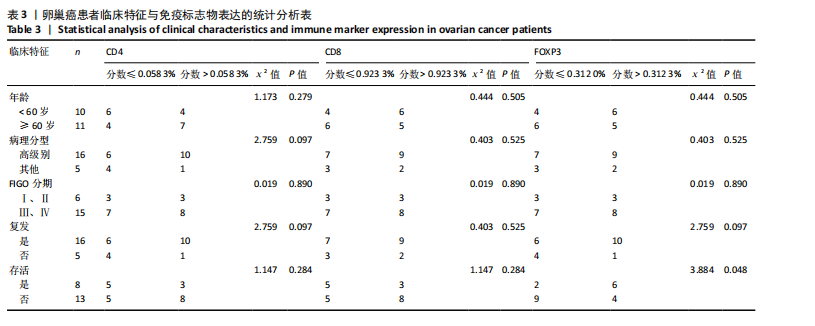
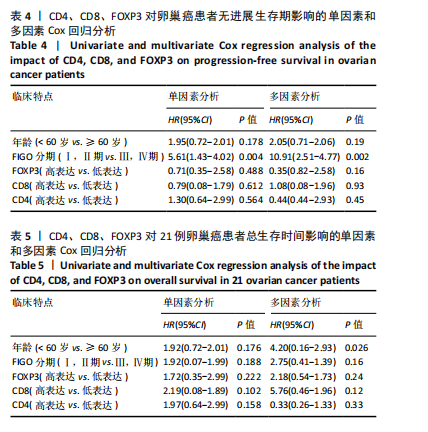
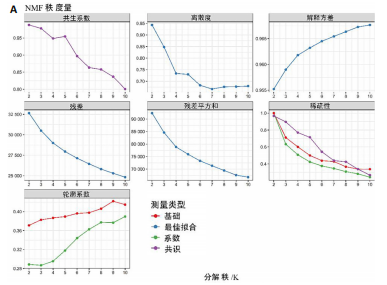
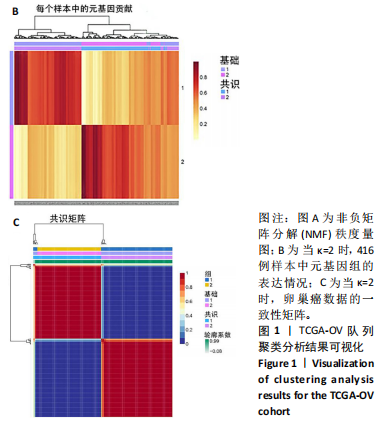
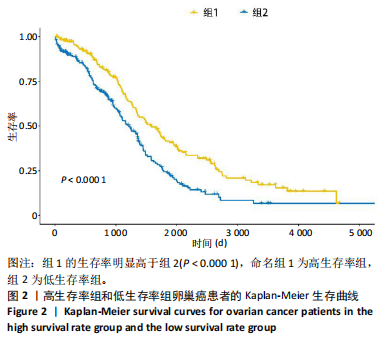
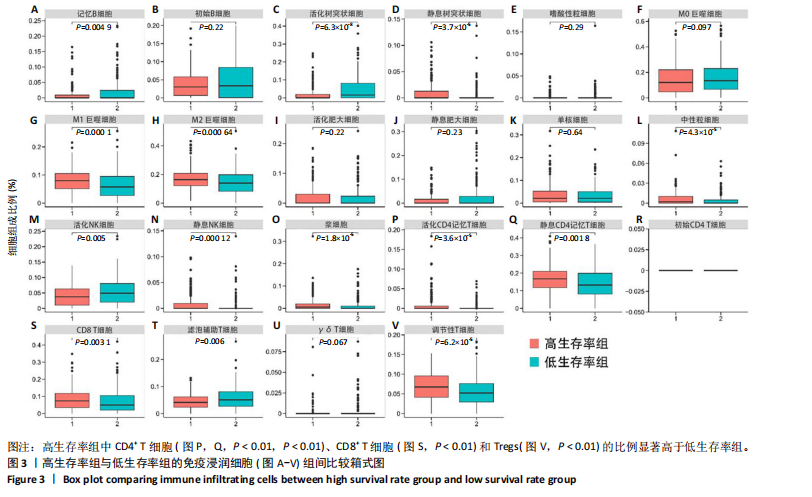
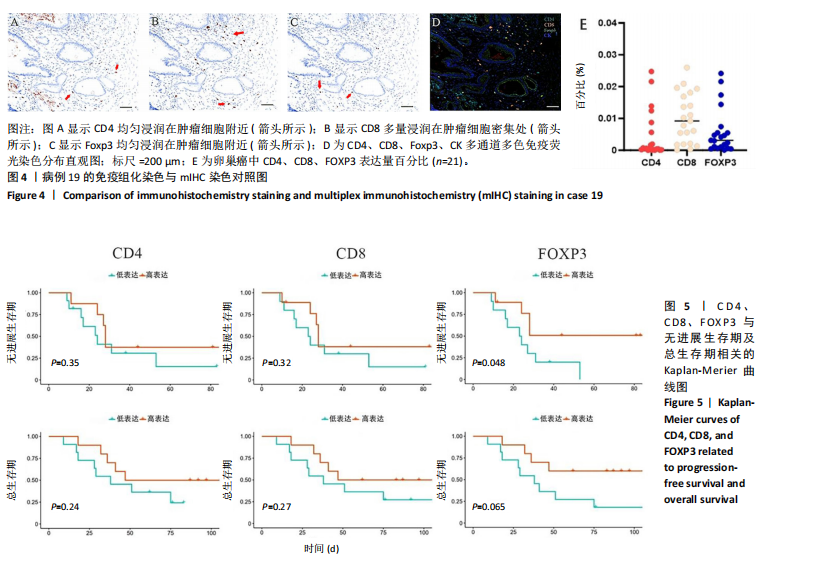
[1] ZHANG S, CHENG C, LIN Z, et al. The global burden and associated factors of ovarian cancer in 1990–2019: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. BMC Public Health. 2022;22(1):1455.
[2] 赵虹琳,李婷婷,丁国武.1990-2019年中国女性卵巢癌疾病负担趋势分析[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志,2023,30(9):507-512.
[3] LV B, WANG Y, MA D, et al. Immunotherapy: Reshape the Tumor Immune Microenvironment. Front Immunol. 2022;13:844142.
[4] TANG Y, QIAO G, ZHENG H. CD8+ T cell-based cancer immunotherapy. J Transl Med. 2024;22(1):394.
[5] RICHARDSON JR, SCHÖLLHORN A, GOUTTEFANGEAS C, et al. CD4+ T Cells: Multitasking Cells in the Duty of Cancer Immunotherapy.Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(4):596.
[6] DUTSCH-WICHEREK M, SZUBERT S, DZIOBEK K, et al. Analysis of the Treg cell population in the peripheral blood of ovarian cancer patients in relation to the long-term outcomes. Ginekol Pol. 2019;90(2):72-79.
[7] SATO S, MATSUSHITA H, SHINTANI D, et al. Association between effector-type regulatory T cells and immune checkpoint expression on CD8+ T cells in malignant ascites from epithelial ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer. 2022;22(1):437.
[8] PANIGORO SS, HERIYANTO DS, STEVEN R, et al. The association of immune cell infiltration with metastasis location in de novo metastatic triple negative breast cancer: A multicenter cross-sectional study in Indonesia. Acta Med Indones. 2023;55(4):376-384.
[9] FANG D.Targeting a Treg-specific deubiquitinase module for antitumor immune therapy. Cancer Immunol Res. 2023;11(12_Supplement):B038.
[10] YU M, ZHOU V, PISANO MD, et al. Transgenic Mouse Model for Translational Immunotherapy Studies on Multiple Myeloma. Blood. 2023;142(Supplement 1):6565.
[11] Li C, JIANG P, WEI S, et al. Regulatory T cells in tumor microenvironment: new mechanisms, potential therapeutic strategies and future prospects. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):116.
[12] SALMI S, LIN A, HIRSCHOVITS-GERZ B, et al. The role of FoxP3+ regulatory T cells and IDO+ immune and tumor cells in malignant melanoma - an immunohistochemical study. BMC Cancer. 2021; 21(1):641.
[13] MA K, SUN Z, LI X, et al. Forkhead box M1 recruits FoxP3+ Treg cells to induce immune escape in hilar cholangiocarcinoma.Immun Inflamm Dis.2022;10(11):e727.
[14] 田亚红,高向东,姚文兵,等.CD4+T细胞在肿瘤免疫治疗中的作用与应用研究进展[J].药学进展,2024,48(6):463-470.
[15] Montauti E, Oh DY, Fong L.CD4 T cells in antitumor immunity. Trends Cancer. 2024;10(10):969-985.
[16] Peres LC, Cushing-Haugen KL, Köbel M,et al.Invasive Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Survival by Histotype and Disease Stage. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2019;111(1):60-68.
[17] LI L, CHEN D, LUO X, et al. Identification of CD8+ T Cell Related Biomarkers in Ovarian Cancer. Front Genet. 2022;13:860161.
[18] SALEH R, ELKORD E.FoxP3+ T regulatory cells in cancer: Prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Cancer Lett. 2020;490:174-185.
[19] SHOHAN, MUS, CHATTERJEE D, OISHY TA ,et al. Role of regulatory immune cells in tumour microenvironment (TME)//Interdisciplinary Cancer Research. Springer, Cham. 2024:1-14.
[20] QIU Y, KE S, CHEN J,et al. FOXP3+ regulatory T cells and the immune escape in solid tumours. Front Immunol. 2022;13:982986.
[21] XIAO J, CHEN X, XU J, et al. The Role of FOXP3 on Tumor Metastasis and Its Interaction with Traditional Chinese Medicine. Molecules. 2022;27(19):6706.
[22] GOLZARI-SORKHEH M, ZÚÑIGA-PFLÜCKER JC. Development and function of FOXP3+ regulators of immune responses. Clin Exp Immunol. 2023;213(1):13-22.
[23] DAKAL TC, GEORGE N, XU C, et al. Predictive and Prognostic Relevance of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells. Cancers (Basel). 2024;16(9):1626.
[24] CHAUDHURI SM, WEINBERG SE, WANG D,et al.Mediator complex subunit 1 architects a tumorigenic Treg cell program independent of inflammation. Cell Rep Med. 2024;5(3):101441.
[25] Hosseinalizadeh H, Rabiee F, Eghbalifard N, et al.Regulating the regulatory T cells as cell therapies in autoimmunity and cancer. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1244298.
[26] LAUNONEN IM, LYYTIKÄINEN N, CASADO J, et al. Single-cell tumor-immune microenvironment of BRCA1/2 mutated high-grade serous ovarian cancer.Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):835.
[27] SHANG B, LIU Y, JIANG SJ, et al. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating FoxP3+ regulatory T cells in cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2015;5:15179.
[28] LEE S, CHO EY, PARK YH, et al. Prognostic impact of FOXP3 expression in triple-negative breast cancer. Acta Oncol. 2013;52(1):73-81.
[29] UKITA M, HAMANISHI J, YOSHITOMI H, et al. CXCL13-producing CD4+ T cells accumulate in the early phase of t ertiary lymphoid structures in ovarian cancer. JCI Insight. 2022;7(12):e157215.
[30] BOBISSE S, GENOLET R, ROBERTI A, et al. Sensitive and frequent identification of high avidity neo-epitope specific CD8+ T cells in immunotherapy-naive ovarian cancer. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1092.
[31] DE MARTINO M, DAVIAUD C, DIAMOND JM,et al. Activin A Promotes Regulatory T-cell-Mediated Immunosuppression in Irradiated Breast Cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. 2021;9(1):89-102.
[32] KOS K, ASLAM MA, VAN DE VEN R, et al. Tumor-educated Tregs drive organ-specific metastasis in breast cancer by impairing NK cells in the lymph node niche.Cell Rep. 2022;38(9):110447.
[33] WANG W, LOPEZ MCDONALD MC, KIM C, et al. The complementary roles of STAT3 and STAT1 in cancer biology: insights into tumor pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies. Front Immunol. 2023;14: 1265818.
[34] SHEIKHHOSSEIN HH, IOMMELLI F, DI PIETRO N, et al. Exosome-like Systems: From Therapies to Vaccination for Cancer Treatment and Prevention-Exploring the State of the Art.Vaccines (Basel). 2024; 12(5):519.
[35] ZHOU Y, SHAO N, AIERKEN N, et al. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in patients with breast cancer: a meta-analysis. J Cancer. 2017;8(19):4098-4105.
[36] ZHENG L, LIN L, SONG J, et al. Prognostic values of regulatory T cells (Tregs) and Treg-related genes in gastric cancer. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2023;48(1):14-25.
[37] LI Y, ZHANG C, JIANG A, et al. Potential anti-tumor effects of regulatory T cells in the tumor microenvironment: a review.J Transl Med. 2024; 22(1):293.
[38] YAMAMOTO T, KAWADA K, OBAMA K.Inflammation-Related Biomarkers for the Prediction of Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer Patients. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(15):8002.
[39] SONG Z, ZHANG J, SUN Y, et al. Establishment and validation of an immune infiltration predictive model for ovarian cancer. BMC Med Genomics. 2023;16(1):227. |