性都得不到保证,这迫使研究者们寻求新的治疗方法。间充质干细胞衍生外泌体:各种不同来源的间充质干细胞均可以产生外泌体,并且无论在生理或者病理状态下都可以正常分泌外泌体。近年来,间充质干细胞衍生外泌体主要通过血管生成、抑制肿瘤细胞增殖和促进肿瘤细胞凋亡来发挥治疗结直肠癌的作用。
摘要
背景:目前结直肠癌的治疗方法包括手术切除、化疗等,但是手术并发症多、化疗后期具有耐药性等原因都使得患者的后续生活质量不能得到提高。
目的:综述间充质干细胞衍生外泌体治疗结直肠癌的作用机制、最新进展及目前存在的问题。
方法:计算机检索PubMed数据库、中国知网、万方数据库收录的相关文献。英文检索词为“mesenchymal stem cells exosomes,colorectal cancer,chemotherapy,treatment”,中文检索词为“间充质干细胞外泌体,结直肠癌,化疗,治疗”,最终纳入96篇文献进行分析。
结果与结论:①间充质干细胞衍生外泌体主要通过自身携带的微小RNA及长链非编码RNA以介导不同的信号通路,在结直肠癌中发挥不同作用;②间充质干细胞衍生外泌体具有高稳定性、高生物相容性的特点,可作为治疗药物的优秀载体;③间充质干细胞衍生外泌体对不同种类的化疗药物的耐药性具有不同的作用。
中图分类号:
引用本文
郭 昭, 庄浩岩, 史学文. 间充质干细胞衍生外泌体在结直肠癌治疗中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(36): 7872-7879.
Guo Zhao, Zhuang Haoyan, Shi Xuewen. Role of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of colorectal cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7872-7879.
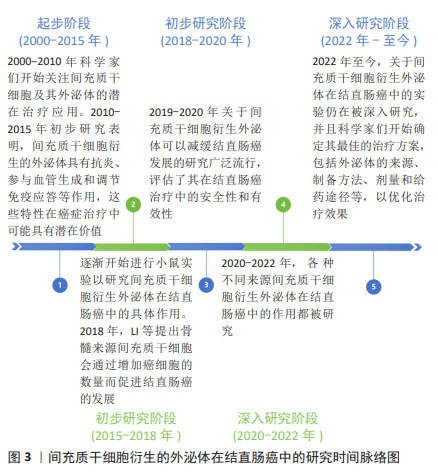
2.2 MSC-Exos
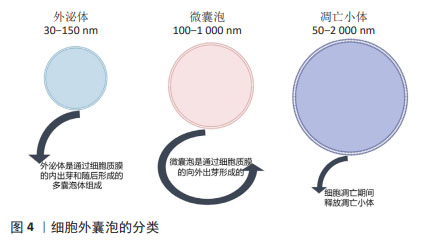
2.2.1 不同来源MSC-Exos 1983年,科学家在绵羊网织红细胞中首次发现了外泌体。外泌体是由多种细胞类型分泌的脂质双层细胞外囊泡。细胞外囊泡可分为3种类型:外泌体(直径30-150 nm)、微囊泡(100-1 000 nm)和凋亡小体(直径50-2 000 nm)。外泌体是通过细胞质膜向内出芽和随后形成的多囊泡体形成的。相反,微囊泡是通过质膜向外出芽产生的。细胞凋亡期间释放凋亡小体。许多传统标志物(CD9、CD63、CD81、TSG101、Alix、Flotillin-1、HSC70、肌动蛋白、MHCⅠ和MHCⅡ)在细胞外囊泡的多种亚型中错综分布,所以很难根据表面标志物将它们进行划分,目前主要通过直径大小进行划分,见图4。
外泌体富含蛋白质、脂质和RNA,包括mRNA和miRNA,可以介导其功能发挥[22]。外泌体由多种细胞分泌,存在于几乎所有体液中[23],包括血液、唾液、尿液、脑脊液和乳汁等。但是根据大量研究证实,不同来源的MSC-Exos存在着各自的独特优势,见表1。
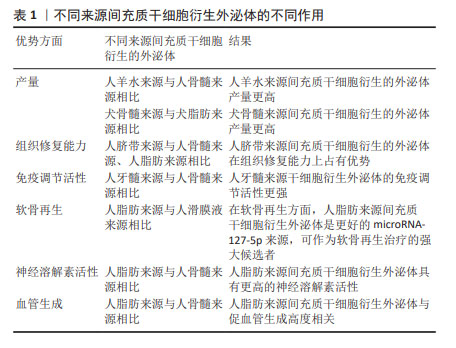
在产量方面,与人骨髓来源MSC-Exos相比,人羊水来源MSC-Exos产量更高[24];与犬脂肪来源MSC-Exos相比,犬骨髓来源MSC-Exos产量更高[25]。在组织修复能力方面,与人骨髓来源、人脂肪来源MSC-Exos相比,人脐带来源MSC-Exos更具优势[26]。在免疫调节活性方面,与人骨髓来源MSC-Exos相比,人牙髓来源MSC-Exos免疫调节活性更强[27]。研究表明,外泌体microRNA-127-5p的产量越高,软骨再生能力越好。人脂肪来源MSC-Exos比人滑膜液来源MSC-Exos表达更多的microRNA-127-5p,可以作为软骨再生的强大候选者[28]。在一项针对阿尔茨海默病的研究中发现,人脂肪来源MSC-Exos具有更高的神经溶解素活性[29]。在血管生成方面,与人骨髓来源MSC-Exos相比,人脂肪来源MSC-Exos与血管生成更具相关性[30]。
2.2.2 MSC-Exos的分离与提取 MSC-Exos的分离和提取一直是研究者所热衷的方向,为了使提取的产量更高、浓度更纯、结构稳定、污染低、操作时间短、花费少,目前科学家主要提出了以下几种分离方法:超速离心、冲洗分离、沉淀、超滤、免疫亲和捕获、微流控技术、质谱法等,见表2。
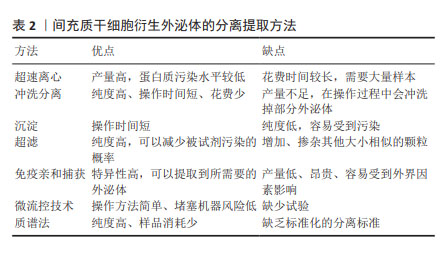
超速离心仍然是目前应用最广泛的方法,提取方案简单,提取的外泌体纯度也较高[31]。冲洗分离的方法相比较超速离心操作时间短,但是在操作过程中不可避免地会冲洗掉部分外泌体,导致提取到的产量不足[32]。沉淀方法最大的优点在于步骤简单、操作时间短[33-35]。超滤方法最大的局限性在于无法过滤出与外泌体大小相似的颗粒[36-38]。免疫亲和捕获可以通过细胞外囊泡的表面标记物很好地区分各种外泌体,从而提取到所需的外泌体类型,但是这种方法具有产量低的缺点[39-41]。此外,最近新兴的提取方法,包括微流控技术和质谱法等[42-47],都还缺少充分的分离标准,其效果还没有得到充分的评估。尽管目前尚未就外泌体分离的“金标准”达成共识,但建议结合使用多种技术以获得最佳外泌体分离结果[43]。
2.2.3 MSC-Exos的生物学特性 2010年,MSC-Exos首次在心肌缺血再灌注损伤中进行了研究[48],随后开展了大量研究探讨MSC-Exos在各类疾病中的作用。自从2012年,ZHU等[49]首次报道MSC-Exos可以促进体内肿瘤生长以来,关于MSC-Exos在肿瘤中的作用就被积极讨论。MSC-Exos在肿瘤中的作用与间充质干细胞类似,参与血管生成、抑制肿瘤细胞增殖和促进肿瘤细胞凋亡,这在李佳林等[50]的研究中也被证实。
(1)参与血管生成。在结肠癌异种移植的小鼠模型中,人骨髓来源MSC-Exos可以通过激活ERK1/2和p38 MAPK通路增加肿瘤细胞中血管内皮生长因子和趋化因子受体4的表达,从而促进血管生成,进而促进结直肠癌的发展[49]。
然而在乳腺癌中科学家们发现了相反的结果,LEE等[51]报道人骨髓来源MSC-Exos可以通过miR-16靶向血管内皮生长因子在乳腺癌细胞中的表达,从而抑制血管生成和肿瘤进展。PAKRAVAN等[52]支持这一观点,他们发现人骨髓来源间充质干细胞携带miR-100,通过下调血管内皮生长因子的表达,抑制乳腺癌血管生成。人月经血来源MSC-Exos通过抑制活性氧通路,下调促血管生成因子和NF-κB转录因子的分泌,抑制前列腺癌的进展[53]。
(2)抑制肿瘤细胞增殖和促进肿瘤细胞凋亡。人脐带来源MSC-Exos可以通过对肿瘤细胞发挥抗增殖和促凋亡作用,从而抑制膀胱癌的进展[54]。REZA等[55]观察到人脂肪来源MSC-Exos可以抑制A2780和SKOV-3癌细胞的增殖,从而抑制卵巢癌的生长与转移。人脂肪来源MSC-Exos通过Caspase-3/7通路诱导细胞凋亡,抑制前列腺癌的发展[56]。人骨髓来源MSC-Exos通过KDM3A/DCLK1/FXYD3轴抑制肿瘤细胞增殖,抑制肺癌的进展[57]。
综上,MSC-Exos在治疗肿瘤方面具有积极性,这毋庸置疑,但是也有部分科学家提出了MSC-Exos对肿瘤具有促进作用,在将来的研究中,应该侧重于研究其促进与抑制作用的不同机制,从而为肿瘤患者提供更完善的方案。
2.3 MSC-Exos治疗结直肠癌
2.3.1 MSC-Exos作为结直肠癌的治疗工具 越来越多的证据表明,从不同来源间充质干细胞中分离出的外泌体可以抑制结直肠癌的进展。此文章主要就人脐带来源、人骨髓来源、人脂肪来源MSC-Exos对结直肠癌的作用展开研究,见表3。

人脐带来源MSC-Exos可以携带miR-3940-5p通过靶向ITGA6和转化生长因子β,抑制结直肠癌细胞的侵袭,并抑制上皮-间质转化,从而抑制了结直肠癌的生长与转移[58]。CHEN等[59]研究也证实了人脐带来源MSC-Exos可以抑制结直肠癌的发生并且对肝转移具有抑制作用,其作用机制是通过诱导miR-1827靶向抑制SUCNR1而发挥作用。QU等[60]研究证实人脐带来源MSC-Exos携带的miR-431-5p 可以通过下调过氧化物还原酶1的表达,从而延缓结直肠癌细胞的生长,抑制结直肠癌的进展。WANG等[61]研究发现人脐带来源MSC-Exos通过miR-146a抑制SUMO1的表达,延缓结肠炎的恶化,避免了结肠炎长期恶化后发生结直肠癌的不良结局。多项实验证明,人骨髓来源MSC-Exos对结直肠癌也具有抑制作用,主要体现在以下几个机制:通过miR-16-5p下调ITGA2的表达[62];通过miR-4461下调 COPB2的表达,抑制HCT116和SW480细胞的迁移和侵袭[63],抑制基质金属蛋白酶2、基质金属蛋白酶9、SNAIL和TWIST的表达;通过miR-100/mTOR/miR-143轴诱导结直肠癌细胞凋亡[64];通过miR-22-3p介导 RAP2B/PI3K/AKT通路,对SW480细胞的增殖和侵袭有抑制作用[65];通过SCARA5抑制结直肠癌细胞中蛋白激酶B和磷酸肌醇3-激酶的磷酸化[66];通过miR-99b-5p靶向 FGFR3来抑制肿瘤进展[67]。在最近的一项研究中,发现人脂肪来源MSC-Exos可以通过抑制水通道蛋白5和表皮生长因子受体的表达,进而抑制结直肠癌的发展[68]。
综上所述,间充质干细胞对结直肠癌的治疗作用可能归因于富含肿瘤抑制性miRNA的外泌体,这可能会成为未来临床实践中治疗结直肠癌的一种有前途的方法。
2.3.2 MSC-Exos作为结直肠癌的潜在治疗靶点 尽管有大量的实验证据已经表明MSC-Exos对结直肠癌具有抑制作用,但仍有研究显示其在结直肠癌的发展中发挥促进作用,这表明MSC-Exos可以作为结直肠癌的潜在治疗靶点,为治疗结直肠癌提供更有价值的方法,见表4。
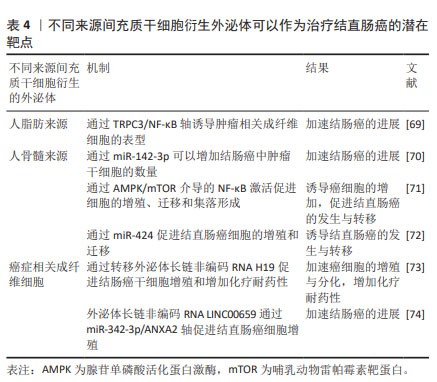
XUE等[69]研究发现,人脂肪来源MSC-Exos可以通过TRPC3/NF-KB轴诱导肿瘤相关成纤维细胞的表型,从而加速结肠癌的进展。人骨髓来源MSC-Exos可以通过携带的miR-142-3p增加结肠癌中肿瘤干细胞的数量,从而加速结肠癌的发生与进展[70]。一项大鼠模型研究中也证实了人骨髓来源间充质干细胞可以通过腺苷单磷酸活化蛋白激酶/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(AMP-activated protein kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin,AMPK/mTOR)介导的NF-κB激活促进癌细胞的增殖、迁移和集落形成,促进结直肠癌的发生与转移[71]。另外,最近的一项体外研究表明,人骨髓来源MSC-Exos中携带的miR-424具有诱导结直肠癌发生的作用[72]。REN等[73]研究发现,癌症相关成纤维细胞通过转移外泌体长链非编码RNA H19促进结肠癌干细胞增殖和增加化疗耐药性,从而加速结直肠癌的进展。同样的结果在ZHOU等 [74]的研究中也被证实,癌症相关成纤维细胞分泌的外泌体长链非编码RNA LINC00659通过miR-342-3p/ANXA2轴促进结直肠癌细胞增殖。通过以上研究可以发现,抑制这些促进结直肠癌进展的靶点可以为治疗结直肠癌提供一种新思路。
2.3.3 MSC-Exos可以作为治疗结直肠癌的载体 外泌体具有高稳定性、高生物相容性的特点,这使其作为药物输送的载体成为可能[75]。同时,外泌体还具有生物利用度高的特点,可以更顺利地通过血脑屏障等生物屏障[76]。有研究报道,MSC-Exos可以通过细胞间连接、P-糖蛋白的高表达、隧道纳米管和胞吐方式与癌细胞相互作用[77-79]。
另外,可以将对癌症具有良好治疗潜力的小干扰 RNA (siRNA)或microRNA (miRNA)装载到MSC-Exos上,使其作为合适的递送系统[80-82]。HAN等[83]研究发现,人脐带来源MSC-Exos可以作为抗miRNA寡核苷酸的载体,被肿瘤细胞特异性摄取,以发挥抗肿瘤作用。在另外一项研究中发现,人骨髓来源MSC-Exos可以作为阿霉素的载体,包封率高达35%,与单纯的游离阿霉素相比,它表现出更显著的抑制结直肠癌的作用[84]。结直肠癌干细胞衍生外泌体携带的miR-1270选择性地增强了对大肠癌细胞的抑制作用[85]。最近的一项研究也证实了MSC-Exos可以作为良好的抗结直肠癌药物的载体,在结直肠癌中发挥着重要作用[86]。以上所有研究都证明了MSC-Exos可以作为一种创新的药物递送策略,其特点是靶向更精确、免疫原性更低,以实现更好的靶向治疗[87]。
2.3.4 MSC-Exos在化疗耐药性中的作用 化疗贯穿着结直肠癌的整个治疗过程,早期手术治疗后,一般需要化疗巩固治疗,晚期无法进行手术时,更需要化疗维持生命。铂类药物、紫杉醇、阿霉素和5-氟尿嘧啶等多种具有不同特性和靶点的化疗药物已被有效应用于晚期癌症患者[88]。然而,长期化疗耐药性成为化疗成功与否的重要挑战[89]。很多研究已经证明MSC-Exos与癌症化疗耐药性密切相关,因为它们可以直接递送功能蛋白和RNA,避免了细胞凋亡,这充分表明MSC-Exos可以通过调节细胞凋亡蛋白来介导化疗耐药性。但是也有很多研究表明MSC-Exos可以通过介导不同的信号通路而增加化疗药物耐药性,见表5。
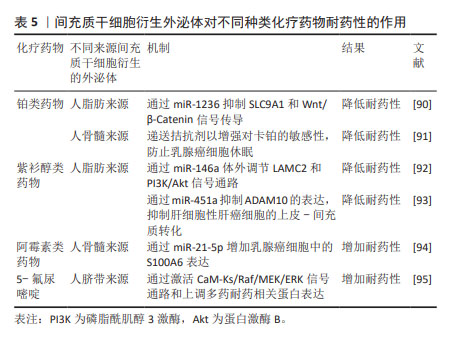
(1) MSC-Exos可以降低铂类药物的耐药性已在很多研究中被报道。人脂肪来源MSC-Exos携带miR-1236通过抑制SLC9A1和Wnt/β-Catenin信号传导,从而降低乳腺癌细胞对顺铂的耐药性[90]。BLISS等[91]研究发现,乳腺癌细胞在体外和体内通过转移miR-222/223促进乳腺癌细胞休眠,这种休眠与卡铂耐药性有关,而人骨髓来源MSC-Exos可以递送拮抗剂以增强对卡铂的敏感性,防止乳腺癌细胞休眠。
(2) MSC-Exos可以降低紫杉醇类化疗药物的耐药性。人脂肪来源MSC-Exos携带miR-146a通过体外调节LAMC2和磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B(phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B,PI3K/Akt)信号通路来逆转卵巢癌细胞对多西紫杉醇和紫杉烷的耐药性[92]。XU等[93] 研究证实,人脂肪来源MSC-Exos通过miR-451a抑制ADAM10的表达,抑制肝细胞性肝癌细胞的上皮-间质转化,从而在体外增加肝癌细胞对紫杉醇的敏感性。
(3) MSC-Exos可以增加阿霉素类化疗药物的耐药性。在近期的一项研究中发现,人骨髓来源MSC-Exos携带的miR-21-5p通过增加乳腺癌细胞中的S100A6表达来增强阿霉素类药物对乳腺癌的耐药性[94],这一发现有助于开发新的治疗策略,以规避乳腺癌患者使用阿霉素耐药。
(4) MSC-Exos对5-氟尿嘧啶的耐药性具有消极作用。人脐带来源MSC-Exos在体外和体内都可以增强胃癌对5-氟尿嘧啶的耐药性,其作用机制为人脐带来源MSC-Exos通过激活CaM-Ks/Raf/MEK/ERK信号通路和上调多药耐药相关蛋白表达,从而增加胃癌对5-氟尿嘧啶的耐药性[95]。
综上,目前MSC-Exos对于不同种类的化疗药物的耐药性具有不同的作用,明确其作用机制,寻求针对各类化疗药物的最合适的MSC-Exos,以降低化疗药物的耐药性,提高癌症患者的生活质量。
| [1] XI Y, XU P. Global colorectal cancer burden in 2020 and projections to 2040. Transl Oncol. 2021;14(10):101174. [2] ALZAHRANI SM, AL DOGHAITHER HA, AL-GHAFARI AB. General insight into cancer: An overview of colorectal cancer (Review). Mol Clin Oncol. 2021;15(6):271. [3] BILLER LH, SCHRAG D. Diagnosis and Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Review. JAMA. 2021;325(7):669-685. [4] SHAHAR N, LARISCH S. Inhibiting the inhibitors: Targeting anti-apoptotic proteins in cancer and therapy resistance. Drug Resist Updat. 2020;52: 100712. [5] GATENBY RA, BROWN JS. Integrating evolutionary dynamics into cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020;17(11):675-686. [6] WYLD L, AUDISIO RA, POSTON GJ. The evolution of cancer surgery and future perspectives. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015;12(2):115-124. [7] CREMOLINI C, ANTONIOTTI C, ROSSINI D, et al. Upfront FOLFOXIRI plus bevacizumab and reintroduction after progression versus mFOLFOX6 plus bevacizumab followed by FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab in the treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (TRIBE2): a multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21(4):497-507. [8] SALEM HK, THIEMERMANN C. Mesenchymal stromal cells: current understanding and clinical status. Stem Cells. 2010;28(3):585-596. [9] TEIXEIRA FG, PANCHALINGAM KM, ANJO SI, et al. Do hypoxia/normoxia culturing conditions change the neuroregulatory profile of Wharton Jelly mesenchymal stem cell secretome? Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6(1):133. [10] KISIEL AH, MCDUFFEE LA, MASAOUD E, et al. Isolation, characterization, and in vitro proliferation of canine mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue, muscle, and periosteum. Am J Vet Res. 2012; 73(8):1305-1317. [11] MURPHY MB, MONCIVAIS K, CAPLAN AI. Mesenchymal stem cells: environmentally responsive therapeutics for regenerative medicine. Exp Mol Med. 2013;45(11):e54. [12] RIDGE SM, SULLIVAN FJ, GLYNN SA. Mesenchymal stem cells: key players in cancer progression. Mol Cancer. 2017;16(1):31. [13] MENG L, ZHAO Y, BU W, et al. Bone mesenchymal stem cells are recruited via CXCL8-CXCR2 and promote EMT through TGF-β signal pathways in oral squamous carcinoma. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(8):e12859. [14] XUNIAN Z, KALLURI R. Biology and therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes. Cancer Sci. 2020;111(9):3100-3110. [15] BIGONI-ORDÓÑEZ GD, CZARNOWSKI D, PARSONS T, et al. Integrin α6 (CD49f), The Microenvironment and Cancer Stem Cells. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;14(5):428-436. [16] BAEK G, CHOI H, KIM Y, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Therapeutics and as a Drug Delivery Platform. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(9):880-886. [17] LIU H, DENG S, HAN L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells, exosomes and exosome-mimics as smart drug carriers for targeted cancer therapy. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022;209(Pt 1):112163. [18] YANG Y, BUCAN V, BAEHRE H, et al. Acquisition of new tumor cell properties by MSC-derived exosomes. Int J Oncol. 2015;47(1):244-252. [19] PESSINA A, SISTO F, COCCÈ V, et al. A mesenchymal stromal cell line resistant to paclitaxel that spontaneously differentiates into osteoblast-like cells. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2011;27(3):169-180. [20] DOS SANTOS GGL, OLIVEIRA ALL, SANTOS DS, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells reduce the oxaliplatin-induced sensory neuropathy through the reestablishment of redox homeostasis in the spinal cord. Life Sci. 2021; 265:118755. [21] ALTANEROVA U, JAKUBECHOVA J, BENEJOVA K, et al. Intracellular prodrug gene therapy for cancer mediated by tumor cell suicide gene exosomes. Int J Cancer. 2021;148(1):128-139. [22] ALZHRANI GN, ALANAZI ST, ALSHARIF SY, et al. Exosomes: Isolation, characterization, and biomedical applications. Cell Biol Int. 2021;45(9): 1807-1831. [23] SIMPSON RJ, KALRA H, MATHIVANAN S. ExoCarta as a resource for exosomal research. J Extracell Vesicles. 2012;1(1):18374. [24] TRACY SA, AHMED A, TIGGES JC, et al. A comparison of clinically relevant sources of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: Bone marrow and amniotic fluid. J Pediatr Surg. 2019;54(1):86-90. [25] VILLATORO AJ, ALCOHOLADO C, MARTÍN-ASTORGA MC, et al. Comparative analysis and characterization of soluble factors and exosomes from cultured adipose tissue and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in canine species. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2019;208:6-15. [26] WANG ZG, HE ZY, LIANG S, et al. Comprehensive proteomic analysis of exosomes derived from human bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020; 11(1):511. [27] JI L, BAO L, GU Z, et al. Comparison of immunomodulatory properties of exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and dental pulp stem cells. Immunol Res. 2019;67(4-5):432-442. [28] SEMERCI SEVIMLI T, SEVIMLI M, QOMI EKENEL E, et al. Comparison of exosomes secreted by synovial fluid-derived mesenchymal stem cells and adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in culture for microRNA-127-5p expression during chondrogenesis. Gene. 2023;865:147337. [29] KATSUDA T, TSUCHIYA R, KOSAKA N, et al. Human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells secrete functional neprilysin-bound exosomes. Sci Rep. 2013;3:1197. [30] POMATTO M, GAI C, NEGRO F, et al. Differential Therapeutic Effect of Extracellular Vesicles Derived by Bone Marrow and Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Wound Healing of Diabetic Ulcers and Correlation to Their Cargoes. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(8):3851. [31] GARDINER C, DI VIZIO D, SAHOO S, et al. Techniques used for the isolation and characterization of extracellular vesicles: results of a worldwide survey. J Extracell Vesicles. 2016;5:32945. [32] CHENG H, FANG H, XU RD, et al. Development of a rinsing separation method for exosome isolation and comparison to conventional methods. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(12):5074-5083. [33] SOARES MARTINS T, CATITA J, MARTINS ROSA I, et al. Exosome isolation from distinct biofluids using precipitation and column-based approaches. PLoS One. 2018;13(6):e0198820. [34] BUSCHMANN D, KIRCHNER B, HERMANN S, et al. Evaluation of serum extracellular vesicle isolation methods for profiling miRNAs by next-generation sequencing. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7(1):1481321. [35] ZHAO L, YU J, WANG J, et al. Isolation and Identification of miRNAs in exosomes derived from serum of colon cancer patients. J Cancer. 2017;8(7): 1145-1152. [36] VAN DEUN J, MESTDAGH P, SORMUNEN R, et al. The impact of disparate isolation methods for extracellular vesicles on downstream RNA profiling. J Extracell Vesicles. 2014;3(1):24858. [37] LAMPARSKI HG, METHA-DAMANI A, YAO JY, et al. Production and characterization of clinical grade exosomes derived from dendritic cells. J Immunol Methods. 2002;270(2):211-226. [38] LOBB RJ, BECKER M, WEN SW, et al. Optimized exosome isolation protocol for cell culture supernatant and human plasma. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015; 4:27031. [39] POPOVIC M, MAZZEGA E, TOFFOLETTO B, et al. Isolation of anti-extra-cellular vesicle single-domain antibodies by direct panning on vesicle-enriched fractions. Microb Cell Fact. 2018;17(1):6. [40] GREENING DW, XU R, JI H, et al. A protocol for exosome isolation and characterization: evaluation of ultracentrifugation, density-gradient separation, and immunoaffinity capture methods. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1295:179-209. [41] ZHU L, SUN HT, WANG S, et al. Isolation and characterization of exosomes for cancer research. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13(1):152. [42] ABRAMOWICZ A, MARCZAK L, WOJAKOWSKA A, et al. Harmonization of exosome isolation from culture supernatants for optimized proteomics analysis. PLoS One. 2018;13(10):e0205496. [43] THÉRY C, WITWER KW, AIKAWA E, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7(1):1535750. [44] LANGEVIN SM, KUHNELL D, ORR-ASMAN MA, et al. Balancing yield, purity and practicality: a modified differential ultracentrifugation protocol for efficient isolation of small extracellular vesicles from human serum. RNA Biol. 2019;16(1):5-12. [45] KANWAR SS, DUNLAY CJ, SIMEONE DM, et al. Microfluidic device (ExoChip) for on-chip isolation, quantification and characterization of circulating exosomes. Lab Chip. 2014;14(11):1891-1900. [46] ILIESCU FS, VRTAČNIK D, NEUZIL P, et al. Microfluidic Technology for Clinical Applications of Exosomes. Micromachines (Basel). 2019; 10(6):392. [47] ZHANG P, ZHOU X, HE M, et al. Ultrasensitive detection of circulating exosomes with a 3D-nanopatterned microfluidic chip. Nat Biomed Eng. 2019;3(6):438-451. [48] LAI RC, ARSLAN F, LEE MM, et al. Exosome secreted by MSC reduces myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2010;4(3):214-222. [49] ZHU W, HUANG L, LI Y, et al. Exosomes derived from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Lett. 2012; 315(1):28-37. [50] 李佳林,张耀东,娄艳茹,等.间充质干细胞分泌组发挥作用的分子机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(7):1512-1522. [51] LEE JK, PARK SR, JUNG BK, et al. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells suppress angiogenesis by down-regulating VEGF expression in breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e84256. [52] PAKRAVAN K, BABASHAH S, SADEGHIZADEH M, et al. MicroRNA-100 shuttled by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes suppresses in vitro angiogenesis through modulating the mTOR/HIF-1α/VEGF signaling axis in breast cancer cells. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2017;40(5):457-470. [53] ALCAYAGA-MIRANDA F, GONZÁLEZ PL, LOPEZ-VERRILLI A, et al. Prostate tumor-induced angiogenesis is blocked by exosomes derived from menstrual stem cells through the inhibition of reactive oxygen species. Oncotarget. 2016;7(28):44462-44477. [54] WU S, JU GQ, DU T, et al. Microvesicles derived from human umbilical cord Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cells attenuate bladder tumor cell growth in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e61366. [55] REZA AMMT, CHOI YJ, YASUDA H, et al. Human adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal-miRNAs are critical factors for inducing anti-proliferation signalling to A2780 and SKOV-3 ovarian cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2016;6:38498. [56] TAKAHARA K, II M, INAMOTO T, et al. microRNA-145 Mediates the Inhibitory Effect of Adipose Tissue-Derived Stromal Cells on Prostate Cancer. Stem Cells Dev. 2016;25(17):1290-1298. [57] LIU J, FENG Y, ZENG X, et al. Extracellular vesicles-encapsulated let-7i shed from bone mesenchymal stem cells suppress lung cancer via KDM3A/DCLK1/FXYD3 axis. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(4):1911-1926. [58] LI T, WAN Y, SU Z, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal microRNA-3940-5p Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Metastasis by Targeting Integrin α6. Dig Dis Sci. 2021;66(6):1916-1927. [59] CHEN J, LI Z, YUE C, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes carrying miR-1827 downregulate SUCNR1 to inhibit macrophage M2 polarization and prevent colorectal liver metastasis. Apoptosis. 2023;28(3-4):549-565. [60] QU M, LI J, HONG Z, et al. The role of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal microRNA-431-5p in survival and prognosis of colorectal cancer patients. Mutagenesis. 2022;37(2):164-171. [61] WANG J, PEI B, YAN J, et al. hucMSC-Derived Exosomes Alleviate the Deterioration of Colitis via the miR-146a/SUMO1 Axis. Mol Pharm. 2022; 19(2):484-493. [62] XU Y, SHEN L, LI F, et al. microRNA-16-5p-containing exosomes derived from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit proliferation, migration, and invasion, while promoting apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells by downregulating ITGA2. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(11):21380-21394. [63] CHEN HL, LI JJ, JIANG F, et al. MicroRNA-4461 derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell exosomes inhibits tumorigenesis by downregulating COPB2 expression in colorectal cancer. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2020; 84(2):338-346. [64] JAHANGIRI B, KHALAJ-KONDORI M, ASADOLLAHI E, et al. MSC-Derived exosomes suppress colorectal cancer cell proliferation and metastasis via miR-100/mTOR/miR-143 pathway. Int J Pharm. 2022;627:122214. [65] WANG Y, LIN C. Exosomes miR-22-3p Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Suppress Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation and Invasion by Regulating RAP2B and PI3K/AKT Pathway. J Oncol. 2021;2021:3874478. [66] FANG Y, WU F, SHANG G, et al. SCARA5 in bone marrow stromal cell-derived exosomes inhibits colorectal cancer progression by inactivating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Genomics. 2023;115(4):110636. [67] NING S, CHEN Y, LI S, et al. Exosomal miR-99b-5p Secreted from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Can Retard the Progression of Colorectal Cancer by Targeting FGFR3. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023;19(8):2901-2917. [68] MANSOURABADI AH, AGHAMAJIDI A, FARAJI F, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells- derived exosomes inhibit the expression of Aquaporin-5 and EGFR in HCT-116 human colorectal carcinoma cell line. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2022;23(1):40. [69] XUE C, GAO Y, LI X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose accelerate the progression of colon cancer by inducing a MT-CAFs phenotype via TRPC3/NF-KB axis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):335. [70] LI H, LI F. Exosomes from BM-MSCs increase the population of CSCs via transfer of miR-142-3p. Br J Cancer. 2018;119(6):744-755. [71] WU XB, LIU Y, WANG GH, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells promote colorectal cancer progression through AMPK/mTOR-mediated NF-κB activation. Sci Rep. 2016;6:21420. [72] ZHANG N, LI L, LUO J, et al. Inhibiting microRNA-424 in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes suppresses tumor growth in colorectal cancer by upregulating TGFBR3. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2021;709:108965. [73] REN J, DING L, ZHANG D, et al. Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts promote the stemness and chemoresistance of colorectal cancer by transferring exosomal lncRNA H19. Theranostics. 2018;8(14):3932-3948. [74] ZHOU L, LI J, TANG Y, et al. Exosomal LncRNA LINC00659 transferred from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes colorectal cancer cell progression via miR-342-3p/ANXA2 axis. J Transl Med. 2021;19(1):8. [75] LI YJ, WU JY, WANG JM, et al. Gemcitabine loaded autologous exosomes for effective and safe chemotherapy of pancreatic cancer. Acta Biomater. 2020;101:519-530. [76] 马宝南,孙丽娜,韩美华.肿瘤治疗的细胞药物递送系统的研究进展[J].现代药物与临床,2024,39(2):503-513. [77] PESSINA A, BONOMI A, COCCÈ V, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells primed with paclitaxel provide a new approach for cancer therapy. PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28321. [78] PESSINA A, COCCÈ V, PASCUCCI L, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells primed with Paclitaxel attract and kill leukaemia cells, inhibit angiogenesis and improve survival of leukaemia-bearing mice. Br J Haematol. 2013; 160(6):766-778. [79] GOODARZI A, VALIKHANI M, AMIRI F, et al. The mechanisms of mutual relationship between malignant hematologic cells and mesenchymal stem cells: Does it contradict the nursing role of mesenchymal stem cells? Cell Commun Signal. 2022;20(1):21. [80] LOU G, SONG X, YANG F, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-122-modified adipose tissue-derived MSCs increase chemosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hematol Oncol. 2015;8:122. [81] GRECO KA, FRANZEN CA, FOREMAN KE, et al. PLK-1 Silencing in Bladder Cancer by siRNA Delivered With Exosomes. Urology. 2016;91:241.e1-7. [82] WANG Y, CHEN X, TIAN B, et al. Nucleolin-targeted Extracellular Vesicles as a Versatile Platform for Biologics Delivery to Breast Cancer. Theranostics. 2017;7(5):1360-1372. [83] HAN S, LI G, JIA M, et al. Delivery of Anti-miRNA-221 for Colorectal Carcinoma Therapy Using Modified Cord Blood Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Exosomes. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:743013. [84] BAGHERI E, ABNOUS K, FARZAD SA, et al. Targeted doxorubicin-loaded mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes as a versatile platform for fighting against colorectal cancer. Life Sci. 2020;261:118369. [85] JIN Y, SUN L, CHEN Y, et al. The homologous tumor-derived-exosomes loaded with miR-1270 selectively enhanced the suppression effect for colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Med. 2024;13(1):e6936. [86] KARAMI FATH M, ANJOMROOZ M, TAHA SR, et al. The therapeutic effect of exosomes from mesenchymal stem cells on colorectal cancer: Toward cell-free therapy. Pathol Res Pract. 2022;237:154024. [87] WANG M, LI J, WANG D, et al. The effects of mesenchymal stem cells on the chemotherapy of colorectal cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023; 160:114373. [88] GHOSH S. Cisplatin: The first metal based anticancer drug. Bioorg Chem. 2019;88:102925. [89] GUERRA F, ARBINI AA, MORO L. Mitochondria and cancer chemoresistance. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg. 2017;1858(8):686-699. [90] JIA Z, ZHU H, SUN H, et al. Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal microRNA-1236 Reduces Resistance of Breast Cancer Cells to Cisplatin by Suppressing SLC9A1 and the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. Cancer Manag Res. 2020;12:8733-8744. [91] BLISS SA, SINHA G, SANDIFORD OA, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Stimulate Cycling Quiescence and Early Breast Cancer Dormancy in Bone Marrow. Cancer Res. 2016;76(19):5832-5844. [92] QIU L, WANG J, CHEN M, et al. Exosomal microRNA‑146a derived from mesenchymal stem cells increases the sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells to docetaxel and taxane via a LAMC2‑mediated PI3K/Akt axis. Int J Mol Med. 2020;46(2):609-620. [93] XU Y, LAI Y, CAO L, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal microRNA-451a represses epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting ADAM10. RNA Biol. 2021;18(10):1408-1423. [94] LUO T, LIU Q, TAN A, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Secreted Exosome Promotes Chemoresistance in Breast Cancer via Enhancing miR-21-5p-Mediated S100A6 Expression. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2020;19:283-293. [95] JI R, ZHANG B, ZHANG X, et al. Exosomes derived from human mesenchymal stem cells confer drug resistance in gastric cancer. Cell Cycle. 2015;14(15):2473-2483. [96] GUO G, TAN Z, LIU Y, et al. The therapeutic potential of stem cell-derived exosomes in the ulcerative colitis and colorectal cancer. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):138. |
| [1] | 赖鹏宇, 梁 冉, 沈 山. 组织工程技术修复颞下颌关节:问题与挑战[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | 余 帅, 刘家伟, 朱 彬, 潘 檀, 李兴龙, 孙广峰, 于海洋, 丁 亚, 王宏亮. 小分子药物治疗骨关节炎的热点问题及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [3] | 周盼盼, 崔应麟, 张文涛, 王姝瑞, 陈佳慧, 杨 潼. 细胞自噬在脑缺血损伤中的作用及中药调控机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1650-1658. |
| [4] | 于经邦, 吴亚云. 非编码RNA在肺纤维化过程中的调控作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1659-1666. |
| [5] | 王秋月, 靳 攀, 蒲 锐. 运动干预与细胞焦亡在骨关节炎中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [6] | 袁维勃, 刘 婵, 余丽梅. 肝脏类器官在肝脏疾病模型与移植治疗中的应用潜力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1684-1692. |
| [7] | 胡涛涛, 刘 兵, 陈 诚, 殷宗银, 阚道洪, 倪 杰, 叶凌霄, 郑祥兵, 严 敏, 邹 勇. 过表达神经调节蛋白1的人羊膜间充质干细胞促进小鼠皮肤创面愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1343-1349. |
| [8] | 金 凯, 唐 婷, 李美乐, 谢裕安. 人脐带间充质干细胞条件培养基及外泌体对肝癌细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭和凋亡的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [9] | 李帝均, 酒精卫, 刘海峰, 闫 磊, 李松岩, 王 斌. 明胶三维微球装载人脐带间充质干细胞修复慢性肌腱病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1356-1362. |
| [10] | 刘 琪, 李林臻, 李玉生, 焦泓焯, 杨 程, 张君涛. 淫羊藿苷含药血清促进3种细胞共培养体系中软骨细胞增殖和干细胞成软骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
| [11] | 艾克帕尔·艾尔肯, 陈晓涛, 吾凡别克·巴合提. 成骨诱导人牙周膜干细胞来源外泌体促进炎症微环境下人牙周膜干细胞成骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [12] | 郭大鑫, 范苏苏, 朱振东, 侯建红, 张 旋. 过表达溶质载体家族1成员5和敲低慢病毒载体构建及稳定转染RAW264.7细胞株[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1414-1421. |
| [13] | 章镇宇, 梁秋健, 杨 军, 韦相宇, 蒋 捷, 黄林科, 谭 桢. 新橙皮苷治疗骨质疏松症的靶点及对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [14] | 吕丽婷, 于 霞, 张金梅, 高巧婧, 刘仁凡, 李 梦, 王 璐. 脑衰老与外泌体研究进程及现状的文献计量学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1457-1465. |
| [15] | 彭洪成, 彭国璇, 雷安毅, 林 圆, 孙 红, 宁 旭, 尚显文, 邓 进, 黄明智. 血小板衍生生长因子BB参与生长板损伤修复的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1497-1503. |
间充质干细胞是多能干细胞,可以自我更新并分化为多谱系细胞[8]。间充质干细胞可以从多种人体组织或器官中提取出来,例如骨髓、脂肪组织、肝组织、脐血、外周血、经血、脑、肺、胰腺等[9-11]。间充质干细胞对肿瘤具有先天的亲和力,可以调节与肿瘤相关的多种生物学过程,如抑制肿瘤细胞增殖、特异性归巢到肿瘤位置和上皮-间质转化[12-13]。值得注意的是,间充质干细胞可以分泌外泌体,外泌体可以与不同的受体细胞相互作用,从而影响靶细胞的不同生物学行为,进而调节生理稳态和/或人类疾病的进展[14]。首先,间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体(mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes,MSC-Exos)可以调节肿瘤微环境,在肿瘤的发展过程中发挥着至关重要的作用[15];第二,尽管有证据表明MSC-Exos对结直肠癌具有抑制作用,但也有研究显示其在动物模型中对结直肠癌具有促进作用;第三,MSC-Exos可以作为递送药物的载体,携带化疗药物以提高疗效并发挥更好的靶向作用[16-17];第四,MSC-Exos与癌症化疗耐药性密切相关,它们直接递送功能蛋白和RNA,调节细胞凋亡相关蛋白以介导化疗耐药性[18];最后,MSC-Exos与化疗药物合用,在癌症的治疗效果上体现出了积极的作用[19-21]。由此可见,MSC-Exos在结直肠癌的治疗中发挥着不可忽视的作用,此文章综述了MSC-Exos治疗结直肠癌的作用机制与最新研究进展,为将来临床应用奠定基础。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者于2024年1月进行文献检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 2002年2月至2024年2月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中文数据库:中国知网、万方;英文数据库:PubMed。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“间充质干细胞外泌体,结直肠癌,化疗,治疗”,英文检索词为“mesenchymal stem cells exosomes,colorectal cancer,chemotherapy,treatment”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 著作、研究性论文和综述。
1.1.6 检索策略 以PubMed数据库为例,检索策略见图1。
1.1.7 检索文献量 中文文献1 438篇,英文文献96篇。
1.2 纳入标准 ①结直肠癌相关文献;②MSC-Exos相关文献;③MSC-Exos治疗结直肠癌的作用机制、疗效、目前研究进展及存在的相关问题等文献。
1.3 排除标准 ①研究内容与主题关系偏离的文献;②质量较差、年代久远、内容陈旧的文献;③相同研究中结论重复的文献。
1.4 文献质量评估和数据的提取 通过计算机筛选出2 400余篇与文章主题有关的文献,通过阅读标题与摘要或全文,排除与主题相关性差的文献,最终共筛选出符合标准的文献96篇,其中中文文献2篇,英文文献94篇。文献筛选流程见图2。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 文章主要探讨了MSC-Exos在结直肠癌中的作用与最新研究进展。MSC-Exos参与血管生成、抑制肿瘤细胞增殖和促进肿瘤细胞凋亡的生物特性,为其在结直肠癌治疗中奠定了基础。相较于以往综述,研究者们更加关注相关细胞因子和信号通路的研究,包括起消极作用的信号通路,提出了可以将其作为靶点进行治疗的观点,并且提出了MSC-Exos可以通过降低化疗药物的耐药性而提高晚期患者生活质量的新思路。
3.3 综述的局限性 ①通过检索国内外相关文献,发现目前的细胞因子和信号通路对于结直肠癌的作用并未完全阐明;②大多数的实验都基于小鼠模型或者细胞培养,缺少临床试验数据,特别是国内的临床试验和基础试验研究更少;③MSC-Exos对结直肠癌的治疗作用仍然存在分歧。
3.4 综述的重要意义 此综述较全面地讨论了目前间充质干细胞治疗结直肠癌的作用机制和最新研究进展。①MSC-Exos主要通过自身携带的microRNA及长链非编码RNA以介导不同的信号通路,在结直肠癌的治疗中发挥不同作用;②MSC-Exos具有高稳定性、高生物相容性的特点,这使其成为治疗药物的优秀载体;③MSC-Exos对不同种类的化疗药物的耐药性具有不同的作用。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 目前,限制MSC-Exos走向临床的主要问题包括:①缺乏大规模培养和分离外泌体的技术;②缺乏长期保存外泌体的最佳方法;③缺乏快速分离、纯化、定量和鉴定外泌体是否符合标准的技术;④外泌体的移植技术还不完善;⑤相较于目前的治疗方法,外泌体治疗结直肠癌的成本高昂;⑥缺乏临床试验。因此,为了促进MSC-Exos治疗结直肠癌早日应用于临床,有必要对以上问题进行更深入的分析与研究。
在将来的研究中,有以下几个方面需要重点关注:①明确MSC-Exos对结直肠癌具有积极作用的信号通路;②研究MSC-Exos对结直肠癌具有消极作用的信号通路,从而进行更准确的靶向治疗;③研究不同来源MSC-Exos对各类化疗药物的不同作用,确定出针对各类化疗药物具有积极作用的外泌体,以更好的完善化疗方案。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
文题释义:
结直肠癌:结直肠癌的发病较为隐匿,通常被诊出时已经是晚期。目前治疗结直肠癌的方法包括早期手术治疗和晚期化学治疗。但是手术治疗的风险较高且术后并发症多,化学治疗需要长期进行,耐药性及患者依从性都得不到保证,这迫使研究者们寻求新的治疗方法。#br# 间充质干细胞衍生外泌体:各种不同来源的间充质干细胞均可以产生外泌体,并且无论在生理或者病理状态下都可以正常分泌外泌体。近年来,间充质干细胞衍生外泌体主要通过血管生成、抑制肿瘤细胞增殖和促进肿瘤细胞凋亡来发挥治疗结直肠癌的作用。#br##br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
结直肠癌目前的治疗方法还不够完善,手术术后并发症的发生、长期化疗产生的药物耐药性、化疗带来的不良反应等都使得患者的预后较差,生活质量得不到保障。近年来,间充质干细胞衍生外泌体在结直肠癌中的作用被广泛研究。虽然有部分科学家提出间充质干细胞衍生外泌体具有促进结直肠癌进展的作用,但是还有学者证实其对结直肠癌具有抑制作用。值得注意的是,目前大多实验都局限于小鼠模型或细胞实验。在将来的研究中,科学家们应当继续进行挖掘,特别是注重进行临床试验研究,使得间充质干细胞衍生外泌体早日应用于临床。
#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||