[1] XIE Y, ZINKLE A, CHEN L, et al. Fibroblast growth factor signalling in osteoarthritis and cartilage repair. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(10):547-564.
[2] WEN C, XU L, XU X, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 in articular cartilage repair for osteoarthritis treatment. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):277.
[3] SHAH SS, MITHOEFER K. Current applications of growth factors for knee cartilage repair and osteoarthritis treatment. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2020;13(6):641-650.
[4] PUJOL JP, CHADJICHRISTOS C, LEGENDRE F, et al. Interleukin-1 and transforming growth factor-beta 1 as crucial factors in osteoarthritic cartilage metabolism. Connect Tissue Res. 2008;49(3):293-297.
[5] VAN DEN BERG WB. The role of cytokines and growth factors in cartilage destruction in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Z Rheumatol. 1999;58(3):136-141.
[6] BOEHME KA, ROLAUFFS B. Onset and progression of human osteoarthritis-can growth factors, inflammatory cytokines, or differential mirna expression concomitantly induce proliferation, ECM degradation, and inflammation in articular cartilage? Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(8):2282.
[7] MURATA M, YUDOH K, MASUKO K. The potential role of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in cartilage: how the angiogenic factor could be involved in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis? Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008;16(3):279-286.
[8] 杨冠,杨晓. TGF-β超家族在软骨发生、发育和维持中的作用[J].遗传,2008, 30(8):953-959.
[9] 谢杨丽,黄俊兰,陈涵纲,等.成纤维细胞生长因子信号在骨损伤修复中的作用[J].生命科学,2020,32(3):239-244.
[10] 黄刚,任富川,冯程程,等.富血小板血浆在骨关节炎方面的全球研究特征及趋势:文献计量分析[J].四川生理科学杂志, 2023,45(9):1750-1756.
[11] VAN ECK NJ, WALTMAN L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. 2010; 84:523-538.
[12] DONTHU N, KUMAR S, MUKHERJEE D, et al. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: an overview and guidelines. J Bus Res. 2021; 133:285-296.
[13] RANJBARI M, SHAMS ESFANDABADI Z, GAUTAM S, et al. Waste management beyond the COVID-19 pandemic: bibliometric and text mining analyses. Gondwana Res. 2023;114:124-137.
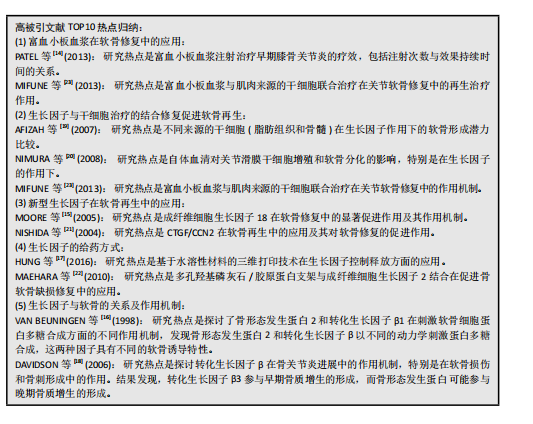
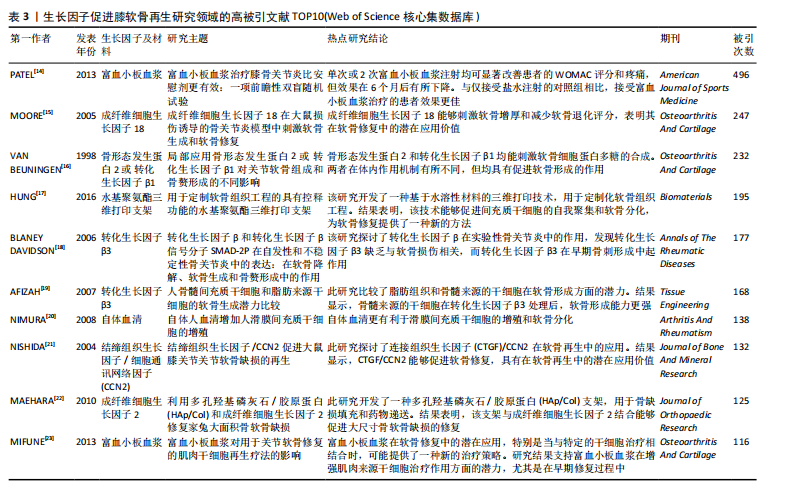
[14] PATEL S, DHILLON MS, AGGARWAL S, et al. Treatment with platelet-rich plasma is more effective than placebo for knee osteoarthritis: a prospective, double-blind, randomized trial. Am J Sports Med. 2013; 41(2):356-364.
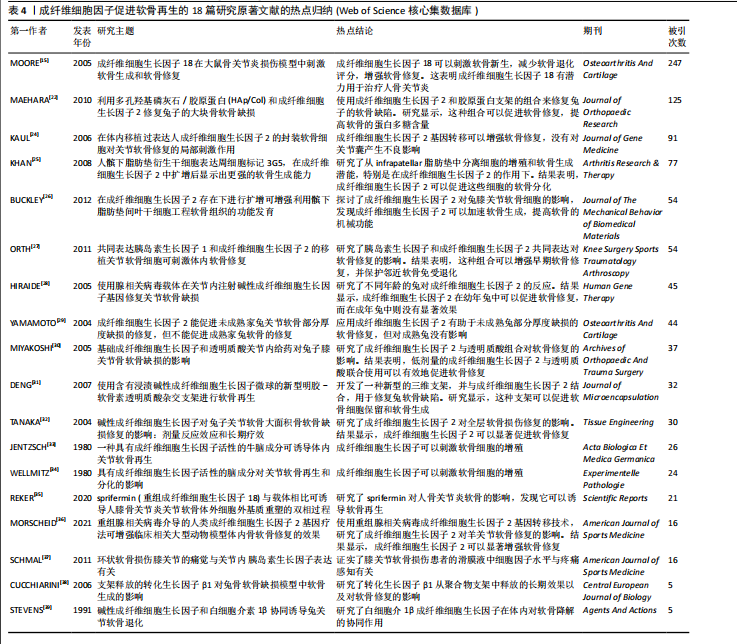
[15] MOORE EE, BENDELE AM, THOMPSON DL, et al. Fibroblast growth factor-18 stimulates chondrogenesis and cartilage repair in a rat model of injury-induced osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005;13(7):623-631.
[16] VAN BEUNINGEN HM, GLANSBEEK HL, VAN DER KRAAN PM, et al. Differential effects of local application of BMP-2 or TGF-beta 1 on both articular cartilage composition and osteophyte formation. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1998;6(5):306-317.
[17] HUNG KC, TSENG CS, DAI LG, et al. Water-based polyurethane 3D printed scaffolds with controlled release function for customized cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2016;83:156-168.
[18] BLANEY DAVIDSON EN, VITTERS EL, VAN DER KRAAN PM, et al. Expression of transforming growth factor-beta (TGFbeta) and the TGFbeta signalling molecule SMAD-2P in spontaneous and instability-induced osteoarthritis: role in cartilage degradation, chondrogenesis and osteophyte formation. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65(11):1414-1421.
[19] AFIZAH H, YANG Z, HUI JH, et al. A comparison between the chondrogenic potential of human bone marrow stem cells (BMSCs) and adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) taken from the same donors. Tissue Eng. 2007;13(4):659-666.
[20] NIMURA A, MUNETA T, KOGA H, et al. Increased proliferation of human synovial mesenchymal stem cells with autologous human serum: comparisons with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and with fetal bovine serum. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(2):501-510.
[21] NISHIDA T, KUBOTA S, KOJIMA S, et al. Regeneration of defects in articular cartilage in rat knee joints by CCN2 (connective tissue growth factor). J Bone Miner Res. 2004;19(8):1308-1319.
[22] MAEHARA H, SOTOME S, YOSHII T, et al. Repair of large osteochondral defects in rabbits using porous hydroxyapatite/collagen (HAp/Col) and fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2). J Orthop Res. 2010;28(5): 677-686.
[23] MIFUNE Y, MATSUMOTO T, TAKAYAMA K, et al. The effect of platelet-rich plasma on the regenerative therapy of muscle derived stem cells for articular cartilage repair. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(1):175-185.
[24] KAUL G, CUCCHIARINI M, ARNTZEN D, et al. Local stimulation of articular cartilage repair by transplantation of encapsulated chondrocytes overexpressing human fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF-2) in vivo. J Gene Med. 2006;8(1):100-111.
[25] KHAN WS, TEW SR, ADESIDA AB, et al. Human infrapatellar fat pad-derived stem cells express the pericyte marker 3G5 and show enhanced chondrogenesis after expansion in fibroblast growth factor-2. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10(4):R74.
[26] BUCKLEY CT, KELLY DJ. Expansion in the presence of FGF-2 enhances the functional development of cartilaginous tissues engineered using infrapatellar fat pad derived MSCs. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2012;11:102-111.
[27] ORTH P, KAUL G, CUCCHIARINI M, et al. Transplanted articular chondrocytes co-overexpressing IGF-I and FGF-2 stimulate cartilage repair in vivo. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(12):2119-2130.
[28] HIRAIDE A, YOKOO N, XIN KQ, et al. Repair of articular cartilage defect by intraarticular administration of basic fibroblast growth factor gene, using adeno-associated virus vector. Hum Gene Ther. 2005;16(12):1413-1421.
[29] YAMAMOTO T, WAKITANI S, IMOTO K, et al. Fibroblast growth factor-2 promotes the repair of partial thickness defects of articular cartilage in immature rabbits but not in mature rabbits. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2004;12(8):636-641.
[30] MIYAKOSHI N, KOBAYASHI M, Nozaka K, et al. Effects of intraarticular administration of basic fibroblast growth factor with hyaluronic acid on osteochondral defects of the knee in rabbits. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2005;125(10):683-692.
[31] DENG T, HUANG S, ZHOU S, et al. Cartilage regeneration using a novel gelatin-chondroitin-hyaluronan hybrid scaffold containing bFGF-impregnated microspheres. J Microencapsul. 2007;24(2):163-174.
[32] TANAKA H, MIZOKAMI H, SHIIGI E, et al. ffects of basic fibroblast growth factor on the repair of large osteochondral defects of articular cartilage in rabbits: dose-response effects and long-term outcomes. Tissue Eng. 2004;10(3-4):633-641.
[33] JENTZSCH KD, WELLMITZ G, HEDER G, et al. A bovine brain fraction with fibroblast growth factor activity inducing articular cartilage regeneration in vivo. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1980;39(8-9):967-971.
[34] WELLMITZ G, PETZOLD E, JENTZSCH KD, et al.The effect of brain fraction with fibroblast growth-factor activity on regeneration and differentiation of articular-cartilage. Exp Pathol-Jena. 1980;18(5):282-287.
[35] REKER D, SIEBUHR AS, THUDIUM CS, et al. Sprifermin (rhFGF18) versus vehicle induces a biphasic process of extracellular matrix remodeling in human knee OA articular cartilage ex vivo. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):6011.
[36] MORSCHEID YP, VENKATESAN JK, SCHMITT G, et al. rAAV-mediated human FGF-2 gene therapy enhances osteochondral repair in a clinically relevant large animal model over time in vivo. Am J Sports Med. 2021;49(4):958-969.
[37] SCHMAL H, NIEMEYER P, SÜDKAMP NP, et al. Pain perception in knees with circumscribed cartilage lesions is associated with intra-articular IGF-1 expression. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(9):1989-1996.
[38] CUCCHIARINI M, SOHIER J, MITOSCH K, et al. Effect of transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1) released from a scaffold on chondrogenesis in an osteochondral defect model in the rabbit. Cent Eur J Biol. 2006;1(1):43-60.
[39] STEVENS P, SHATZEN EM. Synergism of basic fibroblast growth factor and interleukin-1 beta to induce articular cartilage-degradation in the rabbit. Agents Actions. 1991;34(1-2):217-219.
[40] SZWEDOWSKI D, SZCZEPANEK J, PACZESNY Ł, et al. The effect of platelet-rich plasma on the intra-articular microenvironment in knee osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(11):5492.
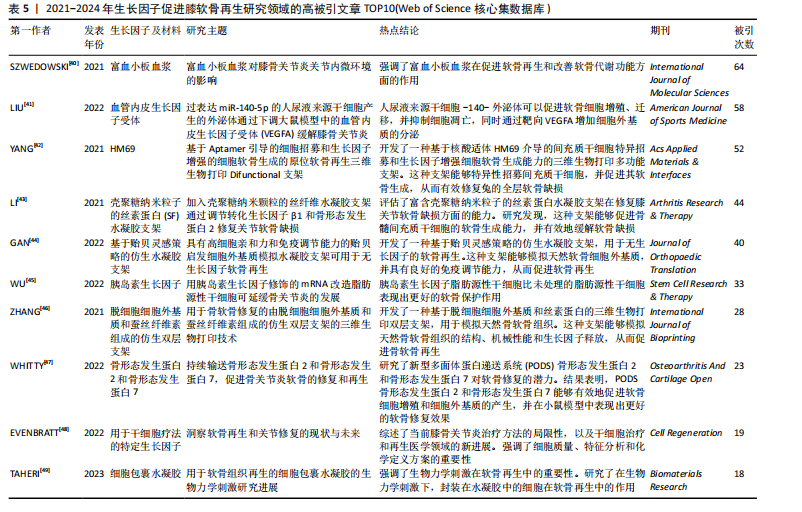
[41] LIU Y, ZENG Y, SI HB, et al. Exosomes derived from human urine-derived stem cells overexpressing miR-140-5p alleviate knee osteoarthritis through downregulation of VEGFA in a rat model. Am J Sports Med. 2022;50(4):1088-1105.
[42] YANG Z, ZHAO T, GAO C, et al. 3D-Bioprinted difunctional scaffold for in situ cartilage regeneration based on aptamer-directed cell recruitment and growth factor-enhanced cell chondrogenesis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(20):23369-23383.
[43] LI Y, LIU Y, GUO Q. Silk fibroin hydrogel scaffolds incorporated with chitosan nanoparticles repair articular cartilage defects by regulating TGF-β1 and BMP-2. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):50.
[44] GAN D, JIANG Y, HU Y, et al. Mussel-inspired extracellular matrix-mimicking hydrogel scaffold with high cell affinity and immunomodulation ability for growth factor-free cartilage regeneration. J Orthop Translat. 2022;33:120-131.
[45] WU H, PENG Z, XU Y, et al. Engineered adipose-derived stem cells with IGF-1-modified mRNA ameliorates osteoarthritis development. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022; 13(1):19.
[46] ZHANG X, LIU Y, ZUO Q, et al. 3D Bioprinting of biomimetic bilayered scaffold consisting of decellularized extracellular matrix and silk fibroin for osteochondral repair. Int J Bioprint. 2021;7(4):401.
[47] WHITTY C, PERNSTICH C, MARRIS C, et al. Sustained delivery of the bone morphogenetic proteins BMP-2 and BMP-7
for cartilage repair and regeneration in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil Open. 2022; 4(1):100240.
[48] EVENBRATT H, ANDREASSON L, BICKNELL V, et al. Insights into the present and future of cartilage regeneration and joint repair. Cell Regen. 2022;11(1):3.
[49] TAHERI S, GHAZALI HS, GHAZALI ZS, et al. Progress in biomechanical stimuli on the cell-encapsulated hydrogels for cartilage tissue regeneration. Biomater Res. 2023; 27(1):22. |